信息网络安全 ›› 2024, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (7): 1062-1075.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2024.07.008
基于上下文的异常根因算法
周书丞1,2,3, 李杨1,2,3( ), 李传荣1,3, 郭璐璐1,3, 贾辛洪1,3, 杨兴华1
), 李传荣1,3, 郭璐璐1,3, 贾辛洪1,3, 杨兴华1
- 1.中国科学院信息工程研究所,北京 100085
2.中国科学院大学网络空间安全学院,北京 100049
3.网络空间安全防御重点实验室,北京 100085
-
收稿日期:2024-03-26出版日期:2024-07-10发布日期:2024-08-02 -
通讯作者:李杨liyang@iie.ac.cn -
作者简介:周书丞(1999—),男,吉林,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为智能运维|李杨(1980—),女,北京,副研究员,博士,主要研究方向为大数据安全、网络安全、智能运维|李传荣(1989—),男,湖北,助理研究员,硕士,主要研究方向为数据安全、数据管理平台|郭璐璐(1996—),女,山西,工程师,硕士,主要研究方向为数据安全、风险监测|贾辛洪(1993—),男,北京,工程师,硕士,主要研究方向为数据安全|杨兴华(1985—),男,山东,工程师,硕士,主要研究方向为移动通信安全、安全智能运维。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(62372450)
Context-Based Abnormal Root Cause Algorithm
ZHOU Shucheng1,2,3, LI Yang1,2,3( ), LI Chuanrong1,3, GUO Lulu1,3, JIA Xinhong1,3, YANG Xinghua1
), LI Chuanrong1,3, GUO Lulu1,3, JIA Xinhong1,3, YANG Xinghua1
- 1. Institute of Information Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100085,China
2. School of Cyber Security, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049,China
3. Key Laboratory of Cyberspace Security Defense, Beijing 100085,China
-
Received:2024-03-26Online:2024-07-10Published:2024-08-02
摘要:
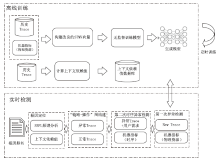
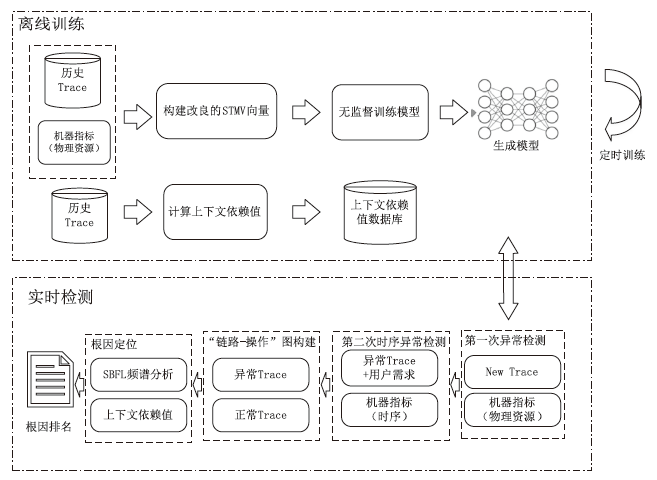
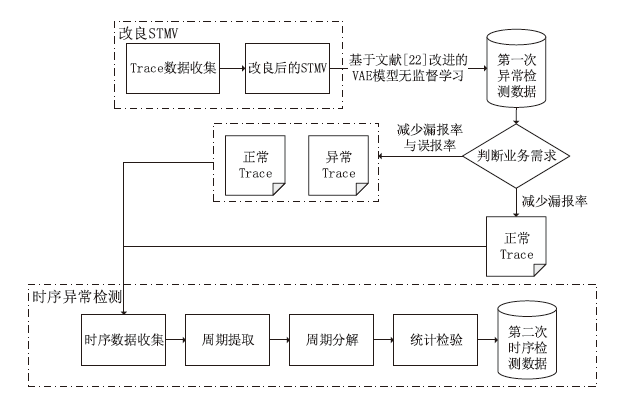
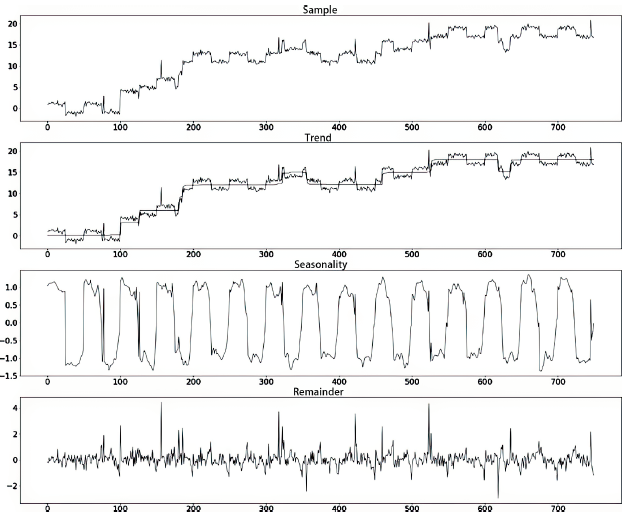
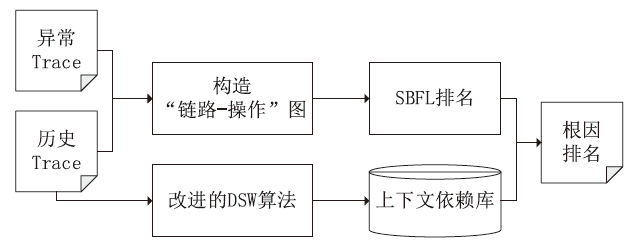
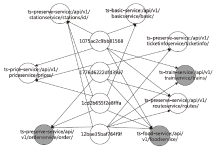
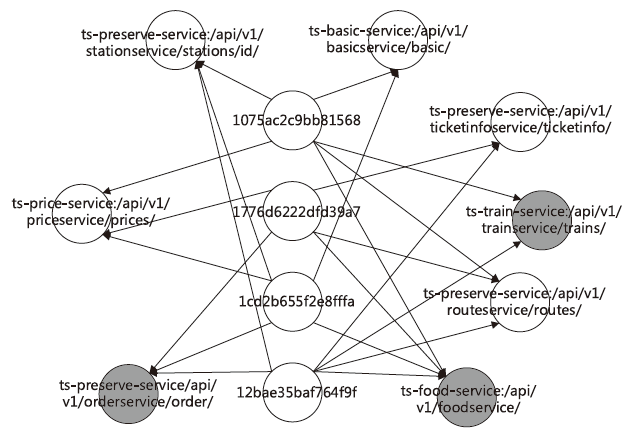
在当今大规模产业数字化转型的时代,云原生架构与微服务技术的结合已经成为转型的核心竞争力。这种开发模式提高了软件开发、部署和测试流程的完整性与灵活性。然而,随着互联网的发展,微服务架构下Trace数据的复杂性和时序问题导致异常检测准确率较低、根因定位较慢。针对这些挑战,文章提出了一种基于时序的多维度指标异常检测算法。该算法将多维度指标与时序异常检测结合,显著提高了异常检测的准确率。通过改良服务Trace度量向量,该算法解决了在物理资源充足的情况下异常检测准确性较低的问题,并通过时序检测进一步克服传统异常检测方法的局限。此外,文章还提出了一种基于“链路-操作”图与上下文结合的根因定位算法。该算法通过深入分析历史Trace数据中服务间的依赖关系,有效提高了根因定位的准确性。该算法将结构相似的Trace图融合,不仅节省了大量的构图时间,而且提高了根因定位的效率和精度。实验结果表明,与传统方法相比,本文所提的方法能更快、更准确地识别并定位异常根因。
中图分类号:
引用本文
周书丞, 李杨, 李传荣, 郭璐璐, 贾辛洪, 杨兴华. 基于上下文的异常根因算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(7): 1062-1075.
ZHOU Shucheng, LI Yang, LI Chuanrong, GUO Lulu, JIA Xinhong, YANG Xinghua. Context-Based Abnormal Root Cause Algorithm[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(7): 1062-1075.
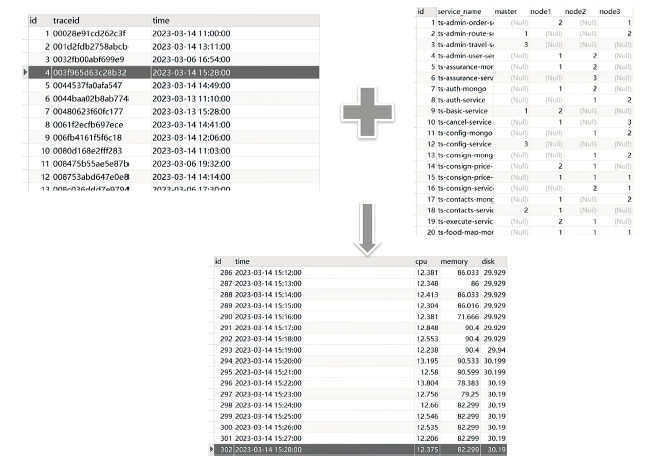
表3
STMV真实示例
| 向量 状态 | STMV ID | 响应时间a/ms | 响应时间b/ms | CPU 使用量 a/core | CPU 使用量 b/core | 内存 使用率 | 内存 使用率 | 硬盘 使用率 | 硬盘 使用率 | 数据库指标a | 数据库指标b | 集群摘要a | 集群摘要b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常 | 1 | 210 | 198 | 0.382 | 0.266 | 22.616% | 21.933% | 29.399% | 25.539% | 2.4 | 2 | 1.854 | 10.542 |
| 正常 | 2 | 201 | 221 | 0.324 | 0.253 | 25.933% | 26.433% | 26.416% | 32.109% | 1.7 | 1.9 | 1.598 | 10.896 |
| 异常 | 3 | 1400 | 1286 | 0.314 | 0.321 | 23.321% | 24.215% | 30.214% | 27.256% | 2.1 | 2.4 | 1.578 | 10.317 |
| 异常 | 4 | 184 | 192 | 0.782 | 0.348 | 89.324% | 26.354% | 84.563% | 27.343% | 2.3 | 1.8 | 95.325 | 10.325 |
| 异常 | 5 | 198 | 231 | 0.332 | 0.278 | 24.954% | 22.436% | 33.532% | 35.513% | 45.9 | 1.9 | 16.235 | 10.235 |
| 异常 | 6 | 220 | 293 | 0.287 | 0.342 | 26.931% | 19.235% | 91.356% | 89.432% | 2.8 | 2.3 | 56.74 | 56.74 |
| 异常 | 7 | 1926 | 2030 | 0.815 | 0.362 | 75.432% | 25.677% | 32.346% | 91.349% | 2.1 | 2.5 | 258.3 | 258.3 |
表4
异常检测算法对比
| 算法名称 | 响应时间 异常检测 | 微服务负载 异常检测 | 充足物理资源异常检测 | 时序 异常检测 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 准确率 | 召回率 | 准确率 | 召回率 | 准确率 | 召回率 | 准确率 | 召回率 | |
| DCW-MSA-AMC 算法[ | 53% | 75% | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 75% | 79% |
| DAEMON 算法[ | 52% | 61% | 41% | 53% | 59% | 82% | 82% | 86% |
| Omni Anomaly 算法[ | 45% | 49% | 58% | 84% | 61% | 88% | 62% | 73% |
| TraceAnomaly 算法[ | 98% | 97% | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 基于多维度指标的异常检测算法[ | 97% | 98% | 89% | 92% | 91% | 95% | N/A | N/A |
| 本文算法 | 98% | 96% | 92% | 95% | 93% | 97% | 91% | 93% |
表5
SBFL公式
| 公式 | 定义 | 公式 | 定义 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ochiai | Dstar2 | ||
| Goodman | Sorensen | ||
| Jaccard | RussellRao | ||
| M2 | Dice |
表6
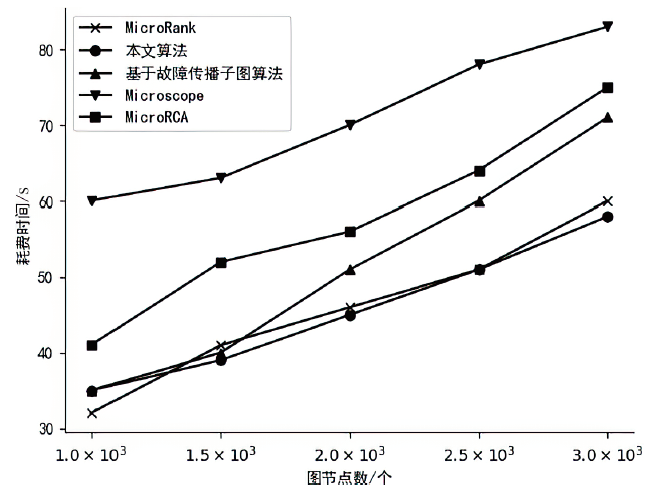
本文算法与其他算法根因定位比较
| Metric | Microscope 算法[ | MicroRCA算法[ | MicroRank 算法[ | 基于故障传播 子图算法[ | 本文算法 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 微服务资源异常根因定位 | |||||
| PR@1 | 39% | 71% | 79% | 85% | 90% |
| PR@3 | 61% | 66% | 84% | 88% | 91% |
| MAP | 57% | 67% | 86% | 88% | 91% |
| 集群主机物理资源充足情况下根因定位 | |||||
| PR@1 | 46% | 72% | 71% | 89% | 91% |
| PR@3 | 51% | 78% | 84% | 91% | 94% |
| MAP | 55% | 76% | 86% | 91% | 93% |
| 时序异常的根因定位 | |||||
| PR@1 | 62% | 52% | 71% | 75% | 89% |
| PR@3 | 67% | 57% | 74% | 78% | 93% |
| MAP | 71% | 58% | 73% | 81% | 95% |
| [1] | JAMSHIDI P, PAHL C, MENDONCA N C, et al. Microservices: The Journey So Far and Challenges Ahead[J]. IEEE Software, 2018, 35(3): 24-35. |
| [2] | RANNEY M. What I Wish I Had Known Before Scaling Uber To 1000 Services[EB/OL]. (2016-03-16)[2024-03-12]. http://gotocon.com/chicago-2016/presentation/What%20I%20Wish%20I%20Had%20Known%20Before%20Scaling%20Uber%20to%201000%20Services. |
| [3] | FAN C F, JINDAL A, GERNDT M. Microservices vs Serverless: A Performance Comparison on a Cloud-Native Web Application[C]// IEEE. 10th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science. New York: IEEE, 2020: 522-533. |
| [4] | NEWMAN S. Building Microservices[M]. Sebastopol: O’Reilly Media, 2015. |
| [5] | SONG Zhihua, ZHANG Han, ZHAO Yongmei, et al. An Intelligent Mission Planning Model for the Air Strike Operations against Islands Based on Neural Network and Simulation[EB/OL]. (2023-07-05)[2024-03-12]. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1155/2022/8172907. |
| [6] | HAMILTON J D. Time Series Analysis[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2020. |
| [7] | HOCHENBAUM J, VALLIS O S, KEJARIWAL A. Automatic Anomaly Detection in the Cloud via Statistical Learning[EB/OL]. (2017-04-24)[2024-03-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.07706. |
| [8] | SÖYLEMEZ M, TEKINERDOGAN B, KOLUKıSA T A. Challenges and Solution Directions of Microservice Architectures: A Systematic Literature Review[EB/OL]. (2022-05-29)[2024-03-12]. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12115507. |
| [9] | NANDI A, MANDAL A, ATREJA S, et al. Anomaly Detection Using Program Control Flow Graph Mining from Execution Logs[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining; Association for Computing Machinery. New York: ACM, 2016: 215-224. |
| [10] | GÜNTHER C W, ALST WMVD. Fuzzy Mining- Adaptive Process Simplification Based on Multi-Perspective Metrics[C]// Springer. International Conference on Business Process Management. Heidelberg: Springer, 2007: 328-343. |
| [11] | LOU J G, FU Q, YANG S, et al. Mining Program Workflow from Interleaved Traces[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 16th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2010: 613-622. |
| [12] | LIU Ping, XU Haowen, OUYANG Qianyu, et al. Unsupervised Detection of Microservice Trace Anomalies through Service-Level Deep Bayesian Networks[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE 31st International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering (ISSRE). New York: IEEE, 2020: 48-58. |
| [13] | NEDELKOSKI S, CARDOSO J, KAO O. Anomaly Detection and Classification Using Distributed Tracing and Deep Learning[C]// IEEE. 2019 19th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Grid Computing (CCGRID). New York: IEEE, 2019: 241-250. |
| [14] | WANG Tao, ZHANG Wenbo, XU Jiwei, et al. Workflow-Aware Automatic Fault Diagnosis for Microservice-Based Applications with Statistics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2020, 17(4): 2350-2363. |
| [15] | GULENKO A, SCHMIDT F, ACKER A, et al. Detecting Anomalous Behavior of Black-Box Services Modeled with Distance-Based Online Clustering[C]// IEEE. 2018 IEEE 11th International Conference on Cloud Computing (CLOUD). New York: IEEE, 2018: 912-915. |
| [16] | MARIANI L, PEZZÈ M, RIGANELLI O, et al. Predicting Failures in Multi-Tier Distributed Systems[EB/OL]. (2019-11-18)[2024-03-12]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2019.110464. |
| [17] | LI Wenze, PENG Xiaosheng, CHENG Kai, et al. A Short-Term Regional Wind Power Prediction Method Based on XGBoost and Multi-Stage Features Selection[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE 3rd Student Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (SCEMS). New York: IEEE, 2020: 614-618. |
| [18] | ZHOU Xiang, PENG Xin, XIE Tao, et al. Fault Analysis and Debugging of Microservice Systems: Industrial Survey, Benchmark System and Empirical Study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering, 2018, 47(2): 243-260. |
| [19] | MI Haibo, WANG Huaimin, ZHOU Yangfan, et al. Toward Fine-Grained, Unsupervised, Scalable Performance Diagnosis for Production Cloud Computing Systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2013, 24(6): 1245-1255. |
| [20] | LIU Dewei, HE Chuan, PENG Xin, et al. MicroHECL: High-Efficient Root Cause Localization in Large-Scale Microservice Systems[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE/ACM 43rd International Conference on Software Engineering:Software Engineering in Practice (ICSE-SEIP). New York: IEEE, 2021: 338-347. |
| [21] | XIN Ruyue, CHEN Peng, ZHAO Zhiming. CausalRCA: Causal Inference Based Precise Fine-Grained Root Cause Localization for Microservice Applications[EB/OL]. (2023-05-06)[2024-03-12]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2023.111724. |
| [22] | SHI Yuan, LI Yang, ZHAN Mengqi. A Multi-Dimensional Root Cause Localization Algorithm for Microservices[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(3): 73-83. |
| 施园, 李杨, 詹孟奇. 一种面向微服务的多维度根因定位算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23 (3): 73-83. | |
| [23] |
SHAN Chengang, WU Chuge, XIA Yuanqing, et al. Adaptive Resource Allocation for Workflow Containerization on Kubernetes[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 34(3): 723-743.
doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2023.000073 |
| [24] | CHODOROW K, DIROLF M. MongoDB - The Definitive Guide: Powerful and Scalable Data Storage[M]. Sebastopol: O’Reilly Media, 2010. |
| [25] | SINGH V, PEDDOJU S K. Container-Based Microservice Architecture for Cloud Applications[C]// IEEE. 2017 International Conference on Computing, Communication and Automation (ICCCA). New York: IEEE, 2017: 847-852. |
| [26] | SHLENS J. A Tutorial on Principal Component Analysis[EB/OL]. (2014-04-03)[2024-03-12]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1404.1100. |
| [27] | DOKUMENTOV A, HYNDMAN R J. Str: A Seasonal-Trend Decomposition Procedure Based on Regression[EB/OL]. (2021-07-02)[2024-03-12]. https://www.xueshufan.com/publication/3121710282. |
| [28] | WEN Qingsong, GAO Jingkun, SONG Xiaomin, et al. RobustSTL: A Robust Seasonal-Trend Decomposition Algorithm for Long Time Series[EB/OL]. (2019-07-17)[2024-03-12]. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v33i01.33015409. |
| [29] | BOX G E, JENKINS G M, REINSEL G C, et al. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2015. |
| [30] | CHEN Xuanhao, DENG Liwei, HUANG Feiteng, et al. DAEMON: Unsupervised Anomaly Detection and Interpretation for Multivariate Time Series[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE 37th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE). New York: IEEE, 2021: 2225-2230. |
| [31] | ZHOU Xiang, PENG Xin, XIE Tao, et al. Benchmarking Microservice Systems for Software Engineering Research[EB/OL]. (2018-05-27)[2024-03-12]. https://doi.org/10.1145/3183440.3194991. |
| [32] | QI Sibo, CHEN Juan, CHEN Peng, et al. An Effective Dynamic Cost-Sensitive Weighting Based Anomaly Multi-Classification Model for Imbalanced Multivariate Time Series[C]// Springer. International Conference on Web Information Systems Engineering. Heidelberg: Springer, 2023: 781-790. |
| [33] | SU Ya, ZHAO Youjian, NIU Chenhao, et al. Robust Anomaly Detection for Multivariate Time Series through Stochastic Recurrent Neural Network[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining (KDD’19). New York: ACM, 2019: 2828-2837. |
| [34] | YU Guangba, CHEN Pengfei, CHEN Hongyang, et al. MicroRank: End-to-End Latency Issue Localization with Extended Spectrum Analysis in Microservice Environments[EB/OL]. (2021-06-03)[2024-03-12]. https://doi.org/10.1145/3442381.3449905. |
| [35] | LI M L, RAMACHANDRAN P, SAHOO S K, et al. Understanding the Propagation of Hard Errors to Software and Implications for Resilient System Design[J]. ACM Sigplan Notices, 2008, 43(3): 265-276. |
| [36] | YANG Tianyi, SHEN Jiacheng, SU Yuxin, et al. Aid: Efficient Prediction of Aggregated Intensity of Dependency in Large-Scale Cloud Systems[C]// IEEE. 2021 36th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering (ASE). IEEE, 2021: 653-665. |
| [37] | PEARSON S, CAMPOS J, JUST R, et al. Evaluating and Improving Fault Localization[C]// IEEE. 2017 IEEE/ACM 39th International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE). New York: IEEE, 2017: 609-620. |
| [38] | LIN Jinjin, CHEN Pengfei, ZHENG Zibin. Microscope: Pinpoint Performance Issues with Causal Graphs in Micro-Service Environments[EB/OL]. (2018-11-07)[2024-03-12]. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-03596-9_1. |
| [39] | WU L, TORDSSON J, ELMROTH E, et al. MicroRCA: Root Cause Localization of Performance Issues in Microservices[EB/OL]. [2024-03-12]. https://www.xueshufan.com/publication/2999561215. |
| [1] | 张浩, 谢大智, 胡云晟, 叶骏威. 基于半监督学习的网络异常检测研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(4): 491-508. |
| [2] | 王健, 陈琳, 王凯崙, 刘吉强. 基于时空图神经网络的应用层DDoS攻击检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(4): 509-519. |
| [3] | 江荣, 刘海天, 刘聪. 基于集成学习的无监督网络入侵检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 411-426. |
| [4] | 宋玉涵, 祝跃飞, 魏福山. 一种基于AdaBoost模型的区块链异常交易检测方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1): 24-35. |
| [5] | 秦中元, 马楠, 余亚聪, 陈立全. 基于双重图神经网络和自编码器的网络异常检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(9): 1-11. |
| [6] | 蒋英肇, 陈雷, 闫巧. 基于双通道特征融合的分布式拒绝服务攻击检测算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(7): 86-97. |
| [7] | 施园, 李杨, 詹孟奇. 一种面向微服务的多维度根因定位算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(3): 73-83. |
| [8] | 吴圣麟, 刘汪根, 严明, 吴杰. 基于无监督系统调用规则生成的容器云实时异常检测系统[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(12): 91-102. |
| [9] | 廖丽云, 张伯雷, 吴礼发. 基于代价敏感学习的物联网异常检测模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 94-103. |
| [10] | 张玉臣, 李亮辉, 马辰阳, 周洪伟. 一种融合变量的日志异常检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(10): 16-20. |
| [11] | 顾兆军, 刘婷婷, 高冰, 隋翯. 基于GAN-Cross的工控系统类不平衡数据异常检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(8): 81-89. |
| [12] | 周婧怡, 李红娇. 针对PMU测量的虚假数据注入攻击检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(5): 75-83. |
| [13] | 陈彬杰, 魏福山, 顾纯祥. 基于KNN的具有隐私保护功能的区块链异常交易检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(3): 78-84. |
| [14] | 徐茹枝, 吕畅冉, 龙燕, 刘远彬. 工业控制系统高隐蔽性数据攻击防御方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(12): 34-46. |
| [15] | 郭森森, 王同力, 慕德俊. 基于生成对抗网络与自编码器的网络流量异常检测模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(12): 7-15. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||