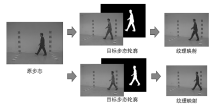
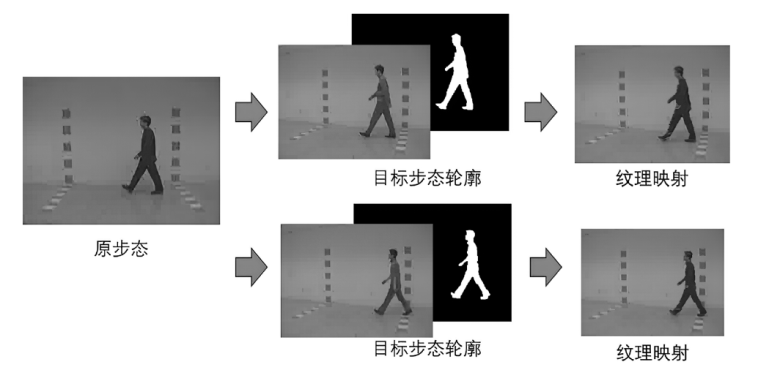
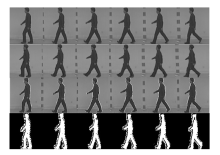
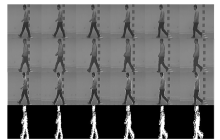
信息网络安全 ›› 2024, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (1): 48-59.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2024.01.005
一种基于轮廓稀疏对抗的视频步态隐私保护算法
- 上海交通大学网络空间安全学院,上海 200240
-
收稿日期:2023-06-28出版日期:2024-01-10发布日期:2024-01-24 -
通讯作者:蒋兴浩 E-mail:xhjiang@sjtu.edu.cn -
作者简介:许可(1990—),男,辽宁,副研究员,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为步态识别和动作识别|李嘉怡(1999—),女,山东,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为步态隐私保护和对抗攻击|蒋兴浩(1976—),男,河南,教授,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为多媒体内容安全和对抗攻防|孙锬锋(1975—),男,吉林,教授,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为多媒体取证 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(62372295);国家自然科学基金(62002220)
A Video Gait Privacy Protection Algorithm Based on Sparse Adversarial Attack on Silhouette
XU Ke, LI Jiayi, JIANG Xinghao( ), SUN Tanfeng
), SUN Tanfeng
- School of Cyber Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
-
Received:2023-06-28Online:2024-01-10Published:2024-01-24 -
Contact:JIANG Xinghao E-mail:xhjiang@sjtu.edu.cn
摘要:
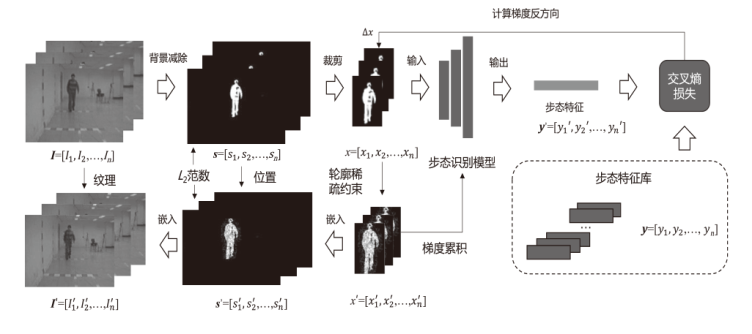
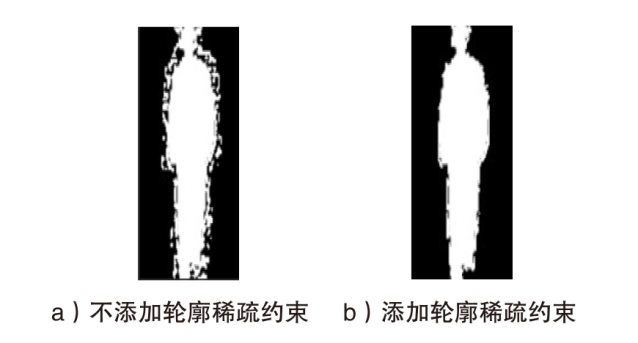
深度网络模型可以从视频步态序列中获取人体步态生物特征并识别人物身份,造成严重的隐私泄露安全威胁。现有方法一般通过对视频画面中的人体进行模糊、变形等处理来保护隐私,这些方法可以在一定程度上改变人体外观,但很难改变人物行走姿态,难以逃避深度网络模型的识别,且这种处理往往伴随着对视频质量的严重破坏,降低了视频的视觉可用性。针对该问题,文章提出一种基于轮廓稀疏对抗的视频步态隐私保护算法,通过对步态识别模型的对抗攻击来计算画面中人体轮廓周围的有效修改位置。与传统方法相比,在具有相同隐私保护能力的情况下,该算法减少了对画面的修改,在隐私安全性和视觉可用性上达到了较好的均衡。该算法在公开步态数据库CASIA-B和OUMVLP上对4种步态识别模型进行测试,通过与不同步态隐私保护方法对比,验证了该算法在步态隐私保护上的有效性和可用性。
中图分类号:
引用本文
许可, 李嘉怡, 蒋兴浩, 孙锬锋. 一种基于轮廓稀疏对抗的视频步态隐私保护算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1): 48-59.
XU Ke, LI Jiayi, JIANG Xinghao, SUN Tanfeng. A Video Gait Privacy Protection Algorithm Based on Sparse Adversarial Attack on Silhouette[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(1): 48-59.
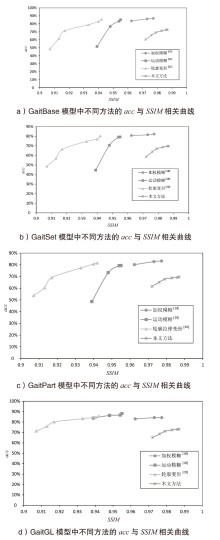
表1
CASIA-B数据集上的测试结果
| 目标模型 | 方法 | NM | BG | CL | 加权平均 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GaitBase[ | 加权模糊*[ | 91.20% | 86.91% | 70.14% | 86.13% |
| 运动模糊*[ | 83.95% | 76.15% | 55.49% | 76.70% | |
| 轮廓拉伸*[ | 88.46% | 83.57% | 66.24% | 83.04% | |
| 本文方法 | 78.60% | 70.97% | 56.73% | 72.70% | |
| GaitSet[ | 加权模糊*[ | 85.95% | 78.78% | 59.75% | 79.28% |
| 运动模糊*[ | 77.89% | 69.55% | 49.39% | 70.52% | |
| 轮廓拉伸*[ | 82.55% | 77.73% | 59.24% | 76.92% | |
| 本文方法 | 75.45% | 68.31% | 53.70% | 69.67% | |
| GaitPart[ | 加权模糊*[ | 85.29% | 77.46% | 63.70% | 79.40% |
| 运动模糊*[ | 80.57% | 70.26% | 54.78% | 73.35% | |
| 轮廓拉伸*[ | 85.25% | 79.45% | 68.21% | 80.68% | |
| 本文方法 | 75.04% | 66.85% | 56.30% | 69.65% | |
| GaitGL[ | 加权模糊*[ | 90.85% | 87.18% | 73.76% | 86.70% |
| 运动模糊*[ | 89.00% | 84.25% | 67.39% | 83.72% | |
| 轮廓拉伸*[ | 88.18% | 85.39% | 72.70% | 84.52% | |
| 本文方法 | 77.55% | 71.57% | 61.21% | 73.09% |
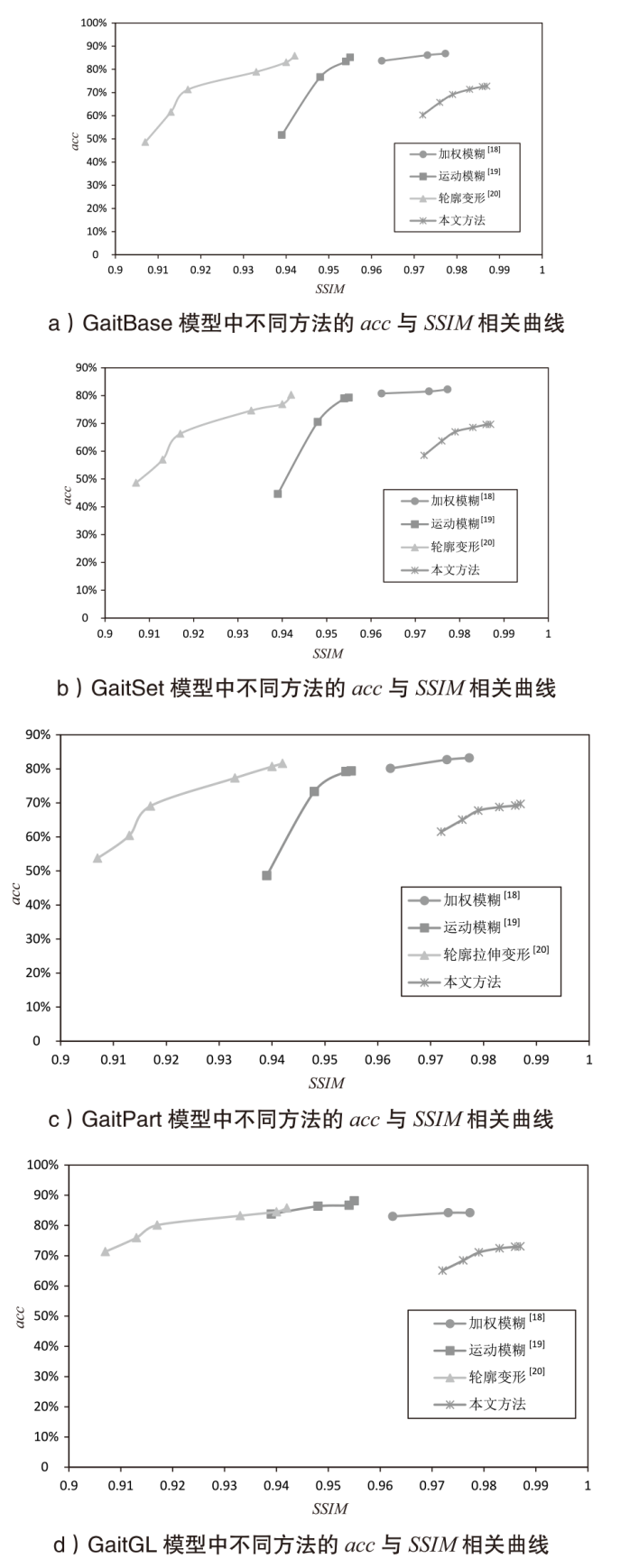
表2
OUMVLP数据集上的测试结果
| 目标模型 | 方法 | NM |
|---|---|---|
| GaitBase[ | 加权模糊*[ | 91.96% |
| 运动模糊*[ | 88.06% | |
| 轮廓拉伸*[ | 90.98% | |
| 本文方法 | 78.48% | |
| GaitSet[ | 加权模糊*[ | 88.85% |
| 运动模糊*[ | 87.63% | |
| 轮廓拉伸*[ | 87.59% | |
| 本文方法 | 78.40% | |
| GaitPart[ | 加权模糊*[ | 88.09% |
| 运动模糊*[ | 87.33% | |
| 轮廓拉伸*[ | 89.93% | |
| 本文方法 | 80.17% | |
| GaitGL[ | 加权模糊*[ | 91.51% |
| 运动模糊*[ | 90.32% | |
| 轮廓拉伸*[ | 92.04% | |
| 本文方法 | 81.40% |
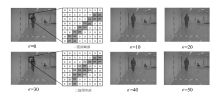
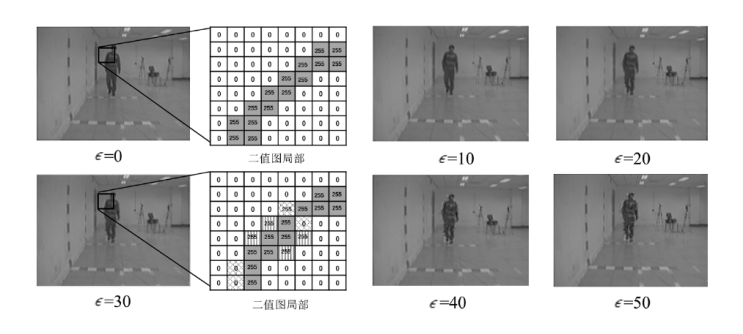
表3
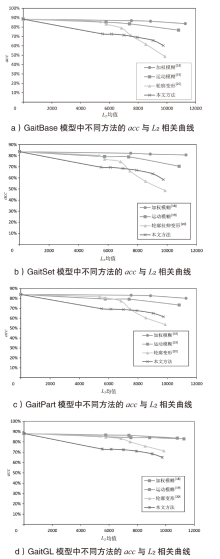
不同$\epsilon $下轮廓稀疏对抗后有效性和隐蔽性变化
| NM | BG | CL | 加权平均 | L2均值 | SSIM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 93.50% | 88.90% | 72.55% | 88.39% | 0 | 1.000 |
| 10 | 78.52% | 71.07% | 56.02% | 72.53% | 5521 | 0.986 |
| 20 | 77.41% | 70.18% | 54.40% | 71.36% | 6152 | 0.983 |
| 30 | 75.50% | 68.14% | 50.95% | 69.12% | 7010 | 0.979 |
| 40 | 72.58% | 64.35% | 46.56% | 65.73% | 7931 | 0.976 |
| 50 | 67.73% | 57.83% | 40.44% | 60.29% | 9036 | 0.972 |
| [1] |
CHEN Xingyuan, GAO Yuanzhao, TANG Huilin, et al. Research Progress on Big Data Security Technology[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2020, 50(1): 25-66.
doi: 10.1360/N112019-00077 URL |
| 陈性元, 高元照, 唐慧林, 等. 大数据安全技术研究进展[J]. 中国科学:信息科学, 2020, 50(1):25-66. | |
| [2] |
ALIREZA S M, ALI E. Deep Gait Recognition: A Survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(1): 264-284.
doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3151865 URL |
| [3] | YU Shiqi, TAN Daoliang, TAN Tieniu. A Framework for Evaluating the Effect of View Angle, Clothing and Carrying Condition on Gait Recognition[C]// IEEE. IEEE 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE. 2006: 441-444. |
| [4] |
IWAMA H, OKUMURA M, MAKIHARA Y, et al. The OU-ISI Gait Database Comprising the Large Population Dataset and Performance Evaluation of Gait Recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2012, 7(5): 1511-1521.
doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2012.2204253 URL |
| [5] |
TAKEMURA N, MAKIHARA Y, MURAMATSU D, et al. Multi-View Large Population Gait Dataset and Its Performance Evaluation for Cross-View Gait Recognition[J]. IPSJ Transactions on Computer Vision and Applications, 2018, 10(4):1-14.
doi: 10.1186/s41074-017-0037-0 |
| [6] | LI Xiang, YASUSHI M, XU Chi, et al. End-to-End Model-Based Gait Recognition Using Synchronized Multi-View Pose Constraint[C]// IEEE. IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. New York: IEEE, 2021: 4089-4098. |
| [7] | LI Xiang, YASUSHI M, XU Chi, et al. End-to-End Model-Based Gait Recognition[C]// Springer. Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Heidelberg: Springer, 2020: 3-20. |
| [8] |
ANNA S, ANTON K. Pose-Based Deep Gait Recognition[J]. IET Biometrics, 2019, 8(2): 134-143.
doi: 10.1049/iet-bmt.2018.5046 |
| [9] | TORBEN T, ALI K, JOHANNES G, et al. Gaitgraph: Graph Convolutional Network for Skeleton-Based Gait Recognition[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). New York: IEEE, 2021: 2314-2318. |
| [10] | HOU Saihui, CAO Chunshui, LIU Xu, et al. Gait Lateral Network: Learning Discriminative and Compact Representations for Gait Recognition[C]// Springer. European Conference on Computer Vision. Heidelberg: Springer, 2020: 382-398. |
| [11] | LIN Beibei, ZHANG Shunli, BAO Feng. Gait Recognition with Multiple-Temporal-Scale 3D Convolutional Neural Network[J]. ACM.Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. New York: ACM, 2020: 3054-3062. |
| [12] | LI Xiang, YASUSHI M, XU Chi, et al. Gait Recognition via Semi-Supervised Disentangled Representation Learning to Identity and Covariate Features[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2020: 13306-13316. |
| [13] | CHAO Hanqing, HE Yiwei, ZHANG Junping, et al. GaitSet: Regarding Gait as a Set for Cross-View Gait Recognition[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the Thirty-Third AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Thirty-First Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence Conference and Ninth AAAI Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence. New York: ACM, 2019: 8126-8133. |
| [14] |
ALIREZA S M, ALI E. View-Invariant Gait Recognition with Attentive Recurrent Learning of Partial Representations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biometrics, Behavior, and Identity Science, 2021, 3(1): 124-137.
doi: 10.1109/TBIOM.8423754 URL |
| [15] | ZHANG Ziyuan, LUAN T, LIU Feng, et al. On Learning Disentangled Representations for Gait Recognition[J]. IEEE, 2022, 44(1): 345-360. |
| [16] | ZHANG Jianwu, SHEN Wei, WU Zhendong. Recognition of Face Privacy Protection Using Convolutional Neural Networks[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2019, 24(5): 744-752. |
| 章坚武, 沈炜, 吴震东. 卷积神经网络的人脸隐私保护识别[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2019, 24(5): 744-752. | |
| [17] | SHAWN S, EMILY W, ZHANG Jiayun, et al. Fawkes: Protecting Privacy Against Unauthorized Deep Learning Models[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 29th USENIX Conference on Security Symposium. New York: ACM, 2020: 1589-1604. |
| [18] |
PRACHI A, NARAYANAN P J. Person De-Identification in Videos[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2011, 21(3): 299 -310.
doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2011.2105551 URL |
| [19] | PARASHAR A, SHEKHAWAT R S. Protection of Gait Data Set for Preserving Its Privacy in Deep Learning Pipeline[J]. IET Biometrics, 2022(11): 557-569. |
| [20] | YUKI H, KAZUAKI N, NAOKO N, et al. Anonymization of Human Gait in Video Based on Silhouette Deformation and Texture Transfer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2022(17): 3375-3390. |
| [21] | NGOC-DUNG T T, HUY H N, HOANG-QUOC, et al. An Approach for Gait Anonymization Using Deep Learning[C]// IEEE. 2017 IEEE Workshop on Information Forensics and Security (WIFS). New York: IEEE, 2017: 1-6. |
| [22] | NGOC-DUNG T T, HUY H N, FANG Fuming, et al. An RGB Gait Anonymization Model for Low-Quality Silhouettes[C]// IEEE. 2019 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC). New York: IEEE, 2019: 1686-1693. |
| [23] | NGOC-DUNG T T, JUNICHI Y, ISAO E. Color Transfer to Anonymized Gait Images While Maintaining Anonymization[C]// IEEE. 2020 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC). New York: IEEE, 2020: 1406-1413. |
| [24] | NGOC-DUNG T T, HUY H N, HOANG-QUOC N, et al. Spatio-Temporal Generative Adversarial Network for Gait Anonymization[J]. Journal of Information Security and Applications, 2019(46): 307-319. |
| [25] | YUKI H, KAZUAKI N, NAOKO N, et al. Anonymization of Gait Silhouette Video by Perturbing Its Phase and Shape Components[C]// IEEE. 2019 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC). New York: IEEE, 2019: 1679-1685. |
| [26] | JIANG Xinghao, ZHAO Zeyu, XU Ke. Adversarial Attack Technology for Vision-Based Aircraft Intelligent Object Detection[J]. Air & Space Defense, 2021, 4(1): 8-13. |
| 蒋兴浩, 赵泽宇, 许可. 基于视觉的飞行器智能目标检测对抗攻击技术[J]. 空天防御, 2021, 4(1): 8-13. | |
| [27] | CHRISTIAN S, WOJCIECH Z, ILYA S, et al. Intriguing Properties of Neural Networks[EB/OL]. (2013-12-21) [2023-07-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.6199. |
| [28] | IAN J G, JONATHON S, CHRISTIAN S. Explaining and Harnessing Adversarial Examples[EB/OL]. (2014-12-20) [2023-07-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6572. |
| [29] | ALEKSANDER M, ALEKSANDAR M, LUDWIG S, et al. Towards Deep Learning Models Resistant to Adversarial Attacks[EB/OL]. (2017-06-19) [2023-07-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.06083. |
| [30] | FAN Chao, LIANG Junhao, SHEN Chuanfu, et al. OpenGait: Revisiting Gait Recognition Toward Better Practicality[EB/OL]. (2022-11-12) [2023-07-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06597. |
| [31] | FAN Chao, PENG Yunjie, CAO Chunshui, et al. GaitPart: Temporal Part-Based Model for Gait Recognition[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2020: 14213-14221. |
| [32] | LIN Beibei, ZHANG Shunli, YU Xin, et al. Gait Recognition via Effective Global-Local Feature Representation and Local Temporal Aggregation[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). New York: IEEE, 2021: 14648-14656. |
| [1] | 沈华, 田晨, 郭森森, 慕志颖. 基于对抗性机器学习的网络入侵检测方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(8): 66-75. |
| [2] | 李晨蔚, 张恒巍, 高伟, 杨博. 基于AdaN自适应梯度优化的图像对抗迁移攻击方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(7): 64-73. |
| [3] | 蒋曾辉, 曾维军, 陈璞, 武士涛. 面向调制识别的对抗样本研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(6): 74-90. |
| [4] | 仝鑫, 金波, 王斌君, 翟晗名. 融合对抗增强和多任务优化的恶意短信检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(10): 21-30. |
| [5] | 胡卫, 赵文龙, 陈璐, 付伟. 基于Logits向量的JSMA对抗样本攻击改进算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(3): 62-69. |
| [6] | 郑耀昊, 王利明, 杨婧. 基于网络结构自动搜索的对抗样本防御方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(3): 70-77. |
| [7] | 夏强, 何沛松, 罗杰, 刘嘉勇. 基于普遍对抗噪声的高效载体图像增强算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(2): 64-75. |
| [8] | 张郅, 李欣, 叶乃夫, 胡凯茜. 融合多重风格迁移和对抗样本技术的验证码安全性增强方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 129-135. |
| [9] | 于克辰, 郭莉, 姚萌萌. 基于空间及能量维度的黑盒对抗样本生成方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(3): 72-78. |
| [10] | 仝鑫, 王罗娜, 王润正, 王靖亚. 面向中文文本分类的词级对抗样本生成方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(9): 12-16. |
| [11] | 李红娇, 陈红艳. 基于WGAN的移动恶意对抗样本生成研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(11): 51-58. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||