信息网络安全 ›› 2024, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (1): 36-47.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2024.01.004
基于区块链和SM9数字签名的代理投票方案
朱郭诚1,2, 何德彪1,2( ), 安浩杨1,2, 彭聪1,2
), 安浩杨1,2, 彭聪1,2
- 1.武汉大学国家网络安全学院,武汉 430072
2.武汉大学空天信息安全与可信计算教育部重点实验室,武汉 430072
-
收稿日期:2023-02-22出版日期:2024-01-10发布日期:2024-01-24 -
通讯作者:何德彪 E-mail:hedebiao@163.com -
作者简介:朱郭诚(1996—),男,安徽,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为密码协议、区块链技术与应用|何德彪(1980—),男,湖北,教授,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为密码协议、信息安全、区块链技术与应用|安浩杨(1997—),男,山西,博士研究生,CCF会员,主要研究方向为密码协议、区块链技术与应用|彭聪(1989—),男,湖北,副研究员,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为公钥密码学 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(U21A20466);国家自然科学基金(62172307);国家自然科学基金(62272350)
The Proxy Voting Scheme Based on the Blockchain and SM9 Digital Signature
ZHU Guocheng1,2, HE Debiao1,2( ), AN Haoyang1,2, PENG Cong1,2
), AN Haoyang1,2, PENG Cong1,2
- 1. School of Cyber Science and Engineering, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China
2. Key Laboratory of Aerospace Information Security and Trusted Computing of Ministry of Education, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China
-
Received:2023-02-22Online:2024-01-10Published:2024-01-24 -
Contact:HE Debiao E-mail:hedebiao@163.com
摘要:
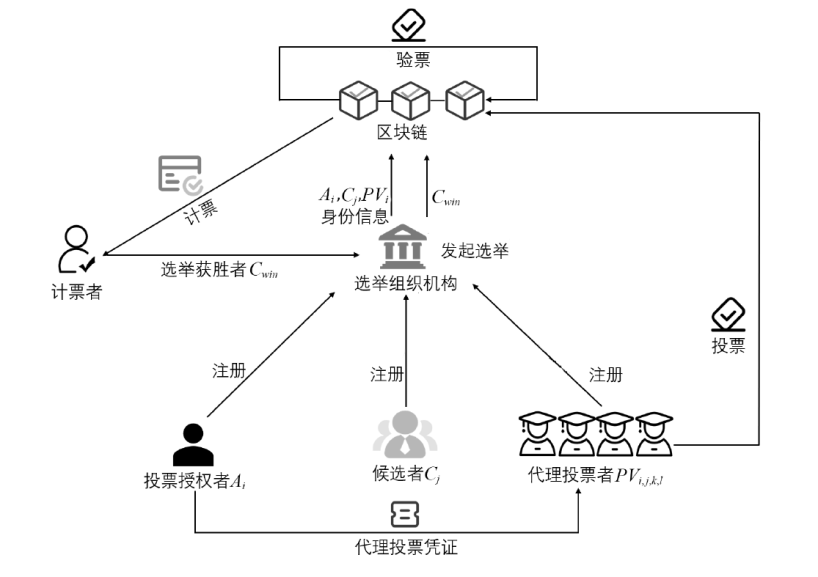
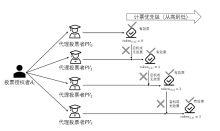
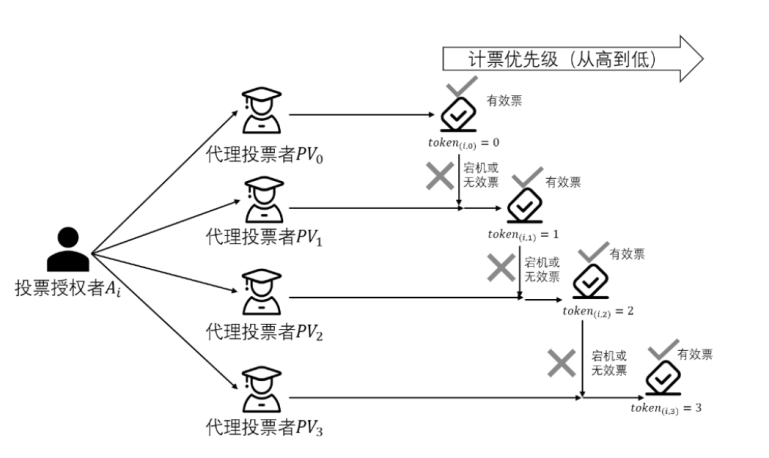
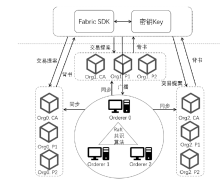
随着互联网的普及,电子投票技术逐渐替代传统纸质投票技术。然而,传统的电子投票方案主要针对一人一票制来设计方案,在一些特殊的投票场景下,一人一票制投票方式不再适用。例如,投票者不具备专业知识却也需要投票的场景,投票者由于不能理解选举的内容而消极投票,造成选举结果不专业和不公正等问题。此外,传统的电子投票技术还存在选举过程不透明和选票不可验证等问题。针对上述问题,文章提出一种基于区块链和SM9数字签名的代理投票方案。该方案首先使用区块链技术解决选票的全局可验证问题,其次使用零知识范围证明技术解决恶意选票值的问题,然后利用基于椭圆曲线的改进ElGamal算法的同态性质实现选票加密和自计票功能,最后使用SM9数字签名算法和变色龙哈希函数设计的代理投票凭证实现投票权的转让过程。通过安全性分析,证明了文章所提方案满足鲁棒性、合法性、机密性、全局可验证性和公平性。理论分析和实验数据表明,文章所提方案性能良好,适用于需要专业知识场景下的选举。
中图分类号:
引用本文
朱郭诚, 何德彪, 安浩杨, 彭聪. 基于区块链和SM9数字签名的代理投票方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1): 36-47.
ZHU Guocheng, HE Debiao, AN Haoyang, PENG Cong. The Proxy Voting Scheme Based on the Blockchain and SM9 Digital Signature[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(1): 36-47.
表1
符号及其定义
| 符号 | 定义 |
|---|---|
| 大素数 | |
| 由 | |
| 阶为 | |
| 阶为 | |
| 群 | |
| 乘法群 | |
| 椭圆曲线上点 | |
| 从 | |
| 由密码杂凑函数派生的密码函数,均为 | |
| x与y的拼接,其中x, y可以是比特串 | |
| EA的公私钥对, | |
| 投票授权者Ai的可辨别标识,部分私钥、秘密值 | |
| 投票授权者Ai的公私钥对 | |
| 代理投票者 | |
| 候选者 | |
| 选票值 | |
| 代理投票者 | |
| Ai对 | |
| 投票授权者授权Ai对代理投票者 |
表3
开销符号及其定义
| 符号 | 定义 |
|---|---|
| 一次模乘运算的时间 | |
| 群G1中的点乘运算 | |
| 群G2中的点乘运算 | |
| 一次模幂运算的时间 | |
| 一次模逆运算的时间 | |
| 一次双线性对运算的时间 | |
| 暴力求解最终选票值的时间 | |
| 候选者人数 | |
| 投票者人数 | |
| G1中元素的比特长度 | |
| G2中元素的比特长度 | |
| GT中元素的比特长度 | |
| 选票中合法分值的最大值 |
表4
性能对比
| 投票阶段 | 本文方案 | 文献[13]方案 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 计算开销 | 通信开销 | 计算开销 | 通信开销 | |
| 系统初始化 | E2+l(tInv+E1) | l|G1|+|G2| | — | 2i(大整数 比特长) |
| 代理投票者 注册 | 2E1 | 2|G1| | tm | 3|Zq*| |
| 投票授权者 注册 | 2E1+2E2+2tInv+ tm+3thash | |G2| | — | — |
| 候选者 注册 | E1 | |G1| | — | (l+2)|Zq*| |
| 代理凭证 生成 | 4(tBP+tm+tp+ 2E1+thash) | |Zq*|+3|G1| | — | — |
| 投票 | nc(7E1+2tBP+ 4tm+th) | nc(7|G1|+|GT|+ 4|Zq*|) | nc(8tp+7tm+ thash) | nc(|GT|+ 11|Zq*|) |
| 验票 | nc(7E1+E2+5tBP+ tm+tp+4thash) | — | nc(8tp+5tm+ thash) | — |
| 计票 | nc(4nvE1+tc) | — | nc((3nv+1)tm+(nv+ 1)tp+tc) | — |
表6
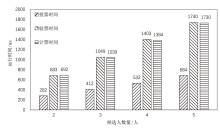
投票方案的性能测试结果
| 投票阶段 | 计算开销(理论) | 实验结果/ms | 通信开销(理论) | 大小/bit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 系统初始化 | E2+l(tInv+E1) | 10.386 | l|G1|+|G2| | 2560 |
| 代理投票者 注册 | 2E1 | 3.46 | 2|G1| | 1024 |
| 投票授权者 注册 | 2E1+2E2+2tInv+ tm+3thash | 13.884 | |G2| | 1024 |
| 候选者 注册 | E1 | 1.73 | |G1| | 512 |
| 代理凭证 生成 | 4(tBP+tm+tp+ 2E1+thash) | 339.64 | |Zq*|+3|G1| | 1792 |
| 投票 | nc(7E1+2tBP+ 4tm+thash) | 684.75 | nc(7|G1|+|GT|+ 4|Zq*|) | 38400 |
| 验票 | nc(7E1+E2+5tBP+ tm+tp+4thash) | 1740.55 | — | — |
| 计票 | nc(4nvE1+tc) | 1730.15 | — | — |
| [1] |
XU Guangxia, DONG Jingnan, MA Chuang, et al. A Certificateless Signcryption Mechanism Based on Blockchain for Edge Computing[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 10(14): 11960-11974.
doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3151359 URL |
| [2] | LIU Feng, YANG Jie, LI Zhibin, et al. A Secure Multi-Party Computation Protocol for Universal Data Privacy Protection Based on Blockchain[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2021, 58(2): 281-290. |
| 刘峰, 杨杰, 李志斌, 等. 一种基于区块链的泛用型数据隐私保护的安全多方计算协议[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2021, 58(2): 281-290. | |
| [3] |
LIU Feng, ZHANG Jiahao, ZHOU Junjie, et al. Novel Hash-Time-Lock-Contract Based Cross-Chain Token Swap Mechanism of Blockchain[J]. Computer Science, 2022, 49(1): 336-344.
doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.210600170 |
|
刘峰, 张嘉淏, 周俊杰, 等. 基于改进哈希时间锁的区块链跨链资产交互协议[J]. 计算机科学, 2022, 49(1): 336-344.
doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.210600170 |
|
| [4] | LIU Feng, LI Zhihan, JIA Kun, et al. Bitcoin Address Clustering Based on Change Address Improvement[EB/OL]. (2023-01-31) [2023-02-10]. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10034437. |
| [5] |
LIU Feng, WANG Yifan, YANG Jie, et al. Blockchain-Based High-Threshold Signature Protocol Integrating DKG and BLS[J]. Computer Science, 2021, 48(11): 46-53.
doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.210200129 |
|
刘峰, 王一帆, 杨杰, 等. 一种基于区块链的融合DKG与BLS的高阈值签名协议[J]. 计算机科学, 2021, 48(11): 46-53.
doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.210200129 |
|
| [6] | HAO Feng, KREEGER M N, RANDELL B, et al. Every Vote Counts: Ensuring Integrity in {Large-Scale} Electronic Voting[C]// USENIX. 2014 Electronic Voting Technology Workshop/Workshop on Trustworthy Elections (EVT/WOTE 14). Berkley: USENIX, 2014: 1-25. |
| [7] | ZHAO Zhichao, CHAN T H H. How to Vote Privately Using Bitcoin[C]// Springer. International Conference on Information and Communications Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2015: 82-96. |
| [8] | NAKAMOTO S. Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System[EB/OL]. (2008-10-31) [2023-02-10]. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228640975_Bitcoin_A_Peer-to-Peer_Electronic_Cash_System. |
| [9] | CRUZ J P, KAJI Y. E-Voting System Based on the Bitcoin Protocol and Blind Signatures[J]. IPSJ Transactions on Mathematical Modeling and Its Applications, 2017, 10(1): 14-22. |
| [10] | KULYK O, NEUMANN S, MARKY K, et al. Coercion-Resistant Proxy Voting[J]. Computers & Security, 2017(71): 88-99. |
| [11] | FAN Xingyue, WU Ting, ZHENG Qiuhua, et al. Hse-Voting: A Secure High-Efficiency Electronic Voting Scheme Based on Homomorphic Signcryption[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2020(111): 754-762. |
| [12] | HUANG Jun, HE Debiao, OBAIDAT M S, et al. The Application of the Blockchain Technology in Voting Systems: A Review[J]. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 2021, 54(3): 1-28. |
| [13] |
HUANG Jun, HE Debiao, CHEN Yitao, et al. A Blockchain-Based Self-Tallying Voting Protocol with Maximum Voter Privacy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2022, 9(5): 3808-3820.
doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2022.3190909 URL |
| [14] | WOOD G. Ethereum: A Secure Decentralised Generalised Transaction Ledger[J]. Ethereum Project Yellow Paper, 2014(151): 1-32. |
| [15] | CAI Juliang, TAO Xiaofeng, WANG Chenyu. Cooperative Authentication Scheme for Heterogeneous Networks Based on Identity Group Signature and Blockchain[EB/OL]. (2023-01-08) [2023-02-10]. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10213226/metrics#metrics. |
| [16] | BEN-OR M, GOLDREICH O, GOLDWASSER S, et al. Everything Provable is Provable in Zero-Knowledge[C]// Springer. Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptography. Heidelberg: Springer, 1988: 37-56. |
| [17] | WATERS B. Efficient Identity-Based Encryption without Random Oracles[C]// Springer. 24th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques. Heidelberg: Springer, 2005: 114-127. |
| [18] | BARRETO P S L M, NAEHRIG M. Pairing-Friendly Elliptic Curves of Prime Order[C]// Springer. Selected Areas in Cryptography(SAC 2005). Heidelberg: Springer, 2006: 319-331. |
| [19] | BONEH D, BOYEN X. Short Signatures without Random Oracles[C]// Springer. International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques. Heidelberg: Springer, 2004: 56-73. |
| [20] | CAMENISCH J, CHAABOUNI R, SHELAT A, et al. Efficient Protocols for Set Membership and Range Proofs[C]// Springer. International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security (ASIACRYPT 2008). Heidelberg: Springer, 2008: 234-252. |
| [21] | KRAWCZYK H, RABIN T. Chameleon Hashing and Signatures[EB/OL]. (1998-03-17) [2023-02-10]. . |
| [22] | CHEN Xiaofeng, ZHANG Fangguo, SUSILO W, et al. Efficient Generic on-Line/off-Line Signatures without Key Exposure[C]// Springer. International Conference on Applied Cryptography and Network Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2007: 18-30. |
| [23] | XU Guangxia, ZHANG Jiajun, CLIFF U G O, et al. An Efficient Blockchain-Based Privacy-Preserving Scheme with Attribute and Homomorphic Encryption[J]. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2022, 178(21): 4192-4203. |
| [24] |
ELGAMAL T. A Public Key Cryptosystem and a Signature Scheme Based on Discrete Logarithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1985, 31(4): 469-472.
doi: 10.1109/TIT.1985.1057074 URL |
| [25] | FAUST S, KOHLWEISS M, MARSON G A, et al. On the Non-Malleability of the Fiat-Shamir Transform[C]// Springer. International Conference on Cryptology in India. Heidelberg: Springer, 2012: 60-79. |
| [26] | YANG Xuechao, YI Xun, NEPAL S, et al. Blockchain Voting: Publicly Verifiable Online Voting Protocol without Trusted Tallying Authorities[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2020(112): 859-874. |
| [27] | KIAYIAS A, YUNG M. Self-Tallying Elections and Perfect Ballot Secrecy[C]// Springer. 5th International Workshop on Practice and Theory in Public Key Cryptosystems. Heidelberg: Springer, 2002: 141-158. |
| [28] | QU Wenlei, WU Lei, WANG Wei, et al. A Electronic Voting Protocol Based on Blockchain and Homomorphic Signcryption[EB/OL]. (2020-06-16) [2023-02-10]. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/cpe.5817. |
| [1] | 吴昊天, 李一凡, 崔鸿雁, 董琳. 基于零知识证明和区块链的联邦学习激励方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1): 1-13. |
| [2] | 公鹏飞, 谢四江, 程安东. 基于HotStuff改进的多主节点共识算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(9): 108-117. |
| [3] | 周权, 陈民辉, 卫凯俊, 郑玉龙. 基于SM9的属性加密的区块链访问控制方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(9): 37-46. |
| [4] | 赵佳豪, 蒋佳佳, 张玉书. 基于动态默克尔哈希树的跨链数据一致性验证模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(9): 95-107. |
| [5] | 邵震哲, 蒋佳佳, 赵佳豪, 张玉书. 面向跨链的改进加权拜占庭容错算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(8): 109-120. |
| [6] | 覃思航, 代炜琦, 曾海燕, 顾显俊. 基于区块链的电力应用数据安全共享研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(8): 52-65. |
| [7] | 郭瑞, 魏鑫, 陈丽. 工业物联网环境下可外包的策略隐藏属性基加密方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(3): 1-12. |
| [8] | 安浩杨, 何德彪, 包子健, 彭聪. 一种基于证书的数字签名方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(3): 13-21. |
| [9] | 李春晓, 王耀飞, 徐恩亮, 赵钰. 基于双线性映射的区块链安全范围搜索技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(3): 22-34. |
| [10] | 王晶宇, 马兆丰, 徐单恒, 段鹏飞. 支持国密算法的区块链交易数据隐私保护方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(3): 84-95. |
| [11] | 李家辉, 秦素娟, 高飞, 孙东旭. 基于属性加密的区块链组织交易可控可监管隐私保护方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(12): 103-112. |
| [12] | 冯怡婷, 马兆丰, 徐单恒, 段鹏飞. 跨链接入的区块链安全强度评估方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(1): 84-92. |
| [13] | 张光华, 刘永升, 王鹤, 于乃文. 基于BiLSTM和注意力机制的智能合约漏洞检测方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(9): 46-54. |
| [14] | 胡艺, 佘堃. 基于区块链和智能合约的双链车联网系统[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(8): 26-35. |
| [15] | 黄保华, 赵伟宏, 彭丽, 谢统义. 基于MPT索引的高效链上PKI模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(8): 72-80. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||