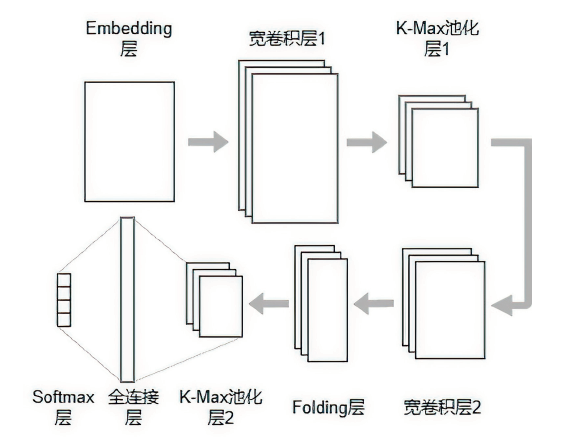
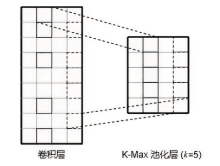
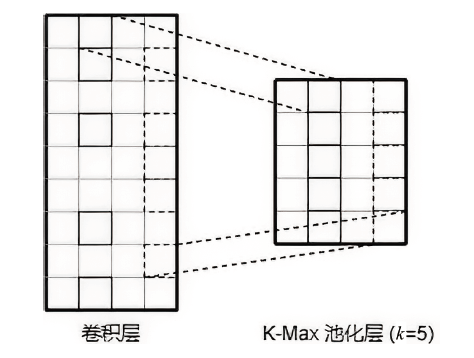
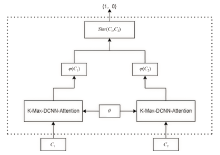
信息网络安全 ›› 2023, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (5): 62-75.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2023.05.007
基于Siamese架构的恶意软件隐藏函数识别方法
- 四川大学网络空间安全学院,成都 610065
-
收稿日期:2022-12-15出版日期:2023-05-10发布日期:2023-05-15 -
通讯作者:贾鹏 E-mail:pengjia@scu.edu.cn -
作者简介:陈梓彤(1997—),男,广西,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为二进制安全|贾鹏(1988—),男,河南,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为漏洞挖掘、软件动静态分析|刘嘉勇(1962—),男,四川,教授,博士,主要研究方向为网络应用安全、信息内容安全 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(61902265)
Identification Method of Malicious Software Hidden Function Based on Siamese Architecture
CHEN Zitong, JIA Peng( ), LIU Jiayong
), LIU Jiayong
- School of Cyber Science and Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, China
-
Received:2022-12-15Online:2023-05-10Published:2023-05-15 -
Contact:JIA Peng E-mail:pengjia@scu.edu.cn
摘要:
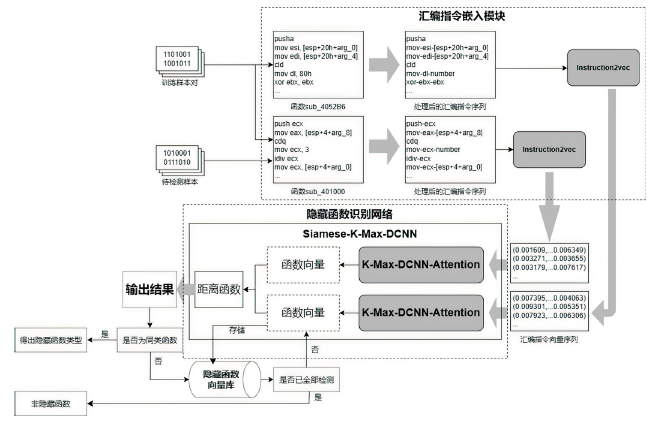
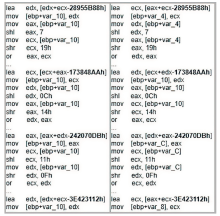
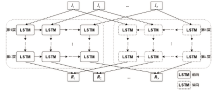
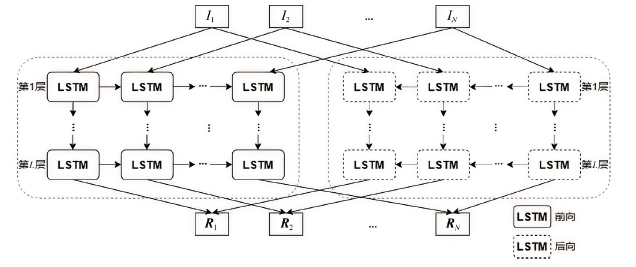
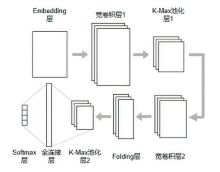
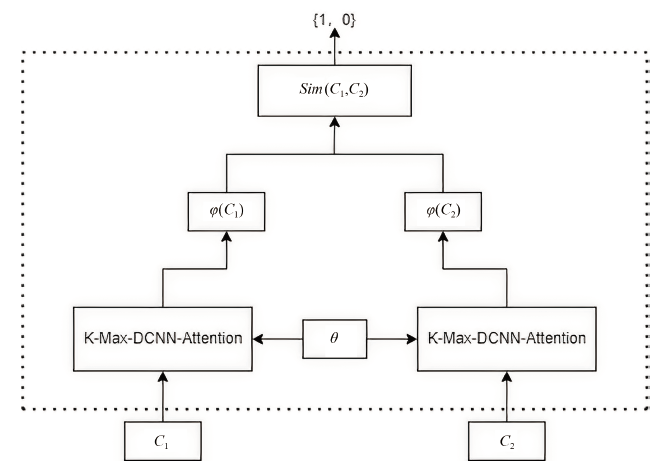
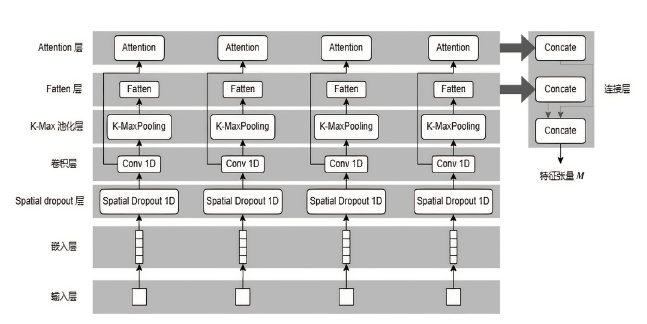
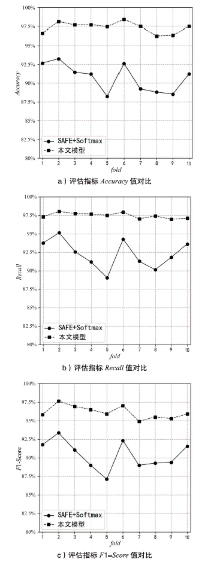
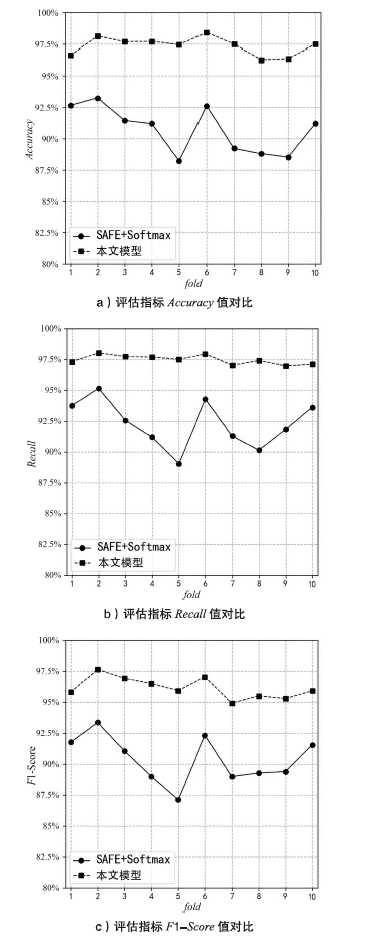
目前,隐藏技术已被普遍应用于恶意软件中,以避免反病毒引擎的检测及研究人员的反向分析,所以有效识别恶意软件中的隐藏函数对于恶意软件代码检测和深度分析具有重要意义。但在该领域上,现有方法不同程度都存在一些问题,如无法取得高准确性、对样本量少或者样本类别分布不平衡的数据集的鲁棒性较差等。为实现实用的针对恶意软件隐藏函数的检测方法,文章提出一种新颖的基于Siamese架构的识别方法来检测隐藏函数的类型。该方法可以有效提高隐藏函数识别的准确性,Siamese架构的引入改善了小样本量数据集鲁棒性差的问题。针对从恶意软件中提取的15种常见类型的隐藏函数的数据集进行实验,结果表明,该方法生成的嵌入向量较嵌入神经网络SAFE具有更好的质量,该方法较几种常用的隐藏函数检测工具有更高的检测精度。
中图分类号:
引用本文
陈梓彤, 贾鹏, 刘嘉勇. 基于Siamese架构的恶意软件隐藏函数识别方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(5): 62-75.
CHEN Zitong, JIA Peng, LIU Jiayong. Identification Method of Malicious Software Hidden Function Based on Siamese Architecture[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(5): 62-75.
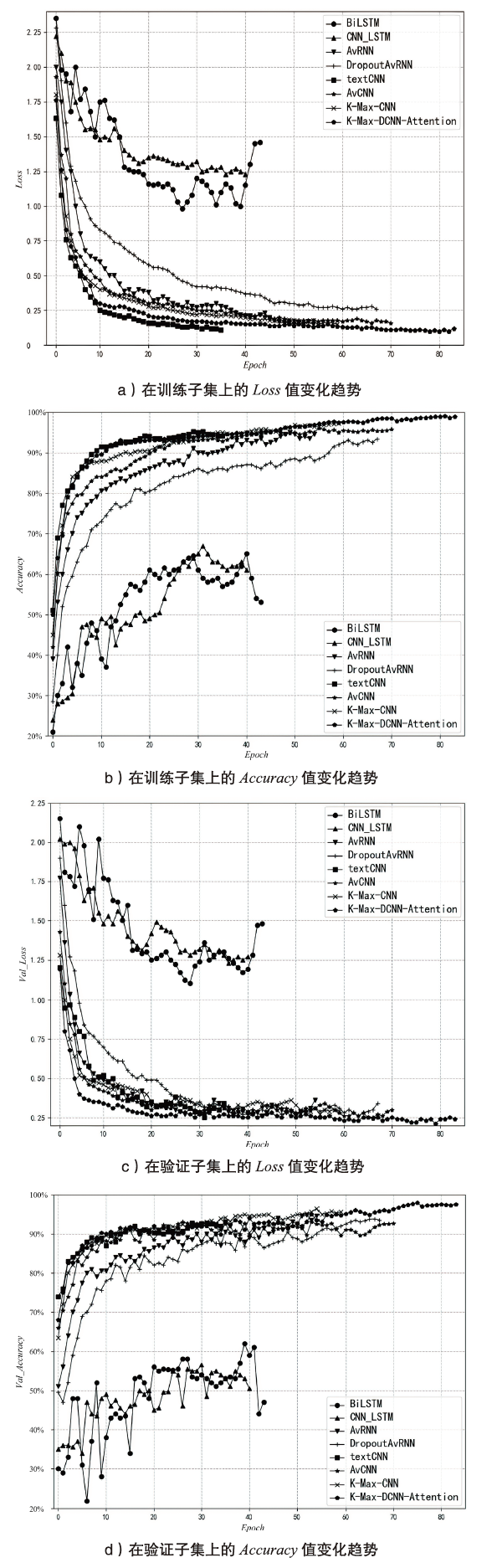
表4
8个模型的评估指标比较
| 神经网络模型 | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BiLSTM | 58.34 % | 54.81 % | 56.93 % | 55.85 % |
| CNN_LSTM | 61.04 % | 60.49 % | 61.04 % | 60.76 % |
| AvRNN | 93.91 % | 93.08 % | 93.40 % | 93.24 % |
| DropoutAvRNN | 92.38 % | 90.76 % | 89.93 % | 90.34 % |
| textCNN | 91.94 % | 90.84 % | 90.35 % | 90.59 % |
| AvCNN | 95.26 % | 93.83 % | 92.67 % | 93.20 % |
| K-MAX-CNN | 96.51 % | 95.72 % | 94.76 % | 95.24 % |
| K-Max-DCNN-Attention | 98.45 % | 97.95 % | 97.03 % | 97.49 % |
表5
各工具支持检测的隐藏算法类型
| 检测工具 算法种类 | 本文方法 | Findcrypt | IDAscope | HCD | Crypto Searcher | DRACA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADLER32 | ○ | ● | ○ | ○ | ● | ● |
| aPLib | ○ | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| BASE64 | ○ | ○ | ● | ○ | ○ | ● |
| BLOWFISH | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| CRC32 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| CRC32[poly] | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ● | ● |
| DES[char] | ○ | ● | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| HAVAL(5 pass) | ○ | ● | ○ | ○ | ● | ● |
| MD5 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| RC5/RC6 | ○ | ● | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| SHA-256 | ○ | ● | ● | ○ | ○ | ● |
| SHA-1 | ○ | ○ | ● | ○ | ● | ○ |
| ZLIB[long] | ○ | ● | ○ | ○ | ● | ● |
| ZLIB[word] | ○ | ● | ○ | ○ | ● | ● |
| Big-number | ○ | ○ | ● | ● | ● | ● |
表6
各工具的检测准确率
| 检测工具 算法种类 | 函数 数量 | 本文方案 | Findcrypt | IDAscope | HCD | Crypto Searcher |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADLER32 | 27 | 25 | 0 | 25 | 22 | 0 |
| aPLib | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| BASE64 | 15 | 13 | 15 | 0 | 13 | 11 |
| BLOWFISH | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| CRC32 | 32 | 28 | 32 | 32 | 26 | 0 |
| CRC32[poly] | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| DES[char] | 9 | 7 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| HAVAL(5 pass) | 10 | 10 | 1 | 2 | 10 | 0 |
| MD5 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 3 | 26 | 28 |
| RC5/RC6 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| SHA-256 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| SHA-1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ZLIB[long] | 8 | 6 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| ZLIB[word] | 10 | 8 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 |
| Big-number | 11 | 7 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 其余函数 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 |
| 总计 | 200 | 178 | 123 | 121 | 136 | 79 |
| 准确率 | — | 89% | 61.5% | 60.5% | 68% | 39.5% |
| [1] | LI Jizhong. Research on Key Technology of Cryptography Algorithm Recognition and Analysis[D]. Zhengzhou: PLA Information Engineering University, 2014. |
| 李继中. 密码算法识别与分析关键技术研究[D]. 郑州: 解放军信息工程大学, 2014. | |
| [2] | CAI Jianzhang, WEI Qiang, ZHU Yuefei. Identification of Encrypted Function in Malicious Software[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2013, 33(11): 3239-3243. |
| 蔡建章, 魏强, 祝跃飞. 识别恶意软件中的加密函数[J]. 计算机应用, 2013, 33(11): 3239-3243. | |
| [3] | WRIGHT J L, MANIC M. Neural Network Approach to Locating Cryptography in Object Code[C]// IEEE. 2009 IEEE Conference on Emerging Technologies & Factory Automation. New York: IEEE, 2009: 1-4. |
| [4] | AIGNER A. Falke-Mc: A Neural Network Based Approach to Locate Cryptographic Functions in Machine Code[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Availability, Reliability and Security. New York: ACM, 2018: 1-8. |
| [5] | CHUA Z L, SHEN S, SAXENA P, et al. Neural Nets Can Learn Function Type Signatures From Binaries[C]// ACM. USENIX Security Symposium. New York: ACM, 2017: 99-116. |
| [6] | DING S H H, FUN B C M, CHARLAND P. Asm2vec: Boosting Static Representation Robustness for Binary Clone Search Against Code Obfuscation and Compiler Optimization[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York: IEEE, 2019: 472-489. |
| [7] | XU Xiaojun, LIU Chang, FENG Qian, et al. Neural Network-Based Graph Embedding for Cross-Platform Binary Code Similarity Detection[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2017: 363-376. |
| [8] | MASSARELLI L, DI LUNA G A, PETRONI F, et al. SAFE: Self-Attentive Function Embeddings for Binary Similarity[C]// Springer. Detection of Intrusions and Malware, and Vulnerability Assessment:16th International Conference, DIMVA 2019. Heidelberg: Springer, 2019: 309-329. |
| [9] | HARVEY I. Cipher Hunting: How to Find Cryptographic Algorithms in Large Binaries[J]. NCipher Corporation Ltd. 2001: 46-51. |
| [10] | CABALLERO J, YIN H, LIANG Z, et al. Polyglot: Automatic Extraction of Protocol Message Format Using Dynamic Binary Analysis[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 14th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2007: 317-329. |
| [11] | CABALLERO J, JOHNSON N M, MCCAMANT S, et al. Binary Code Extraction and Interface Identification for Security Applications[R]. Berkeley: California University Berkeley of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, UCB/EECS-2009-133, 2009. |
| [12] | LIN Z, JIANG X, XU D, et al. Automatic Protocol Format Reverse Engineering through Context-Aware Monitored Execution[C]// NDSS. 15th Annual Network & Distributed System Security Symposium. San Diego: ISOC, 2008: 1-15. |
| [13] | LI Jizhong, JIANG Liehui, YIN Qing, et al. Cryptogram Algorithm Recognition Technology Based on Bayes Decision-Making[J]. Computer Engineering, 2008, 34(20): 159-160. |
| 李继中, 蒋烈辉, 尹青, 等. 基于 Bayes 决策的密码算法识别技术[J]. 计算机工程, 2008, 34(20): 159-160. | |
| [14] | LI Jizhong. Research on Technology of Cryptogram Algorithm Recognition Based on Similarity Decision-Making[D]. Zhenghou: PLA Information Engineering University, 2009. |
| 李继中. 基于相似性判定的密码算法识别技术研究[D]. 郑州: 解放军信息工程大学, 2009. | |
| [15] | LUTZ N. Towards Revealing Attacker’s Intent by Automatically Decrypting Network Traffic[EB/OL]. (2008-08-01)[2022-09-14]. https://pub.tik.ee.ethz.ch/students/2008-FS/MA-2008-08. |
| [16] | WANG Zhi, JIANG Xexian, CUI Weidong, et al. ReFormat: Automatic Reverse Engineering of Encrypted Messages[C]// Springer. Computer Security-ESORICS 2009: 14th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2009: 200-215. |
| [17] | LIU T M, JIANG L, HE H, et al. Researching on Cryptographic Algorithm Recognition Based on Static Characteristic-Code[C]// Springer. Security Technology:International Conference, SecTech 2009, Held as Part of the Future Generation Information Technology Conference, FGIT 2009. Heidelberg: Springer, 2009: 140-147. |
| [18] | SNAKER. KANAL-Krypto Analyzer for PEiD[EB/OL]. (2019-04-18)[2022-03-26]. http://www.dcs.fmph.uniba.sk/zri/6.prednaska/tools/PEiD/plugins/kanal.htm. |
| [19] | X3CHUN. Crypto Searcher[EB/OL]. (2019-05-31)[2022-07-08]. http://quequero.org/uicwiki/images/Cryptosearcher_2004_05_19.zip. |
| [20] | PARADOX/AT4RE. Hash Crypto Detector[EB/OL]. (2019-11-21)[2022-07-10]. https://github.com/felixgr/kerckhoffs/blob/master/static_tools/HCD.rar. |
| [21] | GUILFANOVER. Findcrypt2[EB/OL]. (2018-10-05)[2022-07-02]. http://www.hexblog.com/?p=28. |
| [22] | PLOHMANN D. IDAscope[EB/OL]. (2020-09-23)[2022-07-02]. https://bitbucket.org/daniel_plohmann/simplifire.idascope/. |
| [23] | DRAFT. Draft Crypto Analyzer[EB/OL]. (2019-05-16)[2022-07-08]. http://www.literatecode.com/draca. |
| [24] | GROBERT F, WILLEMS C, HOLZ T. Automated Identification of Cryptographic Primitives in Binary Programs[C]// Springer. Recent Advances in Intrusion Detection:14th International Symposium, RAID 2011. Heidelberg: Springer, 2011: 41-60. |
| [25] | ZHAO R, GU D, LI J, et al. Detection and Analysis of Cryptographic Data Inside Software[C]// Springer. Information Security:14th International Conference. Heidelberg: Springer, 2011: 182-196. |
| [26] | LE Q, MIKOLOV T. Distributed Representations of Sentences and Documents[C]// ACM. International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2014: 1188-1196. |
| [27] | DAI H, DAI B, SONG L. Discriminative Embeddings of Latent Variable Models for Structured Data[C]// ACM. International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2016: 2702-2711. |
| [28] | MASSARELLI L, DI LUNA G A, PETRONI F, et al. Investigating Graph Embedding Neural Networks with Unsupervised Features Extraction for Binary Analysis[C]// NDSS. Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Binary Analysis Research (BAR). San Diego: ISOC, 2019: 1-11. |
| [29] | SHIN E C R, SONG D, MOAZZEZI R. Recognizing Functions in Binaries with Neural Networks[C]// ACM. 24th {USENIX} Security Symposium ({USENIX} Security 15). New York: ACM, 2015: 611-626. |
| [30] | MA Jun, LI Congying. Evolution and Algorithm of Pre-trained Word Embedding Technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Library and Information Science, 2022, 30(12): 31-39. |
| 马俊, 李聪颖. 预训练词嵌入技术的演化与算法[J]. 中华医学图书情报杂志, 2022, 30(12): 31-39. | |
| [31] | MIKOLOV T, CHEN K, CORRADO G, et al. Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space[EB/OL]. (2013-09-07)[2022-09-14]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1301.3781. |
| [32] | MIKOLOV T, SUTSKEVER I, CHEN K, et al. Distributed Representations of Words and Phrases and Their Compositionality[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2013. |
| [33] | KALCHBRENNER N, GREFENSTETTE E, BLUNSOM P. A Convolutional Neural Network for Modelling Sentences[EB/OL]. (2014-04-08)[2022-09-14]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1404.2188. |
| [34] | TOMPSON J, GOROSHIN R, JAIN A, et al. Efficient Object Localization Using Convolutional Networks[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2015: 648-656. |
| [35] | FELBO B, MISLOVE A, SOGAARD A, et al. Using Millions of Emoji Occurrences to Learn Any-Domain Representations for Detecting Sentiment, Emotion and Sarcasm[EB/OL]. (2017-10-07)[2022-09-14]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.00524. |
| [36] | HADSELL R, CHOPRA S, LECUN Y. Dimensionality Reduction by Learning An Invariant Mapping[C]// IEEE. 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR'06). New York: IEEE, 2006: 1735-1742. |
| [37] | VX. VX Heaven Virus Collection[EB/OL]. (2019-05-13)[2021-06-06]. http://academictorrents.com/details/34ebe49a48aa532deb9c0dd08a08a017aa04d810. |
| [1] | 赵小林, 王琪瑶, 赵斌, 薛静锋. 基于机器学习的匿名流量分类方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(5): 1-10. |
| [2] | 赵彩丹, 陈璟乾, 吴志强. 基于多通道联合学习的自动调制识别网络[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(4): 20-29. |
| [3] | 张玉健, 刘代富, 童飞. 基于局部图匹配的智能合约重入漏洞检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(8): 1-7. |
| [4] | 刘光杰, 段锟, 翟江涛, 秦佳禹. 基于多特征融合的移动流量应用识别[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(7): 18-26. |
| [5] | 王浩洋, 李伟, 彭思维, 秦元庆. 一种基于集成学习的列车控制系统入侵检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(5): 46-53. |
| [6] | 胡卫, 赵文龙, 陈璐, 付伟. 基于Logits向量的JSMA对抗样本攻击改进算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(3): 62-69. |
| [7] | 刘峰, 杨成意, 於欣澄, 齐佳音. 面向去中心化双重差分隐私的谱图卷积神经网络[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(2): 39-46. |
| [8] | 林发鑫, 张健. 虚拟化平台异常行为检测系统的设计与实现[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(11): 62-67. |
| [9] | 仝鑫, 金波, 王靖亚, 杨莹. 一种面向Android恶意软件的多视角多任务学习检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 1-7. |
| [10] | 张郅, 李欣, 叶乃夫, 胡凯茜. 融合多重风格迁移和对抗样本技术的验证码安全性增强方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 129-135. |
| [11] | 高昌锋, 肖延辉, 田华伟. 基于多阶段渐进式神经网络的图像相机指纹提取算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 15-23. |
| [12] | 刘家银, 李馥娟, 马卓, 夏玲玲. 基于多尺度卷积神经网络的恶意代码分类方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 31-38. |
| [13] | 朱丽娜, 马铭芮, 朱东昭. 基于图神经网络和通用漏洞分析框架的C类语言漏洞检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 59-68. |
| [14] | 蒋首志, 曹金璇, 殷浩展, 芦天亮. 基于MHA与SDAE的Tor网站指纹识别模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 8-14. |
| [15] | 弋晓洋, 张健. 基于图像的网络钓鱼邮件检测方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(9): 52-58. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||