信息网络安全 ›› 2022, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (5): 75-83.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2022.05.009
针对PMU测量的虚假数据注入攻击检测方法
- 上海电力大学计算机科学与技术学院,上海 201306
-
收稿日期:2022-02-01出版日期:2022-05-10发布日期:2022-06-02 -
通讯作者:李红娇 E-mail:hjli@shiep.edu.cn -
作者简介:周婧怡(1997—),女,江苏,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为电力信息安全|李红娇(1974—),女,上海,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为信息系统安全、可信计算、入侵检测、云计算与大数据安全、隐私保护和电力信息安全 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(61403247)
False Data Injection Attack Detection Method against PMU Measurements
- Department of Computer Science and Technology, Shanghai University of Electric Power, Shanghai 201306, China
-
Received:2022-02-01Online:2022-05-10Published:2022-06-02 -
Contact:LI Hongjiao E-mail:hjli@shiep.edu.cn
摘要:
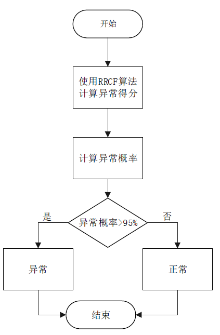
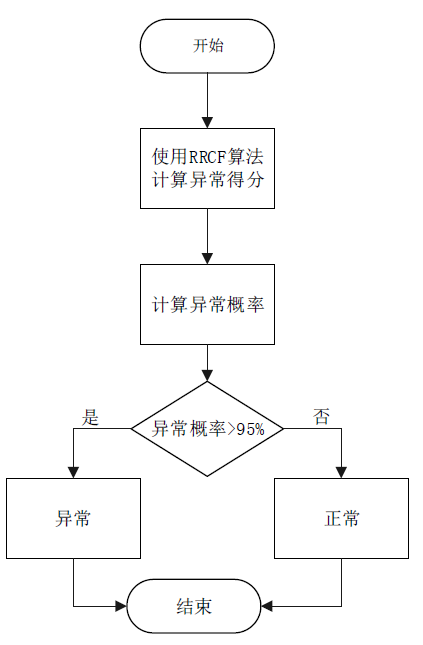
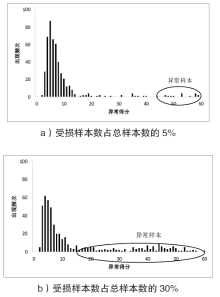
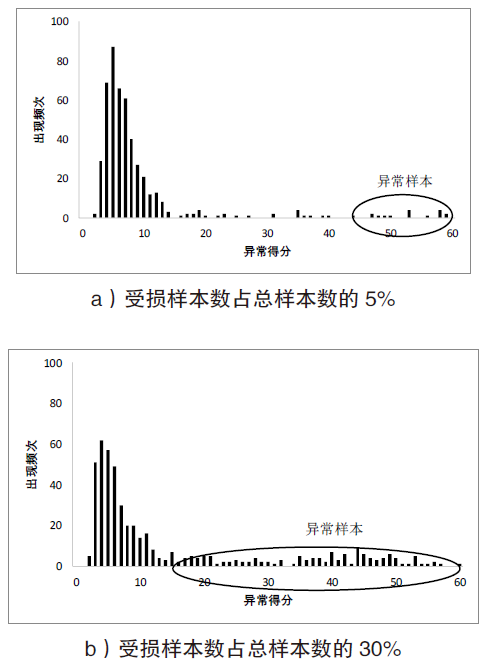
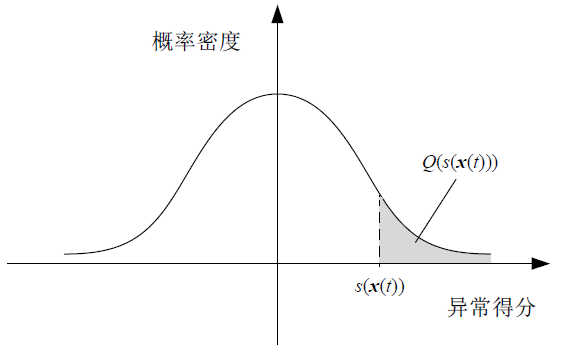
针对向量测量单元(Phasor Measure Unit,PMU)测量的虚假数据注入攻击检测,文章提出了修正鲁棒性随机砍伐森林(Corrected Robust Random Cut Forest,CRRCF)无监督在线学习检测方法。首先,鲁棒性随机砍伐森林(Robust Random Cut Forest,RRCF)是一种无监督在线学习算法,该算法可以快速适应拓扑变化后的PMU测量数据,并通过生成异常得分反映样本的异常程度;然后,根据RRCF的异常得分,CRRCF使用高斯Q函数和滑动窗口计算异常概率;最后,异常概率修正了RRCF对异常程度的判断,以适应攻击数量、攻击幅度的变化。仿真结果表明,与静态学习方法相比,在线学习方法能够解决拓扑变化带来的概念漂移问题;而与其他在线学习方法相比,CRRCF能够在攻击数量、攻击幅度变化时始终保持较高的检测精度和F1分数。
中图分类号:
引用本文
周婧怡, 李红娇. 针对PMU测量的虚假数据注入攻击检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(5): 75-83.
ZHOU Jingyi, LI Hongjiao. False Data Injection Attack Detection Method against PMU Measurements[J]. Netinfo Security, 2022, 22(5): 75-83.
表1
算法1插入样本
| 序号 | 步骤 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 如果T(X)=φ,返回仅含节点x(t)的树 |
| 2 | 否则,选择一个随机数 |
| 3 | 如果该切割将树T(X)和x(t)分开,则作为 |
| 4 | 设 |
| [1] | LIU Andi, LI Yan, XIE Wei, et al. Line Parameter Estimation Method of Distribution Network Based on Multi Source Data and Multi Time Section[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45(2): 46-54. |
| 刘安迪, 李妍, 谢伟, 等. 基于多源数据多时间断面的配电网线路参数估计方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45(2):46-54. | |
| [2] | YUAN Zhiyong, XIAO Zekun, YU Li, et al. Overview of Smart Grid Big Data Research[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2021, 34(1): 1-12. |
| 袁智勇, 肖泽坤, 于力, 等. 智能电网大数据研究综述[J]. 广东电力, 2021, 34(1):1-12. | |
| [3] | LIU Shengyuan, LIN Zhenzhi, LI Jincheng, et al. Overview and Prospect ofPower System Situation Awareness Technology[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2020, 44(3): 229-239. |
| 刘晟源, 林振智, 李金城, 等. 电力系统态势感知技术研究综述与展望[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2020, 44(3):229-239. | |
| [4] | YANG Peng. “Cloud Management” Works at the Same Time and China Mobile's 5g Smart Grid will Take “Three Steps”[J]. Communications World, 2020(23): 18-19. |
| [5] |
LIANG Gaoqi, WELLER S R, ZHAO Junhua, et al. The 2015 Ukraine Blackout: Implications for False Data Injection Attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2017, 32(4): 3317-3318.
doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2016.2631891 URL |
| [6] | BINDRA A. Securing the Power Grid: Protecting Smart Grids and Connected Power Systems from Cyberattacks[J]. IEEE Power Electronics Magazine, 2017, 4(3): 20-27. |
| [7] | LIU Yao, PENG Ning, REITER M K. False Data Injection Attacks against State Estimation in Electric Power Grids[J]. ACM Transactions on Information and System Security, 2011, 14(1): 1-33. |
| [8] | CHU Zhigang, ZHANG Jiazi, KOSUT O, et al. Unobservable False Data Injection Attacks against PMUs: Feasible Conditions and Multiplicative Attacks[C]// IEEE. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Control, and Computing Technologies for Smart Grids. New York: IEEE, 2018: 1-6. |
| [9] |
YU J J Q, HOU Yunhe, LI V O K. Online False Data Injection Attack Detection with Wavelet Transform and Deep Neural Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 14(7): 3271-3280.
doi: 10.1109/TII.2018.2825243 URL |
| [10] |
BASUMALLIK S, MA Rui, EFTEKHARNEJAD S. Packet-Data Anomaly Detection in PMU-Based State Estimator Using Convolutional Neural Network[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2019, 107: 690-702.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijepes.2018.11.013 URL |
| [11] | KHARE G, MOHAPATR A A, SINGH S N. A Real-Time Approach for Detection and Correction of False Data in PMU Measurements[J]. Electric Power Systems Research, 2021, 191(2): 1-11. |
| [12] | AHMED S, LEE Y D, SEUNG H H, et al. Unsupervised Machine Learning-Based Detection of Covert Data Integrity Assault in Smart Grid Networks Utilizing Isolation Forest[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2019, 14(10): 1-13. |
| [13] |
MOHAMMADPOURFARD M, SAMI A, WENG Yang. Identification of False Data Injection Attacks with Considering the Impact of Wind Generation and Topology Reconfigurations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2018, 9(3): 1349-1364.
doi: 10.1109/TSTE.2017.2782090 URL |
| [14] | YAN Jun, TANG Bo, HE Haibo. Detection of False Data Attacks in Smart Grid with Supervised Learning[C]// IEEE. 2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). New York: IEEE. 2016: 1395-1402. |
| [15] | GUHA S, MISHRA N, ROY G, et al. Robust Random Cut Forest Based Anomaly Detection on Streams[C]// JMLR. The 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: JMLR, 2016: 2712-2721. |
| [16] |
BOUANANI F E, MOUCHTAK Y, KARAGIANNIDIS G K. New Tight Bounds for the Gaussian Q-Function and Applications[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 145037-145055.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3015344 URL |
| [17] |
AHMAD S, LAVIN A, PURDY S, et al. Unsupervised Real-Time Anomaly Detection for Streaming Data[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 262(1): 134-147.
doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.04.070 URL |
| [18] |
TENG S Y, Máša V, TOU M, et al. Waste-to-Energy Forecasting and Real-Time Optimization: An Anomaly-Aware Approach[J]. Renewable Energy, 2022, 181: 142-155.
doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2021.09.026 URL |
| [19] | ANGIULLI F, PIZZUTI C. Fast Outlier Detection in High Dimensional Spaces[C]// ACM. 6th European Conference on Principles of Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, New York: ACM, 2002: 15-27. |
| [20] | LIU F T, MING T K, ZHOU Z H. Isolation-Based Anomaly Detection[J]. ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data, 2012, 6(1): 1-39. |
| [21] |
PEVNY T. Loda: Lightweight Online Detector of Anomalies[J]. Machine Learning, 2016, 102(2): 275-304.
doi: 10.1007/s10994-015-5521-0 URL |
| [22] | SATHE S, AGGARWAL C C. Subspace Outlier Detection in Linear Time with Randomized Hashing[C]// IEEE. 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM). New York: IEEE, 2016: 459-468. |
| [23] |
LIU Yuxiao, WANG Yi, ZHANG Ning, et al. A Data-Driven Approach to Linearize Power Flow Equations Considering Measurement Noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2020, 11(3): 2576-2587.
doi: 10.1109/TSG.2019.2957799 URL |
| [24] |
KONAKALLA S A R, CALLAFON R A D. Spectrum-Based Optimal Filtering for Short-Term Phasor Data Prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2020, 56(2): 2069-2077.
doi: 10.1109/TIA.2020.2966186 URL |
| [25] | BROWN M, BISWAL M, BRAHMA S, et al. Characterizing and Quantifying Noise in PMU Data[C]// IEEE. 2016 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting(PESGM). New York: IEEE, 2016: 1-5. |
| [1] | 陈彬杰, 魏福山, 顾纯祥. 基于KNN的具有隐私保护功能的区块链异常交易检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 23(3): 78-84. |
| [2] | 秦中元, 胡宁, 方兰婷. 基于免疫仿生机理和图神经网络的网络异常检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(8): 10-16. |
| [3] | 徐洪平, 马泽文, 易航, 张龙飞. 基于卷积循环神经网络的网络流量异常检测技术[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(7): 54-62. |
| [4] | 吴驰, 帅俊岚, 龙涛, 于俊清. 基于Linux Shell命令的用户异常操作检测方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(5): 31-38. |
| [5] | 李佳玮, 吴克河, 张波. 基于高斯混合聚类的电力工控系统异常检测研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(3): 53-63. |
| [6] | 吴佳洁, 吴绍岭, 王伟. 基于TCN和注意力机制的异常检测和定位算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(11): 85-94. |
| [7] | 陆佳丽. 基于改进时间序列模型的日志异常检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(9): 1-5. |
| [8] | 黄娜, 何泾沙, 吴亚飚, 李建国. 基于LSTM回归模型的内部威胁检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(9): 17-21. |
| [9] | 顾兆军, 任怡彤, 刘春波, 王志. 基于一致性预测算法的内网日志检测模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(3): 45-50. |
| [10] | 王玉娣, 刘晓洁, 王运鹏. 基于改进否定选择算法的异常检测方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(10): 75-82. |
| [11] | 王伟, 沈旭东. 基于实例的迁移时间序列异常检测算法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(3): 11-18. |
| [12] | 杨威超, 郭渊博, 钟雅, 甄帅辉. 基于设备型号分类和BP神经网络的物联网流量异常检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(12): 53-63. |
| [13] | 朱海麒, 姜峰. 人工智能时代面向运维数据的异常检测技术研究与分析[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(11): 24-35. |
| [14] | 邓海莲, 刘宇靖, 葛一漩, 苏金树. 域间路由异常检测技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(11): 63-70. |
| [15] | 李巍, 狄晓晓, 王迪, 李云春. 基于子图的服务器网络行为建模及异常检测方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(2): 1-9. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||