信息网络安全 ›› 2024, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (4): 640-649.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2024.04.013
基于特征恶意度排序的恶意软件对抗防御模型
- 深圳大学计算机与软件学院,深圳 518060
-
收稿日期:2023-11-14出版日期:2024-04-10发布日期:2024-05-16 -
通讯作者:闫巧yanq@szu.edu.cn -
作者简介:徐子荣(1999—),男,广东,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为对抗样本攻击|郭焱平(1996—),男,湖南,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为入侵检测|闫巧(1972—),女,广西,教授,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为网络安全和人工智能 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(61976142);深圳市科技计划(JCYJ20210324093609025)
Malicious Software Adversarial Defense Model Based on Feature Severity Ranking
XU Zirong, GUO Yanping, YAN Qiao( )
)
- College of Computer Science and Software Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
-
Received:2023-11-14Online:2024-04-10Published:2024-05-16
摘要:
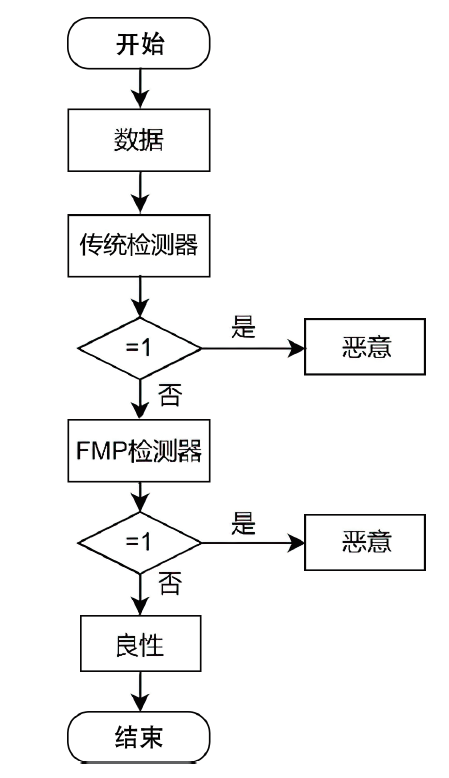
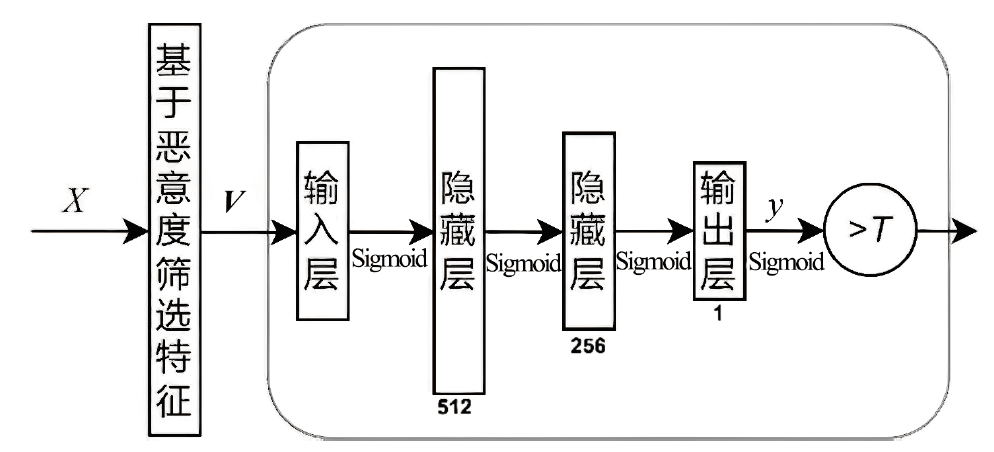
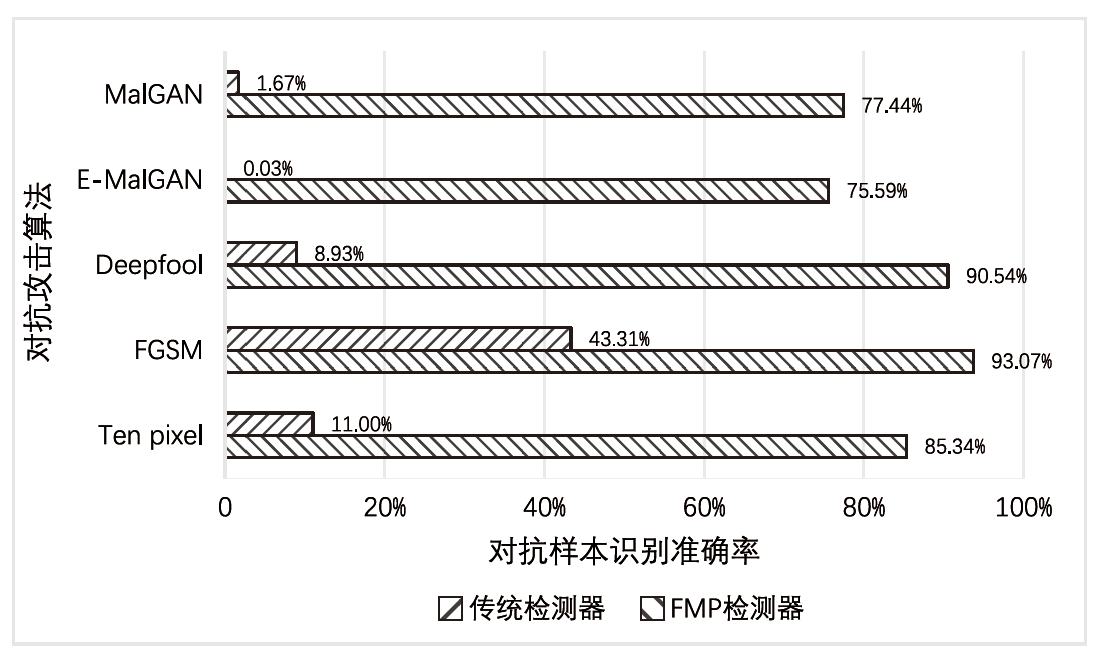
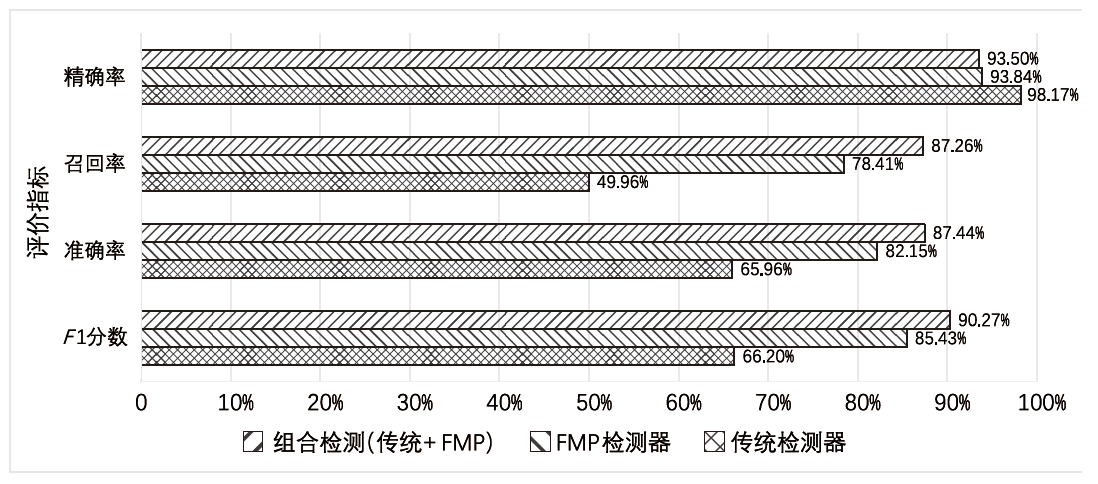
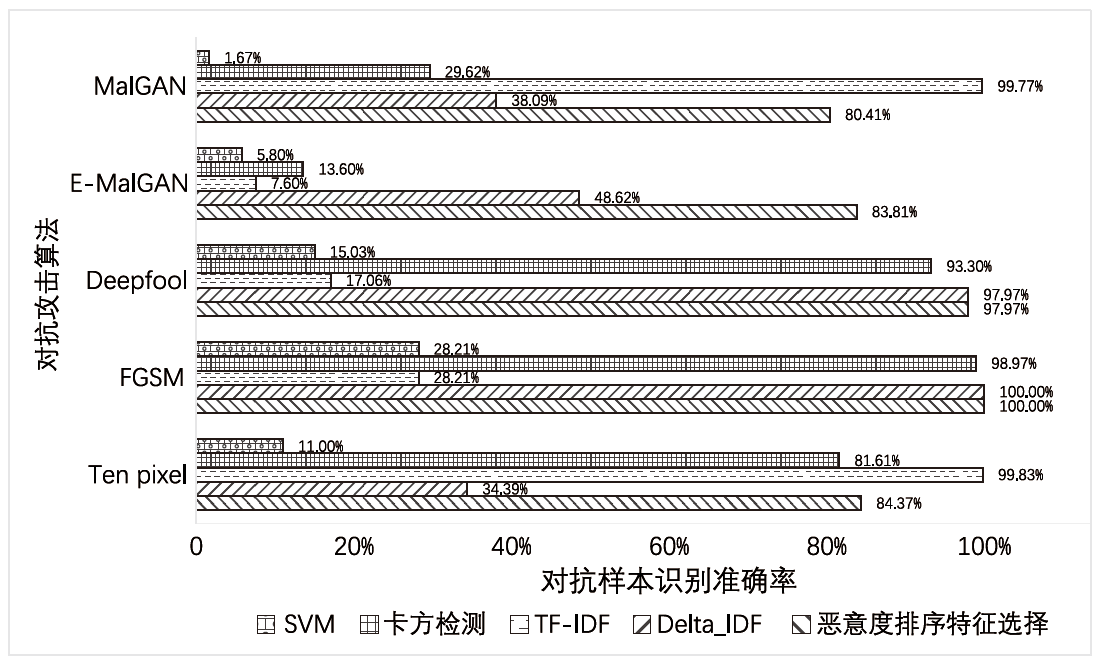
深度学习模型应用于安卓恶意软件检测可以使检测的准确率不断提升,但对抗样本可以轻易规避深度学习模型的检测,导致深度学习模型的检测能力受到质疑。对于安卓恶意软件的对抗攻击,现阶段多采用对抗训练方法进行防御,文章针对对抗训练在面对多类型对抗样本时表现较差的问题,提出特征恶意度的概念。特征恶意度通过计算特征的恶意程度对特征进行排序,利用排序后的特征构建一个具有对抗防御能力的恶意软件对抗防御模型FMP(Feature Maliciousness Processing),该模型可以提取待检测软件的高恶意度特征进行检测,避免出现对抗扰动导致的模型错误分类问题。在开源数据集DefenceDroid上,相比于对抗训练方法和其他特征选择方法,FMP模型所采用的特征选择方法有效提高了对各类对抗样本的检测率,在多种对抗样本的攻击下具有较好的鲁棒性。
中图分类号:
引用本文
徐子荣, 郭焱平, 闫巧. 基于特征恶意度排序的恶意软件对抗防御模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(4): 640-649.
XU Zirong, GUO Yanping, YAN Qiao. Malicious Software Adversarial Defense Model Based on Feature Severity Ranking[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(4): 640-649.
| [1] | CHRISTIAAN B, SANDEEP C, TAYLOR D, et al. McAfee Labs Threats Report: November 2020[EB/OL]. (2020-11-10)[2023-11-10]. https://www.trellix.com/enterprise/zh-cn/assets/reports/rp-quarterly-threats-nov-2020.pdf. |
| [2] | GOODFELLOW I J, SHLENS J, SZEGEDY C. Explaining and Harnessing Adversarial Examples[EB/OL]. (2014-12-20)[2023-11-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6572. |
| [3] | FENG Yu, ANAND S, DILLIG I, et al. Apposcopy: Semantics-Based Detection of Android Malware through Static Analysis[C]// ACM. 22nd ACM SIGSOFT International Symposium on the Foundations of Software Engineering. New York: ACM, 2014: 576-587. |
| [4] | FENG Yu, BASTANI O, MARTINS R, et al. Automated Synthesis of Semantic Malware Signatures Using Maximum Satisfiability[EB/OL]. (2016-08-22)[2023-11-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1608.06254. |
| [5] | ARZT S, RASTHOFER S, FRITZ C, et al. FlowDroid: Precise Context, Flow, Field, Object-Sensitive and Lifecycle-Aware Taint Analysis for Android Apps[J]. ACM SIGPLAN Notices, 2014, 49(6): 259-269. |
| [6] | PANDITA R, XIAO Xusheng, YANG Wei, et al. WHYPER: Towards Automating Risk Assessment of Mobile Applications[C]// USENIX. 22nd USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 13). Berkeley: USENIX, 2013: 527-542. |
| [7] | TEUFL P, FERK M, FITZEK A, et al. Malware Detection by Applying Knowledge Discovery Processes to Application Metadata on the Android Market (Google Play)[J]. Security & Communication Networks, 2016, 9(5): 389-419. |
| [8] | ZHANG Mu, DUAN Yue, YIN Heng, et al. Semantics-Aware Android Malware Classification Using Weighted Contextual API Dependency Graphs[C]// ACM. 2014 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security(CCS). New York: ACM, 2014: 1105-1116. |
| [9] | YUAN Zhenlong, LU Yongqiang, WANG Zhaoguo, et al. Droid-Sec: Deep Learning in Android Malware Detection[J]. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2014, 44(4): 371-372. |
| [10] | PEYNIRCI G, EMINAĞAOĞLU M, KARABULUT K. Feature Selection for Malware Detection on the Android Platform Based on Differences of IDF Values[J]. Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 2020, 35(4): 946-962. |
| [11] | CHEN Sen, XUE Minhui, FAN Lingling, et al. Automated Poisoning Attacks and Defenses in Malware Detection Systems: An Adversarial Machine Learning Approach[J]. Computers & Security, 2018(73): 326-344. |
| [12] | LI Xiangjun, KONG Ke, XU Su, et al. Feature Selection-Based Android Malware Adversarial Sample Generation and Detection Method[J]. IET Information Security, 2021, 15(6): 401-416. |
| [13] | HU Weiwei, TAN Ying. Generating Adversarial Malware Examples for Black-Box Attacks Based on GAN[C]// Springer. Data Mining and Big Data-7th International Conference (DMBD 2022). Heidelberg: Springer, 2022: 409-423. |
| [14] | KAWAI M, OTA K, DONG Mianxing. Improved MalGAN: Avoiding Malware Detector by Leaning Cleanware Features[C]// IEEE. The 1st International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication (ICAIIC). New York: IEEE, 2019: 40-45. |
| [15] | LI Heng, ZHOU Shiyao, YUAN Wei, et al. Adversarial-Example Attacks Toward Android Malware Detection System[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2019, 14(1): 653-656. |
| [16] | ONWUZURIKE L, MARICONTI E, ANDRIOTIS P, et al. MaMaDroid: Detecting Android Malware by Building Markov Chains of Behavioral Models (Extended Version)[J]. ACM Transaction on Information and System Security, 2019, 22(2): 1-34. |
| [17] | CHEN Xiao, LI Chaoran, WANG Derui, et al. Android HIV: A Study of Repackaging Malware for Evading Machine-Learning Detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2019(15): 987-1001. |
| [18] | PAPERNOT N, MCDANIEL P, JHA S, et al. The Limitations of Deep Learning in Adversarial Settings[C]// IEEE. The 1st IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy (Euro S&P). New York: IEEE, 2016: 372-387. |
| [19] | CARLINI N, WAGNER D. Towards Evaluating the Robustness of Neural Networks[C]// IEEE. The 38th IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York: IEEE, 2017: 39-57. |
| [20] | SZEGEDY C, ZAREMBA W, SUTSKEVER I, et al. Intriguing Properties of Neural Networks[EB/OL]. (2014-02-19)[2023-11-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.6199. |
| [21] | RATHORE H, SAHAY S K, NIKAM P, et al. Robust Android Malware Detection System against Adversarial Attacks Using Q-Learning[J]. Information Systems Frontiers, 2021, 23(4): 867-882. |
| [22] | RATHORE H, SAHAY S K, DHILLON J, et al. Designing Adversarial Attack and Defence for Robust Android Malware Detection Models[C]// IEEE. The 51st Annual IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks(DSN). New York: IEEE, 2021: 29-32. |
| [23] | TAHERI R, JAVIDAN R, POORANIAN Z. Adversarial Android Malware Detection for Mobile Multimedia Applications in IoT Environments[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2021, 80(11): 16713-16729. |
| [24] | CHEN Yiming, YANG C H, CHEN G C. Using Generative Adversarial Networks for Data Augmentation in Android Malware Detection[C]// IEEE. The 2021 IEEE Conference on Dependable and Secure Computing(DSC). New York: IEEE, 2021: 1-8. |
| [25] | LI Heng, ZHOU Shiyao, YUAN Wei, et al. Robust Android Malware Detection against Adversarial Example Attacks[C]// ACM. The Web Conference 2021 (WWW’21). New York: ACM, 2021: 3603-3612. |
| [26] | CHEN Lingwei, HOU Shifu, YE Yanfang. SecureDroid: Enhancing Security of Machine Learning-Based Detection against Adversarial Android Malware Attacks[C]// ACM. The 33rd Annual Computer Security Applications Conference (ACSAC’17). New York: ACM, 2017: 362-372. |
| [27] | CLINE W C, MANDAR D B, SIDDHARTH A B, et al. DefenseDroid: A Modern Approach to Android Malware Detection[EB/OL]. (2021-12-07)[2023-11-10]. https://github.com/DefenseDroid/DefenseDroid. |
| [28] | MAHDAVIFAR S, KADIR A F A, FATEMI R, et al. Dynamic Android Malware Category Classification Using Semi-Supervised Deep Learning[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Dependable, Autonomic and Secure Computing, International Conference on Pervasive Intelligence and Computing, International Conference on Cloud and Big Data Computing, International Conference on Cyber Science and Technology Congress (DASC/PiCom/CBDCom/CyberSciTech). New York: IEEE, 2020: 515-522. |
| [29] | MAHDAVIFAR S, ALHADIDI D, GHORBANI A. Effective and Efficient Hybrid Android Malware Classification Using Pseudo-Label Stacked Auto-Encoder[J]. Journal of Network and Systems Management, 2022, 30(1): 1-34. |
| [30] | WANG Haoyu, SI Junjun, LI Hao, et al. RmvDroid: Towards a Reliable Android Malware Dataset with App Metadata[C]// IEEE. 16th International Conference on Mining Software Repositories (MSR2019). New York: IEEE, 2019: 404-408. |
| [31] | ALLIX K, BISSYANDÉ T F, KLEIN J, et al. AndroZoo: Collecting Millions of Android Apps for the Research Community[C]// IEEE. 2016 IEEE/ACM 13th International Conference on Mining Software Repositories (MSR2016). New York: IEEE, 2016: 468-471. |
| [32] | MOOSAVI-DEZFOOLI S M, FAWZI A, FROSSARD P. Deepfool: A Simple and Accurate Method to Fool Deep Neural Networks[C]// IEEE. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2016: 2574-2582. |
| [33] | SU Jiawei, VARGAS D V, SAKURAI K. One Pixel Attack for Fooling Deep Neural Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2019, 23(5): 828-841. |
| [34] | WILSON E B, HILFERTY M M. The Distribution of Chi-Square[J]. National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1931, 17(12): 684-688. |
| [35] | HIEMSTRA D. A Probabilistic Justification for Using TF×IDF Term Weighting in Information Retrieval[J]. International Journal on Digital Libraries, 2000, 3(2): 131-139. |
| [1] | 张光华, 刘亦纯, 王鹤, 胡勃宁. 基于JSMA对抗攻击的去除深度神经网络后门防御方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(4): 545-554. |
| [2] | 钟静, 方冰, 朱江. 基于稀疏矩阵结构的特征选择算法现状研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 352-362. |
| [3] | 杨志鹏, 刘代东, 袁军翼, 魏松杰. 基于自注意力机制的网络局域安全态势融合方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 398-410. |
| [4] | 江荣, 刘海天, 刘聪. 基于集成学习的无监督网络入侵检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 411-426. |
| [5] | 冯光升, 蒋舜鹏, 胡先浪, 马明宇. 面向物联网的入侵检测技术研究新进展[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 167-178. |
| [6] | 赵鹏程, 于俊清, 李冬. 一种基于深度学习的SRv6网络流量调度优化算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 272-281. |
| [7] | 金志刚, 丁禹, 武晓栋. 融合梯度差分的双边校正联邦入侵检测算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 293-302. |
| [8] | 许可, 李嘉怡, 蒋兴浩, 孙锬锋. 一种基于轮廓稀疏对抗的视频步态隐私保护算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1): 48-59. |
| [9] | 薛羽, 张逸轩. 深层神经网络架构搜索综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(9): 58-74. |
| [10] | 沈华, 田晨, 郭森森, 慕志颖. 基于对抗性机器学习的网络入侵检测方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(8): 66-75. |
| [11] | 李晨蔚, 张恒巍, 高伟, 杨博. 基于AdaN自适应梯度优化的图像对抗迁移攻击方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(7): 64-73. |
| [12] | 刘宇啸, 陈伟, 张天月, 吴礼发. 基于稀疏自动编码器的可解释性异常流量检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(7): 74-85. |
| [13] | 蒋英肇, 陈雷, 闫巧. 基于双通道特征融合的分布式拒绝服务攻击检测算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(7): 86-97. |
| [14] | 蒋曾辉, 曾维军, 陈璞, 武士涛. 面向调制识别的对抗样本研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(6): 74-90. |
| [15] | 赵彩丹, 陈璟乾, 吴志强. 基于多通道联合学习的自动调制识别网络[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(4): 20-29. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||