信息网络安全 ›› 2023, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (11): 69-83.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2023.11.008
多模态对比学习中的靶向投毒攻击
- 1.华中科技大学电子信息与通信学院,武汉 430074
2.智能互联网技术湖北省重点实验室,武汉 430074
3.武汉龙安集团有限责任公司,武汉 430074
-
收稿日期:2023-06-20出版日期:2023-11-10发布日期:2023-11-10 -
通讯作者:王琛chenwang@hust.edu.cn -
作者简介:刘高扬(1991—),男,湖北,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为人工智能安全|吴伟玲(1998—),女,湖北,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为对比学习和对抗机器学习|张锦升(1986—),男,湖北,工程师,硕士,主要研究方向为系统设计与算法安全|王琛(1985—),男,湖北,副研究员,博士,CCF高级会员,主要研究方向为物联网、数据安全和可信机器学习 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(62272183);湖北省重点研发计划(2021BAA026)
Targeted Poisoning Attacks against Multimodal Contrastive Learning
LIU Gaoyang1,2, WU Weiling1, ZHANG Jinsheng3, WANG Chen1,2( )
)
- 1. School of Electronic Information and Communication, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
2. Hubei Key Laboratory of Smart Internet Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
3. Wuhan Long’an Group Co., Ltd., Wuhan 430074, China
-
Received:2023-06-20Online:2023-11-10Published:2023-11-10
摘要:
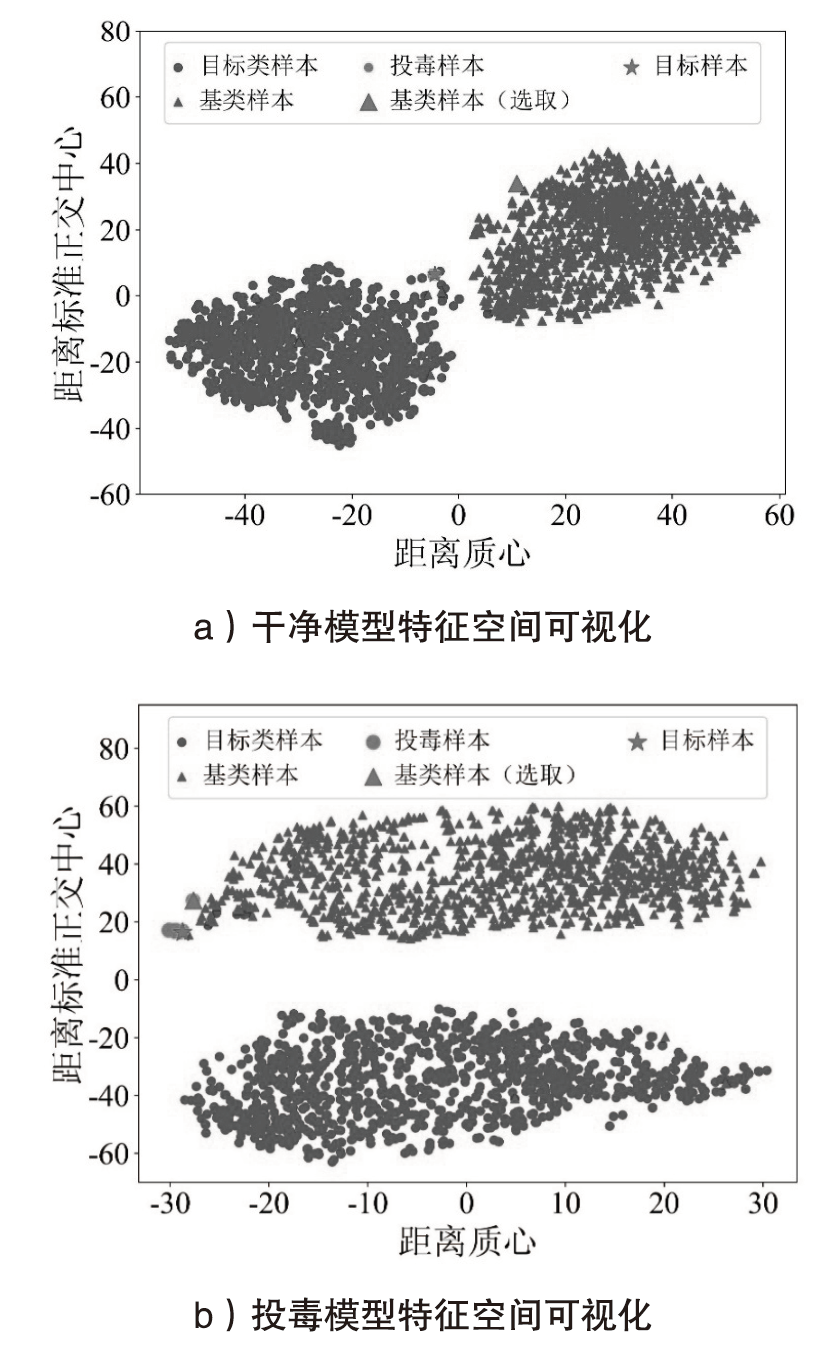
近年来,使用对比学习技术在大规模无标注数据上所构建的预训练模型得到了广泛的应用(如车道检测、人脸识别等)。然而,其面临的安全和隐私问题也引起学者的广泛关注。文章聚焦于针对多模态对比学习模型的投毒攻击,该攻击将精心构造的数据注入训练集,以改变模型在特定数据上的预测行为。针对现有投毒攻击主要针对文本或图像单模态模型,没有利用文本或者图像间的多模态信息的问题,文章提出一种同时对文本与图像编码器投毒的靶向投毒攻击。首先,基于Beta分布自动生成水印图像透明度;然后,根据透明度生成添加水印后的样本,并根据水印样本与目标样本之间的欧式距离得到该透明度下应当投毒的样本数;最后,通过特定的优化算法生成投毒数据集。与现有的投毒攻击相比,文章所提方法具有更低的投毒率,并能够保持目标模型的性能。
中图分类号:
引用本文
刘高扬, 吴伟玲, 张锦升, 王琛. 多模态对比学习中的靶向投毒攻击[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 69-83.
LIU Gaoyang, WU Weiling, ZHANG Jinsheng, WANG Chen. Targeted Poisoning Attacks against Multimodal Contrastive Learning[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(11): 69-83.
表1
术语符号对照表
| 术语 | 符号 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 目标标签 | 攻击者指定的标签,在清洁标签投毒攻击中也叫做基类 | |
| 目标样本 | 攻击者指定的特定样本,包含图像和描述性文本 | |
| 源标签 | 目标样本对应的真实标签 | |
| 基类样本 | 从基类中选取的样本 | |
| 原样本 | 包含目标样本与其他所有干净样本 | |
| 原标签 | 原样本对应的真实标签 | |
| 投毒样本 | 攻击者精心构造的毒化样本 | |
| 干净数据集 | 未经投毒的数据集 | |
| 投毒数据集 | 包含所有的投毒样本和干净样本 | |
| 干净模型 | 攻击者的目标模型, | |
| 受害者模型 | 被攻击后的模型 |
表4
在多个数据集上不同攻击规模投毒表现
| 数据集 | ASR | 攻击方式 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Poisoning | Inter-polationCP | Image- Interp | TextAug | DE-Interp | ||
| CIFAR-10 | 30% 50% 80% 90% 95% | 0.10% 0.20% 0.30% 0.50% 0.60% | 0.05% 0.10% 0.40% 0.80% 0.80% | 0.30% 0.50% 0.60% 0.65% 0.75% | 0.15% 0.20% 0.30% 0.45% 0.50% | 0.01% 0.02% 0.03% 0.05% 0.06% |
| SVHN | 30% 50% 80% 90% 95% | 0.10% 0.30% 0.60% 0.75% 0.80% | 0.20% 0.50% 0.65% 0.80% 0.85% | 0.30% 0.50% 0.50% 0.60% 0.70% | 0.30% 0.50% 0.50% 0.60% 0.60% | 0.02% 0.03% 0.04% 0.05% 0.10% |
| GTSRB | 30% 50% 80% 90% 95% | 0.15% 0.30% 0.35% 0.50% 0.50% | 0.20% 0.30% 0.35% 0.50% 0.70% | 0.10% 0.20% 0.25% 0.55% 0.55% | 0.10% 0.30% 0.30% 0.50% 0.60% | 0.02% 0.03% 0.08% 0.10% 0.10% |
| [1] |
GU Xin, SHEN Yinghua, LYU Chaohui. A Dual-Path Cross-Modal Network for Video-Music Retrieval[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(2): 805-818.
doi: 10.3390/s23020805 URL |
| [2] | LUO Huaishao, JI Lei, SHI Botian, et al. Univl: A Unified Video and Language Pre-Training Model for Multimodal Understanding and Generation[EB/OL]. (2020-02-15)[2023-06-01]. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:211132410. |
| [3] | LU Jiasen, BATRA D, PARIKH D, et al. Vilbert: Pretraining Task-Agnostic Visiolinguistic Representations for Vision-and-Language Tasks[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2019, 2: 13-23. |
| [4] | CARLINI N, TERZIS A. Poisoning and Backdooring Contrastive Learning[EB/OL]. (2021-06-17)[2023-06-01]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2106.09667. |
| [5] | JIA Jinyuan, LIU Yupei, GONG N Z. Badencoder: Backdoor Attacks to Pre-Trained Encoders in Self-Supervised Learning[C]// IEEE. IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. New York: IEEE, 2022: 2043-2059. |
| [6] | HE Hao, ZHA Kaiwen, KATABI D. Indiscriminate Poisoning Attacks on Unsupervised Contrastive Learning[EB/OL]. (2022-02-22)[2023-06-01]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2202.11202. |
| [7] | CUBUK E D, ZOPH B, SHLENS J, et al. Randaugment: Practical Automated Data Augmentation with a Reduced Search Space[C]// IEEE. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. New York: IEEE, 2020: 702-703. |
| [8] | ZHONG Zhun, ZHENG Liang, KANG Guoliang, et al. Random Erasing Data Augmentation[C]// AAAI. AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. NewYork: AAAI, 2020: 13001-13008. |
| [9] | ZHANG Xinyang, ZHANG Zheng, JI Shuoling, et al. Trojaning Language Models for Fun and Profit[C]// IEEE. IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy. New York: IEEE, 2021: 179-197. |
| [10] | DEVLIN J, CHANG M W, LEE K, et al. Bert: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding[EB/OL]. (2018-10-11)[2023-06-01]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1810.04805. |
| [11] | NELSON B, BARRENO M, CHI F J, et al. Exploiting Machine Learning to Subvert Your Spam Filter[J]. LEET, 2008, 7: 1-9. |
| [12] | SHARMA P, DING Nan, GOODMAN S, et al. Conceptual Captions:A Cleaned, Hypernymed, Image Alt-Text Dataset for Automatic Image Captioning[C]// ACL. 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: ACL Anthology, 2018: 2556-2565. |
| [13] | THOMEE B, SHAMMA D A, FRIEDLAND G, et al. YFCC100M: The New Data in Multimedia Research[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2016, 59(2): 64-73. |
| [14] |
RUSSAKOVSKY O, DENG Jia, SU Hao, et al. Imagenet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 115: 211-252.
doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y URL |
| [15] | PAUDICE A, MUÑOZ-GONZÁLEZ L, LUPU E C. Label Sanitization against Label Flipping Poisoning Attacks[C]// ECML. ECML PKDD 2018 Workshops. Berlin: Springer, 2019: 5-15. |
| [16] | ZHANG Mengmei, HU Linmei, SHI Chuan, et al. Adversarial Label-Flipping Attack and Defense for Graph Neural Networks[C]// IEEE. IEEE International Conference on Data Mining. New York: IEEE, 2020: 791-800. |
| [17] | HE Kaiming, FAN Haoqi, WU Yuxin, et al. Momentum Contrast for Unsupervised Visual Representation Learning[C]// IEEE. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2020: 9729-9738. |
| [18] | SOHN K. Improved Deep Metric Learning with Multi-Class N-Pair Loss Objective[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2016, 29: 1857-1865. |
| [19] | CHEN Ting, KORNBLITH S, NOROUZI M, et al. A Simple Framework for Contrastive Learning of Visual Representations[C]// ICML. International Conference on Machine Learning. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2020: 1597-1607. |
| [20] | RADFORD A, KIM J W, HALLACY C, et al. Learning Transferable Visual Models from Natural Language Supervision[C]// ICML. International Conference on Machine Learning. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2021: 8748-8763. |
| [21] | VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is All You Need[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017, 30: 6000-6010. |
| [22] | HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition[C]// IEEE. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2016: 770-778. |
| [23] | LAMPERT C H, NICKISCH H, HARMELING S. Learning to Detect Unseen Object Classes by Between-Class Attribute Transfer[C]// IEEE. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2009: 951-958. |
| [24] | ZHU Chen, HUANG W R, LI Hengduo, et al. Transferable Clean-Label Poisoning Attacks on Deep Neural Nets[C]// ICML. International Conference on Machine Learning. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2019: 7614-7623. |
| [25] | CHEN Jinyin, ZOU Jianfei, SU Mengmeng, et al. Review of Poisoning Attack and Defense in Deep Learning Models[J]. Journal of Cyber Security, 2020, 5(4): 14-29. |
| [26] | WU Jianhan, SI Shijing, WANG Jianzong, et al. Review of Federation Learning Attack and Defense[J]. Big Data, 2022, 8(5): 12-32. |
|
吴建汉, 司世景, 王健宗, 等. 联邦学习攻击与防御综述[J]. 大数据, 2022, 8(5):12-32.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-0271.2022038 |
|
| [27] | SHAFAHI A, HUANG W R, NAJIBI M, et al. Poison Frogs! Targeted Clean-Label Poisoning Attacks on Neural Networks[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2018, 31: 6106-6116. |
| [28] | SZEGEDY C, ZAREMBA W, SUTSKEVER I, et al. Intriguing Properties of Neural Networks[EB/OL]. (2013-12-21)[2023-06-01]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1312.6199. |
| [29] | GONG Yuan, LI Boyang, POELLABAUER C, et al. Real-Time Adversarial Attacks[EB/OL]. (2019-05-31)[2023-06-01]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1905.13399. |
| [30] | DOAN K D, LAO Yingjie, LI Ping. Marksman Backdoor: Backdoor Attacks with Arbitrary Target Class[EB/OL]. (2022-10-17)[2023-06-01]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2210.09194.pdf. |
| [31] | DU Wei, LIU Gongshen. Review of Backdoor Attacks in Deep Learning[J]. Journal of Cyber Security, 2022, 7(3): 1-16. |
| [32] | CARLINI N. Poisoning the Unlabeled Dataset of Semi-Supervised Learning[EB/OL]. (2019-05-31)[2023-06-01]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1905.13399. |
| [33] | KRIZHEVSKY A. Learning Multiple Layers of Features from Tiny Images[EB/OL]. (2012-05-08)[2023-06-01]. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/265748773_Learning_Multiple_Layers_of_Features_from_Tiny_Images. |
| [34] | COATES A, NG A, LEE H. An Analysis of Single-Layer Networks in Unsupervised Feature Learning[C]// ICML. 14th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2011: 215-223. |
| [35] |
STALLKAMP J, SCHLIPSING M, SALMEN J, et al. Man vs. Computer: Benchmarking Machine Learning Algorithms for Traffic Sign Recognition[J]. Neural Networks, 2012, 32: 323-332.
doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2012.02.016 pmid: 22394690 |
| [36] | RUBINSTEIN B I P, NELSON B, HUANG Ling, et al. Antidote: Understanding and Defending Against Poisoning of Anomaly Detectors[C]// ACM. 9th ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Internet Measurement. New York: ACM, 2009: 1-14. |
| [37] |
BARRENO M, NELSON B, JOSEPH A D, et al. The Security of Machine Learning[J]. Machine Learning, 2010, 81: 121-148.
doi: 10.1007/s10994-010-5188-5 URL |
| [38] | BIGGIO B, CORONA I, FUMERA G, et al. Bagging Classifiers for Fighting Poisoning Attacks in Adversarial Classification Tasks[C]// MCS. Multiple Classifier Systems. Berlin:Springer, 2011: 350-359. |
| [39] | MA Yuzhe, ZHU Xiaojin, HSU J. Data Poisoning Against Differentially-Private Learners: Attacks and Defenses[EB/OL]. (2019-05-23)[2023-06-01]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1903.09860. |
| [40] | ROSENFELD E, WINSTON E, RAVIKUMAR P, et al. Certified Robustness to Label-Flipping Attacks via Randomized Smoothing[C]// ICML. International Conference on Machine Learning. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2020: 8230-8241. |
| [41] | PERI N, GUPTA N, HUANG W R, et al. Deep K-NN Defense Against Clean-Label Data Poisoning Attacks[EB/OL]. (2021-01-10)[2023-06-01]. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-66415-2_4. |
| [42] |
CHEN Jian, ZHANG Xuxin, ZHANG Rui, et al. De-Pois: An Attack-Agnostic Defense Against Data Poisoning Attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2021, 16: 3412-3425.
doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2021.3080522 URL |
| [1] | 姚远, 樊昭杉, 王青, 陶源. 基于多元时序特征的恶意域名检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 1-8. |
| [2] | 李思聪, 王坚, 宋亚飞, 黄玮. 基于BiTCN-DLP的恶意代码分类方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 104-117. |
| [3] | 郇鑫焘, 缪凯焘, 陈稳, 吴畅帆. 基于自主舍弃与校准的鲁棒物联网设备无线密钥生成方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 17-26. |
| [4] | 孙永奇, 宋泽文, 朱卫国, 赵思聪. 基于安全多方计算的图像分类方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 27-37. |
| [5] | 宋丽华, 张津威, 张少勇. 基于博弈论对手建模的物联网SSH自适应蜜罐策略[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 38-47. |
| [6] | 许盛伟, 邓烨, 刘昌赫, 谭莉. 一种基于国密算法的音视频选择性加密方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 48-57. |
| [7] | 姚昌华, 许浩, 付澍, 刘鑫. 基于边界点过滤的多智能体快速协同探索算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 58-68. |
| [8] | 黄恺杰, 王剑, 陈炯峄. 一种基于大语言模型的SQL注入攻击检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 84-93. |
| [9] | 陈立全, 薛雨欣, 江英华, 朱雅晴. 基于国密SM2算法的证书透明日志系统设计[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 9-16. |
| [10] | 廖丽云, 张伯雷, 吴礼发. 基于代价敏感学习的物联网异常检测模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 94-103. |
| [11] | 王智, 张浩, 顾建军. SDN网络中基于联合熵与多重聚类的DDoS攻击检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(10): 1-7. |
| [12] | 张玉臣, 李亮辉, 马辰阳, 周洪伟. 一种融合变量的日志异常检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(10): 16-20. |
| [13] | 仝鑫, 金波, 王斌君, 翟晗名. 融合对抗增强和多任务优化的恶意短信检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(10): 21-30. |
| [14] | 朱怡昕, 苗张旺, 甘静鸿, 马存庆. 基于细粒度访问控制的勒索软件防御系统设计[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(10): 31-38. |
| [15] | 张璐, 屠晨阳, 苗张旺, 甘静鸿. 位置信息端云可信传输方案设计[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(10): 39-47. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||