信息网络安全 ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (4): 630-639.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.04.011
基于自适应采样的机器遗忘方法
- 太原理工大学计算机科学与技术学院,太原 030024
-
收稿日期:2025-01-09出版日期:2025-04-10发布日期:2025-04-25 -
通讯作者:陈永乐chenyongle@tyut.edu.cn -
作者简介:何可(2002—),女,河南,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为人工智能安全|王建华(1995—),男,山西,讲师,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为人工智能安全|于丹(1983—),女,山西,讲师,博士,主要研究方向为物联网安全|陈永乐(1983—),男,山东,教授,博士,CCF高级会员,主要研究方向为物联网安全。 -
基金资助:中央引导地方科技发展资金项目(YDZJSX2024C003);山西省科技成果转化引导专项(202304021301037)
Adaptive Sampling-Based Machine Unlearning Method
HE Ke, WANG Jianhua, YU Dan, CHEN Yongle( )
)
- School of Computer Science and Technology, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, China
-
Received:2025-01-09Online:2025-04-10Published:2025-04-25
摘要:
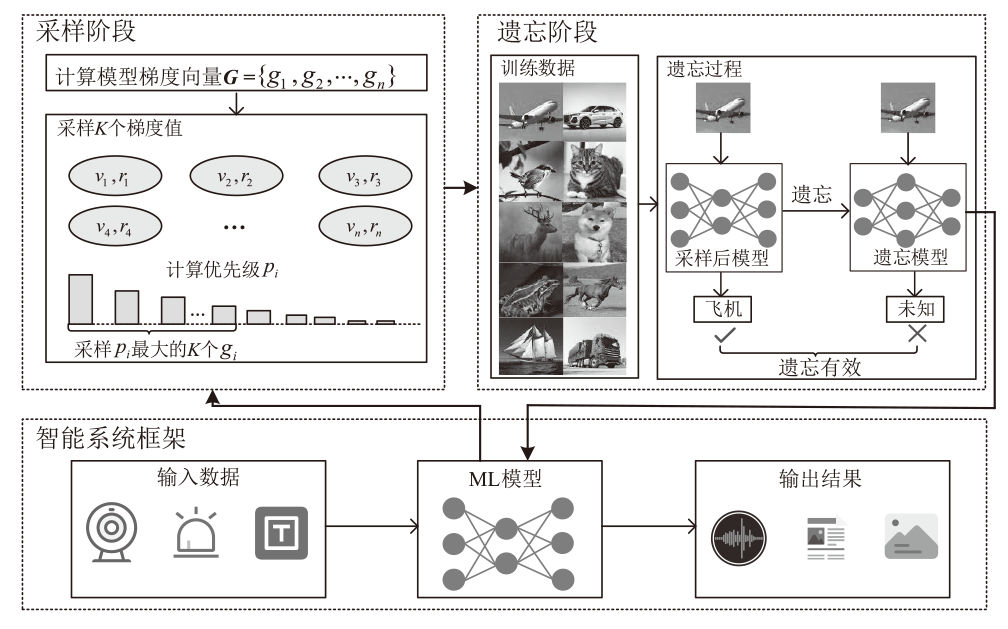
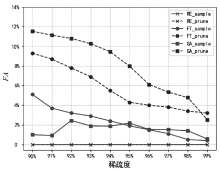
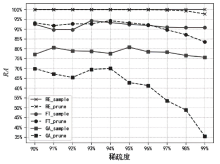
随着人工智能技术的快速发展,智能系统在医疗、工业等多个领域得到广泛应用。然而,智能系统中存储的大量用户数据一旦遭受恶意攻击,将对用户隐私构成严重威胁。为保护用户数据隐私,许多国家已出台相关法律法规,以确保用户享有“被遗忘权”。机器遗忘技术通常分为精确遗忘和近似遗忘两类,旨在通过调整模型参数,从已训练好的模型中消除特定数据的影响。精确遗忘方法利用剩余数据重新训练模型实现遗忘,但其计算成本较高;近似遗忘方法则通过少量参数更新实现遗忘,然而现有方法存在遗忘性能不足、遗忘时间过长等问题。文章提出一种基于自适应采样的机器遗忘方法,该方法先对模型训练过程中的梯度进行采样,随后利用少量梯度信息完成遗忘,具有广泛的适用性,可适配多种机器遗忘方法。实验结果表明,“先采样后遗忘”策略显著提升了近似遗忘性能,同时将精确遗忘时间减少了约22.9%,近似遗忘时间减少了约38.6%。
中图分类号:
引用本文
何可, 王建华, 于丹, 陈永乐. 基于自适应采样的机器遗忘方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(4): 630-639.
HE Ke, WANG Jianhua, YU Dan, CHEN Yongle. Adaptive Sampling-Based Machine Unlearning Method[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(4): 630-639.
| [1] | TIAN Zhiyi, CUI Lei, LIANG Jie, et al. A Comprehensive Survey on Poisoning Attacks and Countermeasures in Machine Learning[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2023, 55(8): 1-35. |
| [2] | JONAS G, BAUERMEISTER H, DROGE H, et al. Inverting Gradients-How Easy is It to Break Privacy in Federated Learning[J]. Neural Information Processing Systems, 2020, 33: 16937-16947. |
| [3] | ZHAO Wei, REN Xiaoning, XUE Yinxing. Membership Inference Attacks Method Based on Ensemble Learning[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(8): 1252-1264. |
| 赵伟, 任潇宁, 薛吟兴. 基于集成学习的成员推理攻击方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1252-1264. | |
| [4] | CHEN Guangke, ZHANG Yedi, SONG Fu. SLMIA-SR: Speaker-Level Membership Inference Attacks against Speaker Recognition Systems[EB/OL]. (2023-11-27)[2024-12-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.07983. |
| [5] | XIA Hui, QIAN Xiangyun. Invisible Backdoor Attack Based on Feature Space Similarity[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(8): 1163-1172. |
| 夏辉, 钱祥运. 基于特征空间相似的隐形后门攻击[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1163-1172. | |
| [6] | LIU Gaoyang, WU Weiling, ZHANG Jinsheng, et al. Targeted Poisoning Attacks against Multimodal Contrastive Learning[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(11): 69-83. |
| 刘高扬, 吴伟玲, 张锦升, 等. 多模态对比学习中的靶向投毒攻击[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 69-83. | |
| [7] | VOIGT P, VON D B A. The EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): A Practical Guide[M]. Heidelberg: Springer, 2024. |
| [8] | PARDAU S L. The California Consumer Privacy ACT: Towards a European-Style Privacy Regime in the United States[EB/OL]. (2018-06-28)[2024-12-20]. https://scholarship.law.ufl.edu/jtlp/vol23/iss1/2/. |
| [9] | WANG Weiqi, TIAN Zhiyi, ZHANG Chenhan, et al. Machine Unlearning: A Comprehensive Survey[EB/OL]. (2024-05-13)[2024-12-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.07406v2. |
| [10] | CHUNDAWAT V S, TARUN A K, MANDAL M, et al. Zero-Shot Machine Unlearning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2023(18): 2345-2354. |
| [11] | CAO Yinzhi, YANG Junfeng. Towards Making Systems Forget with Machine Unlearning[C]// IEEE. 2015 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. New York: IEEE, 2015: 463-480. |
| [12] | BOURTOULE L, CHANDRASEKARAN V, CHOQUETTE-CHOO C A, et al. Machine Unlearning[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York: IEEE, 2021: 141-159. |
| [13] | WARNECKE A, PIRCH L, WRESSNEGGER C, et al. Machine Unlearning of Features and Labels[EB/OL]. (2021-08-26)[2024-12-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.11577v4. |
| [14] | THUDI A, DEZA G, CHANDRASEKARAN V, et al. Unrolling SGD: Understanding Factors Influencing Machine Unlearning[C]// IEEE. 2022 IEEE 7th European Symposium on Security and Privacy (EuroS&P). New York: IEEE, 2022: 303-319. |
| [15] | BECKER A, LIEBIG T. Evaluating Machine Unlearning via Epistemic Uncertainty[EB/OL]. (2022-09-19)[2024-12-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.10836v2. |
| [16] | IZZO Z, SMART M A, CHAUDHURI K, et al. Approximate Data Deletion from Machine Learning Models[C]// PMLR. International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. New York: PMLR, 2021: 2008-2016. |
| [17] | GRAVES L, NAGISETTY V, GANESH V. Amnesiac Machine Learning[EB/OL]. (2020-10-21)[2024-12-20]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2010.10981. |
| [18] | BROPHY J, LOWD D. Machine Unlearning for Random Forests[C]// PMLR. International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: PMLR, 2021: 1092-1104. |
| [19] | GINART A, GUAN M Y, VALIANT G, et al. Making AI Forget You: Data Deletion in Machine Learning[J]. Neural Information Processing Systems, 2019, 316: 3518-3531. |
| [20] | MIRZASOLEIMAN B, KARBASI A, KRAUSE A. Deletion-Robust Submodular Maximization: Data Summarization with “ The Right to be Forgotten”[C]// ACM. The 34th International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2017: 2449-2458. |
| [21] | NGUYEN Q P, LOW B K H, JAILLET P. Variational Bayesian Unlearning[J]. Neural Information Processing Systems, 2020, 33: 16025-16036. |
| [22] | GUO Chuan, GOLDSTEIN T, HANNUN A, et al. Certified Data Removal from Machine Learning Models[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML’20). New York: ACM, 2020: 3832-3842. |
| [23] | MAHADEVAN A, MATHIOUDAKIS M. Certifiable Machine Unlearning for Linear Models[EB/OL]. (2021-06-29)[2024-12-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.15093v3. |
| [24] | SEKHARI A, ACHARYA J, KAMATH G, et al. Remember What You Want to Forget: Algorithms for Machine Unlearning[J]. Neural Information Processing Systems, 2021, 34: 18075-18086. |
| [25] | LIU Jinghan, RAM P, YAO Yuguang, et al. Model Sparsity Can Simplify Machine Unlearning[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems(NIPS’23). New York: ACM, 2024, 2246: 51584-51605. |
| [26] | TARUN A K, CHUNDAWAT V S, MANDAL M, et al. Fast Yet Effective Machine Unlearning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(9): 13046-13055. |
| [27] | GOLATKAR A, ACHILLE A, SOATTO S. Eternal Sunshine of the Spotless Net: Selective Forgetting in Deep Networks[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2020: 9304-9312. |
| [28] | ZHAO Yikai, ZHANG Yinda, LI Yuanpeng, et al. MinMax Sampling: A Near-Optimal Global Summary for Aggregation in the Wide Area[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Management of Data. New York: ACM, 2022: 744-758. |
| [29] | THUDI A, DEZA G, CHANDRASEKARAN V, et al. Unrolling SGD: Understanding Factors Influencing Machine Unlearning[C]// IEEE. 2022 IEEE 7th European Symposium on Security and Privacy (EuroS&P). New York: IEEE, 2022: 303-319. |
| [1] | 胡宇涵, 杨高, 蔡红叶, 付俊松. 三维分布式无线智能系统数据传输路径隐私保护方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(4): 536-549. |
| [2] | 李佳东, 曾海涛, 彭莉, 汪晓丁. 一种保护数据隐私的匿名路由联邦学习框架[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(3): 494-503. |
| [3] | 温金明, 刘庆, 陈洁, 吴永东. 基于错误学习的全同态加密技术研究现状与挑战[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(9): 1328-1351. |
| [4] | 林湛航, 向广利, 李祯鹏, 徐子怡. 基于同态加密的前馈神经网络隐私保护方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(9): 1375-1385. |
| [5] | 郭倩, 赵津, 过弋. 基于分层聚类的个性化联邦学习隐私保护框架[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1196-1209. |
| [6] | 李增鹏, 王思旸, 王梅. 隐私保护近邻检测研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(6): 817-830. |
| [7] | 傅彦铭, 陆盛林, 陈嘉元, 覃华. 基于深度强化学习和隐私保护的群智感知动态任务分配策略[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 449-461. |
| [8] | 徐健锋, 张炜, 涂敏, 魏勍颋, 赖展晴, 王倩倩. 基于语义融合轨迹生成的k匿名轨迹集补全方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(12): 1911-1921. |
| [9] | 顾海艳, 柳琪, 马卓, 朱涛, 钱汉伟. 基于可用性的数据噪声添加方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(11): 1731-1738. |
| [10] | 宋玉涵, 祝跃飞, 魏福山. 一种基于AdaBoost模型的区块链异常交易检测方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1): 24-35. |
| [11] | 许可, 李嘉怡, 蒋兴浩, 孙锬锋. 一种基于轮廓稀疏对抗的视频步态隐私保护算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1): 48-59. |
| [12] | 赖成喆, 赵益宁, 郑东. 基于同态加密的隐私保护与可验证联邦学习方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1): 93-105. |
| [13] | 俞惠芳, 乔一凡, 孟茹. 面向区块链金融的抗量子属性基门限环签密方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(7): 44-52. |
| [14] | 唐雨, 张驰. 一种基于Intel SGX的信息中心网络隐私保护方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(6): 55-65. |
| [15] | 杜卫东, 李敏, 韩益亮, 王绪安. 基于密文转换的高效通用同态加密框架[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(4): 51-60. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||