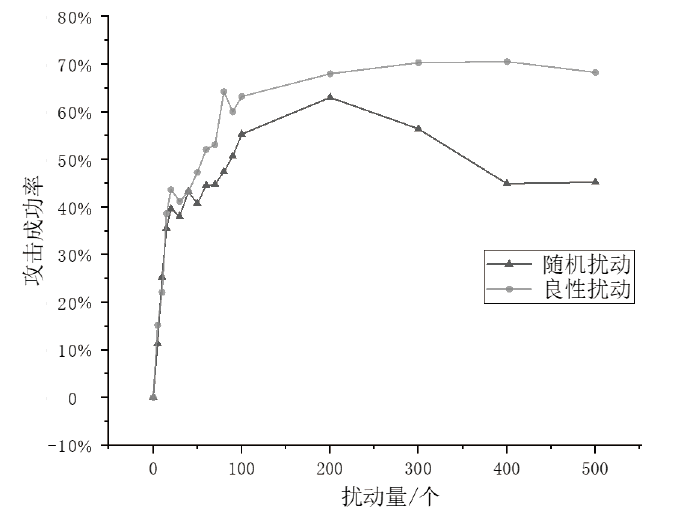
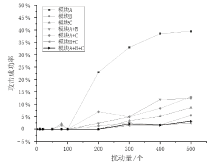
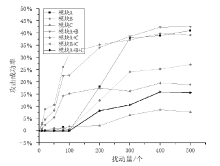
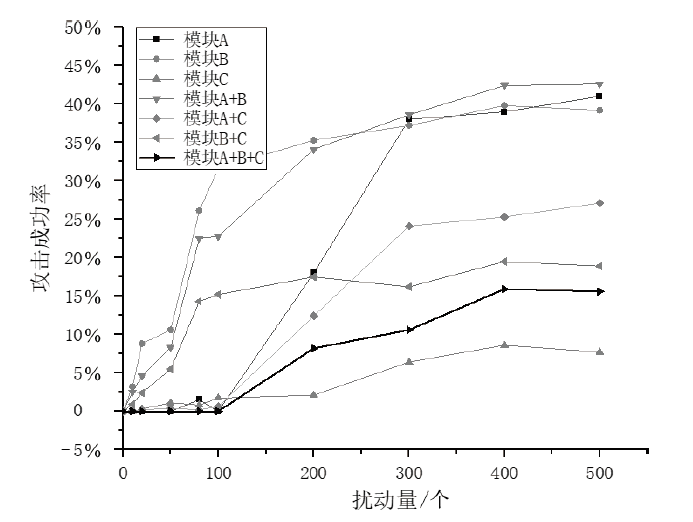
信息网络安全 ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (1): 159-172.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.01.014
基于集成学习的恶意代码动态检测方法
- 1.空军工程大学防空反导学院,西安 710051
2.空军工程大学研究生院,西安 710051
3.中国人民解放军94789部队,南京 210018
-
收稿日期:2024-09-25出版日期:2025-01-10发布日期:2025-02-14 -
通讯作者:王亚男 E-mail:wyn1988814@163.com -
作者简介:刘强(1993—),男,陕西,助理工程师,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为网络空间安全和恶意代码检测|王坚(1982—),男,陕西,副教授,硕士,主要研究方向为智能信息处理和网络安全防护|王亚男(1988—),女,陕西,讲师,博士,主要研究方向为网络信息安全和人工智能|王珊(1989—),女,江苏,工程师,硕士,主要研究方向为信息通信技术 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(61806219);国家自然科学基金(61703426);国家自然科学基金(61876189);陕西省高校科协青年人才托举计划(20190108);陕西省高校科协青年人才托举计划(20220106);陕西省创新能力支撑计划(2020KJXX-065)
A Dynamic Malware Detection Method Based on Ensemble Learning
LIU Qiang1,2, WANG Jian1, WANG Yanan1( ), WANG Shan3
), WANG Shan3
- 1. School of Air Defense and Antimissile, Air Force Engineering University, Xi’an 710051, China
2. Graduate School of Air Force Engineering University, Xi’an 710051, China
3. 94789 Troop of PLA, Nanjing 210018, China
-
Received:2024-09-25Online:2025-01-10Published:2025-02-14 -
Contact:WANG Yanan E-mail:wyn1988814@163.com
摘要:
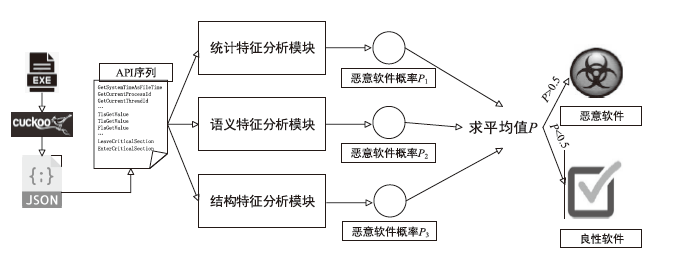
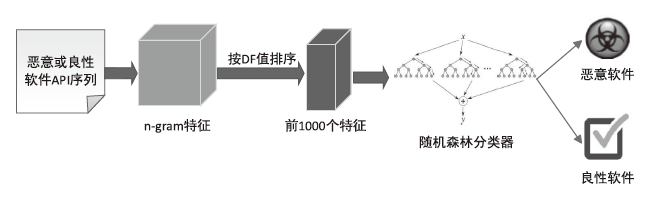
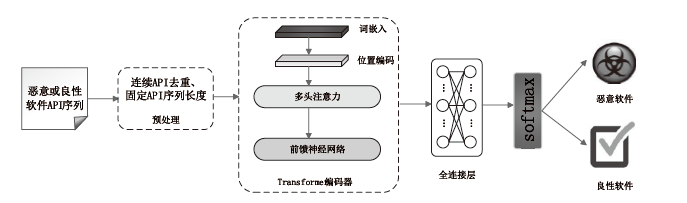
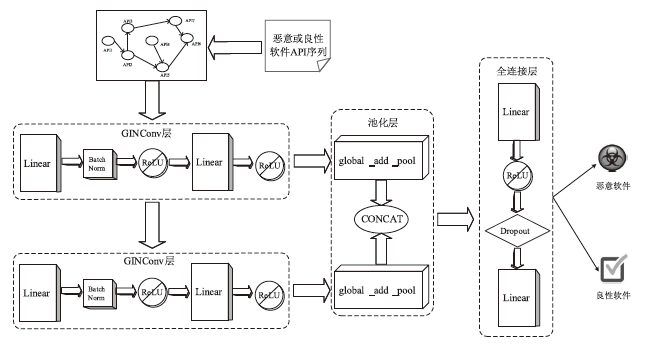
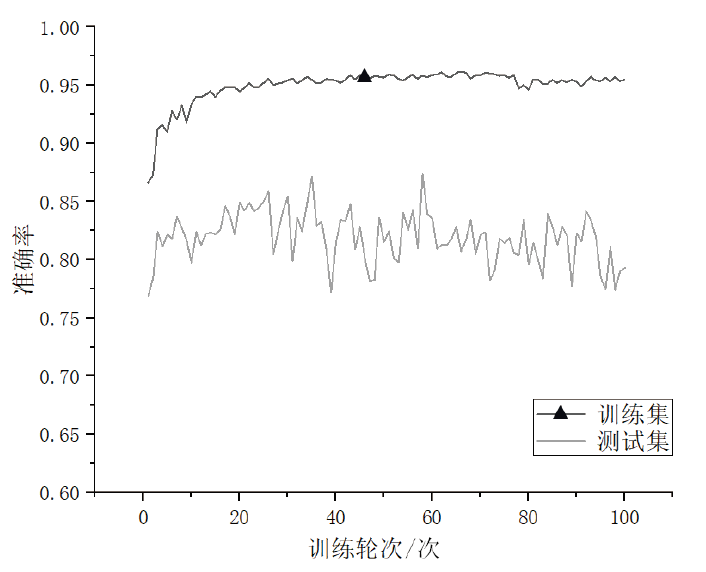
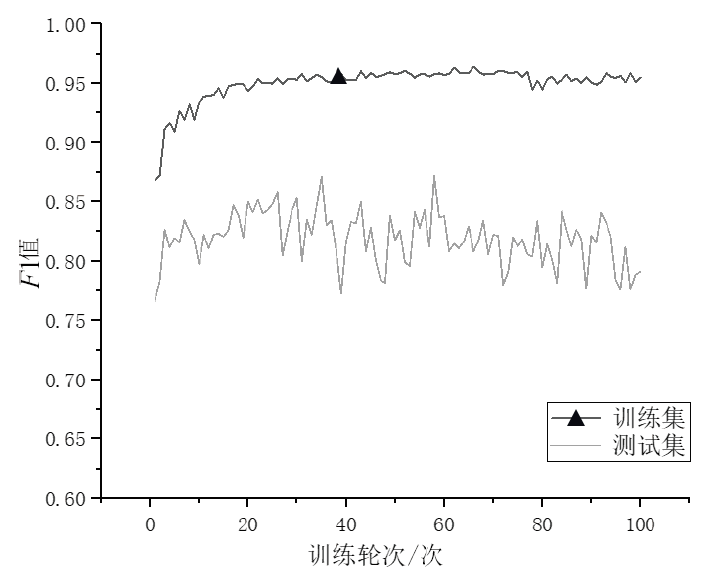
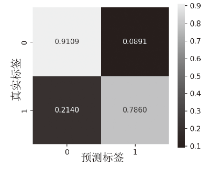
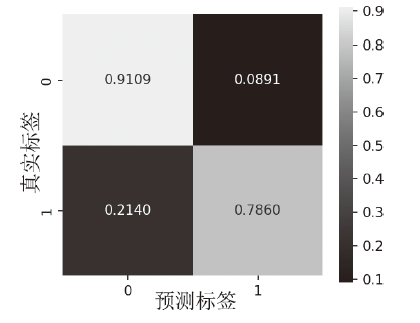
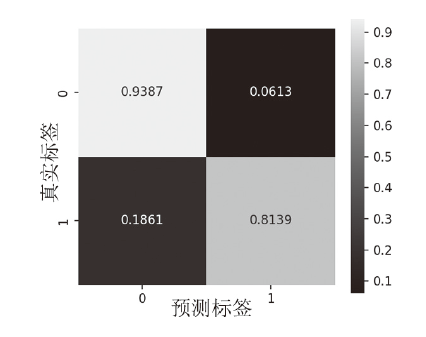
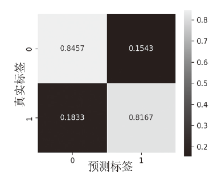
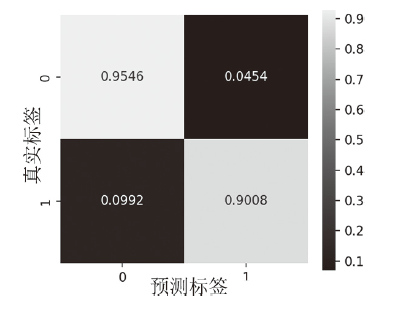
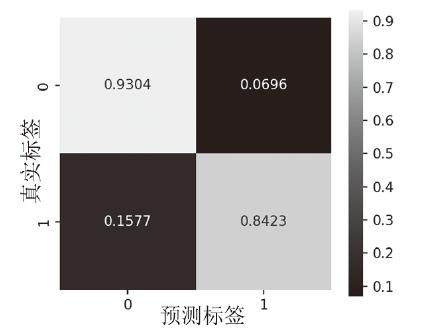
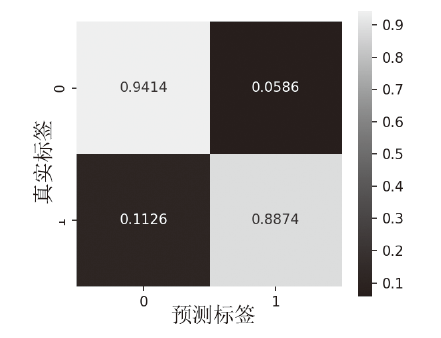
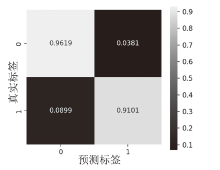
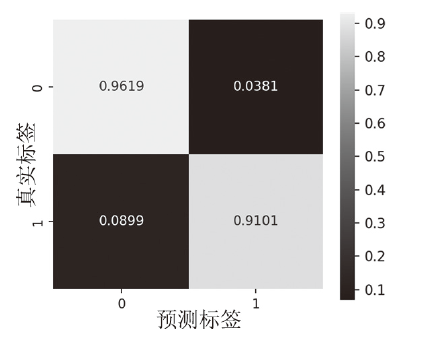
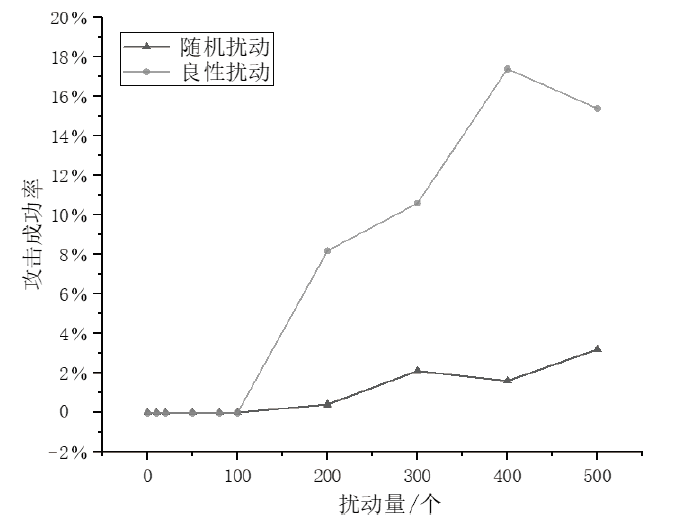
在当前网络环境中,不断升级的恶意代码变种为网络安全带来了巨大挑战。现有的人工智能模型虽然在恶意代码检测方面成效明显,但仍存在两个不可忽视的缺点。一是泛化能力较差,虽然在训练数据上表现优异,但受概念漂移现象的影响,在实际测试中性能不够理想;二是鲁棒性不佳,容易受到对抗样本的攻击。为解决上述问题,文章提出一种基于集成学习的恶意代码动态检测方法,根据API序列的不同特征,分别构建统计特征分析模块、语义特征分析模块和结构特征分析模块,各模块针对性地进行恶意代码检测,最后融合各模块分析结果,得出最终检测结论。在Speakeasy数据集上的实验结果表明,与现有研究方法相比,该方法各项性能指标具有明显优势,同时具有较好的鲁棒性,能够有效抵抗针对API序列的两种对抗攻击。
中图分类号:
引用本文
刘强, 王坚, 王亚男, 王珊. 基于集成学习的恶意代码动态检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(1): 159-172.
LIU Qiang, WANG Jian, WANG Yanan, WANG Shan. A Dynamic Malware Detection Method Based on Ensemble Learning[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(1): 159-172.
表4
不同n值n-gram特征效果对比
| 训练集 | 测试集 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | F1-值 | TPR(FPR=10-3) | AUC | Accuracy | F1-值 | TPR(FPR=10-3) | AUC | |
| 2-gram | 0.9592 | 0.9701 | 0.7962 | 0.9918 | 0.8432 | 0.8446 | 0.3879 | 0.9360 |
| 3-gram | 0.9515 | 0.9646 | 0.7616 | 0.9879 | 0.8334 | 0.8363 | 0.3806 | 0.9351 |
| 4-gram | 0.9348 | 0.9529 | 0.7207 | 0.9793 | 0.8317 | 0.8367 | 0.3856 | 0.9284 |
| 5-gram | 0.9159 | 0.9404 | 0.6827 | 0.9665 | 0.8261 | 0.8386 | 0.3694 | 0.9202 |
| [1] | Kaspersky Security Network. The Mobile Malware Threat Landscape in 2023[EB/OL]. (2024-02-06)[2024-09-10]. https://securelist.com/mobile-malware-report-2023/111964. |
| [2] | LI Sicong, WANG Jian, SONG Yafei, et al. Malicious Code Classification Method Based on BiTCN-DLP[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(11): 104-117. |
| 李思聪, 王坚, 宋亚飞, 等. 基于BiTCN-DLP的恶意代码分类方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11):104-117. | |
| [3] | SUN Hongzhe, WANG Jian, WANG Peng, et al. Network Intrusion Detection Method Based on Attention-BiTCN[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(2): 309-318. |
| 孙红哲, 王坚, 王鹏, 等. 基于Attention-BiTCN的网络入侵检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 309-318. | |
| [4] |
ZHANG Dandan, SONG Yafei, LIU Shu. MalMKNet: A Multi-Scale Convolutional Neural Network Used for Malware Classification[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2023, 51(5): 1359-1369.
doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20221069 |
|
张丹丹, 宋亚飞, 刘曙. MalMKNet:一种用于恶意代码分类的多尺度卷积神经网络[J]. 电子学报, 2023, 51(5): 1359-1369.
doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20221069 |
|
| [5] | GALLORO N, POLINO M, CARMINATI M, et al. A Systematical and Longitudinal Study of Evasive Behaviors in Windows Malware[EB/OL]. (2021-12-05)[2024-09-10]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2021.102550. |
| [6] | CHAI Yuhan. Research on Key Technologies for Malware Classification in Open World[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University, 2023. |
| 柴瑜晗. 开放场景下恶意软件分类关键技术研究[D]. 广州: 广州大学, 2023. | |
| [7] | QIAO Yong, YANG Yueyang, JI Lin, et al. Analyzing Malware by Abstracting the Frequent Itemsets in API Call Sequences[C]// IEEE. 2013 12th IEEE International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications. New York: IEEE, 2013: 265-270. |
| [8] | UPPAL D, SINHA R, MEHRA V, et al. Malware Detection and Classification Based on Extraction of API Sequences[C]// IEEE. 2014 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI). New York: IEEE, 2014: 2337-2342. |
| [9] | ALAZAB M, ALAZAB M, SHALAGINOV A, et al. Intelligent Mobile Malware Detection Using Permission Requests and API Calls[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2020, 107: 509-521. |
| [10] | KOLOSNJAJI B, ZARRAS A, WEBSTER G, et al. Deep Learning for Classification of Malware System Call Sequences[C]// Springer. Advances in Artificial Intelligence:29th Australasian Joint Conference (AI 2016). Heidelberg: Springer, 2016: 137-149. |
| [11] | AGRAWAL R, STOKES J W, MARINESCU M, et al. Neural Sequential Malware Detection with Parameters[C]// IEEE. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). New York: IEEE, 2018: 2656-2660. |
| [12] | ZHANG Zhaoqi, QI Panpan, WANG Wei. Dynamic Malware Analysis with Feature Engineering and Feature Learning[C]// AAAI. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York: AAAI, 2020, 34(1): 1210-1217. |
| [13] | LI Ce, LYU Qiujian, LI Ning, et al. A Novel Deep Framework for Dynamic Malware Detection Based on API Sequence Intrinsic Features[EB/OL]. (2022-03-17)[2024-09-10]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2022.102686. |
| [14] | ZHANG Sanfeng, WU Jiahao, ZHANG Mengzhe, et al. Dynamic Malware Analysis Based on API Sequence Semantic Fusion[EB/OL]. (2023-05-26)[2024-09-10]. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116526. |
| [15] | DEMIRKIRAN F, ÇAYIR A, UNAL U, et al. An Ensemble of Pre-Trained Transformer Models for Imbalanced Multiclass Malware Classification[EB/OL]. (2022-08-06)[2024-09-10]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2022.102846. |
| [16] | LI Yaping, LI Yuancheng. IoT Malware Threat Hunting Method Based on Improved Transformer[J]. International Journal of Network Security, 2023, 25(2): 267-276. |
| [17] | TRIZNA D, DEMETRIO L, BIGGIO B, et al. Nebula: Self-Attention for Dynamic Malware Analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2024, 19: 6155-6167. |
| [18] | JIANG Haodi, TURKI T, WANG J T L. DLGraph: Malware Detection Using Deep Learning and Graph Embedding[C]// IEEE. 2018 17th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA). New York: IEEE, 2018: 1029-1033. |
| [19] | AMER E, ZELINKA I. A Dynamic Windows Malware Detection and Prediction Method Based on Contextual Understanding of API Call Sequence[EB/OL]. (2020-02-20)[2024-09-10]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2020.101760. |
| [20] | XIAO Fei, LIN Zhaowen, SUN Yi, et al. Malware Detection Based on Deep Learning of Behavior Graphs[EB/OL]. (2019-02-11)[2024-09-10]. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8195395. |
| [21] | LI Ce, CHENG Zijun, ZHU He, et al. DMalNet: Dynamic Malware Analysis Based on API Feature Engineering and Graph Learning[EB/OL]. (2022-08-21)[2024-09-10]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2022.102872. |
| [22] | DONG Shishi, HUANG Zhexue. A Brief Theoretical Overview of Random Forests[J]. Journal of Integration Technology, 2013, 2(1): 1-7. |
| [23] | PARMAR A, KATARIYA R, PATEL V. A Review on Random Forest: An Ensemble Classifier[C]// Springer. International Conference on Intelligent Data Communication Technologies and Internet of Things (ICICI). Heidelberg: Springer, 2019: 758-763. |
| [24] | VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is All You Need[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017, 30: 5998-6008. |
| [25] | MIKOLOV T, CHEN Kai, CORRADO G, et al. Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space[EB/OL]. (2013-09-07)[2024-09-10]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1301.3781. |
| [26] | XU Keyulu, HU Weihua, LESKOVEC J, et al. How Powerful are Graph Neural Networks?[EB/OL]. (2018-10-04)[2024-09-10]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1810.00826.pdf. |
| [27] | TRIZNA D. Quo Vadis: Hybrid Machine Learning Meta-Model Based on Contextual and Behavioral malware Representations[C]// ACM.Proceedings of the 15th ACM Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Security. New York: ACM, 2022: 127-136. |
| [28] | MANDIANT. Speakeasy: Portable, Modular, Binary Emulator Designed to Emulate Windows Kernel and User Mode Malware[EB/OL]. (2021-10-11)[2024-09-10]. https://github.com/mandiant/speakeasy. |
| [29] | JINDAL C, SALLS C, AGHAKHANI H, et al. Neurlux: Dynamic Malware Analysis without Feature Engineering[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 35th Annual Computer Security Applications Conference. New York: ACM, 2019: 444-455. |
| [30] | ROSENBERG I, SHABTAI A, ELOVICI Y, et al. Query-Efficient Black-Box Attack against Sequence-Based Malware Classifiers[C]// ACM.Proceedings of the 36th Annual Computer Security Applications Conference. New York: ACM, 2020: 611-626. |
| [31] | YU Lantao, ZHANG Weinan, WANG Jun, et al. Seqgan: Sequence Generative Adversarial Nets with Policy Gradient[EB/OL]. (2017-02-13)[2024-09-10]. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v31i1.10804. |
| [32] | Cuckoo Sandbox. Cuckoo Sandbox Hooked APIs and Categories[EB/OL]. (2019-08-24)[2024-09-10]. https://github.com/cuckoosandbox/cuckoo/wiki/Hooked-APIs-and-Categories. |
| [1] | 王健, 陈琳, 王凯崙, 刘吉强. 基于时空图神经网络的应用层DDoS攻击检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(4): 509-519. |
| [2] | 戚晗, 王敬童, ABDULLAH Gani, 拱长青. 基于随机量子层的变分量子卷积神经网络鲁棒性研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 363-373. |
| [3] | 张新有, 孙峰, 冯力, 邢焕来. 基于多视图表征的虚假新闻检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 438-448. |
| [4] | 余尚戎, 肖景博, 殷琪林, 卢伟. 关注社交异配性的社交机器人检测框架[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 319-327. |
| [5] | 李奕轩, 贾鹏, 范希明, 陈尘. 基于控制流变换的恶意程序检测GNN模型对抗样本生成方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(12): 1896-1910. |
| [6] | 张选, 万良, 罗恒, 杨阳. 基于两阶段图学习的僵尸网络自动化检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(12): 1933-1947. |
| [7] | 李鹏超, 张全涛, 胡源. 基于双注意力机制图神经网络的智能合约漏洞检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(11): 1624-1631. |
| [8] | 芦效峰, 程天泽, 龙承念. 基于随机游走的图神经网络黑盒对抗攻击[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(10): 1570-1577. |
| [9] | 秦中元, 马楠, 余亚聪, 陈立全. 基于双重图神经网络和自编码器的网络异常检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(9): 1-11. |
| [10] | 仝鑫, 金波, 王靖亚, 杨莹. 一种面向Android恶意软件的多视角多任务学习检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 1-7. |
| [11] | 朱丽娜, 马铭芮, 朱东昭. 基于图神经网络和通用漏洞分析框架的C类语言漏洞检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 59-68. |
| [12] | 秦中元, 胡宁, 方兰婷. 基于免疫仿生机理和图神经网络的网络异常检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(8): 10-16. |
| [13] | 李云春, 鲁文涛, 李巍. 基于Shapelet的恶意代码检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(3): 70-77. |
| [14] | 张家旺, 李燕伟. 基于N-gram算法的恶意程序检测系统研究与设计[J]. 信息网络安全, 2016, 16(8): 74-80. |
| [15] | . 电力移动智能终端安全技术研究[J]. , 2014, 14(4): 70-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||