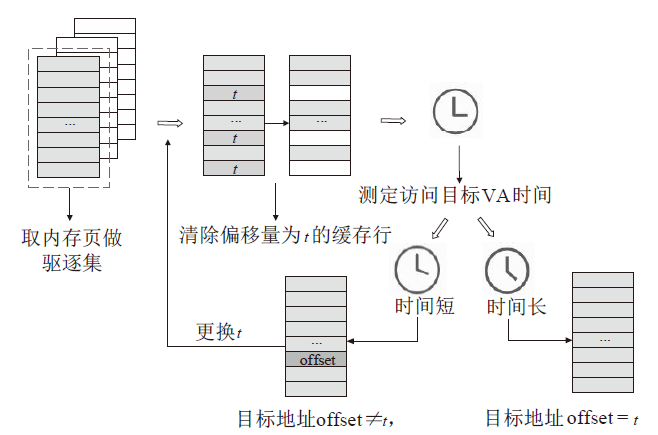
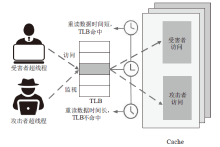
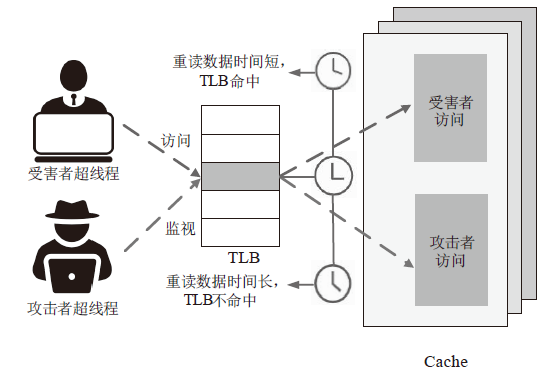
信息网络安全 ›› 2022, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (6): 26-37.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2022.06.003
处理器微架构存储体系侧信道协同安全技术研究
- 1.北京航空航天大学网络空间安全学院,北京 100191
2.南昌大学信息工程学院,南昌 330031
3.北京智芯微电子科技有限公司,北京 100192
4.北京航空航天大学高等理工学院,北京 100191
-
收稿日期:2022-01-13出版日期:2022-06-10发布日期:2022-06-30 -
通讯作者:洪晟 E-mail:shenghong@buaa.edu.cn -
作者简介:洪晟(1981—),男,江西,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为信息网络安全、集成电路安全性、复杂系统安全性和软件安全|李雷(1982—),男,河北,工程师,硕士,主要研究方向为CPU内核微架构、存储子系统功能安全和信息安全防护技术|原义栋(1980—),男,河北,工程师,硕士,主要研究方向为电力通信技术|高欣妍(2002—),女,安徽,本科,主要研究方向为网络空间安全和信息系统安全 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2019YFB1706001)
Research on Cooperative Security Technology of Side Channel in Processor Microarchitecture Storage System
HONG Sheng1,2( ), LI Lei3, YUAN Yidong3, GAO Xinyan4
), LI Lei3, YUAN Yidong3, GAO Xinyan4
- 1. School of Cyber Science and Technology, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
2. School of Information Engineering, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330031, China
3. Beijing Smart Chip Microelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing 100192, China
4. College of SHENYUAN Honors, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
-
Received:2022-01-13Online:2022-06-10Published:2022-06-30 -
Contact:HONG Sheng E-mail:shenghong@buaa.edu.cn
摘要:
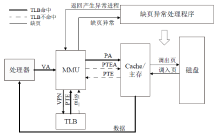
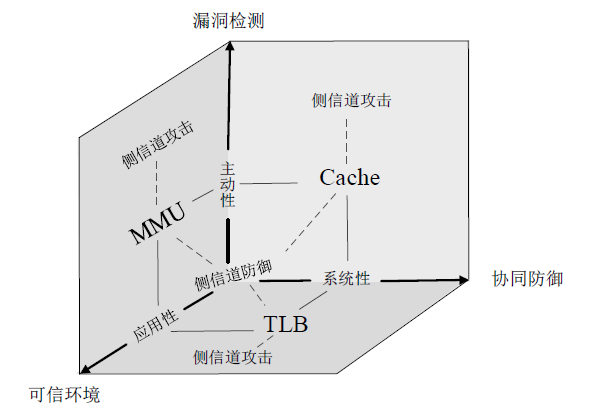
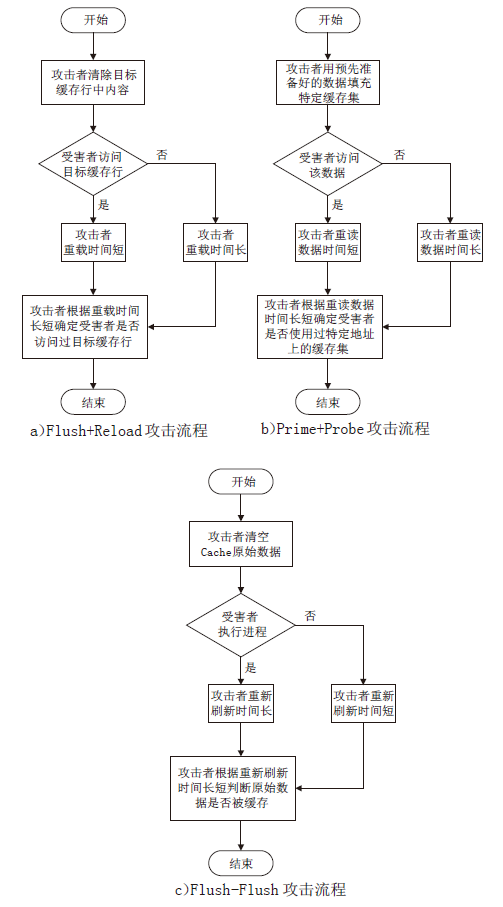
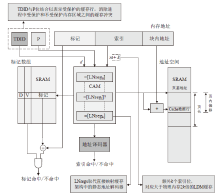
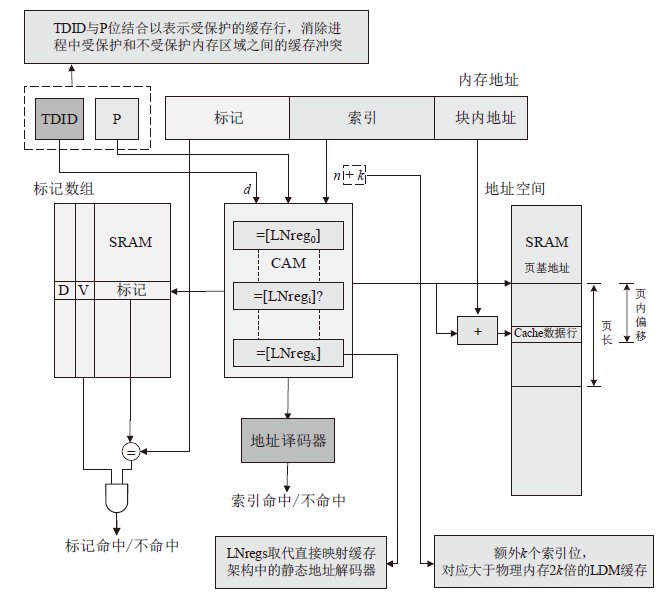
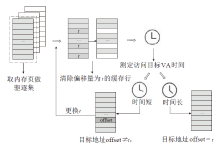
侧信道攻击是一种利用设备运行过程中侧信道的信息泄露展开的攻击,其可绕开加密算法,这对用户隐私安全产生了严重威胁。在处理器微架构存储体系中,频繁的内存访问和程序执行的快慢差别为侧信道攻击的产生创造了条件。微架构侧信道攻击不需要物理接触,只要攻击者与受害者处于同一环境即可进行攻击,其危害性较传统侧信道攻击更大。文章首先从攻击对象出发,分别从Cache、MMU和TLB三方面总结侧信道攻击技术和防御技术,提出协同安全模型框架;然后以检测进程风险、增加攻击难度和隔离安全区域为安全架构中心思想总结侧信道安全措施,提出处理器微架构存储体系侧信道协同安全模型,以指导新型架构设计;最后展望未来技术发展趋势,为研究侧信道防御技术提供参考。
中图分类号:
引用本文
洪晟, 李雷, 原义栋, 高欣妍. 处理器微架构存储体系侧信道协同安全技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(6): 26-37.
HONG Sheng, LI Lei, YUAN Yidong, GAO Xinyan. Research on Cooperative Security Technology of Side Channel in Processor Microarchitecture Storage System[J]. Netinfo Security, 2022, 22(6): 26-37.
使用本文
表1
缓存侧信道防御技术的优缺点
| 缓存侧信道 防御技术 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| RPCache | 使干扰随机化,性能下降,几乎不依赖软件和底层硬件架构 | 功耗增加 |
| PLCache | 可防御基于内部干扰的攻击,相较于传统分区缓存更灵活,性能下降幅度较小 | 当受保护内存大于缓存容量时,性能明显下降 |
| NewCache | 功率高、开销低,访问时延不受CAM限制 | 平均不命中率有所降低,功耗和面积增加幅度较大 |
| NoMoCache | 开销低,通过隐藏关键访问使设计复杂性最小化,保证稳定状态下的安全性 | 无法解决重新配置期间侧信道泄露问题 |
| ScatterCache | 防御基于驱逐的侧信道攻击,软件层面改动最小 | 页表开销稍有增加 |
| CEASE | 减速较小,新添加的存储开销小,可容忍100年以上的攻击,不依赖任何操作系统/软件支持 | 随机化影响缓存不命中率,LLC的错误率增加,平均MPKI增加 |
| PhantomCache | 随机化空间限制在小范围的缓存位置,性能下降幅度小,平均引入的减速小、效率高,平均放缓幅度极小 | 影响跨不同片的内存访问并行性的效果,比基准LLC消耗功率更多,逻辑开销和存储开销较大 |
| SHARP | 有效抵御跨核攻击,对基于缓存的侧信道攻击有效,对性能的影响可忽略不计 | 性能有所下降 |
| [1] | KOCHER P, HORN J, FOGH A, et al. Spectre Attacks: Exploiting Speculative Execution[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York:IEEE, 2019: 1-19. |
| [2] | LIPP M, SCHWARZ M, GRUSS D, et al. Meltdown: Reading Kernel Memory from User Space[C]// USENIX. 27th USENIX Security Symposium. Berkeley: USENIX, 2018: 973-990. |
| [3] | QIN Leihua, WU Fei, MO Zhengkun. Principle of Computer Composition[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Publishing House, 2011. |
| 秦磊华, 吴非, 莫正坤. 计算机组成原理[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2011. | |
| [4] | WANG Chong, WEI Shuai, ZHANG Fan, et al. A Survey of Cache-Based Side Channel Countermeasure[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2021, 58(4): 794-810. |
| 王崇, 魏帅, 张帆, 等. 缓存侧信道防御研究综述[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2021, 58(4): 794-810. | |
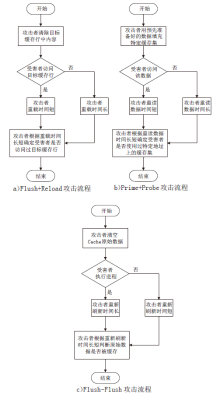
| [5] | YAROM Y, FALKNER K. Flush+Reload: A High Resolution, Low Noise, L3 Caches-Channel Attack[C]// USENIX. 23rd USENIX Security Symposium. Berkeley: USENIX, 2014: 719-732. |
| [6] | RISTENPART T, TROMER E, SHACHAM H, et al. Hey, You, Get off of My Cloud: Exploring Information Leakage in Third-Party Compute Clouds[C]// ACM. 16th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2009: 199-212. |
| [7] | GRUSS D, MAURICE C, WAGNER K, et al. Flush+Flush: A Fast and Stealthy Cache Attack[C]// Springer. 2016 International Conference on Detection of Intrusions and Malware, and Vulnerability Assessment. Heidelberg: Springer, 2016: 279-299. |
| [8] | GALLAIS J, KIZHVATOV I, TUNSTALL M. Improved Trace-Driven Cache-Collision Attacks against Embedded AES Implementations[C]// Springer. 2010 International Workshop on Information Security Applications. Heidelberg: Springer, 2010: 243-257. |
| [9] | CHEN Caisen, WANG Tao, GUO Shize, et al. Research on Trace Driven Data Cache Timing Attack against RSA[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2014, 37(5): 1039-1051. |
| 陈财森, 王韬, 郭世泽, 等. 针对RSA算法的踪迹驱动数据Cache计时攻击研究[J]. 计算机学报, 2014, 37(5): 1039-1051. | |
| [10] | ZHU Jialiang, WEI Yongzhuang. Trace Driven Cache Attack on LBlock Algorithm[J]. Computer Engineering, 2015, 41(5): 153-158. |
| 朱嘉良, 韦永壮. 针对LBlock算法的踪迹驱动Cache攻击[J]. 计算机工程, 2015, 41(5): 153-158. | |
| [11] | LOU Xiaoxuan, ZHANG Fan, HUANG Jing, et al. Research on Trace Driven Cache Analysis on SM4[J]. Journal of Cryptologic Research, 2018, 5(4): 430-441. |
| [12] |
WANG Zhenghong, LEE R B. New Cache Designs for Thwarting Software Cache-Based Side Channel Attacks[J]. ACM SIGARCH Computer Architecture News, 2007, 35(2): 494-505.
doi: 10.1145/1273440.1250723 URL |
| [13] | LIU Fangfei, WU Hao, LEE R B. Can Randomized Mapping Secure Instruction Caches from Side-Channel Attacks?[C]// ACM. 4th Workshop on Hardware and Architectural Support for Security and Privacy. New York: ACM, 2015: 41-48. |
| [14] | LIU Fangfei, WU Hao, MAI K, et al. Newcache: Secure Cache Architecture Thwarting Cache Side-Channel Attacks[J]. IEEE Micro, 2016, 36(5): 8-16. |
| [15] | DOMNITSER L, JALEEL A, LOEW J, et al. Non-Monopolizable Caches: Low-Complexity Mitigation of Cache Side Channel Attacks[J]. ACM Transactions on Architecture and Code Optimization, 2012, 8(4): 1-21. |
| [16] | WERNER M, UNTERLUGGAUER T, GINER L, et al. ScatterCache: Thwarting Cache Attacks via Cache Set Randomization[C]// USENIX. 28th USENIX Security Symposium. Berkeley: USENIX, 2019: 675-692. |
| [17] | QURESHI M K. CEASER: Mitigating Conflict-Based Cache Attacks via Encrypted-Address and Remapping[C]// IEEE. 2018 51st Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture (MICRO). New York:IEEE, 2018: 775-787. |
| [18] | QURESHI M K. New Attacks and Defense for Encrypted-Address Cache[C]// ACM. 2019 ACM/IEEE 46th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA). New York:ACM, 2019: 360-371. |
| [19] | TAN Qinhan, ZENG Zhihua, BU Kai, et al. PhantomCache: Obfuscating Cache Conflicts with Localized Randomization[EB/OL]. (2021-03-13) [2021-11-01]. https://list.zju.edu.cn/kaibu/phantomcache.pdf. |
| [20] | YAN Mengjia, GOPIREDDY, SHULL, et al. Secure Hierarchy-Aware Cache Replacement Policy (SHARP): Defending against Cache-Based Side Channel Atacks[C]// ACM. 2017 ACM/IEEE 44th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA). New York:ACM, 2017: 347-360. |
| [21] | COSTAN V, DEVADAS S. Intel SGX Explained[EB/OL]. (2017-02-21) [2021-10-22]. https://eprint.iacr.org/2016/086.pdf. |
| [22] | ARM. ARM Architecture Reference Manual ARMv7-A and ARMv7-R Edition[EB/OL]. (2018-03-29) [2020-05-20]. https://developer.arm.com/documentation/ddi0406/cd/. |
| [23] | LIPP M, GRUSS D, SPREITZER R, et al. ARMageddon: Cache Attacks on Mobile Devices[C]// USENIX. 25th USENIX Security Symposium. Berkeley: USENIX, 2016: 549-564. |
| [24] | YANG Fan, ZHANG Qianying, SHI Zhiping, et al. Survey on Software Side-Channel Attacks in Trusted Execution Environment[EB/OL]. (2021-10-20) [2021-12-27]. http://www.jos.org.cn/jos/article/abstract/6501. |
| 杨帆, 张倩颖, 施智平, 等. 可信执行环境软件侧信道攻击研究综述[EB/OL]. (2021-10-20) [2021-12-27]. http://www.jos.org.cn/jos/article/abstract/6501. | |
| [25] | WANG Shuai, BAO Yuyan, LIU Xiao, et al. Identifying Cache-Based Side Channels through Secret-Augmented Abstract Interpretation[C]// USENIX. 28th USENIX Security Symposium. Berkeley: USENIXA, 2019: 657-674. |
| [26] | DOYCHEV G, KÖPF B, MAUBORGNE L, et al. CacheAudit: A Tool for the Static Analysis of Cache Side Channels[J]. ACM Transactions on Information and System Security, 2015, 18(1): 1-32. |
| [27] | IRAZOQUI G, CONG Kai, GUO Xiaofei, et al. Did We Learn from LLC Side Channel Attacks? A Cache Leakage Detection Tool for Crypto Libraries[EB/OL]. (2017-09-05) [2021-11-23]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1709.01552. |
| [28] | BROTZMAN R, LIU Shen, ZHANG Danfeng, et al. CaSym: Cache Aware Symbolic Execution for Side Channel Detection and Mitigation[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York:IEEE, 2019: 505-521. |
| [29] | GRAS B, RAZAVI K, BOSMAN E, et al. ASLR on the Line: Practical Cache Attacks on the MMU[EB/OL]. (2017-12-28) [2021-08-23]. https://download.vusec.net/papers/anc_ndss17.pdf. |
| [30] | SCHAIK S, RAZAVI K, GRAS B, et al. RevAnC: A Framework for Reverse Engineering Hardware Page Table Caches[C]// ACM. 10th European Workshop on Systems Security. New York: ACM, 2017: 1-6. |
| [31] | GRAS B, RAZAVI K, BOS H, et al. Translation Leak-Aside Buffer: Defeating Cache Side-Channel Protections with TLB Attacks[C]// USENIX. 27th USENIX Conference on Security Symposium. Berkeley: USENIX, 2018: 955-972. |
| [32] | RALF H, CARSTEN W, THORSTEN H. Practical Timing Side Channel Attacks against Kernel Space ASLR[C]// IEEE. 2013 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, New York: IEEE, 2013: 191-205. |
| [33] | YUAN Fengkai, HOU Rui. Processor Time-Based Microarchitecture Side Channels, Attacks and Defenses[J]. Journal of Guangzhou University, 2020, 19(2): 24-34. |
| 苑风凯, 侯锐. 处理器微体系结构时间侧信道攻击与防御[J]. 广州大学学报, 2020, 19(2): 24-34. | |
| [34] | COSTAN V, LEBEDEV I A, DEVADAS S. Sanctum: Minimal Hardware Extensions for Strong Software Isolation[C]// USENIX. 25th USENIX Security Symposium. Berkeley: USENIX, 2016: 857-874. |
| [35] | YAN Mengjia, CHOI J, SKARLATOS D, et al. InvisiSpec: Making Speculative Execution Invisible in the Cache Hierarchy[C]// IEEE. 2018 51st Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture (MICRO). New York:IEEE, 2018: 428-441. |
| [36] | DENG Shuwen, XIONG Wenjie, SZEFER J. Secure TLBs[C]// IEEE. 2019 ACM/IEEE 46th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA). New York:IEEE, 2019: 346-359. |
| [37] | GRAS B. Anc-VUSec[EB/OL]. (2021-12-01) [2021-12-28]. https://www.vusec.net/projects/anc/. |
| [1] | 段晓毅, 李邮, 令狐韫行, 胡荣磊. 基于RF算法的侧信道攻击方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(1): 19-26. |
| [2] | 张良峰, 汪毅, 吴源燚, 孔睿. 基于统计的浏览器指纹采集技术[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(11): 49-55. |
| [3] | 王庆, 屠晨阳, shenjiahui@iie.ac.cn. 侧信道攻击通用框架设计及应用[J]. 信息网络安全, 2017, 17(5): 57-62. |
| [4] | 贾徽徽, 王潮, 顾健, 陆臻. 基于Grover量子中间相遇搜索算法的ECC攻击错误bit的修正[J]. 信息网络安全, 2016, 16(6): 28-34. |
| [5] | 陈宇航, 贾徽徽, 姜丽莹, 王潮. 基于Grover算法的ECC扫描式攻击[J]. 信息网络安全, 2016, 16(2): 28-32. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 271
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 494
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||