信息网络安全 ›› 2022, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (4): 20-29.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2022.04.003
基于多模态特征融合的Fast-Flux恶意域名检测方法
- 北京航空航天大学软件开发环境国家重点实验室,北京 100191
-
收稿日期:2021-11-12出版日期:2022-04-10发布日期:2022-05-12 -
通讯作者:郎波 E-mail:langbo@buaa.edu.cn -
作者简介:郎波(1968—),女,辽宁,教授,博士,主要研究方向为大数据分析和信息安全|谢冲(1997—),男,河北,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为大数据分析|陈少杰(1992—),男,山西,博士研究生,主要研究方向为深度学习、入侵检测和恶意代码检测|刘宏宇(1992—),男,吉林,博士研究生,主要研究方向为机器学习 -
基金资助:软件开发环境国家重点实验室探索性课题(SKLSDE-2020ZX-02)
Fast-Flux Malicious Domain Name Detection Method Based on Multimodal Feature Fusion
LANG Bo( ), XIE Chong, CHEN Shaojie, LIU Hongyu
), XIE Chong, CHEN Shaojie, LIU Hongyu
- State Key Laboratory of Software Development Environment, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
-
Received:2021-11-12Online:2022-04-10Published:2022-05-12 -
Contact:LANG Bo E-mail:langbo@buaa.edu.cn
摘要:
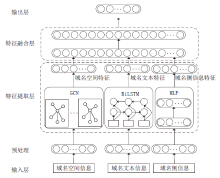
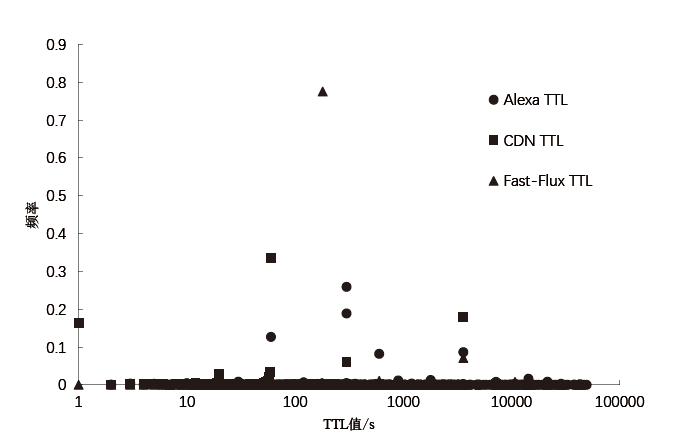
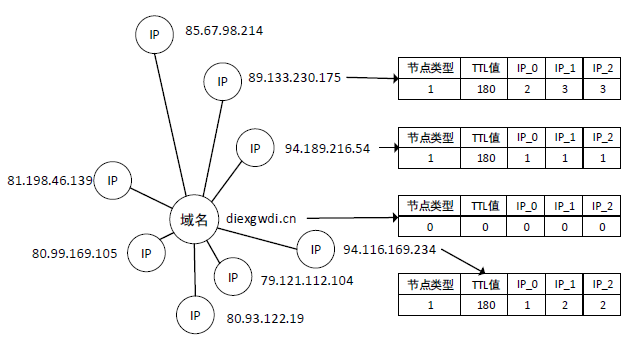
Fast-Flux恶意域名是僵尸网络通信中的一种重要载体,通过快速变换域名解析的IP抵御检测。目前,恶意域名检测系统大多基于传统机器学习模型,需要对数据进行复杂处理和特征提取,并且需要借助大量第三方数据源,导致检测的实时性较差。域名解析是一个复杂的过程,并且具有丰富的特征,文章设计了基于多模态特征融合的Fast-Flux恶意域名检测方法。首先利用GCN模块提取空间特征,采用BiLSTM模块提取域名文本特征,然后利用MLP模块提取侧信息特征,最后利用神经网络将这3种特征进行融合。在Fast-Flux-Attack-Datasets公开数据集上进行实验,实验结果表明,该方法的精确率达99.94%、召回率达99.76%、准确率达99.69%,总体效果优于当前同类方法。文章所提方法有效融合了域名解析的多模态特征,明显提升了检测效果,对于提高僵尸网络检测能力具有重要意义。
中图分类号:
引用本文
郎波, 谢冲, 陈少杰, 刘宏宇. 基于多模态特征融合的Fast-Flux恶意域名检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(4): 20-29.
LANG Bo, XIE Chong, CHEN Shaojie, LIU Hongyu. Fast-Flux Malicious Domain Name Detection Method Based on Multimodal Feature Fusion[J]. Netinfo Security, 2022, 22(4): 20-29.
使用本文
| [1] | FEILY M, SHAHRESTANI A, RAMADASS S. A Survey of Botnet and Botnet Detection[C]// IEEE. 2009 Third International Conference on Emerging Security Information, Systems and Technologies. New York: IEEE, 2009: 268-273. |
| [2] | NAZARIO J, HOLZ T. As the Net Churns: Fast-Flux Botnet Observations[EB/OL]. (2008-10-07)[2020-12-27]. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4690854 . |
| [3] | HOLZ T, GORECKI C, RIECK K, et al. Measuring and Detecting Fast-Flux Service Networks[EB/OL]. (2008-01-01)[2021-01-22]. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/221655419_Measuring_and_Detecting_Fast-Flux_Service_Networks . |
| [4] | PASSERINI E, PALEARI R, MARTIGNONI L, et al. Fluxor: Detecting and Monitoring Fast-Flux Service Networks[C]// Springer. International Conference on Detection of Intrusions and Malware, and Vulnerability Assessment. Heidelberg: Springer, 2008: 186-206. |
| [5] | HSU C H, HUANG Chunying, CHEN K T. Fast-Flux Bot Detection in Real Time[C]// Springer. International Workshop on Recent Advances in Intrusion Detection. Heidelberg: Springer, 2010: 464-483. |
| [6] | NIU Weina, JIANG Tianyu, ZHANG Xiaosong, et al. Fast-Flux Botnet Detection Method Based on Spatiotemporal Feature of Network Traffic[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2020, 42(8): 1872-1880. |
| 牛伟纳, 蒋天宇, 张小松, 等. 基于流量时空特征的fast-flux僵尸网络检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(8): 1872-1880. | |
| [7] | ALMOMANI A, AL-NAWASRAH A, ALAUTHMAN M, et al. Botnet Detection Used Fast-Flux Technique, Based on Adaptive Dynamic Evolving Spiking Neural Network Algorithm[J]. International Journal of Ad Hoc and Ubiquitous Computing, Inderscience Publishers (IEL), 2021, 36(1): 50-65. |
| [8] | TRUONG D T, TRAN D T, HUYNH B. Detecting Malicious Fast-Flux Domains Using Feature-Based Classification Techniques[J]. Journal of Internet Technology, 2020, 21(4): 1061-1072. |
| [9] | ALMOMANI A. Fast-Flux Hunter: A System for Filtering Online Fast-Flux Botnet[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2018, 29(7): 483-493. |
| [10] | HUANG Siyu, MAO C H, LEE H M. Fast-Flux Service Network Detection based on Spatial Snapshot Mechanism for Delay-Free Detection[C]// ACM. 5th ACM Symposium on Information, Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2010: 101-111. |
| [11] | AL-DUWAIRI B, JARRAH M, SHATNAWI A. PASSVM: A Highly Accurate Online Fast Flux Detection System[EB/OL]. (2020-06-05)[2021-04-11]. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/341998237_PASSVM_A_Highly_Accurate_Online_Fast_Flux_Detection_System . |
| [12] | LOMBARDO P, SAELI S, BISIO F, et al. Fast Flux Service Network Detection via Data Mining on Passive DNS Traffic[C]// Springer. International Conference on Information Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2018: 463-480. |
| [13] | CHANDAVARKAR B R. MalDetect: A Framework to Detect Fast Flux Domains[C]// IEEE. Distributed Computing, VLSI, Electrical Circuits and Robotics (DISCOVER). New York: IEEE, 2018: 141-146. |
| [14] | CHEN Xunxun, LI Gaochao, ZHANG Yongzheng, et al. A Deep Learning Based Fast-Flux and CDN Domain Names Recognition Method[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 2019 2nd International Conference on Information Science and Systems. New York: ACM, 2019: 54-59. |
| [15] | XU Bingbing, CEN Keting, HUANG Junjie, et al. A Survey on Graph Convolutional Neural Network[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2020, 43(5): 755-780. |
| 徐冰冰, 岑科廷, 黄俊杰, 等. 图卷积神经网络综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2020, 43(5): 755-780. | |
| [16] | ZHAUNIAROVICH Y, KHALIL I, YU Ting, et al. A Survey on Malicious Domains Detection through DNS Data Analysis[J]. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 2018, 51(4): 1-36. |
| [17] | WANG Jiajia, CHEN Yu. Fast-Flux Detection Method Based on DNS Attribute[EB/OL]. (2019-12-18)[2021-05-13]. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1742-6596/1325/1/012049/pdf . |
| [18] | Github. CDN Domain[EB/OL]. (2018-08-14)[2021-01-21]. https://github.com/vysecurity/DomainFrontingLists . |
| [19] | HUANG Siyu. Fluxor Public Datase[EB/OL]. (2013-12-05)[2021-01-21]. https://sites.google.com/site/huangpublication/datasets/-1-fast-flux-attaack-datasets . |
| [20] | Phishstats. Phishstats[EB/OL]. (2021-01-20)[2021-02-23]. https://phishstats.info/ . |
| [21] | ALEXA. Alexa Domain[EB/OL]. (2019-12-18)[2021-02-23]. https://www.alexa.com/ . |
| [1] | 马骁, 蔡满春, 芦天亮. 基于CNN改进模型的恶意域名训练数据生成技术[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(10): 69-75. |
| [2] | 吴迪, 崔翔, 刘奇旭, 张方娇. 泛在僵尸网络发展研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(7): 16-28. |
| [3] | 宋金伟, 杨进, 李涛. 基于加权支持向量机的Domain Flux僵尸网络域名检测方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(12): 66-71. |
| [4] | 李旬, 徐剑, 焦英楠, 严寒冰. 基于异常特征的社交网页检测技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2015, 15(5): 41-46. |
| [5] | 李娜, 杜彦辉, 高峰. 移动僵尸网络综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2015, 15(4): 19-27. |
| [6] | 巫锡洪;刘宝旭;杨沛安. 基于域名的僵尸网络行为分析[J]. , 2013, 13(9): 0-0. |
| [7] | 蒲石;陈周国;郝尧;黄宸. Conficker蠕虫事件回顾与思考[J]. , 2013, 13(7): 0-0. |
| [8] | 李杰. 浅述物联网设备系统存在的安全风险及僵尸家电网络[J]. , 2012, 12(8): 0-0. |
| [9] | 缪林;汤锦淮;刘煜杰;朱剑磊. 从南京"1.9"破坏信息系统案看侦办DDos类攻击案件[J]. , 2011, 11(4): 0-0. |
| [10] | 温森浩. 2010年12月网络安全监测数据分析[J]. , 2011, 11(2): 0-0. |
| [11] | 何世平. 2010年11月网络安全监测数据分析[J]. , 2011, 11(1): 0-0. |
| [12] | 赵慧. 僵尸网络威胁增加木马数量持续下降[J]. , 2010, (9): 0-0. |
| [13] | 何世平. 警惕网页仿冒关注境外攻击[J]. , 2010, (7): 0-0. |
| [14] | 徐原. 木马和僵尸网络呈下降趋势[J]. , 2010, (6): 0-0. |
| [15] | 王营康. 安全治理初见成效恶意代码需警惕[J]. , 2010, (5): 0-0. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 293
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 483
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||