信息网络安全 ›› 2018, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (7): 16-28.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2018.07.003
泛在僵尸网络发展研究
吴迪1,2, 崔翔1,3, 刘奇旭1,2( ), 张方娇1,2
), 张方娇1,2
- 1. 中国科学院信息工程研究所,北京 100093
2. 中国科学院大学网络空间安全学院, 北京 100049
3. 广州大学网络空间先进技术研究院,广东广州 510006
-
收稿日期:2018-03-15出版日期:2018-07-15发布日期:2020-05-11 -
作者简介:作者简介:吴迪(1991—),男,山西,博士研究生,主要研究方向为网络攻防技术;崔翔(1978—),男,黑龙江,研究员,博士,主要研究方向为网络攻防技术;刘奇旭(1984—),男,江苏,副研究员,博士,主要研究方向为网络攻防技术、网络安全评测;张方娇(1989—),女,山东,助理研究员,硕士,主要研究方向为网络攻防技术。
-
基金资助:国家重点研发计划[2016YFB0801604];东莞市引进创新科研团队计划[201636000100038];中国科学院网络测评技术重点实验室和网络安全防护技术北京市重点实验室资助项目
Research on Ubiquitous Botnet
Di WU1,2, Xiang CUI1,3, Qixu LIU1,2( ), Fangjiao ZHAGN1,2
), Fangjiao ZHAGN1,2
- 1. Institute of Information Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100093, China
2. School of Cyber Security, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3. Cyberspace Institute of Advanced Technology, Guangzhou University, Guangzhou Guangdong 510006, China
-
Received:2018-03-15Online:2018-07-15Published:2020-05-11
摘要:
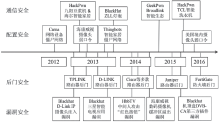
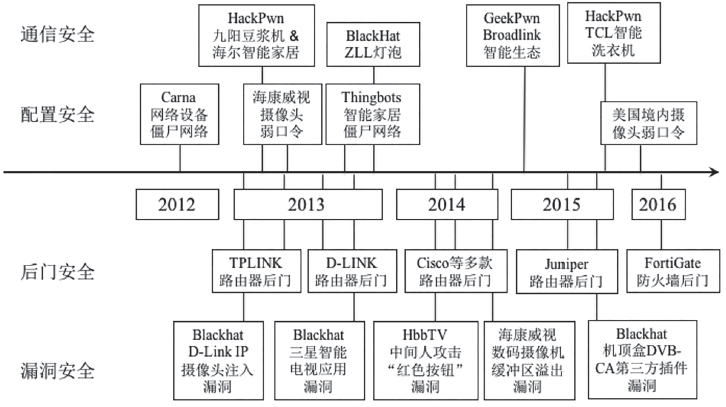
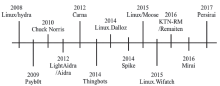
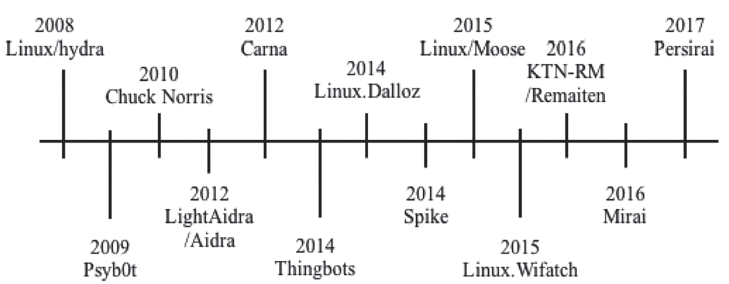
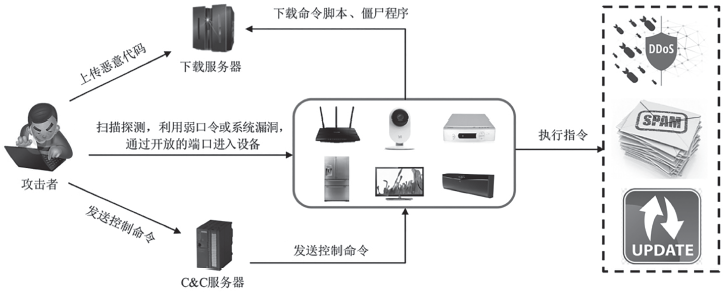
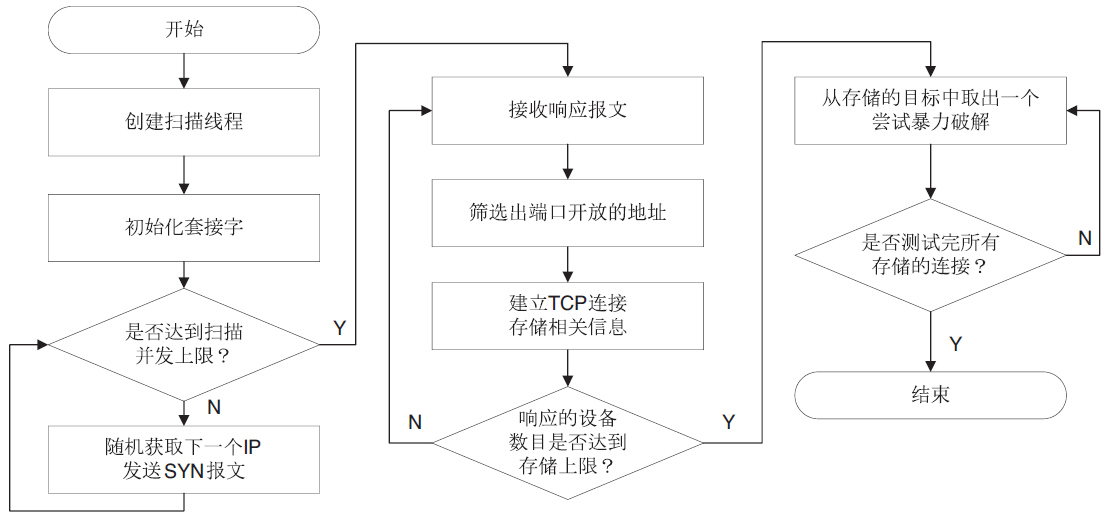
泛在网络环境下,各类设备处于智能化初期,安全问题众多,同时用户的安全意识并没有随着设备的智能化而同步提升,加之泛在网络互联互通的特性,这些都为恶意代码的生存、传播、发展提供了巨大的空间。僵尸网络作为传统的最有效的网络攻击方法之一,在泛在网络环境下其形态和命令控制机制都发生了变化,这为防御人员带来了新的安全挑战。在了解泛在网络环境特征的基础上,文章给出泛在僵尸网络的形式化定义,并从机理特性、构建流程、技术手段等方面对泛在僵尸网络进行了全面介绍。按照时间顺序将泛在僵尸网络的发展历程分为PC攻击阶段、手机攻击阶段、广泛攻击阶段3个阶段。从传播感染技术、生存驻留技术和控制管理技术3个角度分析了泛在僵尸网络所用的核心技术细节。文章总结了当前泛在僵尸网络的主要防御对抗方法,并对未来可能的研究热点进行了展望。
中图分类号:
引用本文
吴迪, 崔翔, 刘奇旭, 张方娇. 泛在僵尸网络发展研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(7): 16-28.
Di WU, Xiang CUI, Qixu LIU, Fangjiao ZHAGN. Research on Ubiquitous Botnet[J]. Netinfo Security, 2018, 18(7): 16-28.
| [1] | WEISER M.The Computer for the 21st Century[J]. Scientific amer-ican, 1991, 265(3): 94-104. |
| [2] | ITU-T Y. Overview of Ubiquitous Networking and of Its Support in NGN[EB/OL]. https://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-Y.2002-200910-I/en, 2017-7-15. |
| [3] | GARTNER. Gartner Says 6.4 Billion Connected "Things" Will Be in Use in 2016, Up 30 Percent From 2015[EB/OL]. . |
| [4] | LI Ke, FANG Binxing, CUI Xiang, et al.Study of Botnets Trends[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2016, 53(10): 2189-2206. |
| 李可,方滨兴,崔翔,等. 僵尸网络发展研究[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2016, 53(10): 2189-2206. | |
| [5] | TRAYNOR P,LIN M,ONGTANG M, et al.On Cellular Botnets: Meas-uring the Impact of Malicious Devices on a Cellular Network Core[C]// ACM.16th ACM conference on Computer and communi-cations security, November 9-13, 2009, Chicago, Illinois, USA. New York: ACM, 2009:223-234. |
| [6] | DURFINA L,KROUSTEK J,ZEMEK P. PsybOt Malware: A Step-by-step Decompilation Case Study[EB/OL]. https://retdec.com/web/files/publications/DEC_WCRE_13.pdf, 2017-7-15. |
| [7] | INTELLIGENCE B. There will be 24 Billion IoT Devices insTalled on Earth by 2020[EB/OL]. . |
| [8] | IDC. Worldwide and Regional Internet of Things (IoT) 2014-2020 Forecast: A Virtuous Circle of Proven Value and Demand[EB/OL]. |
| [9] | LI Zhicong,ZHOU Zhiping.Enhanced Secure RFID Authentication Protocol in IoT[J].Netinfo Security, 2018, 18(11):80-87. |
| 李智聪,周治平.物联网中增强安全的RFID认证协议[J].信息网络安全,2018,18(1):80-87. | |
| [10] | ZILLNER T, STROBL S.ZigBee Exploited: The Good the bad and the Ugly[J].Magdeburger Journal zur Sicherheitsforschung, 2015(12):699-704. |
| [11] | QIU Yue.Security Analysis for the Information of Wearable De-vices[J]. Netinfo Security, 2016, 16(9):79-83. |
| 裘玥. 智能可穿戴设备信息安全分析[J].信息网络安全,2016,16(9):79-83. | |
| [12] | Wrightwood Surveillance Support. Hikvision Default IP address, user name,password[EB/OL]. , 2017-7-15. |
| [13] | CVE. CVE-2015-7755[EB/OL]. , 2017-7-15. |
| [14] | SEKURAK. TP-Link http/tftp Backdoor[EB/OL]. , 2017-7-15. |
| [15] | HEWLETT PACKARD. Internet of Things Research Study[EB/OL]. , 2017-7-15. |
| [16] | HEFFNER C. Exploiting Network Surveillance Cameras Like a Hollywood Hacker [EB/OL]. ,2017-7-15. |
| [17] | MACESANU G, CODAS T T, SULIMAN C, et al.Development of GTBoT, A High Performance and Modular Indoor Ro-bot[C]//IEEE.AQTR '10 Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Automation, Quality and Testing, Robotics (AQTR) , May 28 - 30, 2010 ,Cluj-Napoca,Romania.New York: IEEE, 2010: 1-6. |
| [18] | ARCE I,LEVY E.An Analysis of the Slapper Worm[J]. IEEE Security & Privacy, 2003, 99(1): 82-87. |
| [19] | F-Secure. Bobax Description [EB/OL]. , 2017-7-15. |
| [20] | SHIN S,GU G.Conficker and Beyond: A Large-scale Empirical Study[C]//ACM.26th Annual Computer Security Applications Conference, December 6-10, 2010, Austin, Texas, USA. New York: ACM, 2010:151-160. |
| [21] | AXELLE A. Symbian Worm Yxes Towards Mobile Botnets[EB/OL]. , 2017-7-15. |
| [22] | PORRAS P, SAIDI H,YEGNESWARAN V. An Analysis of the Ikee.B iphone Botnet[EB/OL]. , 2017-7-15. |
| [23] | WYATT TIM. Security Alert: Geinimi, Sophisticated New Android Trojan Found in Wild[EB/OL]. , 2017-7-15. |
| [24] | INSECURETY RESEARCH. Hydra IRC Bot, the 25 Minute Overview of the Kit[EB/OL]. , 2017-7-15. |
| [25] | CELEDA P, KREJCI R,VYKOPAL J, et al.Embedded Malware-an Analysis of the Chuck Norris Botnet[EB/OL]. , 2010. |
| [26] | BOTNET C. Internet Census 2012: Port Scanning/0 Using Insecure Embedded Devices[EB/OL]., 2017-7-15. |
| [27] | GITHUB. Lightaidra[EB/OL]., 2017-7-15. |
| [28] | PROOFPOINT. Proofpoint Uncovers Internet of Things (IoT) CybeRattack[EB/OL]. ,2017-7-15. |
| [29] | SYMANTEC. Linux.Darlloz[EB/OL]. , 2017-7-15. |
| [30] | AKAMAI. Spike DDoS Toolkit[EB/OL]. , 2017-7-15. |
| [31] | ESET. Dissecting Linux/Moose[EB/OL]. , 2017-7-15. |
| [32] | SYMANTEC. Is There an Internet-of-Things Vigilante out There?[EB/OL]. , 2017-7-15. |
| [33] | ESET. Meet Remaiten-a Linux Bot on Steroids Targeting Routers and Potentially other IoT Devices[EB/OL]. , 2017-7-15. |
| [34] | PALOALTO.New IoT/Linux Malware Targets DVRs, Forms Botnet[EB/OL]., 2017-7-15. |
| [35] | THREAT Post.BASHLITE Family Of Malware Infects 1 Million IoT Devices [EB/OL]. , 2017-7-15. |
| [36] | GITHUB. Mirai-Source-Code[EB/OL]., 2017-7-15. |
| [37] | TRENDMICRO. ELF_PERSIRAI.A[EB/OL]., 2017-7-15. |
| [38] | TRENDMICRO. Persirai: New Internet of Things (IoT) Botnet Targets IP Cameras[EB/OL]. , 2017-7-15. |
| [39] | PERAKOVIC D,PERISA M,CVITIC I. Analysis of the IoT Impact on Volume of DDoS Attacks[EB/OL]. , 2017-7-15. |
| [40] | KOLIAS C,KAMBOURAKIS G, STAVROU A, et al.DDoS in the IoT: Mirai and other Botnets[J]. Computer, 2017, 50(7): 80-84. |
| [41] | PAGANINI P. More than 900k Routers of Deutsche Telekom German Users Went Offline[EB/OL]. , 2017-7-15. |
| [42] | OHARROW J R. Cyber Search Engine Shodan Exposes Industrial Control Systems to New Risks[EB/OL]. , 2017-7-15. |
| [43] | RAPID7. R7-2014-18: Hikvision DVR Devices-Multiple Vulnerabilities[EB/OL]. , 2017-7-15. |
| [44] | US-CERT. Heightened DDoS Threat Posed by Mirai and Other Botnets[EB/OL]., 2017-7-15. |
| [45] | FAN Hong, SHAO Hua, LI Haitao.Implementation and Application of Internet of Things Security Technology[J]. Netinfo Security, 2017,17(9):38-41. |
| 范红,邵华,李海涛.物联网安全技术实现与应用[J].信息网络安全,2017,17(9):38-41. |
| [1] | 宋金伟, 杨进, 李涛. 基于加权支持向量机的Domain Flux僵尸网络域名检测方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(12): 66-71. |
| [2] | 李旬, 徐剑, 焦英楠, 严寒冰. 基于异常特征的社交网页检测技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2015, 15(5): 41-46. |
| [3] | 李娜, 杜彦辉, 高峰. 移动僵尸网络综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2015, 15(4): 19-27. |
| [4] | 巫锡洪;刘宝旭;杨沛安. 基于域名的僵尸网络行为分析[J]. , 2013, 13(9): 0-0. |
| [5] | 蒲石;陈周国;郝尧;黄宸. Conficker蠕虫事件回顾与思考[J]. , 2013, 13(7): 0-0. |
| [6] | 李杰. 浅述物联网设备系统存在的安全风险及僵尸家电网络[J]. , 2012, 12(8): 0-0. |
| [7] | 缪林;汤锦淮;刘煜杰;朱剑磊. 从南京"1.9"破坏信息系统案看侦办DDos类攻击案件[J]. , 2011, 11(4): 0-0. |
| [8] | 温森浩. 2010年12月网络安全监测数据分析[J]. , 2011, 11(2): 0-0. |
| [9] | 何世平. 2010年11月网络安全监测数据分析[J]. , 2011, 11(1): 0-0. |
| [10] | 赵慧. 僵尸网络威胁增加木马数量持续下降[J]. , 2010, (9): 0-0. |
| [11] | 何世平. 警惕网页仿冒关注境外攻击[J]. , 2010, (7): 0-0. |
| [12] | 徐原. 木马和僵尸网络呈下降趋势[J]. , 2010, (6): 0-0. |
| [13] | 王营康. 安全治理初见成效恶意代码需警惕[J]. , 2010, (5): 0-0. |
| [14] | 蔡敏. 僵尸网络流的识别[J]. , 2010, (4): 0-0. |
| [15] | 王明华. 网络安全波澜不惊[J]. , 2010, (4): 0-0. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||