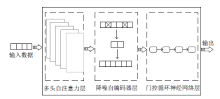
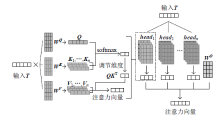
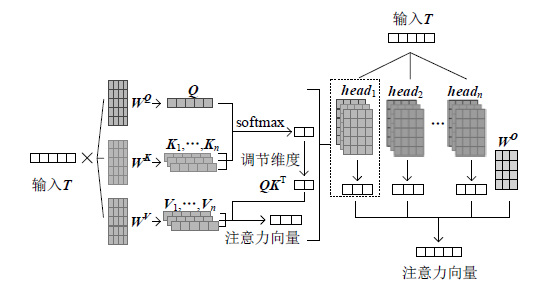
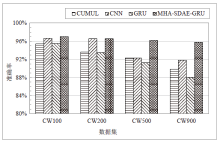
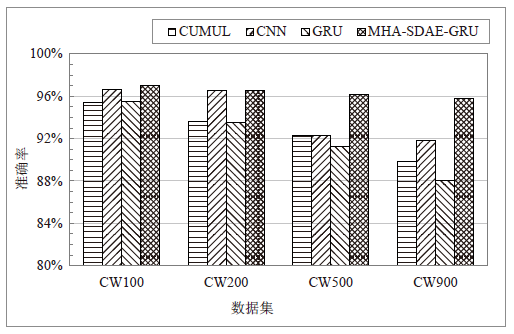
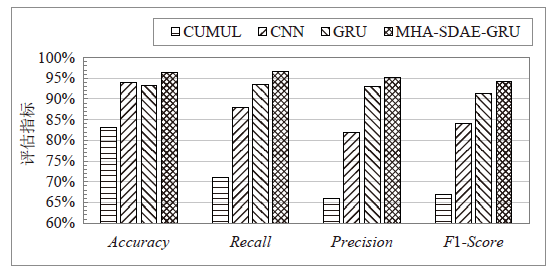
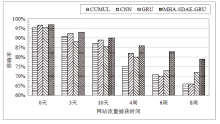
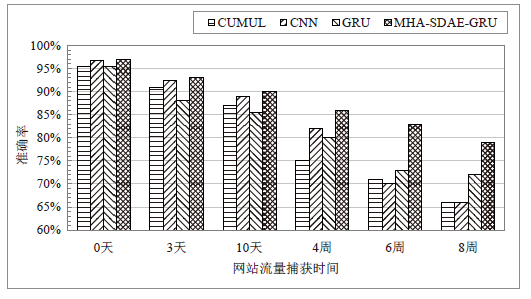
| [1] |
DINGLEDINE R, MATHEWSON N, SYVERSON P. Tor: The Second-Generation Onion Router[C]// USENIX. 13th USENIX Security Symp. Berkeley: USENIX Association, 2004: 1-18.
|
| [2] |
LUO Junzhou, YANG Ming, LING Zhen, et al. Anonymous Communication and Darknet: A Survey[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2019, 56(1): 103-130.
|
|
罗军舟, 杨明, 凌振, 等. 匿名通信与暗网研究综述[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2019, 56(1):103-130.
|
| [3] |
MINARIK T, OSULA A M. Tor Does Not Stink: Use and Abuse of the Tor Anonymity Network from the Perspective of Law[J]. Computer Law & Security Report, 2016, 32(1): 111-127.
|
| [4] |
YU Wei, FU Xinwen, GRAHAM S, et al. DSSS-Based Flow Marking Technique for Invisible Traceback[C]// IEEE. 28th IEEE Symp on Security and Privacy. New York: IEEE, 2007: 18-32.
|
| [5] |
HINTZ A. Fingerprinting Websites Using Traffic Analysis[C]// Springer. 2rd International Workshop on Privacy Enhancing Technologies. Heidelberg: Springer, 2002: 171-178.
|
| [6] |
DINGLEDINE R, MURDOCH S J. Performance Improvements on Tor or, Why Tor is Slow and What We’re Going to Do about It[EB/OL]. (2009-03-11)[2022-01-25]. http://www.torproject.org/press/presskit/2009-03-11-performance.pdf.
|
| [7] |
PANCHENKO A, NIESSEN L, ZINNEN A, et al. Website Fingerprinting in Onion Routing Based Anonymization Networks[C]// ACM. 10th Annual ACM Workshop on Privacy in the Electronic Society. New York: ACM, 2011: 103-114.
|
| [8] |
WANG Tao, CAI Xiang, NITHYANAND R, et al. Effective Attacks and Provable Defenses for Website Fingerprinting[C]// USENIX. 23rd USENIX Security Symp. Berkeley: USENIX Association, 2014: 143-157.
|
| [9] |
HAYES J, DANEZIS G. k-Fingerprinting: A Robust Scalable Website Fingerprinting Technique[C]// USENIX. 25th USENIX Security Symp. Berkeley: USENIX Association, 2016: 1187-1203.
|
| [10] |
PANCHENKO A, LANZE F, PENNEKAMP J, et al. Website Fingerprinting at Internet Scale[EB/OL]. (2016-05-03)[2022-01-25]. https://nymity.ch/tor-dns/pdf/Panchenko2016a.pdf.
|
| [11] |
CAI Manchun, WANG Tengfei, YUE Ting, et al. ARF-Based Tor Website Fingerprint Recognition Technology[J]. Netinfo Security, 2021, 21(4): 39-48.
|
|
蔡满春, 王腾飞, 岳婷, 等. 基于ARF的Tor网站指纹识别技术[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(4):39-48.
|
| [12] |
RIMMER V, PREUVENEERS D, JUAREZ M, et al. Automated Website Fingerprinting through Deep Learning[EB/OL]. (2017-12-05)[2022-01-25]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1708.06376.
|
| [13] |
SIRINAM P, IMANI M, JUAREZ M, et al. Deep Fingerprinting: Undermining Website Fingerprinting Defenses with Deep Learning[C]// ACM. Audit and Control Conf on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2018: 1928-1943.
|
| [14] |
SIRINAM P, MATHEWS N, RAHMAN M S, et al. Triplet Fingerprinting: More Practical and Portable Website Fingerprinting with N-Shot Learning[C]// ACM. 2019 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2019: 1131-1148.
|
| [15] |
RAHMAN M S, SIRINAM P, MATTHEW M, et al. Tik-Tok: The Utility of Packet Timing on Website Fingerprinting Attacks[EB/OL]. (2019-11-01)[2022-01-25]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.06421.pdf.
|
| [16] |
BHAT S, LU D, KWON A, et al. Var-CNN: A Data-Efficient Website Fingerprinting Attack Based on Deep Learning[J]. Proc on Privacy Enhancing Technologies, 2019(4): 292-310.
|
| [17] |
MA Chencheng, DU Xuehui, CAO Lifeng, et al. Burst-Analysis Website Fingerprinting Attack Based on Deep Neural Network[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2020, 57(4): 746-766.
|
|
马陈城, 杜学绘, 曹利峰, 等. 基于深度神经网络burst特征分析的网站指纹攻击方法[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2020, 57(4):746-766.
|
| [18] |
VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is All You Need[EB/OL]. (2017-12-05)[2022-01-25]. https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2017/file/3f5ee243547dee91fbd053c1c4a845aa-Paper.pdf.
|
| [19] |
VINCENT P, LAROCHELLE H, BENGIO Y, et al. Extracting and Composing Robust Features with Denoising Autoencoders[EB/OL]. (2008-07-05)[2022-01-25].https://dl.acm.org/doi/pdf/10.1145/1390156.1390294?casa_token=9MVkr4Lh_44AAAAA: r0HdWtWFk8zIjQcpaPuCN_TQ5Zjr6i17-7f7Dk0YrCjzp89WkuhcJpD4DRdeQ6LfxNGyuQLuIHWEJ6M.
|
| [20] |
JUAREZ M, AFROZ S, ACAR G, et al. A Critical Evaluation of Website Fingerprinting Attacks[C]// ACM. ACM Special Interest Group on Security. Audit and Control Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2014: 263-274.
|
 ), YIN Haozhan, LU Tianliang
), YIN Haozhan, LU Tianliang