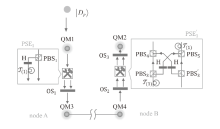
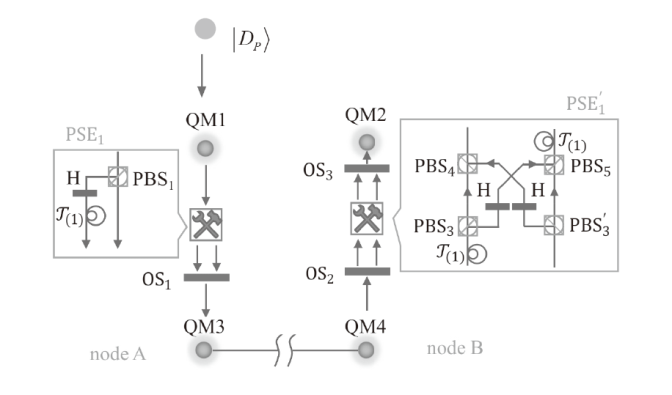
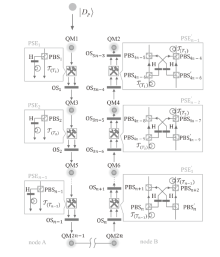
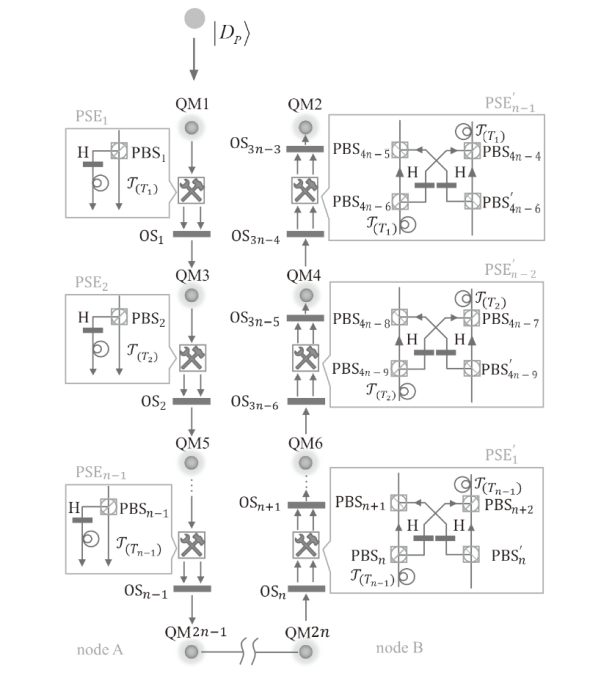
Netinfo Security ›› 2024, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (6): 879-892.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2024.06.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
High-Dimensional Quantum Key Distribution via Time-Bin Multiplexing and Applications
YANG Yuguang1( ), LIU Bingxin1, XU Guangbao2, JIANG Donghuan3
), LIU Bingxin1, XU Guangbao2, JIANG Donghuan3
- 1. Faculty of Information Technology, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing 100124, China
2. College of Computer Science and Engineering, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266590, China
3. College of Mathematics and Systems Science, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266590, China
-
Received:2024-02-14Online:2024-06-10Published:2024-07-05
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YANG Yuguang, LIU Bingxin, XU Guangbao, JIANG Donghuan. High-Dimensional Quantum Key Distribution via Time-Bin Multiplexing and Applications[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(6): 879-892.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://netinfo-security.org/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2024.06.006
| [1] | EKERT A, RENNER R. The Ultimate Physical Limits of Privacy[J]. Nature, 2014, 507(7493): 443-447. |
| [2] | GISIN N, RIBORDY G, TITTEL W, et al. Quantum Cryptography[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2002, 74(1): 145-195. |
| [3] | PIRANDOLA S, ANDERSEN U L, BANCHI L, et al. Advances in Quantum Cryptography[J]. Advances in Optics and Photonics, 2020, 12(4): 1012-1236. |
| [4] | BENNETT C H, BRASSARD G. Quantum Cryptography: Public Key Distribution and Coin Tossing[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing. New York: IEEE, 1984: 175-179. |
| [5] | EKERT A K. Quantum Cryptography Based on Bell’s Theorem[EB/OL]. (1991-08-05)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.67.661. |
| [6] | RALPH T C. Continuous Variable Quantum Cryptography[EB/OL]. (1999-12-08)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.61.010303. |
| [7] | HILLERY M. Quantum Cryptography with Squeezed States[EB/OL]. (2000-01-14)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.61.022309. |
| [8] | INOUE K, WAKS E, YAMAMOTO Y. Differential Phase Shift Quantum Key Distribution[EB/OL]. (2002-06-27)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.89.037902. |
| [9] | LO H K, CURTY M, QI B. Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution[EB/OL]. (2012-03-30)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.130503. |
| [10] | PIPARO N L, RAZAVI M, MUNRO W J. Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution with Nitrogen Vacancy Centers in Diamond[EB/OL]. (2017-02-27)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.95.022338. |
| [11] | ZHOU Yiheng, YU Zongwen, WANG Xiangbin. Making the Decoy-State Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution Practically Useful[EB/OL]. (2016-04-18)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.93.042324. |
| [12] | YIN Hualei, CHEN Tengyun, YU Zongwen, et al. Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution over a 404km Optical Fiber[EB/OL]. (2016-11-02)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.117.190501. |
| [13] | WANG Chao, SONG Xiaotian, YIN Zhenqiang, et al. Phase-Reference-Free Experiment of Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution[EB/OL]. (2015-12-15)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.115.160502. |
| [14] | ZHAO Yi, QI Bing, MA Xiongfeng, et al. Experimental Quantum Key Distribution with Decoy States[EB/OL]. (2006-02-22)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.96.070502. |
| [15] | LIAO Shengkai, CAI Wenqi, LIU Weiyue, et al. Satellite-to-Ground Quantum Key Distribution[J]. Nature, 2017, 549(7670): 43-47. |
| [16] | ZHU Haotao, HUANG Yizhi, LIU Hui, et al. Experimental Mode-Pairing Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution without Global Phase Locking[EB/OL]. (2023-01-17)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.130.030801. |
| [17] | LUCAMARINI M, YUAN Zhiliang, DYNES J F, et al. Overcoming the Rate-Distance Limit of Quantum Key Distribution without Quantum Repeaters[J]. Nature, 2018, 557(7705): 400-403. |
| [18] | WANG Rong, YIN Zhenqiang, LU Fengyu, et al. Optimized Protocol for Twin-Field Quantum Key Distribution[EB/OL]. (2020-08-28)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42005-020-00415-0. |
| [19] | TENG Jun, YIN Zhenqiang, FANYUAN Guanjie, et al. Sending-or-not-Sending Twin-Field Quantum Key Distribution with Multiphoton States[EB/OL]. (2021-12-27)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.104.062441. |
| [20] | PIRANDOLA S, LAURENZA R, OTTAVIANI C, et al. Fundamental Limits of Repeaterless Quantum Communications[EB/OL]. (2017-04-26)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15043. |
| [21] | ERKILIÇ Ö, CONLON L, SHAJILAL B, et al. Surpassing the Repeaterless Bound with a Photon-Number Encoded Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution Protocol[EB/OL]. (2023-03-28)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-023-00698-5. |
| [22] | TREIBER A, POPPE A, HENTSCHEL M, et al. A Fully Automated Entanglement-Based Quantum Cryptography System for Telecom Fiber Networks[EB/OL]. (2009-03-30)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/11/4/045013. |
| [23] | ERHARD M, KRENN M, ZEILINGER A. Advances in High-Dimensional Quantum Entanglement[J]. Nature Reviews Physics, 2020, 2(7): 365-381. |
| [24] | HOWLAND G A, HOWELL J C. Efficient High-Dimensional Entanglement Imaging with a Compressive-Sensing Double-Pixel Camera[EB/OL]. (2013-02-20)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevX.3.011013. |
| [25] | HU Xiaomin, CHEN Jiangshan, LIU Biheng, et al. Experimental Test of Compatibility-Loophole-Free Contextuality with Spatially Separated Entangled Qutrits[EB/OL]. (2016-10-24)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.117.170403. |
| [26] | ZHANG Lijian, SILBERHORN C, WALMSLEY I A. Secure Quantum Key Distribution Using Continuous Variables of Single Photons[EB/OL]. (2008-03-18)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.110504. |
| [27] | ALI-KHAN I, BROADBENT C J, HOWELL J C. Large-Alphabet Quantum Key Distribution Using Energy-Time Entangled Bipartite States[EB/OL]. (2007-02-08)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.98.060503. |
| [28] | SHERIDAN L, SCARANI V. Security Proof for Quantum Key Distribution Using Qudit Systems[EB/OL]. (2010-09-07)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.82.030301. |
| [29] | SHERIDAN L, SCARANI V. Erratum: Security Proof for Quantum Key Distribution Using Qudit Systems[Phys. Rev. A 82, 030301 (R)( 2010)][EB/OL]. (2011-03-07)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.83.039901. |
| [30] | TITTEL W, BRENDEL J, ZBINDEN H, et al. Quantum Cryptography Using Entangled Photons in Energy-Time Bell States[EB/OL]. (2000-05-15)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.84.4737. |
| [31] | ALI-KHAN I, BROADBENT C J, HOWELL J C. Large-Alphabet Quantum Key Distribution Using Energy-Time Entangled Bipartite States[EB/OL]. (2007-02-08)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.98.060503. |
| [32] | ZHONG Tian, ZHOU Hongchao, HORANSKY R D, et al. Photon-Efficient Quantum Key Distribution Using Time-Energy Entanglement with High-Dimensional Encoding[EB/OL]. (2015-02-04)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/17/2/022002. |
| [33] | ETCHEVERRY S, CAÑAS G, GÓMEZ E S, et al. Quantum Key Distribution Session with 16-Dimensional Photonic States[EB/OL]. (2013-07-30)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep02316. |
| [34] | LI Dongdong, ZHAO Meisheng, LI Zhi, et al. High Dimensional Quantum Key Distribution with Temporal and Polarization Hybrid Encoding[EB/OL]. (2022-01-21)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yofte.2022.102828. |
| [35] | MAIR A, VAZIRI A, WEIHS G, et al. Entanglement of the Orbital Angular Momentum States of Photons[J]. Nature, 2001, 412(6844): 313-316. |
| [36] | MOLINA-TERRIZA G, VAZIRI A, ŘEHÁČEK J, et al. Triggered Qutrits for quantum Communication Protocols[EB/OL]. (2004-04-23)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.92.167903. |
| [37] | MAFU M, DUDLEY A, GOYAL S, et al. Higher-Dimensional Orbital-Angular-Momentum-Based Quantum Key Distribution with Mutually Unbiased Bases[EB/OL]. (2013-09-05)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.88.032305. |
| [38] | ISLAM N T, LIM C C W, CAHALL C, et al. Provably Secure and High-Rate Quantum Key Distribution with Time-Bin Qudits[EB/OL]. (2017-11-24)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1701491. |
| [39] | VAGNILUCA I, DA L B, RUSCA D, et al. Efficient Time-Bin Encoding for Practical High-Dimensional Quantum Key Distribution[EB/OL]. (2020-07-17)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevApplied.14.014051. |
| [40] | PIPARO N L, MUNRO W J, NEMOTO K. Quantum Multiplexing[EB/OL]. (2019-02-27)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.99.022337. |
| [41] | XIE Zhihao, LIU Yijie, MO Xiang, et al. Quantum Entanglement Creation for Distant Quantum Memories via Time-Bin Multiplexing[EB/OL]. (2021-12-06)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.104.062409. |
| [42] | LIU Chenxu, DUTT M G, PEKKER D. Single-Photon Heralded Two-Qubit Unitary Gates for Pairs of Nitrogen-Vacancy Centers in Diamond[EB/OL]. (2018-11-27)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.98.052342. |
| [43] | CHILDRESS L, HANSON R. Diamond NV Centers for Quantum Computing and Quantum Networks[J]. MRS Bulletin, 2013, 38(2): 134-138. |
| [44] |
BLOK M S, KALB N, REISERER A, et al. Towards Quantum Networks of Single Spins: Analysis of a Quantum Memory with an Optical Interface in Diamond[J]. Faraday Discussions, 2015, 184: 173-182.
doi: 10.1039/c5fd00113g pmid: 26411802 |
| [45] | DOHERTY M W, MANSON N B, DELANEY P, et al. The Nitrogen-Vacancy Colour Centre in Diamond[J]. Physics Reports, 2013, 528(1): 1-45. |
| [46] | XIE Yuanmei, LU Yushuo, WENG Chenxun, et al. Breaking the Rate-Loss Bound of Quantum Key Distribution with Asynchronous Two-Photon Interference[EB/OL]. (2022-04-21)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PRXQuantum.3.020315. |
| [47] | ZHOU Lai, LIN Jinping, XIE Yuanmei, et al. Experimental Quantum Communication Overcomes the Rate-Loss Limit without Global Phase Tracking[EB/OL]. (2023-06-20)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.130.250801. |
| [48] | ŻUKOWSKI M, ZEILINGER A, HORNE M A, et al. ‘‘Event-Ready-Detectors’’ Bell Experiment via Entanglement Swapping[EB/OL]. (1993-12-27)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.71.4287. |
| [49] | NING Yu, KANG Yihao, SHI Zhicheng, et al. Efficient Implementation of Complete and Nondestructive Bell-State Measurement for Trapped Ions with Reverse Engineering[EB/OL]. (2020-11-18)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1088/1612-202X/abc32d. |
| [50] | WELTE S, THOMAS P, HARTUNG L, et al. A Nondestructive Bell-State Measurement on Two Distant Atomic Qubits[J]. Nature Photonics, 2021, 15(7): 504-509. |
| [51] | BARRETT S D, KOK P, NEMOTO K, et al. Symmetry Analyzer for Nondestructive Bell-State Detection Using Weak Nonlinearities[EB/OL]. (2005-06-07)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.71.060302. |
| [52] | REN Xifeng, GUO Guoping, GUO Guangcan. Complete Bell-States Analysis Using Hyper-Entanglement[J]. Physics Letters A, 2005, 343(1-3): 8-11. |
| [53] | LI Tao, MIRANOWICZ A, HU Xuedong, et al. Quantum Memory and Gates Using a Λ-Type Quantum Emitter Coupled to a Chiral Waveguide[EB/OL]. (2018-06-11)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.97.062318. |
| [54] | JIANG Dong, CHEN Yuanyuan, GU Xuemei, et al. Deterministic Secure Quantum Communication Using a Single d-Level System[EB/OL]. (2017-03-22)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep44934. |
| [55] | YANG Yuguang, DONG Jingru, YANG Yongli, et al. High-Capacity Measurement-Device-Independent Deterministic Secure Quantum Communication[EB/OL]. (2021-06-05)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03129-6. |
| [56] | ROY S, MAITRA A, MUKHOPADHYAY S. Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Private Query with Qutrits[EB/OL]. (2018-09-07)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219749918500454. |
| [57] | GAO Fei, LIU Bin, HUANG Wei, et al. Postprocessing of the Oblivious Key in Quantum Private Query[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2014, 21(3): 98-108. |
| [58] |
GAO Fei, LIU Bin, WEN Qiaoyan, et al. Flexible Quantum Private Queries Based on Quantum Key Distribution[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(16): 17411-17420.
doi: 10.1364/OE.20.017411 pmid: 23038294 |
| [59] | WEI T C, BARREIRO J T, KWIAT P G. Hyperentangled Bell-State Analysis[EB/OL]. (2007-06-27)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.75.060305. |
| [60] | PISENTI N, GAEBLER C P E, LYNN T W. Distinguishability of Hyperentangled Bell States by Linear Evolution and Local Projective Measurement[EB/OL]. (2011-08-26)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.84.022340. |
| [61] | SHENG Yubo, DENG Fuguo, LONG Guilu. Complete Hyperentangled-Bell-State Analysis for Quantum Communication[EB/OL]. (2010-09-21)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.82.032318. |
| [62] | XIA Yan, CHEN Qingqin, SONG Jie, et al. Efficient Hyperentangled Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger States Analysis with Cross-Kerr Nonlinearity[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 2012, 29: 1029-1037. |
| [63] | LI Xihan, GHOSE S. Self-Assisted Complete Maximally Hyperentangled State Analysis via the Cross-Kerr Nonlinearity[EB/OL]. (2016-02-01)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.93.022302. |
| [64] | LI Xihan, GHOSE S. Hyperentangled Bell-State Analysis and Hyperdense Coding Assisted by Auxiliary Entanglement[EB/OL]. (2017-08-21)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.96.020303. |
| [65] | JAKOBI M, SIMON C, GISIN N, et al. Practical Private Database Queries Based on a Quantum-Key-Distribution Protocol[EB/OL]. (2011-02-02)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.83.022301. |
| [66] | BORREGAARD J, PICHLER H, SCHRÖDER T, et al. One-Way Quantum Repeater Based on Near-Deterministic Photon-Emitter Interfaces[EB/OL]. (2020-06-30)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevX.10.021071. |
| [67] | DONOHUE J M, AGNEW M, LAVOIE J, et al. Coherent Ultrafast Measurement of Time-Bin Encoded Photons[EB/OL]. (2013-12-09)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.153602. |
| [68] | REED G T, MASHANOVICH G, GARDES F Y, et al. Silicon Optical Modulators[J]. Nature Photonics, 2010, 4(8): 518-526. |
| [69] | WANG Cheng, ZHANG Mian, CHEN Xi, et al. Integrated Lithium Niobate Electro-Optic Modulators Operating at CMOS-Compatible Voltages[J]. Nature, 2018, 562(7725): 101-104. |
| [70] | BULUTA I, ASHHAB S, NORI F. Natural and Artificial Atoms for Quantum Computation[EB/OL]. (2011-09-19)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1088/0034-4885/74/10/104401. |
| [71] | AWSCHALOM D D, HANSON R, WRACHTRUP J, et al. Quantum Technologies with Optically Interfaced Solid-State Spins[J]. Nature Photonics, 2018, 12(9): 516-527. |
| [72] | JANITZ E, BHASKAR M K, CHILDRESS L. Cavity Quantum Electrodynamics with Color Centers in Diamond[J]. Optica, 2020, 7(10): 1232-1252. |
| [73] | LÜTKENHAUS N, CALSAMIGLIA J, SUOMINEN K A. Bell Measurements for Teleportation[EB/OL]. (1999-05-01)[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.59.3295. |
| [74] | HAQ S U, KHALIQUE A. Long Distance Cavity Entanglement by Entanglement Swapping Using Atomic Momenta[J]. Optics Communications, 2015, 334: 290-293. |
| [1] | BAI Junlin, YIN Hualei. Improved Decoy State Method for Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(6): 926-936. |
| [2] | XIE Sijiang, GAO Qiong, FENG Yan. A Multiple Paths Routing Scheme with Least Number of Public Nodes Based on Trust Relaying Quantum Key Distribution Network [J]. Netinfo Security, 2021, 21(7): 35-42. |
| [3] | FENG Yan, LIU Nian, XIE Sijiang. A Bi-directional Use Scheme of Quantum Key Pool [J]. Netinfo Security, 2020, 20(12): 40-46. |
| [4] | LIU Lijuan, LI Zhihui, ZHI Danli. A Multi-party Quantum Key Distribution Protocol with Quantum Identity Authentication [J]. Netinfo Security, 2020, 20(11): 59-66. |
| [5] | Peng HUANG, Guihua ZENG. The Development of Study on Practical Security of Continuous-variable Quantum Key Distribution [J]. Netinfo Security, 2017, 17(11): 7-12. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||