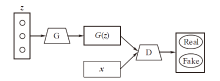
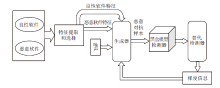
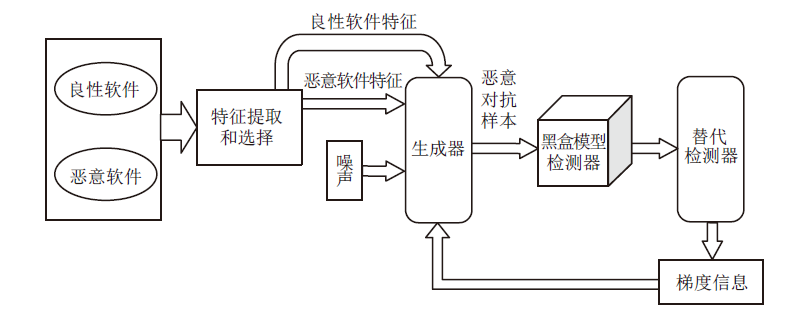
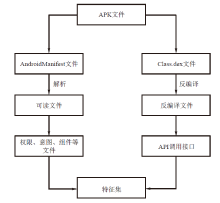
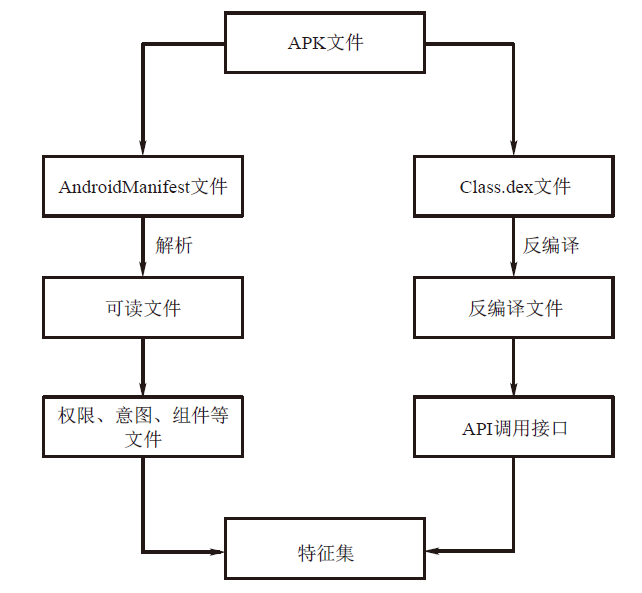
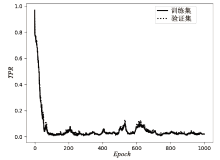
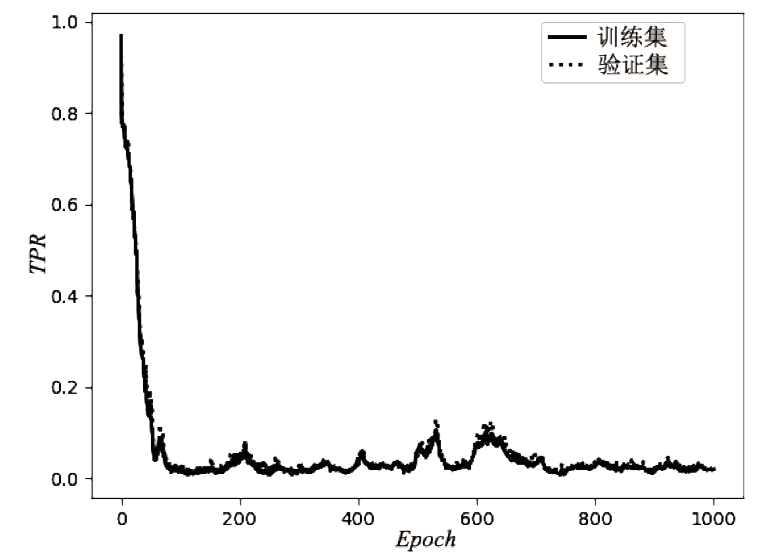
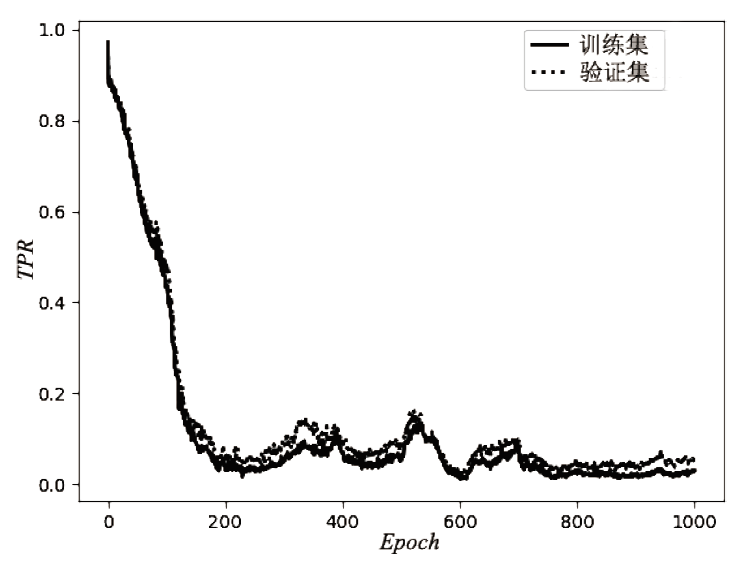
| [1] |
McAfee. McAfee Mobile Threat Report Q1 2018[EB/OL]. https://www.mcafee.com/enterprise/en-us/assets/reports/rp-mobile-threat-report-2018.pdf, 2020-3-20.
|
| [2] |
OUYANG Li, LU Tianliang. Android Malware Detection Based on Deep Belief Network[J]. Information Technology and Network Security, 2019,5(5):22-27.
|
|
欧阳立、 卢天亮. 基于深度置信网络的Android恶意软件检测[J]. 信息技术与网络安全, 2019,5(5):22-27.
|
| [3] |
CARLINI N, WAGNER D. Towards Evaluating the Robustness of Neural Networks[C]//IEEE. 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), May 22-26, 2017, San Jose, CA, USA. NJ: IEEE, 2017: 39-57.
|
| [4] |
GOODFELLOW I, SHLENS J, SZEGEDY C. Explaining and Harnessing Adversarial Examples[EB/OL]. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/269935591_Explaining_and_Harnessing_Adversarial_Examples, 2020-3-20.
|
| [5] |
KURAKIN A, GOODFELLOW I, BENGIO S. Adversarial Examples in the Physical World[EB/OL]. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/305186613_Adversarial_examples_in_the_physical_world, 2020-3-20.
|
| [6] |
PAPERNOT N, MCDANIEL P, JHA S, et al. The Limitations of Deep Learning in Adversarial Settings[C]//IEEE. 2016 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy (EuroS&P), March 21-24, 2016, Saarbrucken, Germany. NJ: IEEE, 2016: 372-387.
|
| [7] |
KATHRIN G, NICOLAS P, PRAVEEN M, et al. Adversarial Perturbations against Deep Neural Networks for Malware Classification[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.04435, 2016-6-16.
|
| [8] |
PAPERNOT N, MCDANIEL P, GOODFELLOW I, et al. Practical Black-box Attacks against Deep Learning Systems Using Adversarial Examples[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1602.02697v2, 2016-2-19.
|
| [9] |
PAPERNOT N, MCDANIEL P, GOODFELLOW I. Transferability in Machine Learning: from Phenomena to Black-box Attacks Using Adversarial Samples[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1605.07277, 2016-5-24.
|
| [10] |
LIU Yanpei, CHEN Xinyun, LIU Chang, et al. Delving into Transferable Adversarial Examples and Black-box Attacks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.02770, 2017-2-7.
|
| [11] |
HU Weiwei, TAN Ying. Generating Adversarial Malware Examples for Black-Box Attacks Based on GAN[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1702.05983, 2017-2-20.
|
| [12] |
GOODFELLOW I, POUGETABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative Adversarial Networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1406.2661, 2014-1-10.
|
| [13] |
TANG Chuan, ZHANG Yi, YANG Yuexiang, et al. DroidGAN: an Android Adversarial Sample Generation Framework Based on DCGAN[J]. Journal on Communications, 2018,18(S1):64-69.
|
|
唐川, 张义, 杨岳湘, 等. DroidGAN:基于DCGAN 的 Android 对抗样本生成框架[J]. 通信学报, 2018,18(S1):64-69.
|
| [14] |
ARJOVSKY M, CHINTALA S, BOTTOU L, Wasserstein GAN[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1701.07875, 2017-12-6.
|
| [15] |
ARJOVSKY M, BOTTOU L. Towards Principled Methods for Training generative Adversarial Networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1701.04862, 2017-1-17.
|
| [16] |
CHEN Sen, XUE Minhui, FAN Lingling, et al. Automated Poisoning Attacks and Defenses in Malware Detection Systems: An Adversarial Machine Learning Approach[J]. Computers & Security, 2018,73(3):326-344.
|
| [17] |
DEMONTIS A, MELIS M, BIGGIO B, et al. Yes, Machine Learning Can Be More Secure! A Case Study on Android Malware Detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2019,16(4):711-724.
|
| [18] |
ONWUZURIKE L, MARICONTI E, ANDRIOTIS P, et al. MaMaDroid: Detecting Android Malware by Building Markov Chains of Behavioral Models[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.07477, 2019-3-2.
|
| [19] |
Corvus Forensics. VirusShare[EB/OL]. https://virusshare.com/, 2020-3-20.
|