信息网络安全 ›› 2024, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (9): 1409-1421.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2024.09.009
基于ViT的轻量级恶意代码检测架构
- 1.广西大学计算机与电子信息学院,南宁 530004
2.武汉数字工程研究所,武汉 430070
-
收稿日期:2024-06-01出版日期:2024-09-10发布日期:2024-09-27 -
通讯作者:黄保华bhhuang66@gxu.edu.cn -
作者简介:黄保华(1973—),男,贵州,副教授,博士,CCF高级会员,主要研究方向为信息安全|杨婵娟(2000—),女,广西,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为信息安全|熊宇(1987—),女,湖北,工程师,硕士,主要研究方向为信息安全|庞飔(1999—),男,广西,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为信息安全 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(61962005);中国高校产学研创新基金-新一代信息技术创新项目(2021ITA11003)
Lightweight Malicious Code Detection Architecture Based on Vision Transformer
HUANG Baohua1( ), YANG Chanjuan1, XIONG Yu2, PANG Si1
), YANG Chanjuan1, XIONG Yu2, PANG Si1
- 1. School of Computer and Electronic Information, Guangxi University, Nanning 530004, China
2. Wuhan Digital Engineer Institute, Wuhan 430070, China
-
Received:2024-06-01Online:2024-09-10Published:2024-09-27
摘要:
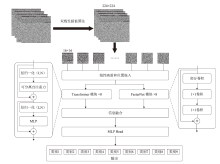
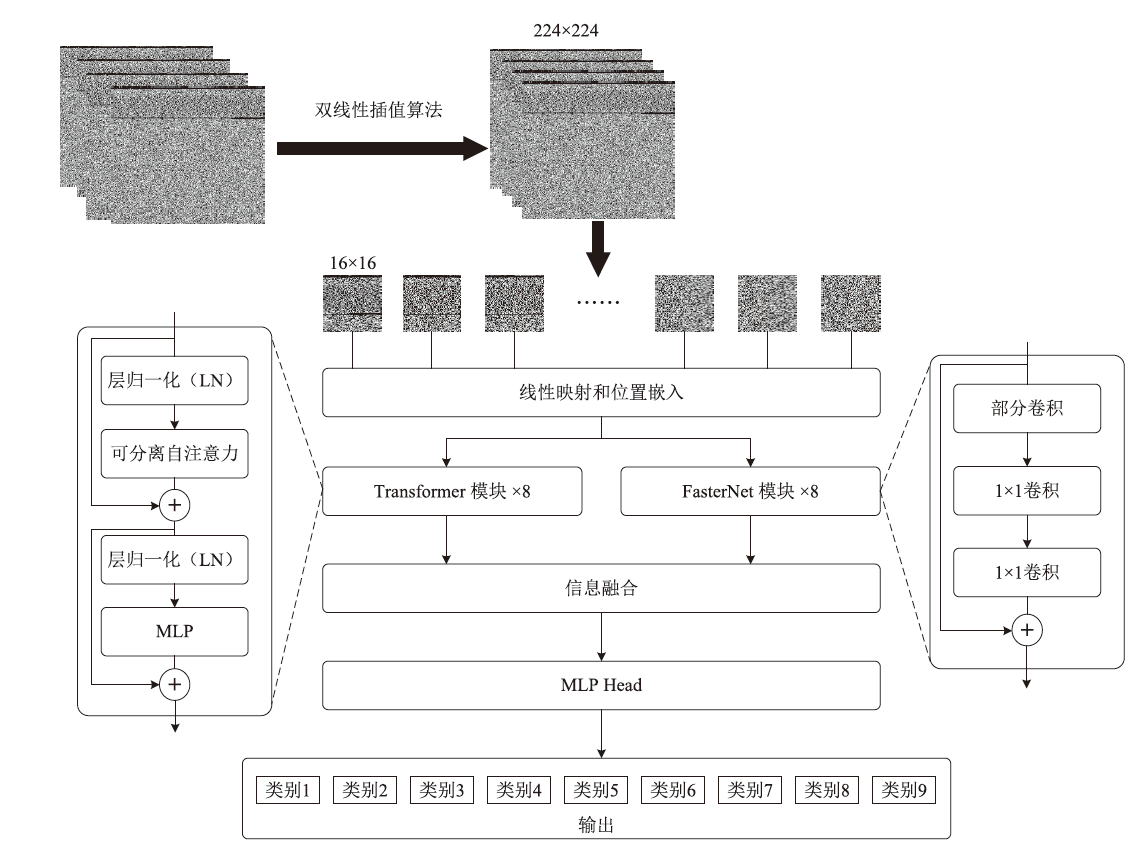
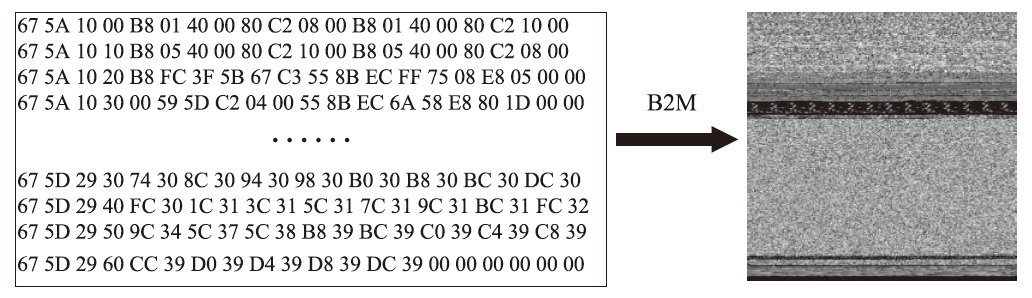
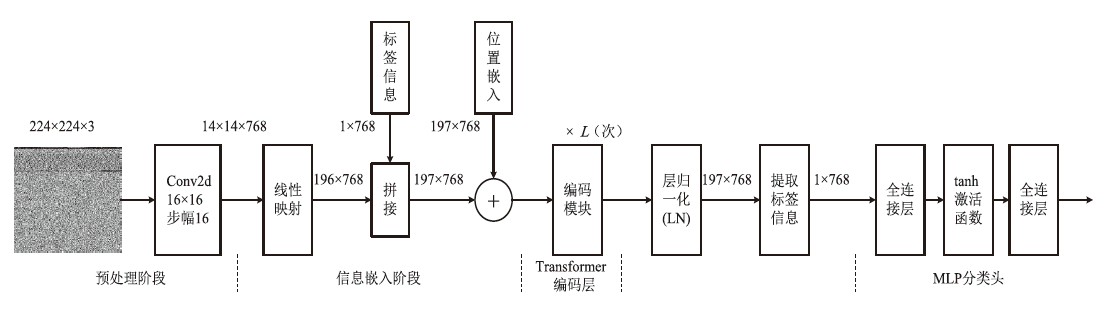
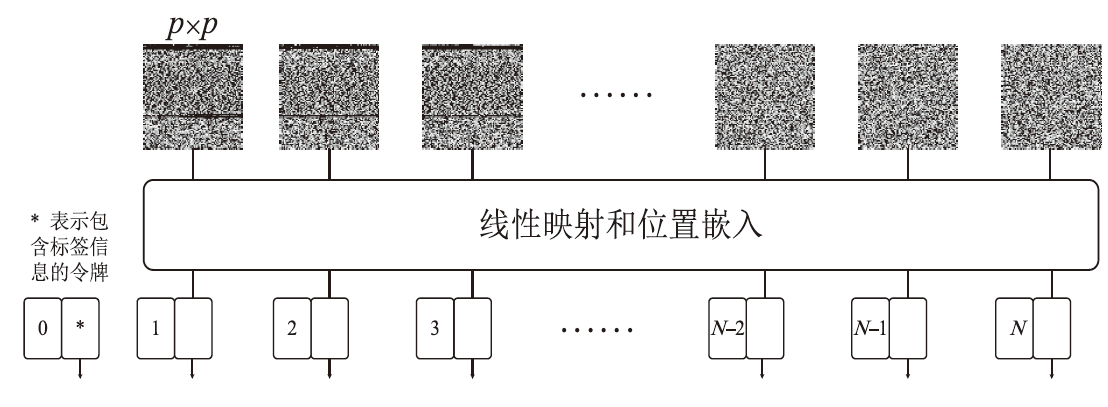
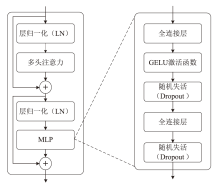
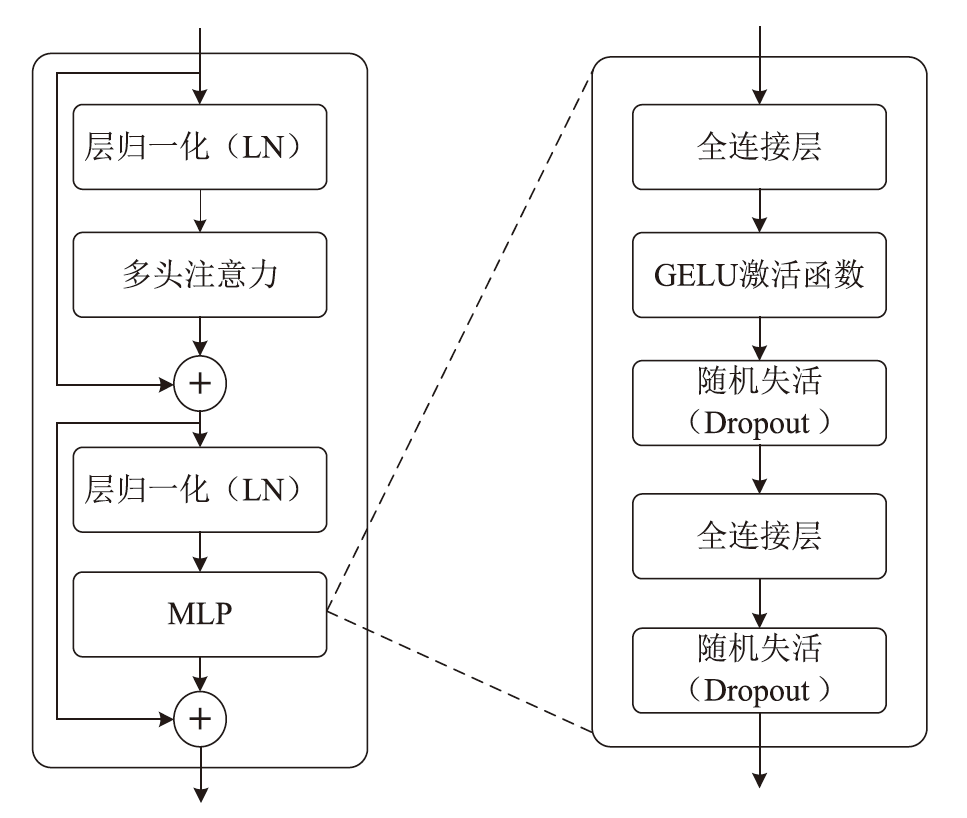
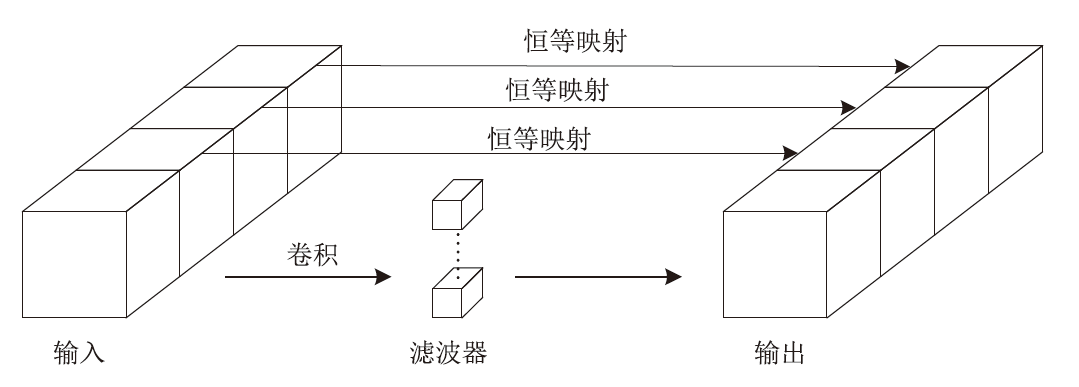
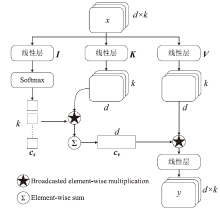
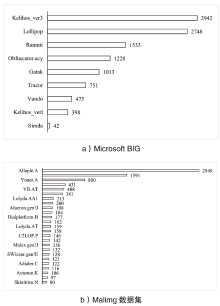
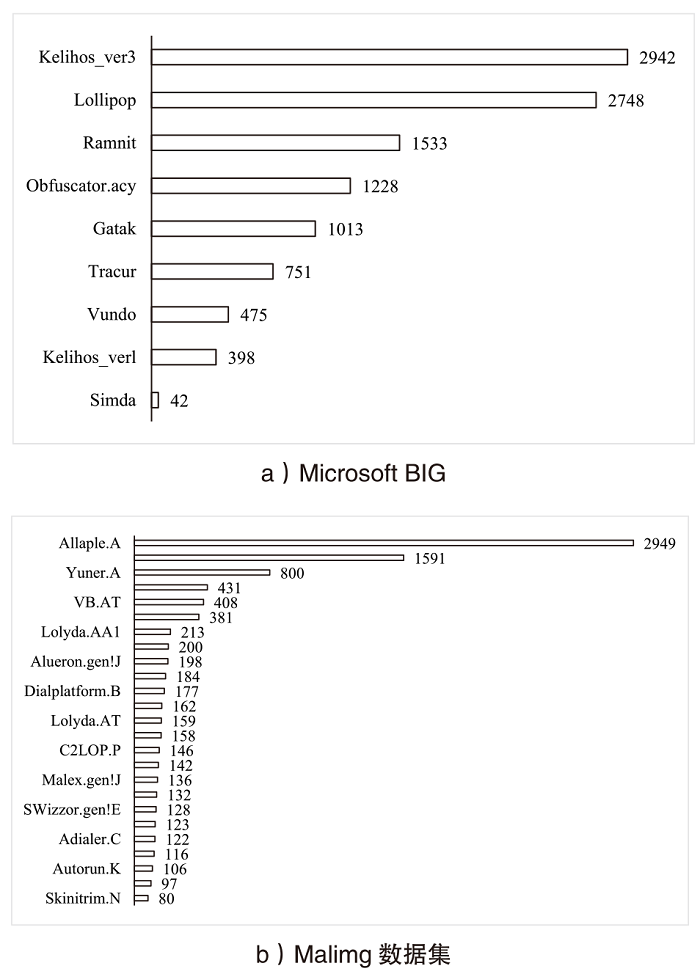
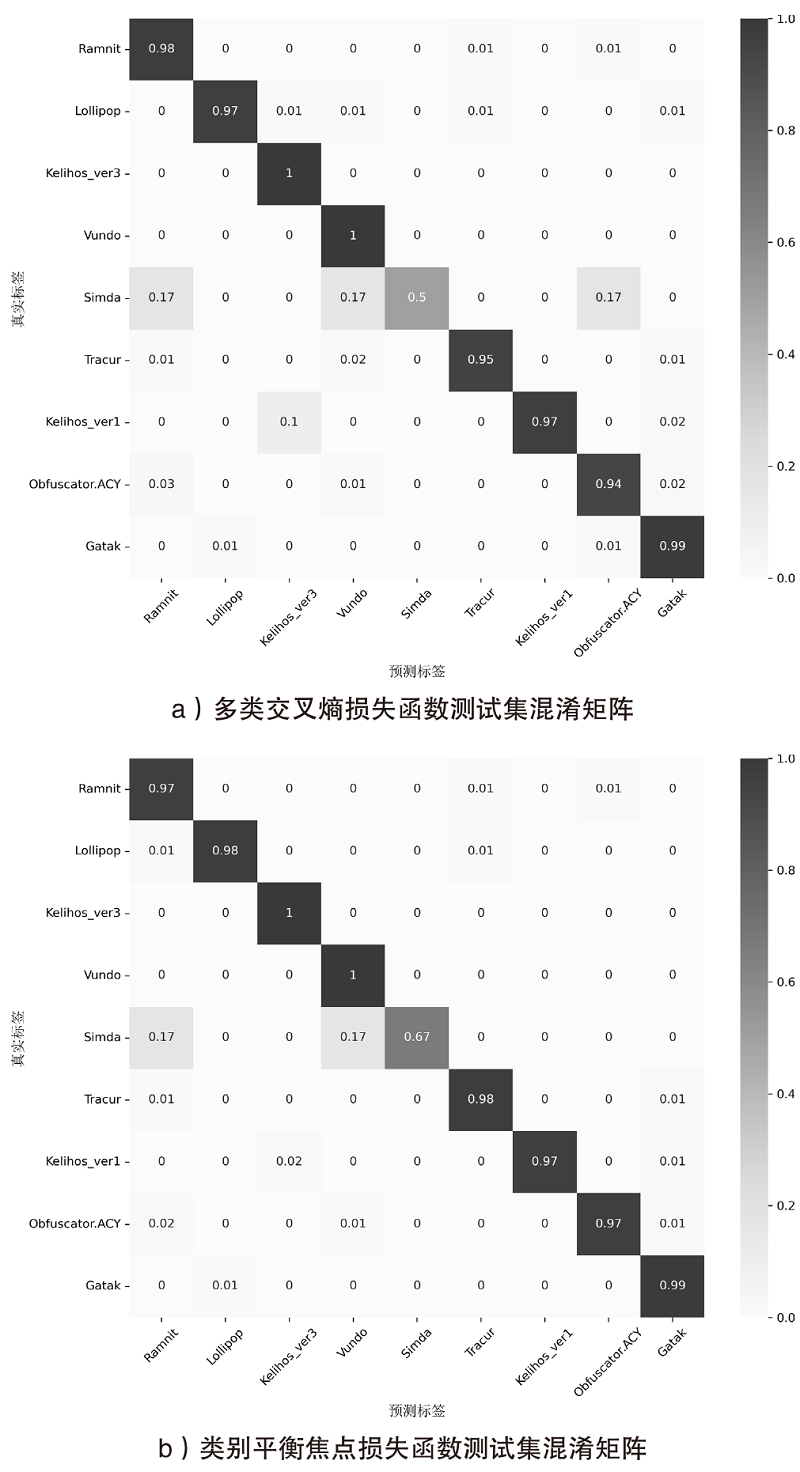
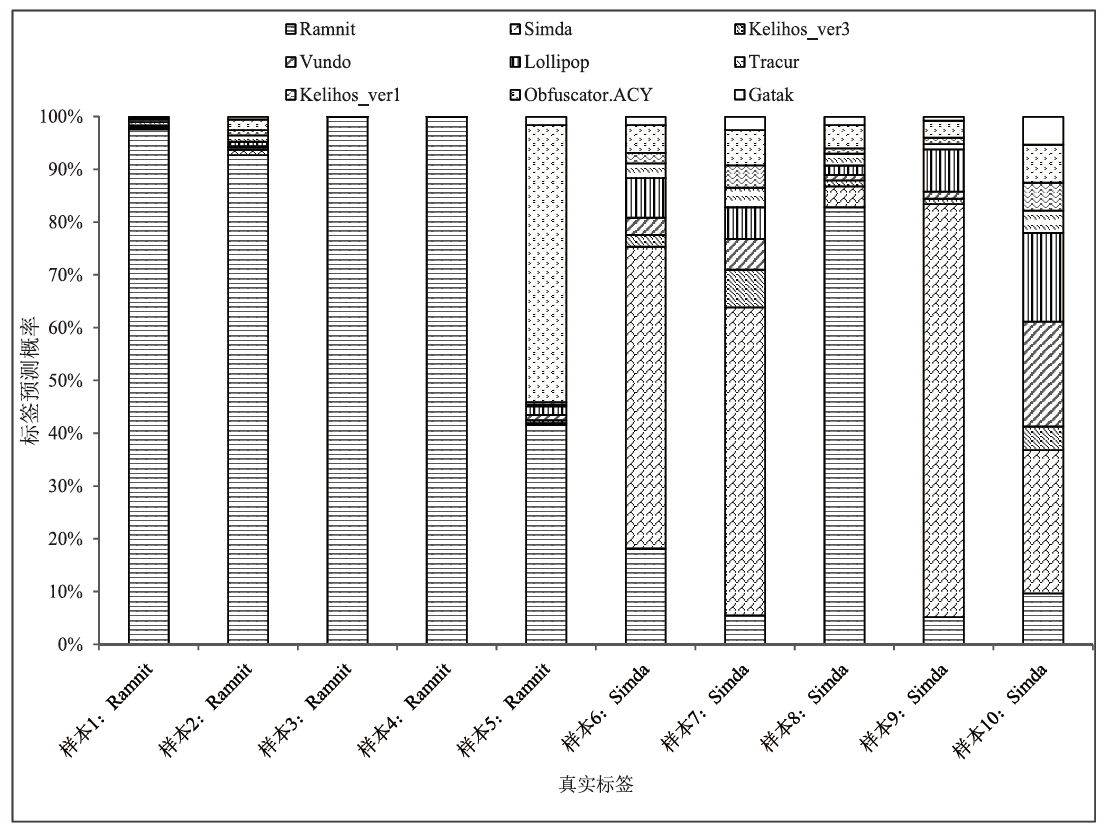
随着信息社会的快速发展,恶意代码变体日益增多,给现有的检测方法带来了挑战。为了提高恶意代码变体的检测准确率和效率,文章提出一种新的混合架构FasterMalViT。该架构通过融合部分卷积结构改进ViT,显著提升其在恶意代码检测领域的性能。为了解决引入卷积操作导致参数量增加的问题,文章采用可分离自注意力机制替代传统的多头注意力,有效减少了参数量,降低了计算成本。针对恶意代码数据集中各类样本分布不均衡的问题,文章引入类别平衡焦点损失函数,引导模型在训练过程中更关注样本数量较少的类别,从而提高难分类别的性能。在Microsoft BIG、Malimg数据集和MalwareBazaar数据集上的实验结果表明,FasterMalViT具有较好的检测性能和泛化能力。
中图分类号:
引用本文
黄保华, 杨婵娟, 熊宇, 庞飔. 基于ViT的轻量级恶意代码检测架构[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(9): 1409-1421.
HUANG Baohua, YANG Chanjuan, XIONG Yu, PANG Si. Lightweight Malicious Code Detection Architecture Based on Vision Transformer[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(9): 1409-1421.
表5
Microsoft BIG上恶意代码检测方法的结果比较
| 恶意代码 检测方法 | 年份 | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文献[ | 2021 | 94.88% | — | 92.47% | 0.8988 |
| 文献[ | 2021 | 98.46% | 98.58% | 97.84% | 0.9821 |
| 文献[ | 2022 | 96.83% | — | — | — |
| DTMIC[ | 2022 | 93.19% | — | — | — |
| IMCBL[ | 2024 | 95.49% | 95.31% | 95.49% | 0.9536 |
| FasterMalViT | 2024 | 98.53% | 96.23% | 98.53% | 0.9732 |
表6
Malimg数据集上恶意代码检测方法的结果比较
| 恶意代码 检测方法 | 年份 | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文献[ | 2020 | 98.58% | 98.04% | 98.06% | 0.9805 |
| 文献[ | 2021 | 98.23% | 97.78% | 97.92% | 0.9785 |
| 文献[ | 2021 | 98.97% | 99.50% | 97.06% | 0.9697 |
| 文献[ | 2022 | 97.76% | 97.84% | 97.76% | 0.9769 |
| 3D-VGG-16[ | 2024 | 96.14% | 97.00% | 95.00% | 0.9500 |
| FasterMalViT | 2024 | 98.43% | 98.44% | 98.43% | 0.9841 |
| [1] | ASLAN O, SAMET R. A Comprehensive Review on Malware Detection Approaches[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 6249-6271. |
| [2] | MANIRIHO P, MAHMOOD A N, CHOWDHURY M J M. A Study on Malicious Software Behaviour Analysis and Detection Techniques: Taxonomy, Current Trends and Challenges[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2022, 130: 1-18. |
| [3] | GOPINATH M, SETHURAMAN S C. A Comprehensive Survey on Deep Learning Based Malware Detection Techniques[EB/OL]. (2023-12-21)[2024-04-30]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosrev.2022.100529. |
| [4] | GABER M G, AHMED M, JANICKE H. Malware Detection with Artificial Intelligence: A Systematic Literature Review[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2024, 56(6): 1-33. |
| [5] | ZHANG Jixin, QIN Zheng, YIN Hui, et al. A Feature-Hybrid Malware Variants Detection Using CNN Based Opcode Embedding and BPNN Based API Embedding[J]. Computers & Security, 2019, 84: 376-392. |
| [6] | JEON J, JEONG B, BAEK S, et al. Hybrid Malware Detection Based on Bi-LSTM and SPP-Net for Smart IoT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(7): 4830-4837. |
| [7] | VERMA V, MUTTOO S K, SINGH V B. Multiclass Malware Classification via First- and Second-Order Texture Statistics[EB/OL]. (2020-07-23)[2024-04-30]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2020.101895. |
| [8] | SHAUKAT K, LUO Suhai, VARADHARAJAN V. A Novel Deep Learning-Based Approach for Malware Detection[EB/OL]. (2023-03-09)[2024-04-30]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2023.106030. |
| [9] | DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An Image is Worth 16×16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale[C]// ICLR. 9th International Conference on Learning Representations(ICLR 2021). Washington: ICLR, 2021: 1-21. |
| [10] | VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is All You Need[C]// ACM. 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: ACM, 2017(11): 6000-6010. |
| [11] | CHEN Jierun, KAO S H, HE Hao, et al. Run, Don’t Walk: Chasing Higher FLOPS for Faster Neural Networks[C]// IEEE. 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2023: 12021-12031. |
| [12] | MEHTA S, RASTEGARI M. Separable Self-Attention for Mobile Vision Transformers[J]. Transactions on Machine Learning Research, 2023: 1-22. |
| [13] | NATARAJ L, KARTHIKEYAN S, JACOB G, et al. Malware Images: Visualization and Automatic Classification[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Visualization for Cyber Security. New York: ACM, 2011: 1-7. |
| [14] | ZHU Huijuan, GU Wei, WANG Liangmin, et al. Android Malware Detection Based on Multi-Head Squeeze-and-Excitation Residual Network[EB/OL]. (2023-08-30)[2024-04-30]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.118705. |
| [15] | LI Ce, CHENG Zijun, ZHU He, et al. DMalNet: Dynamic Malware Analysis Based on API Feature Engineering and Graph Learning[EB/OL]. (2022-08-08)[2024-04-30]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2022.102872. |
| [16] | NGUYEN T N, NGO Q D, NGUYEN H T, et al. An Advanced Computing Approach for IoT-Botnet Detection in Industrial Internet of Things[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(11): 8298-8306. |
| [17] | DENG Huaxin, GUO Chun, SHEN Guowei, et al. MCTVD: A Malware Classification Method Based on Three-Channel Visualization and Deep Learning[EB/OL]. (2023-01-04)[2024-04-30]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2022.103084. |
| [18] | RADHAKRISHNAN P. Why Transformers are Slowly Replacing CNNs in Computer Vision?[EB/OL]. (2021-09-11)[2024-04-30]. https://becominghuman.ai/transformers-in-vision-e2e87b739feb. |
| [19] | LI M Q, FUNG B C M, CHARLAND P, et al. I-MAD: Interpretable Malware Detector Using Galaxy Transformer[EB/OL]. (2021-06-18)[2024-04-30]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2021.102371. |
| [20] | RAHALI A, AKHLOUFI M. MalBERT: Using Transformers for Cybersecurity and Malicious Software Detection[EB/OL]. (2021-03-05)[2024-04-30]. |
| [21] | BU S J, CHO S B. Triplet-Trained Graph Transformer with Control Flow Graph for Few-Shot Malware Classification[EB/OL]. (2023-08-28)[2024-04-30]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2023.119598. |
| [22] | DENG Xiaoheng, WANG Zhe, PEI Xinjun, et al. TransMalDE: An Effective Transformer Based Hierarchical Framework for IoT Malware Detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2024, 11(1): 140-151. |
| [23] | PARK K W, CHO S B. A Vision Transformer Enhanced with Patch Encoding for Malware Classification[C]// Springer. 23rd International Conference on Intelligent Data Engineering and Automated Learning-IDEAL 2022. Heidelberg: Springer, 2022: 289-299. |
| [24] | DEMIRKIRAN F, ÇAYIR A, ÜNAL U, et al. An Ensemble of Pre-Trained Transformer Models for Imbalanced Multiclass Malware Classification[EB/OL]. (2022-07-27)[2024-04-30]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2022.102846. |
| [25] | VASAN D, ALAZAB M, WASSAN S, et al. IMCFN: Image-Based Malware Classification Using Fine-Tuned Convolutional Neural Network Architecture[EB/OL]. (2020-02-16)[2024-04-30]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2020.107138. |
| [26] | RAVI A, CHATURVEDI V, SHAFIQUE M. ViT4Mal: Lightweight Vision Transformer for Malware Detection on Edge Devices[J]. ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems, 2023, 22(5s): 1-26. |
| [27] | BELAL M M, SUNDARAM D M. Global-Local Attention-Based Butterfly Vision Transformer for Visualization-Based Malware Classification[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 69337-69355. |
| [28] | FREITAS S, DUGGAL R, CHAU D H. MalNet: A Large-Scale Image Database of Malicious Software[C]// ACM. 31st ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management. New York: ACM, 2022: 3948-3952. |
| [29] | SENEVIRATNE S, SHARIFFDEEN R, RASNAYAKA S, et al. Self-Supervised Vision Transformers for Malware Detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 103121-103135. |
| [30] | ZHANG Jinnian, PENG Houwen, WU Kan, et al. MiniViT: Compressing Vision Transformers with Weight Multiplexing[C]// IEEE. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2022: 12145-12154. |
| [31] | KHAN A, RAUF Z, SOHAIL A, et al. A Survey of the Vision Transformers and Their CNN-Transformer Based Variants[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2023, 56(3): 2917-2970. |
| [32] | LOSHCHILOV I, HUTTER F. Decoupled Weight Decay Regularization[C]// ICLR. 7th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2019). Washington: ICLR, 2019(6): 4061-4078. |
| [33] | LOSHCHILOV I, HUTTER F. SGDR: Stochastic Gradient Descent with Warm Restarts[C]// ICLR. 5th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2017). Washington: ICLR, 2017(3): 1769-1784. |
| [34] | LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection[C]// IEEE. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). New York: IEEE, 2017: 2999-3007. |
| [35] | CUI Yin, JIA Menglin, LIN T Y, et al. Class-Balanced Loss Based on Effective Number of Samples[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2019: 9268-9277. |
| [36] | RONEN R, RADU M, FEUERSTEIN C, et al. Microsoft Malware Classification Challenge[EB/OL]. (2018-02-22)[2024-04-30]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.10135. |
| [37] | CAO Chang, CHICCO D, HOFFMAN M M. The MCC-F 1 Curve: A Performance Evaluation Technique for Binary Classification[EB/OL]. (2020-06-17)[2024-08-13]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11278v1. |
| [38] | ASLAN Ö, YILMAZ A. A New Malware Classification Framework Based on Deep Learning Algorithms[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 87936-87951. |
| [39] | HEMALATHA J, ROSELINE S A, GEETHA S, et al. An Efficient DenseNet-Based Deep Learning Model for Malware Detection[EB/OL]. (2021-03-15)[2024-04-30]. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23030344. |
| [40] | KUMAR S, JANET B. DTMIC: Deep Transfer Learning for Malware Image Classification[EB/OL]. (2021-12-01)[2024-04-30]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jisa.2021.103063. |
| [41] | VASAN D, HAMMOUDEH M, ALAZAB M. Broad Learning: A GPU-Free Image-Based Malware Classification[EB/OL]. (2024-02-15)[2024-04-30]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2024.111401. |
| [42] | WONG W K, JUWONO F H, APRIONO C. Vision-Based Malware Detection: A Transfer Learning Approach Using Optimal ECOC-SVM Configuration[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 159262-159270. |
| [43] | BARROS P H, CHAGAS E T C, OLIVEIRA L B, et al. Malware-SMELL: A Zero-Shot Learning Strategy for Detecting Zero-Day Vulnerabilities[EB/OL]. (2022-06-03)[2024-04-30]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2022.102785. |
| [44] | AL-KHATER W, AL-MADEED S. Using 3D-VGG-16 and 3D-Resnet-18 Deep Learning Models and FABEMD Techniques in the Detection of Malware[J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2024, 89: 39-52. |
| [1] | 刘军, 武志超, 吴建, 谭振华. 一种融合图像空间特征注意力机制的恶意代码识别模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(12): 29-37. |
| [2] | 李思聪, 王坚, 宋亚飞, 黄玮. 基于BiTCN-DLP的恶意代码分类方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 104-117. |
| [3] | 刘家银, 李馥娟, 马卓, 夏玲玲. 基于多尺度卷积神经网络的恶意代码分类方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 31-38. |
| [4] | 李鹏超, 刘彦飞. 基于删除PE文件头的恶意代码内存取证方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(12): 38-43. |
| [5] | 朱朝阳, 周亮, 朱亚运, 林晴雯. 基于行为图谱筛的恶意代码可视化分类算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(10): 54-62. |
| [6] | 谭杨, 刘嘉勇, 张磊. 基于混合特征的深度自编码器的恶意软件家族分类[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(12): 72-82. |
| [7] | 文伟平, 陈夏润, 杨法偿. 基于Rootkit隐藏行为特征的Linux恶意代码取证方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(11): 32-42. |
| [8] | 乔延臣, 姜青山, 古亮, 吴晓明. 基于汇编指令词向量与卷积神经网络的恶意代码分类方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(4): 20-28. |
| [9] | 李云春, 鲁文涛, 李巍. 基于Shapelet的恶意代码检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(3): 70-77. |
| [10] | 周振飞, 方滨兴, 崔翔, 刘奇旭. 基于相似性分析的WordPress主题恶意代码检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2017, 17(12): 47-53. |
| [11] | 王毅, 唐勇, 卢泽新, 俞昕. 恶意代码聚类中的特征选取研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2016, 16(9): 64-68. |
| [12] | 蔡林, 陈铁明. Android移动恶意代码检测的研究概述与展望[J]. 信息网络安全, 2016, 16(9): 218-222. |
| [13] | 张家旺, 李燕伟. 基于N-gram算法的恶意程序检测系统研究与设计[J]. 信息网络安全, 2016, 16(8): 74-80. |
| [14] | 梁宏, 张慧云, 肖新光. 基于社会工程学的邮件样本关联分析[J]. 信息网络安全, 2015, 15(9): 180-185. |
| [15] | 芦天亮, 周运伟, 曹巍. 移动互联网攻击技术及违法犯罪手段分析[J]. 信息网络安全, 2014, 14(9): 176-179. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||