信息网络安全 ›› 2024, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (3): 449-461.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2024.03.010
基于深度强化学习和隐私保护的群智感知动态任务分配策略
- 1.广西大学计算机与电子信息学院,南宁 530004
2.广西高校并行分布与智能计算重点实验室,南宁 530004
3.广西智能数字服务工程技术研究中心,南宁 530004
-
收稿日期:2024-01-29出版日期:2024-03-10发布日期:2024-04-03 -
通讯作者:陈嘉元 E-mail:ycq_cjy@163.com -
作者简介:傅彦铭(1976—),男,广西,副教授,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为智能计算、网络安全|陆盛林(1999—),男,广东,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为群智感知、隐私保护|陈嘉元(1997—),男,山西,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为群智感知、隐私保护|覃华(1972—),男,广西,教授,博士,主要研究方向为量子计算理论、近似动态规划最优化方法、数据挖掘 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(61962005)
Dynamic Task Allocation for Crowd Sensing Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning and Privacy Protection
FU Yanming1,2,3, LU Shenglin1, CHEN Jiayuan1( ), QIN Hua1
), QIN Hua1
- 1. School of Computer, Electronic and Information, Guangxi University, Nanning 530000, China
2. Key Laboratory of Parallel, Distributed and Intelligent Computing(Guangxi), Nanning 530000, China
3. Guangxi Intelligent Digital Services Research Center of Engineering Technology, Nanning 530000, China
-
Received:2024-01-29Online:2024-03-10Published:2024-04-03 -
Contact:CHEN Jiayuan E-mail:ycq_cjy@163.com
摘要:
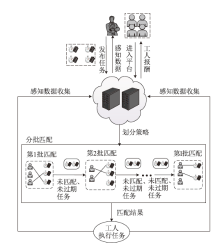
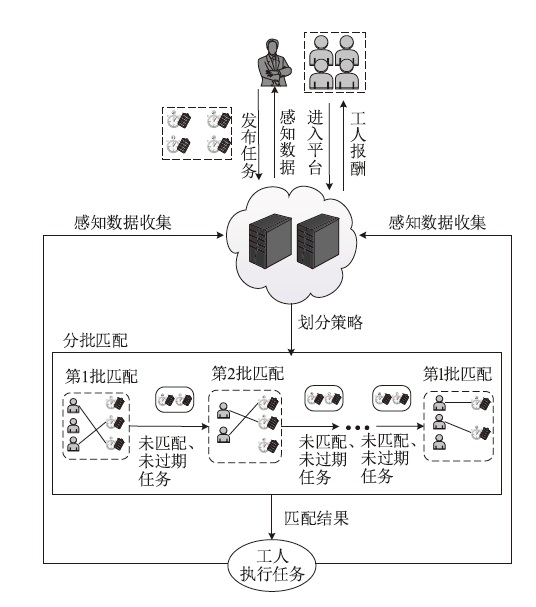
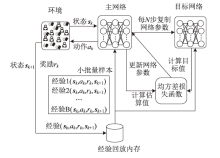
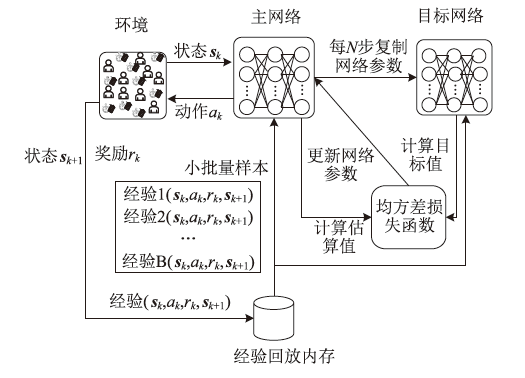
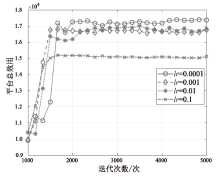
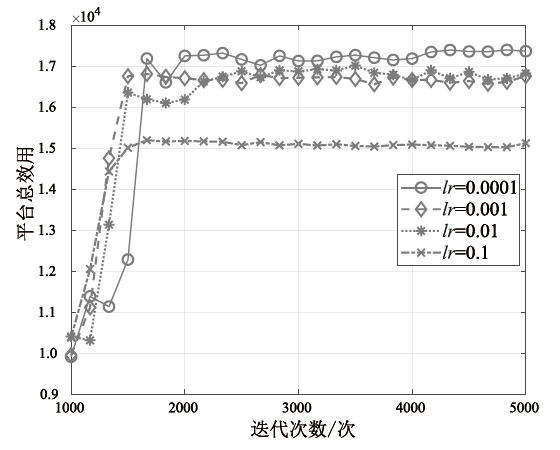
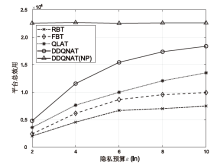
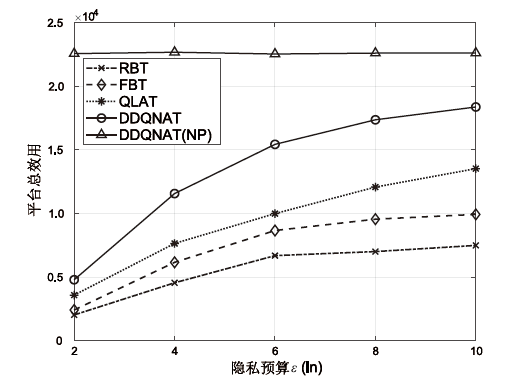
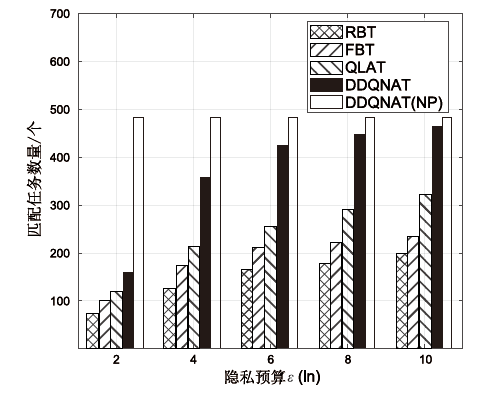
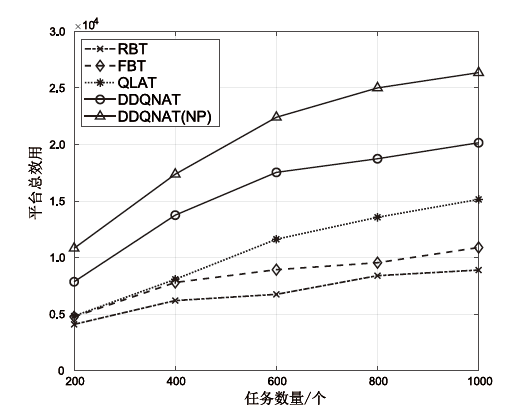
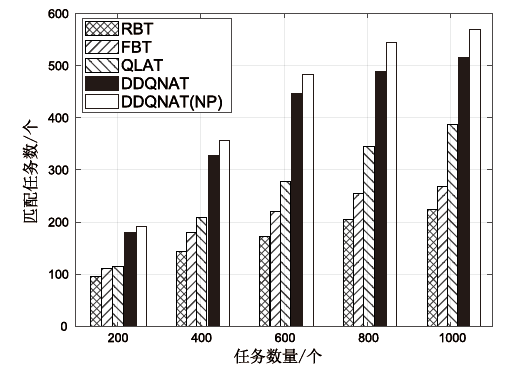
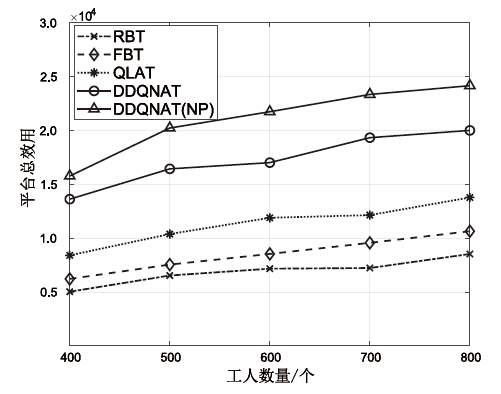
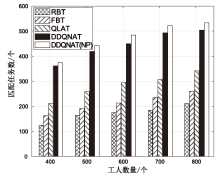
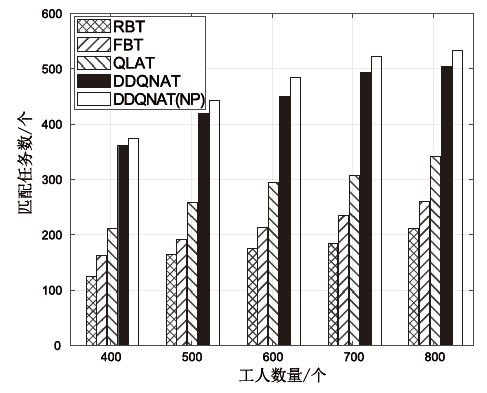
在移动群智感知(Mobile Crowd Sensing,MCS)中,动态任务分配的结果对提高系统效率和确保数据质量至关重要。然而,现有的大部分研究在处理动态任务分配时,通常将其简化为二分匹配模型,该简化模型未充分考虑任务属性与工人属性对匹配结果的影响,同时忽视了工人位置隐私的保护问题。针对这些不足,文章提出一种基于深度强化学习和隐私保护的群智感知动态任务分配策略。该策略首先通过差分隐私技术为工人位置添加噪声,保护工人隐私;然后利用深度强化学习方法自适应地调整任务批量分配;最后使用基于工人任务执行能力阈值的贪婪算法计算最优策略下的平台总效用。在真实数据集上的实验结果表明,该策略在不同参数设置下均能保持优越的性能,同时有效地保护了工人的位置隐私。
中图分类号:
引用本文
傅彦铭, 陆盛林, 陈嘉元, 覃华. 基于深度强化学习和隐私保护的群智感知动态任务分配策略[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 449-461.
FU Yanming, LU Shenglin, CHEN Jiayuan, QIN Hua. Dynamic Task Allocation for Crowd Sensing Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning and Privacy Protection[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(3): 449-461.
| [1] | GANTI R K, YE Fan, LEI Hui. Mobile Crowdsensing: Current State and Future Challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2011, 49(11): 32-39. |
| [2] | CAPPONI A, FIANDRINO C, KANTARCI B, et al. A Survey on Mobile Crowdsensing Systems: Challenges, Solutions, and Opportunities[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2019, 21(3): 2419-2465. |
| [3] |
ZHENG Zhenzhe, WU Fan, GAO Xiaofeng, et al. A Budget Feasible Incentive Mechanism for Weighted Coverage Maximization in Mobile Crowdsensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2016, 16(9): 2392-2407.
doi: 10.1109/TMC.2016.2632721 URL |
| [4] |
WANG Xiong, ZHANG Jinbei, TIAN Xiaohua, et al. Crowdsensing-Based Consensus Incident Report for Road Traffic Acquisition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 19(8): 2536-2547.
doi: 10.1109/TITS.2017.2750169 URL |
| [5] |
BALLESTEROS J, CARBUNAR B, RAHMAN M, et al. Towards Safe Cities: A Mobile and Social Networking Approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2013, 25(9): 2451-2462.
doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2013.190 URL |
| [6] |
ALEMDAR H, ERSOY C. Wireless Sensor Networks for Healthcare: A Survey[J]. Computer Networks, 2010, 54(15): 2688-2710.
doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2010.05.003 URL |
| [7] | JIANG Weijin, CHEN Junpeng, LIU Xiaoliang, et al. Participant Recruitment Method Aiming at Service Quality in Mobile Crowd Sensing[J]. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2021(3): 1-14. |
| [8] |
WANG Jiangtao, WANG Yasha, ZHANG Daqing, et al. Multi-Task Allocation in Mobile Crowd Sensing with Individual Task Quality Assurance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2018, 17(9): 2101-2113.
doi: 10.1109/TMC.7755 URL |
| [9] | WU Shengnan, WANG Yingjie, TONG Xiangrong. Multi-Objective Task Assignment for Maximizing Social Welfare in Spatio-Temporal Crowdsourcing[J]. China Communications, 2021, 18(11): 11-25. |
| [10] |
LI Xin, ZHANG Xinglin. Multi-Task Allocation under Time Constraints in Mobile Crowdsensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2019, 20(4): 1494-1510.
doi: 10.1109/TMC.7755 URL |
| [11] |
TAO Xi, SONG Wei. Profit-Oriented Task Allocation for Mobile Crowdsensing with Worker Dynamics: Cooperative Offline Solution and Predictive Online Solution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2020, 20(8): 2637-2653.
doi: 10.1109/TMC.2020.2983688 URL |
| [12] |
SONG Tianshu, XU Ke, LI Jiangneng, et al. Multi-Skill Aware Task Assignment in Real-Time Spatial Crowdsourcing[J]. GeoInformatica, 2020, 24: 153-173.
doi: 10.1007/s10707-019-00351-4 |
| [13] |
XIAO Mingjun, WU Jie, HUANG Liusheng, et al. Online Task Assignment for Crowdsensing in Predictable Mobile Social Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2016, 16(8): 2306-2320.
doi: 10.1109/TMC.2016.2616473 URL |
| [14] | MIAO Xin, KANG Yanrong, MA Qiang, et al. Quality-Aware Online Task Assignment in Mobile Crowdsourcing[J]. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks, 2020, 16(3): 1-21. |
| [15] | ZHAO Pengcheng, LI Xiang, GAO Shang, et al. Cooperative Task Assignment in Spatial Crowdsourcing via Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning[EB/OL]. (2022-05-23)[2023-12-12]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sysarc.2022.102551. |
| [16] |
PAN Qingxian, PAN Tingwei, DONG Hongbin, et al. An Online Task Assignment Based on Quality Constraint for Spatio-Temporal Crowdsourcing[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 170292-170303.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2942155 |
| [17] |
ZHAO Bingxu, DONG Hongbin, WANG Yingjie, et al. A Task Allocation Algorithm Based on Reinforcement Learning in Spatio-Temporal Crowdsourcing[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2023, 53(11): 13452-13469.
doi: 10.1007/s10489-022-04151-6 |
| [18] | TO H, SHAHABI C, KAZEMI L. A Server-Assigned Spatial Crowdsourcing Framework[J]. ACM Transactions on Spatial Algorithms and Systems, 2015, 1(1): 1-28. |
| [19] | WANG Mingze, WANG Yingjie, SAI A, et al. Task Assignment for Hybrid Scenarios in Spatial Crowdsourcing: A Q-Learning-Based Approach[EB/OL]. (2022-11-04)[2023-12-12]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2022.109749. |
| [20] |
SUN Lijun, YU Xiaojie, GUO Jiachen, et al. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Task Assignment in Spatial Crowdsourcing and Sensing[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(22): 25323-25330.
doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3057376 URL |
| [21] | YANG Hai, QIN Xiaoran, KE Jintao, et al. Optimizing Matching Time Interval and Matching Radius in on-Demand Ride-Sourcing Markets[J]. Transportatio Research Part B: Met-Hodological, 2020, 131: 84-105. |
| [22] | WANG Yansheng, TONG Yongxin, LONG Cheng, et al. Adaptive Dynamic Bipartite Graph Matching: A Reinforcement Learning Approach[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE 35th International Conference on Data Engineering(ICDE). New York: IEEE, 2019: 1478-1489. |
| [23] |
SUN Yong, TAN Wenan. A Trust-Aware Task Allocation Method Using Deep Q-Learning for Uncertain Mobile Crowdsourcing[J]. Human-Centric Computing and Information Sciences, 2019, 9: 1-27.
doi: 10.1186/s13673-018-0162-5 |
| [24] |
LIU Chi, DAI Zipeng, ZHAO Yinuo, et al. Distributed and Energy-Efficient Mobile Crowdsensing with Charging Stations by Deep Reinforcement Learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2019, 20(1): 130-146.
doi: 10.1109/TMC.7755 URL |
| [25] | YAO Changhua, XU Hao, FU Shu, et al. Fast Multi-Agent Collaborative Exploration Algorithm Based on Boundary Point Filtering[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(11): 58-68. |
| 姚昌华, 许浩, 付澍, 等. 基于边界点过滤的多智能体快速协同探索算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11):58-68. | |
| [26] | TAO Xi, SONG Wei. Task Allocation for Mobile Crowdsensing with Deep Reinforcement Learning[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference(WCNC). New York: IEEE, 2020: 1-7. |
| [27] | DWORK C. Differential Privacy[C]// Springer. International Colloquium on Automata, Languages, and Programming. Heidelberg: Springer, 2006: 1-12. |
| [28] |
TO H, GHINITA G, SHAHABI C. Framework for Protecting Worker Location Privacy in Spatial Crowdsourcing[J]. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 2014, 7(10): 919-930.
doi: 10.14778/2732951.2732966 URL |
| [29] | YAN Yan, ZHANG Xiong, FENG Tao. Proportional Differential Privacy Budget Allocation Method for Partition and Publishing of Statistical Big Data[J]. Netinfo Security, 2022, 22(11): 24-35. |
| 晏燕, 张雄, 冯涛. 大数据统计划分发布的等比差分隐私预算分配方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(11):24-35. | |
| [30] |
WANG Leye, YANG Dingqi, HAN Xiao, et al. Mobile Crowdsourcing Task Allocation with Differential-and-Distortion Geo-Obfuscation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2019, 18(2): 967-981.
doi: 10.1109/TDSC.8858 URL |
| [31] | ANDRÉS M E, BORDENABE N E, CHATZIKOKOLAKIS K, et al. Geo-Indistinguishability: Differential Privacy for Location-Based Systems[C]// ACM. The 2013 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer & Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2013: 901-914. |
| [32] |
ZHANG Qi, WANG Yingjie, CAI Zhipeng, et al. Multi-Stage Online Task Assignment Driven by Offline Data under Spatio-Temporal Crowdsourcing[J]. Digital Communications and Networks, 2022, 8(4): 516-530.
doi: 10.1016/j.dcan.2021.10.005 URL |
| [33] | SONG Tianshu, TONG Yongxin, WANG Libin, et al. Trichromatic Online Matching in Real-Time Spatial Crowdsourcing[C]// IEEE. 2017 IEEE 33rd International Conference on Data Engineering(ICDE). New York: IEEE, 2017: 1009-1020. |
| [1] | 宋玉涵, 祝跃飞, 魏福山. 一种基于AdaBoost模型的区块链异常交易检测方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1): 24-35. |
| [2] | 许可, 李嘉怡, 蒋兴浩, 孙锬锋. 一种基于轮廓稀疏对抗的视频步态隐私保护算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1): 48-59. |
| [3] | 赖成喆, 赵益宁, 郑东. 基于同态加密的隐私保护与可验证联邦学习方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1): 93-105. |
| [4] | 俞惠芳, 乔一凡, 孟茹. 面向区块链金融的抗量子属性基门限环签密方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(7): 44-52. |
| [5] | 唐雨, 张驰. 一种基于Intel SGX的信息中心网络隐私保护方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(6): 55-65. |
| [6] | 杜卫东, 李敏, 韩益亮, 王绪安. 基于密文转换的高效通用同态加密框架[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(4): 51-60. |
| [7] | 尹曙, 陈兴蜀, 朱毅, 曾雪梅. 基于字符空间构造的域名匿名化算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(4): 80-89. |
| [8] | 郭瑞, 魏鑫, 陈丽. 工业物联网环境下可外包的策略隐藏属性基加密方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(3): 1-12. |
| [9] | 李晓华, 王苏杭, 李凯, 徐剑. 一种支持隐私保护的传染病人际传播分析模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(3): 35-44. |
| [10] | 张学旺, 张豪, 姚亚宁, 付佳丽. 基于群签名和同态加密的联盟链隐私保护方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(3): 56-61. |
| [11] | 王晶宇, 马兆丰, 徐单恒, 段鹏飞. 支持国密算法的区块链交易数据隐私保护方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(3): 84-95. |
| [12] | 李家辉, 秦素娟, 高飞, 孙东旭. 基于属性加密的区块链组织交易可控可监管隐私保护方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(12): 103-112. |
| [13] | 孙永奇, 宋泽文, 朱卫国, 赵思聪. 基于安全多方计算的图像分类方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 27-37. |
| [14] | 于晶, 袁曙光, 袁煜琳, 陈驰. 基于k匿名数据集的鲁棒性水印技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(9): 11-20. |
| [15] | 张学旺, 刘宇帆. 可追踪身份的物联网感知层节点匿名认证方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(9): 55-62. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||