信息网络安全 ›› 2022, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (2): 76-85.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2022.02.009
面向SDN数据层的双虚假IP地址动态跳变技术
胡瑞钦1,2( ), 谭晶磊1,2, 彭心荷3, 张红旗1,2
), 谭晶磊1,2, 彭心荷3, 张红旗1,2
- 1.信息工程大学密码工程学院,郑州 450001
2.河南省信息安全重点实验室,郑州 450001
3.延安大学经济与管理学院,延安 716000
-
收稿日期:2021-09-15出版日期:2022-02-10发布日期:2022-02-16 -
通讯作者:胡瑞钦 E-mail:zero_hrq@163.com -
作者简介:胡瑞钦(1995—),男,湖北,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为网络信息安全、移动目标防御|谭晶磊(1994—),男,山东,博士研究生,主要研究方向为网络信息安全、移动目标防御、安全博弈决策|彭心荷(2000—),女,陕西,本科,主要研究方向为网络安全、软件定义网络|张红旗(1962—),男,河北,教授、博士生导师,主要研究方向为网络信息安全、移动目标防御、等级保护、信息安全管理 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(61902427);河南省科技攻关计划(212102210162)
Dynamic Hopping Technology of Double Virtual IP Address for SDN Data Layer
HU Ruiqin1,2( ), TAN Jinglei1,2, PENG Xinhe3, ZHANG Hongqi1,2
), TAN Jinglei1,2, PENG Xinhe3, ZHANG Hongqi1,2
- 1. Department of Cryptogram Engineering, Information Engineering University, Zhengzhou 450001, China
2. Henan Key Laboratory of Information Security, Zhengzhou 450001, China
3. School of Economics and Management, Yan’an University, Yan’an 716000, China
-
Received:2021-09-15Online:2022-02-10Published:2022-02-16 -
Contact:HU Ruiqin E-mail:zero_hrq@163.com
摘要:
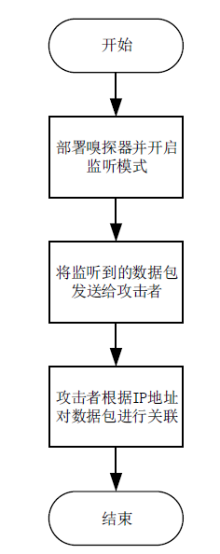
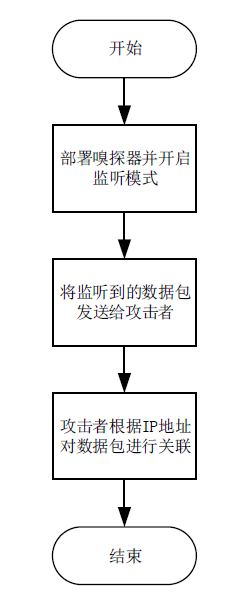
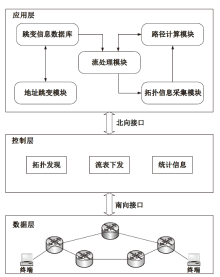
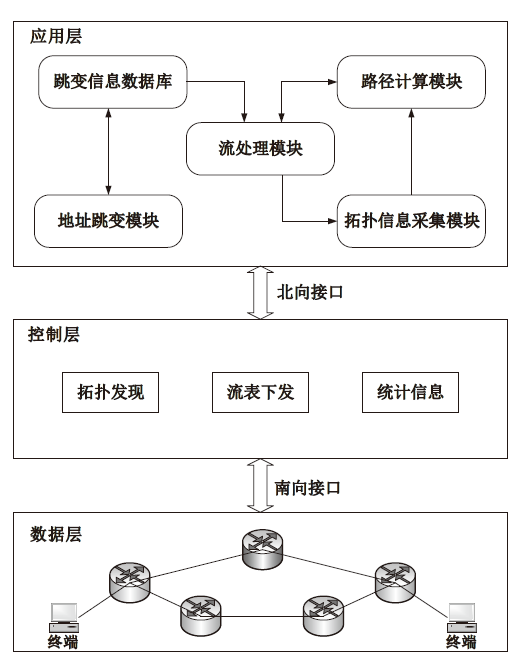
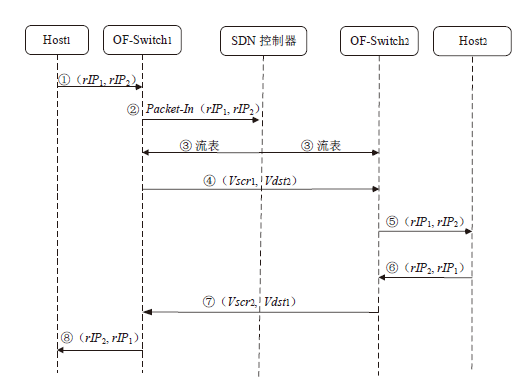
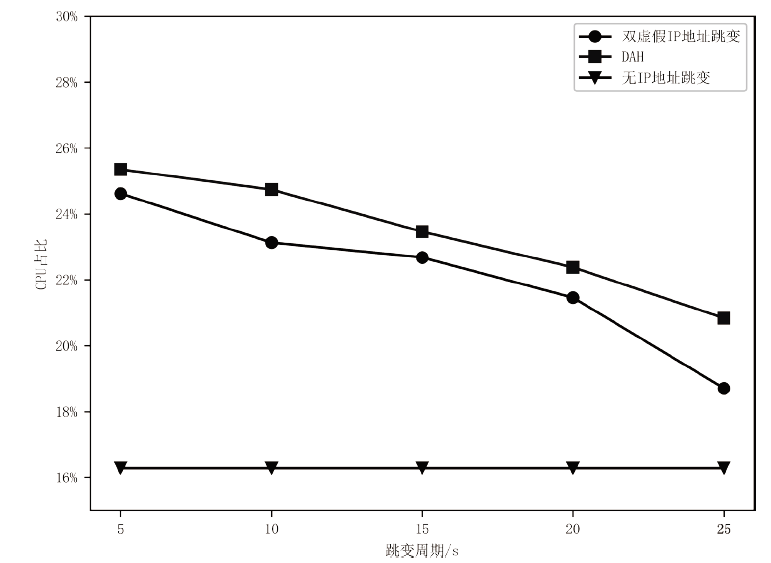
嗅探攻击是一种常见且隐蔽性很强的网络攻击方式,这种攻击方式对通信数据的机密性造成了严重威胁,然而传统的防御手段受制于网络攻防对抗的严重不对称性,难以有效应对这种威胁。文章提出了一种面向SDN数据层的双虚假IP地址动态跳变技术,首先利用双虚假IP地址破坏通信数据在空间维度上的关联性,然后通过周期性IP地址跳变破坏通信数据在时间维度上的关联性,从而提高嗅探攻击者重组通信数据的难度以及成本。抗攻击有效性分析以及仿真实验表明,文章所提技术在提高抗嗅探攻击能力的同时,能保证较低的CPU消耗和通信时延。
中图分类号:
引用本文
胡瑞钦, 谭晶磊, 彭心荷, 张红旗. 面向SDN数据层的双虚假IP地址动态跳变技术[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(2): 76-85.
HU Ruiqin, TAN Jinglei, PENG Xinhe, ZHANG Hongqi. Dynamic Hopping Technology of Double Virtual IP Address for SDN Data Layer[J]. Netinfo Security, 2022, 22(2): 76-85.
表2
仿真实验结果
| 防御策略 | 嗅探到的IP地址 | 关联后的数据包 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 单个跳变周期 | 无IP地址跳变 | 10.0.0.1、10.0.0.20 | (10.0.0.1,10.0.0.20) |
| DAH | 10.0.0.78、10.0.0.64 | (10.0.0.78,10.0.0.64) | |
| 双虚假IP地址跳变 | 10.0.0.230、10.0.0.159、10.0.0.144、10.0.0.67 | (10.0.0.230,10.0.0.67)、(10.0.0.144,10.0.0.159) | |
| 多个跳变周期 | 无IP地址跳变 | 10.0.0.1、10.0.0.20 | (10.0.0.1,10.0.0.20) |
| DAH | 10.0.0.78、10.0.0.64、10.0.0.45、10.0.0.88、10.0.0.253、10.0.0.79、10.0.0.158、10.0.0.243、10.0.0.153、10.0.0.22 | (10.0.0.78,10.0.0.64)、 (10.0.0.45,10.0.0.88)、(10.0.0.253,10.0.0.79)、(10.0.0.158,10.0.0.243)、(10.0.0.153,10.0.0.22) | |
| 双虚假IP地址跳变 | 10.0.0.230、10.0.0.67、10.0.0.144、10.0.0.159、10.0.0.183、10.0.0.115、10.0.0.94、10.0.0.131、10.0.0.244、10.0.0.120、10.0.0.125、10.0.0.204、10.0.0.68、10.0.0.134、10.0.0.32、10.0.0.218、10.0.0.52、10.0.0.163、10.0.0.128、10.0.0.90 | (10.0.0.230,10.0.0.67)、(10.0.0.144,10.0.0.159)、(10.0.0.183,10.0.0.115)、(10.0.0.94,10.0.0.131)、(10.0.0.244,10.0.0.120)、(10.0.0.125,10.0.0.204)、(10.0.0.68,10.0.0.134)、(10.0.0.32,10.0.0.218)、(10.0.0.52,10.0.0.163)、(10.0.0.128,10.0.0.90) | |
| [1] | WANG Juan, YANG Hongyuan, FAN Chengyang. A SDN Dynamic Honeypot with Multi-phase Attack Response[J]. Netinfo Security, 2021, 21(1):27-40. |
| 王鹃, 杨泓远, 樊成阳. 一种基于多阶段攻击响应的SDN动态蜜罐[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(1):27-40. | |
| [2] | FU Yu, LI Hongcheng, WU Xiaoping, et al. Detecting APT Attacks: A Survey from the Perspective of Big Data Analysis[J]. Journal on Communications. 2015, 36(11):1-14. |
| 付钰, 李洪成, 吴晓平, 等. 基于大数据分析的APT攻击检测研究综述[J]. 通信学报, 2015, 36(11):1-14. | |
| [3] | YANG Wentao. A Study on the Attacks to Networks[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan University, 2004. |
| 杨文涛. 网络攻击技术研究[D]. 成都: 四川大学, 2004. | |
| [4] | JAJODIA S, GHOSH A K, SWARUP V, et al. Moving Target Defense: Creating Asymmetric Uncertainty for Cyber Threats[M]. Heidelberg: Springer Science & Business Media, 2011. |
| [5] | CHO J H, SHARMA D P, ALAVIZADEH H, et al. Toward Proactive, Adaptive Defense: A Survey on Moving Target Defense[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2020, 22(1):709-745. |
| [6] | XU Xiaoyu, HU Hao, ZHANG Hongqi, et al. Moving Target Defense Method of Random Routing Based on Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient[J]. Journal on Communications, 2021, 42(6):41-51. |
| 徐潇雨, 胡浩, 张红旗, 等. 基于深度确定性策略梯度的随机路由移动目标防御方法[J]. 通信学报, 2021, 42(6):41-51. | |
| [7] | CAI Guilin, WANG Baosheng, WANG Tianzuo, et al. Research and Development of Moving Target Defense Technology[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2016, 53(5):968-987. |
| 蔡桂林, 王宝生, 王天佐, 等. 移动目标防御技术研究进展[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2016, 53(5):968-987. | |
| [8] | KRYLOV V, KRAVTSOV K. Interception Resistance IP Fast Hopping Based Protocol[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1403.7371, 2014-03-28. |
| [9] | JAFARIAN J H, AL-SHAER E, DUAN Qi. OpenFlow Random Host Mutation: Transparent Moving Target Defense Using Software Defined Networking[C]//ACM. 1st Workshop on Hot Topics in Software Defined Networks, August 13-14, 2012, Helsinki, Finland. New York: ACM, 2012: 127-132. |
| [10] | MCKEOWN N, ANDERSON T, BALAKRISHNAN H, et al. OpenFlow: Enabling Innovation in Campus Networks[J]. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2008, 38(2):69-74. |
| [11] | BJORNER N, MOURA L D. Z310: Applications, Enablers, Challenges and Directions[EB/OL]. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.147.5558, 2009-10-16. |
| [12] | DUNLOP M, GROAT S, URBANSKI W, et al. MT6D: A Moving Target Ipv6 Defense[C]//IEEE. 2011-MILCOM 2011 Military Communications Conference, November 7-10, 2011, Baltimore, MD, USA. Piscataway: IEEE, 2011: 1321-1326. |
| [13] | SHARMA D P, KIM D S, YOON S, et al. FRVM: Flexible Random Virtual IP Multiplexing in Software-defined Networks[C]//IEEE. 2018 17th IEEE International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications, August 1-3, 2018, New York, USA. Piscataway: IEEE, 2018: 579-587. |
| [14] | JAFARIAN J H, AL-SHAER E, DUAN Qi. Spatio-temporal Address Mutation for Proactive Cyber Agility Against Sophisticated Attackers[C]//ACM. Proceedings of the First ACM Workshop on Moving Target Defense, November 7-8, 2014, Scottsdale, Arizona, USA. New York: ACM, 2014: 69-78. |
| [15] |
WANG Pengkun, ZHOU Momiao, DING Zhizhong. A Two-layer IP Hopping-based Moving Target Defense Approach to Enhancing the Security of Mobile Ad-hoc Networks[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(7):2355-2369.
doi: 10.3390/s21072355 URL |
| [16] |
MATSUMOTO M, NISHIMURA T. Mersenne Twister: A 623-dimensionally Equidistributed Uniform Pseudo-random Number Generator[J]. ACM Transactions on Modeling and Computer Simulation (TOMACS), 1998, 8(1):3-30.
doi: 10.1145/272991.272995 URL |
| [17] |
HE Yun, ZHANG Min, YANG Xiaolong, et al. The Intelligent Offense and Defense Mechanism of Internet of Vehicles Based on the Differential Game-IP Hopping[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8(99):115217-115227.
doi: 10.1109/Access.6287639 URL |
| [18] | LI Chaoyang, TAN Jinglei, HU Ruiqin, et al. Moving Target Defense Method Based on Double Address Hopping[J]. Netinfo Security, 2021, 21(2):24-33. |
| 李朝阳, 谭晶磊, 胡瑞钦, 等. 基于双重地址跳变的移动目标防御方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(2):24-33. | |
| [19] | HU Fei, HAO Qi, BAO Ke. A Survey on Software-defined Network and OpenFlow: From Concept to Implementation[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2014, 16(4):2181-2206. |
| [20] | ZHANG Chaokun, CUI Yong, TANG Hehe, et al. State-of-the-art Survey on Software-defined Networking(SDN)[J]. Journal of Software, 2015, 26(1):62-81. |
| 张朝昆, 崔勇, 唐翯翯, 等. 软件定义网络(SDN)研究进展[J]. 软件学报, 2015, 26(1):62-81. | |
| [21] | LI Yuanchen, LIU Weiqun. Analysis of the Shortest Route in Network on Dijkstra Algorithm[J]. Microcomputer Applications, 2004, 25(3):295-298, 362. |
| 李元臣, 刘维群. 基于Dijkstra算法的网络最短路径分析[J]. 微计算机应用, 2004, 25(3):295-298, 362. | |
| [22] | LI Yan, HAO Zhian, LI Ning, et al. Research on SDN Architecture Simulation Based on Mininet[J]. Computer & Network, 2014, 40(5):57-59. |
| 李艳, 郝志安, 李宁, 等. 基于mininet的SDN架构仿真研究[J]. 计算机与网络, 2014, 40(5):57-59. |
| [1] | 李朝阳, 谭晶磊, 胡瑞钦, 张红旗. 基于双重地址跳变的移动目标防御方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(2): 24-33. |
| [2] | 魏占祯, 彭星源, 赵洪. SDN中基于用户信任度的资源访问控制方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(10): 33-40. |
| [3] | 吴云坤, 姜博, 潘瑞萱, 刘玉岭. 一种基于零信任的SDN网络访问控制方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(8): 37-46. |
| [4] | 时向泉, 陶静, 赵宝康. 面向虚拟化环境的网络访问控制系统[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(10): 1-9. |
| [5] | 董庆贺, 何倩, 江炳城, 刘鹏. 面向云数据库的多租户属性基安全隔离与数据保护方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(7): 60-68. |
| [6] | 朱维军, 樊永文, 班绍桓. 动态虚拟MSISDN的拟态自动机模型与安全性验证方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(4): 15-22. |
| [7] | 魏占祯, 王守融, 李兆斌, 李伟隆. 基于OpenFlow的SDN终端接入控制研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(4): 23-31. |
| [8] | 门红, 姚顺利. 安全监控虚拟云安全网络架构研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2017, 17(3): 14-20. |
| [9] | 梁昊鸣, 陈春林, 刘锡, 刘志鹏. 基于OpenFlow的恶意网站防范模型设计与研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2017, 17(1): 77-83. |
| [10] | 王鑫, 高能, 马存庆, 薛聪. 分布式SDN控制器的规则冲突解决方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2014, 14(9): 6-6. |
| [11] | 薛聪, 马存庆, 刘宗斌, 章庆隆. 一种安全SDN控制器架构设计[J]. 信息网络安全, 2014, 14(9): 34-38. |
| [12] | 胡章丰;郭春梅;毕学尧. 云计算及SDN与安全技术研究[J]. , 2013, 13(10): 0-0. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||