信息网络安全 ›› 2023, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (6): 74-90.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2023.06.008
面向调制识别的对抗样本研究综述
- 1.陆军工程大学通信工程学院,南京 210001
2.中国人民解放军31693部队,哈尔滨 150036
-
收稿日期:2023-04-23出版日期:2023-06-10发布日期:2023-06-20 -
通讯作者:曾维军zwj3103@126.com -
作者简介:蒋曾辉(1998—),男,湖南,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为信号处理、对抗攻击、对抗防御|曾维军(1986—),男,江西,讲师,博士,主要研究方向为信号处理与机器学习|陈璞(1992—),男,吉林,讲师,硕士,主要研究方向为通信网络技术|武士涛(1986—),男,山东,工程师,主要研究方向为通信技术 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(62001515)
Review of Adversarial Samples for Modulation Recognition
JIANG Zenghui1, ZENG Weijun1( ), CHEN Pu1, WU Shitao2
), CHEN Pu1, WU Shitao2
- 1. Institute of Communication Engineering, Army Engineering University of PLA, Nanjing 210001, China
2. 31693 Troops of PLA, Harbin 150036, China
-
Received:2023-04-23Online:2023-06-10Published:2023-06-20
摘要:
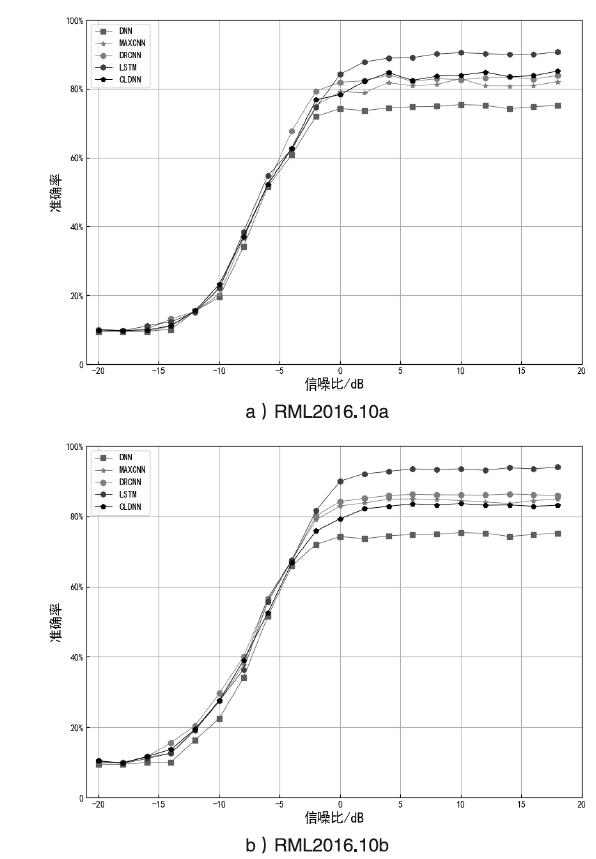
调制方式识别是认知无线电、电磁对抗等领域中的关键一环,也是进行接收机高效信号处理的重要前提。深度学习具有自主分析、自动特征提取和非线性拟合等传统手段无法比拟的独特优势,其在调制方式识别中表现出了具大潜力,但深度学习模型容易受到对抗样本的攻击,对调制识别任务造成严重影响。尽管对抗样本攻击在计算机视觉、自然语言处理等领域得到了广泛研究,但其在调制识别领域的研究成果较为零散。本文基于调制识别的独特特性,介绍了基于深度学习的调制识别技术,构建了调制识别的问题模型,阐述了目前常见的神经网络在调制识别中的应用现状并列举和对比了调制识别常用数据集及其仿真结果。通过回顾攻击类型、对抗样本生成和防御策略总结了最新的研究成果,建立了不同攻击和防御类别的分类法,并讨论了对抗样本在无线通信中的未来前景。
中图分类号:
引用本文
蒋曾辉, 曾维军, 陈璞, 武士涛. 面向调制识别的对抗样本研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(6): 74-90.
JIANG Zenghui, ZENG Weijun, CHEN Pu, WU Shitao. Review of Adversarial Samples for Modulation Recognition[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(6): 74-90.
表1
常用RadioML数据集
| 数据集 | 信号调制类型 | 样本数 | 信噪比/dB |
|---|---|---|---|
| RML2016.04c | BPSK、8PSK、QPSK、CPFSK、GFSK、PAM4、16QAM、64QAM、AM-SSB、AM-DSB、WBFM | 220000 | -20~18 |
| RML2016.10a | BPSK、8PSK、QPSK、CPFSK、GFSK、PAM4、16QAM、64QAM、AM-SSB、AM-DSB、WBFM | 220000 | -20~18 |
| RML2016.10b | BPSK、8PSK、QPSK、CPFSK、GFSK、PAM4、16QAM、64QAM、AM-DSB、WBFM | 1200000 | -20~18 |
| RML2018.01a | BPSK、8PSK、16PSK、32PSK、QPSK、OQPSK、4ASK、8ASK、16APSK、32APSK、64APSK、128APSK、16QAM、32QAM、64QAM、128QAM、256QAM、FM、GMSK、OOK、AM-SSB-WC、AM-SSB-SC、AM-DSB-WC、AM-DSB-SC | 2000000 | -20~30 |
表2
面向调制识别的对抗攻击总结
| 方案 | 攻击类型 | 描述 | 攻击 算法 | 数据库 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文献[ | 非定向、白盒 | 评估基于原始I/Q的调制分类的漏洞 | FGSM | RML2016.10a |
| 文献[ | 定向、白盒 | 检验基于DL的自动调制分类器在直接访问其输入的对手存在的情况下是如何崩溃的,验证定向攻击优于非定向攻击 | FGSM、MIM | RML2016.10a |
| 文献[ | 白盒 | 测试FGSM、L-BFGS两种类型的对抗性攻击的攻击 效率 | FGSM、 L-BFGS | RML2016.04c |
| 文献[ | 定向、非定向、白盒 | 比较了常见攻击算法在调制识别领域的性能差异,探索对抗性攻击的可行性和有效性,并确定攻击不可见性和成功的最佳扰动规模 | FGSM、BIM、PGD、MIM | RML2016.10a |
| 文献[ | 定向、非定向、白盒 | 提出一种基于动态迭代的用于攻击DNN模型的对抗攻击方法 | MIM、DIM | RML2016.10a |
| 文献[ | 定向、非定向、白盒 | 通过干扰信道输入符号,最大限度地降低入侵者确定发射机使用的调制方案的 准确性 | PGD | 本地生成数据 |
| 文献[ | 定向、白盒 | 通过传输对抗性扰动的合作干扰器欺骗基于DL的窃听者,以向窃听者隐藏5G通信 | FGM | 本地生成数据 |
| 文献[ | 定向、白盒 | 应用CW攻击在合成和实时捕获的RF数据点上生成有目标的对抗性样本 | CW | RML2018.01a 和本地生成 数据 |
| 文献[ | 定向、白盒 | 研究使用多个天线在无线接收器处对基于DNN的调制分类器的输入产生不同信道效应(根据总功率预算)的多个并发扰动 | FGM | RML2016.10a |
| 文献[ | 定向、白盒 | 利用不同的数据驱动下采样策略,研究对抗攻击对AMR模型的影响 | CW | RML2016.10b |
| 文献[ | 定向、非定向、白盒 | 探索如何通过考虑信道效应以及对手的功率约束来发起逼真的对抗攻击 | MRPP | 本地生成数据 |
| 文献[ | 定向、非定向、白盒 | 研究了信道对代理模型的影响,并针对基于DNN的无线信号分类器进行对抗性攻击 | MRPP | 本地生成数据 |
| 文献 [ | 黑盒 | 提出了一种检测容忍的黑盒对抗攻击模型,可以极大降低对抗样本被检测的概率 | DTBA | RML2016.10a |
| 文献[ | 非定向、黑盒 | 提出了位置不变的对抗性攻击方法用于提升对抗样本迁移性 | FGSM、PGD | RML2016.10a |
| 文献[ | 定向、非定向、黑盒 | 探索在不同接收器存在真实的信道效应和多个分类器的情况下设计真实的对抗性攻击 | FGM、UAP | RML2016.10a |
| 文献[ | 定向、非定向、黑盒 | 展示了DL模型对对抗攻击的易感性,并提出了在调制分类中制作对抗样本的实用方法 | UAP、FGM | RML2016.10a |
| 文献[ | 定向、黑盒 | 通过使用前向纠错(FEC)扩展通信感知对抗攻击 | ATN | 本地生成数据 |
| 文献 [ | 定向、非定向、黑盒 | 通过在训练过程中引入频谱欺骗损失度量,使频谱形状更符合原始信号 | AMN | 本地生成数据 |
| 文献[ | 定向、非定向、黑盒 | 基于AdvGAN,提出一个输入不可知的对抗攻击 | AdvGAN | RML2016.10a |
| 文献[ | 定向、非定向、黑盒 | 提出了一种基于L2范数的LIW生成方法,该方法可以降低调制方式被第三方识别的概率,而不影响友方的可靠通信 | MIM | RML2016.10a |
表3
面向调制识别的对抗样本防御总结
| 方案 | 防御类别 | 防御策略 |
|---|---|---|
| 文献[ | 统计方法 | PAPR和DL分类器的Softmax输出检测对抗样本 |
| 文献[ | 增强模型鲁棒性 | 使用对抗性训练训练调制识别模型 |
| 文献[ | 增强模型鲁棒性 | 使用带有随机平滑技术的对抗性训练方法训练调制识别模型 |
| 文献[ | 增强模型鲁棒性 | 使用带有认证防御技术的对抗性训练方法训练调制识别模型 |
| 文献[ | 增强模型鲁棒性 | 使用自动编码器对模型进行预训练 |
| 文献[ | 增强模型鲁棒性 | 通过对于信号进行标签平滑和高斯噪声注入达到增强的目的 |
| 文献[ | 添加组件 | 利用知识提炼防御来自攻击者的黑盒检测攻击 |
| 文献[ | 添加组件 | 基于多特征融合的对抗样本检测 |
| 文献[ | 添加组件 | 使用DL分类器的自动编码器去除非显著特征 |
| 文献[ | 添加组件 | 利用GAN的生成特性,提出了防御GAN |
| 文献[ | 添加组件 | 利用混合生成对抗网络思想解决了AdvGAN的模式坍塌问题 |
| [1] | HUANG Zhitao, YANG Jie, WANG Xiang, et al. A Survey of Modulation Recognition Algorithms in Non-Cooperative Communication[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2019, 37(4): 55-62. |
| [2] |
ZEBARJADI M, TEIMOURI M. Non-Cooperative Burst Detection and Synchronisation in Downlink TDMA-Based Wireless Communication Networks[J]. IET Communications, 2019, 13(7): 863-872.
doi: 10.1049/cmu2.v13.7 URL |
| [3] |
O’SHEA T J, ROY T, CLANCY T C. Over-the-Air Deep Learning Based Radio Signal Classification[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2018, 12(1): 168-179.
doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2018.2797022 URL |
| [4] |
O’SHEA T, HOYDIS J. An Introduction to Deep Learning for the Physical Layer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2017, 3(4): 563-575.
doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2017.2758370 URL |
| [5] |
SHI Qinghua, KARASAWA Y. Automatic Modulation Identification Based on the Probability Density Function of Signal Phase[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2012, 60(4): 1033-1044.
doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2012.021712.100638 URL |
| [6] | SZEGEDY C, ZAREMBA W, SUTSKEVER I, et al. Intriguing Properties of Neural Networks[EB/OL]. (2014-02-19)[2023-04-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.6199. |
| [7] |
SADEGHI M, LARSSON E G. Physical Adversarial Attacks Against End-to-End Autoencoder Communication Systems[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2019, 23(5): 847-850.
doi: 10.1109/COML.4234 URL |
| [8] | WEAVER C S, COLE C A, KRUMLAND R B, et al. The Automatic Classification of Modulation Types by Pattern Recognition[EB/OL]. (1969-04-01)[2023-04-10]. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/THE-AUTOMATIC-CLASSIFICATION-OF-MODULATION-TYPES-BY-Weaver-Cole/bbfd299d0beb7e66f2662625717327211d352709. |
| [9] |
LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-Based Learning Applied to Document Recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324.
doi: 10.1109/5.726791 URL |
| [10] |
HOCHREITER S, SCHMIDHUBER J. Long Short-Term Memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735-1780.
doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 pmid: 9377276 |
| [11] | O’SHEA T J, CORGAN J, CLANCY T C. Convolutional Radio Modulation Recognition Networks[C]// Springer. Engineering Applications of Neural Networks:17th International Conference. Berlin:Springer, 2016: 213-226. |
| [12] |
HU Shisheng, PEI Yiyang, LIANG P P, et al. Deep Neural Network for Robust Modulation Cassification Under Uncertain Noise Conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 69(1): 564-577.
doi: 10.1109/TVT.25 URL |
| [13] |
ZHENG Shilian, QI Peihan, CHEN Shichuan, et al. Fusion Methods for CNN-Based Automatic Modulation Classification[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 66496-66504.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2918136 |
| [14] |
PENG Shengliang, JIANG Hanyu, WANG Huaxia, et al. Modulation Classification Based on Signal Constellation Diagrams and Deep Learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 30(3): 718-727.
doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2850703 URL |
| [15] |
TU Ya, LIN Yun. Deep Neural Network Compression Technique Towards Efficient Digital Signal Modulation Recognition in Edge Device[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 58113-58119.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2913945 |
| [16] | ZHANG Zhibo, FAN Yaxuan, MENG Xiao. Pattern Recognition Method of Communication Interference Based on Power Spectrum Density and Neural Network[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2019, 17(6): 959-963. |
| 张智博, 樊雅玄, 孟骁. 基于谱图和神经网络的通信干扰模式识别方法[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2019, 17(6): 959-963. | |
| [17] |
ZHA Xiong, PENG Hua, QIN Xin, et al. Modulation Recognition Method Based on Multi-Inputs Convolution Neural Network[J]. Journal on Communications, 2019, 40(11): 30-37.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2019206 |
|
查雄, 彭华, 秦鑫, 等. 基于多端卷积神经网络的调制识别方法[J]. 通信学报, 2019, 40(11): 30-37.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2019206 |
|
| [18] | TU Ya, LIN Yun, WANG Jin, et al. Semi-Supervised Learning with Generative Adversarial Networks on Digital Signal Modulation Classification[J]. Computers, Materials&Continua, 2018, 55(2): 243-254. |
| [19] | WU Hao, ZHOU Liang, LI Yaxing, et al. Modulation Recognition Method Based on Convolutional Neural Networks and Sparse Filtering[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(9): 2114-2121. |
| 吴灏, 周亮, 李亚星, 等. 基于卷积神经网络和稀疏滤波的调制识别方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(9): 2114-2121. | |
| [20] |
TANG Bin, TU Ya, ZHANG Zhaoyue, et al. Digital Signal Modulation Classification with Data Augmentation Using Generative Adversarial Nets in Cognitive Radio Networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 15713-15722.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2815741 URL |
| [21] | O’SHEA T J, WEST N. Radio Machine Learning Dataset Generation with GNU Radio[EB/OL]. (2016-09-06)[2023-04-10]. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Radio-Machine-Learning-Dataset-Generation-with-GNU-O'Shea-West/227e0591634cef50d0bcfc73fe6c5b34a2256e5f. |
| [22] |
WANG Yu, LIU Miao, YANG Jie, et al. Data-Driven Deep Learning for Automatic Modulation Recognition in Cognitive Radios[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(4): 4074-4077.
doi: 10.1109/TVT.25 URL |
| [23] | WEST N E, O’SHEA T. Deep Architectures for Modulation Recognition[C]// IEEE. 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks (DySPAN). New York:IEEE, 2017: 1-6. |
| [24] | GOODFELLOW I J, SHLENS J, SZEGEDY C. Explaining and Harnessing Adversarial Examples[EB/OL]. (2015-03-20)[2023-04-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6572. |
| [25] | KURAKIN A, GOODFELLOW I J, BENGIO S. Adversarial Examples in the Physical World[EB/OL]. (2017-02-11)[2023-04-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.02533. |
| [26] | DONG Yinpeng, LIAO Fangzhou, PANG Tianyu, et al. Boosting Adversarial Attacks with Momentum[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. New York: IEEE. 2018: 9185-9193. |
| [27] | MADRY A, MAKELOV A, SCHMIDT L, et al. Towards Deep Learning Models Resistant to Adversarial Attacks[EB/OL]. (2019-09-04)[2023-04-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.06083. |
| [28] | SRIRAMANAN G, ADDEPALLI S, BABURAJ A. Guided Adversarial Attack for Evaluating and Enhancing Adversarial Defenses[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2020, 33: 20297-20308. |
| [29] | CARLINI N, WAGNER D. Towards Evaluating the Robustness of Neural Networks[C]// IEEE. 2017 IEEE symposium on security and privacy (sp). New York:IEEE, 2017: 39-57. |
| [30] | BALUJA S, FISCHER I. Adversarial Transformation Networks: Learning to Generate Adversarial Examples[EB/OL]. (2017-03-28)[2023-04-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.09387. |
| [31] |
SU Jiawei, VARGAS D V, SAKURAI K. One Pixel Attack for Fooling Deep Neural Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2019, 23(5): 828-841.
doi: 10.1109/TEVC.4235 URL |
| [32] | MOOSAVI-DEZFOOLI S M, FAWZI A, FAWZI O, et al. Universal Adversarial Perturbations[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2017: 1765-1773. |
| [33] | XIAO Chaowei, LI Bo, ZHU Junyan, et al. Generating Adversarial Examples with Adversarial Networks[EB/OL]. (2019-02-14)[2023-04-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.02610. |
| [34] |
FLOWERS B, BUEHRER R M, HEADLEY W C. Evaluating Adversarial Evasion Attacks in the Context of Wireless Communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2019, 15: 1102-1113.
doi: 10.1109/TIFS.10206 URL |
| [35] | BAIR S, DELVECCHIO M, FLOWERS B, et al. On the Limitations of Targeted Adversarial Evasion Attacks Against Deep Learning Enabled Modulation Recognition[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the ACM Workshop on Wireless Security and Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2019 : 25-30. |
| [36] | KE Da, HUANG Zhitao, WANG Xiang, et al. Application of Adversarial Examples in Communication Modulation Classification[C]// IEEE. 2019 International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW). New York:IEEE, 2019: 877-882. |
| [37] |
LIN Yun, ZHAO Haojun, MA Xuefei, et al. Adversarial Attacks in Modulation Recognition with Convolutional Neural Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2020, 70(1): 389-401.
doi: 10.1109/TR.24 URL |
| [38] | LIU Mingqian, ZHANG Zhenju, ZHAO Nan, et al. Adversarial Attacks on Deep Neural Networks Based Modulation Recognition[C]// IEEE. IEEE INFOCOM 2022-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS). New York:IEEE, 2022: 1-6. |
| [39] |
HAMEED M Z, GYÖRGY A, GÜNDÜZ D. The Best Defense is a Good Offense: Adversarial Attacks to Avoid Modulation Detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 16: 1074-1087.
doi: 10.1109/TIFS.10206 URL |
| [40] | HAMEED M Z, GYÖRGY A, GÜNDÜZ D. Communication Without Interception: Defense Against Modulation Detection[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP ). New York:IEEE, 2019: 1-5. |
| [41] | KIM B, SAGDUYU Y E, DAVASLIOGLU K, et al. How to Make 5G Communications" Invisible": Adversarial Machine Learning for Wireless Privacy[C]// IEEE. 2020 54th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers. New York: IEEE, 2020: 763-767. |
| [42] | KOKALJ-FILIPOVIC S, MILLER R, MORMAN J. Targeted Adversarial Examples Against RF Deep Classifiers[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the ACM Workshop on Wireless Security and Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2019: 6-11. |
| [43] | KIM B, SAGDUYU Y E, ERPEK T, et al. Adversarial Attacks with Multiple Antennas Against Deep Learning-Based Modulation Classifiers[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps). New York:IEEE, 2020: 1-6. |
| [44] |
YI J, GAMAL A E. Gradient-Based Adversarial Deep Modulation Classification with Data-Driven Subsamplings[EB/OL]. (2021-04-03)[2023-04-10]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2104.06375.
doi: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2104.06375 |
| [45] | KIM B, SAGDUYU Y E, DAVASLIOGLU K, et al. Over-the-Air Adversarial Attacks on Deep Learning Based Modulation Classifier over Wireless Channels[C]// IEEE. 2020 54th Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems (CISS). New York:IEEE, 2020: 1-6. |
| [46] | KIM B, SAGDUYU Y E, ERPEK T, et al. Channel Effects on Surrogate Models of Adversarial Attacks Against Wireless Signal Classifiers[C]// IEEE. ICC 2021-IEEE International Conference on Communications. New York: IEEE, 2021: 1-6. |
| [47] |
QI Peihan, JIANG Tao, WANG Lizhan, et al. Detection Tolerant Black-Box Adversarial Attack Against Automatic Modulation Classification with Deep Learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2022, 71(2): 674-686.
doi: 10.1109/TR.2022.3161138 URL |
| [48] | YU Zhen, XIONG Yifeng, HE Kun, et al. Position-Invariant Adversarial Attacks on Neural Modulation Recognition[C]// IEEE. ICASSP 2022-2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). New York:IEEE, 2022: 3483-3487. |
| [49] |
KIM B, SAGDUYU Y E, DAVASLIOGLU K, et al. Channel-Aware Adversarial Attacks Against Deep Learning-Based Wireless Signal Classifiers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 21(6): 3868-3880.
doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3124855 URL |
| [50] |
SADEGHI M, LARSSON E G. Adversarial Attacks on Deep-Learning Based Radio Signal Classification[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2018, 8(1): 213-216.
doi: 10.1109/LWC.2018.2867459 URL |
| [51] | DELVECCHIO M, FLOWERS B, HEADLEY W C. Effects of Forward Error Correction on Communications Aware Evasion Attacks[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE 31st Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications. New York: IEEE, 2020: 1-7. |
| [52] | DELVECCHIO M, ARNDORFER V, HEADLEY W C. Investigating a Spectral Deception Loss Metric for Training Machine Learning-Based Evasion Attacks[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 2nd ACM Workshop on Wireless Security and Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2020: 43-48. |
| [53] | BAHRAMALI A, NASR M, HOUMANSADR A, et al. Robust Adversarial Attacks Against DNN-Based Wireless Communication Systems[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 2021 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2021: 126-140. |
| [54] | XIE Haidong, TAN Jia, ZHANG Xiaoying, et al. Low-Interception Waveform: To Prevent the Recognition of Spectrum Waveform Modulation via Adversarial Examples[C]// IEEE. 2021 XXXIVth General Assembly and Scientific Symposium of the International Union of Radio Science (URSI GASS). New York:IEEE, 2021: 1-4. |
| [55] | PAPERNOT N, MCDANIEL P, GOODFELLOW I, et al. Practical Black-Box Attacks Against Machine Learning[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 2017 ACM on Asia Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2017: 506-519. |
| [56] | PAPERNOT N, MCDANIEL P, GOODFELLOW I. Transferability in Machine Learning: From Phenomena to Black-Box Attacks Using Adversarial Samples[EB/OL]. (2016-05-24)[2023-04-10]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1605.07277. pdf. |
| [57] |
VITTER J S. Random Sampling with a Reservoir[J]. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software (TOMS), 1985, 11(1): 37-57.
doi: 10.1145/3147.3165 URL |
| [58] | LI Pengcheng, YI Jinfeng, ZHANG Lijun. Query-Efficient Black-Box Attack by Active Learning[C]// IEEE. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM). New York:IEEE, 2018: 1200-1205. |
| [59] | XIE Cihang, ZHANG Zhishuai, ZHOU Yuyin, et al. Improving Transferability of Adversarial Examples with Input Diversity[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2019 : 2730-2739. |
| [60] | ZOU Junhua, PAN Zhisong, QIU Junyang, et al. Improving the Transferability of Adversarial Examples with Resized-Diverse-Inputs, Diversity-Ensemble and Region Fitting[C]// Springer. Computer Vision-ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference. Berlin:Springer. 2020: 563-579. |
| [61] |
GOODFELLOW I, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative Adversarial Networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2020, 63(11): 139-144.
doi: 10.1145/3422622 URL |
| [62] | XIAO Chaowei, LI Bo, ZHU Junyan, et al. Generating Adversarial Examples with Adversarial Networks[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York: ACM, 2018: 3905-3911. |
| [63] | SAHAY R, BRINTON C G, LOVE D J. Frequency-Based Automated Modulation Classification in the Presence of Adversaries[C]// IEEE. ICC 2021-IEEE International Conference on Communications. New York: IEEE, 2021: 1-6. |
| [64] | BERIAN A, STAAB K, DITZLER G, et al. Adversarial Filters for Secure Modulation Classification[C]// IEEE. 2021 55th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers. New York: IEEE, 2021: 361-367. |
| [65] |
SAGDUYU Y E, SHI Yi, ERPEK T. Adversarial Deep Learning for Over-the-Air Spectrum Poisoning Attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2019, 20(2): 306-319.
doi: 10.1109/TMC.7755 URL |
| [66] | RESTUCCIA F, D’ORO S, AL-SHAWABKA A, et al. Hacking the Waveform: Generalized Wireless Adversarial Deep Learning[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 2nd ACM Workshop on Wireless Security and Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2020: 49-54. |
| [67] | KOKALJ-FILIPOVIC S, MILLER R, VANHOY G. Adversarial Examples in RF Deep Learning: Detection and Physical Robustness[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP). New York:IEEE, 2019: 1-5. |
| [68] | MAROTO J, BOVET G, FROSSARD P. SafeAMC: Adversarial Training for Robust Modulation Recognition Models[C]// IEEE. 2022 30th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO). New York:IEEE, 2022: 1-6. |
| [69] | COHEN J, ROSENFELD E, KOLTER Z. Certified Adversarial Robustness via Randomized Smoothing[EB/OL]. (2019-06-15)[2023-04-10]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.02918. pdf. |
| [70] | KOKALJ-FILIPOVIC S, MILLER R, CHANG N, et al. Mitigation of Adversarial Examples in RF Deep Classifiers Utilizing AutoEncoder Pre-training[C]// IEEE. 2019 International Conference on Military Communications and Information Systems (ICMCIS). New York:IEEE, 2019: 1-6. |
| [71] |
ZHANG Lu, LAMBOTHARAN S, ZHENG Gan, et al. Countermeasures Against Adversarial Examples in Radio Signal Classification[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(8): 1830-1834.
doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3083099 URL |
| [72] | AN Zhihui, QI Peihan, ZHOU Xiaoyu, et al. A Robust Signal Modulation Recognition Method Against Black-Box Detection Attack[C]// Springer. 15th EAI International Conference, Mobile Multimedia Communications. Berlin:Springer, 2023: 329-339. |
| [73] |
XU Dongwei, YANG Hao, GU Chuntao, et al. Adversarial Examples Detection of Radio Signals Based on Multifeature Fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2021, 68(12): 3607-3611.
doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2021.3095663 URL |
| [74] | SAMANGOUEI P, KABKAB M, CHLLAPPA R. Defense-Gan: Protecting Classifiers Against Adversarial Attacks Using Generative Models[EB/OL]. (2018-05-18)[2023-04-10]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1805.06605.pdf. |
| [75] | SHTAIWI E, El OUADRHIRI A, MORADIKIA M, et al. Mixture GAN For Modulation Classification Resiliency Against Adversarial Attacks[C]// IEEE. GLOBECOM 2022-2022 IEEE Global Communications Conference. New York: IEEE, 2022: 1472-1477. |
| [76] |
XU Weilin, EVANS D, QI Yanjun. Feature Squeezing: Detecting Adversarial Examples in Deep Neural Networks[EB/OL]. (2017-11-05)[2023-04-10]. https://doi.org/10.14722/ndss.2018.23198.
doi: https://doi.org/10.14722/ndss.2018.23198 |
| [77] | ROTH K, KILCHER Y, HOFMANN T. The Odds are Odd: A Statistical Test for Detecting Adversarial Examples[EB/OL]. (2019-05-09)[2023-04-10]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.04818.pdf. |
| [78] | HOANG Quan, NGUYEN T D, LE T, et al. MGAN: Training Generative Adversarial Nets with Multiple Generators[EB/OL]. (2017-10-27)[2023-04-10]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1708.02556.pdf. |
| [1] | 李志华, 王志豪. 基于LCNN和LSTM混合结构的物联网设备识别方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(6): 43-54. |
| [2] | 赵小林, 王琪瑶, 赵斌, 薛静锋. 基于机器学习的匿名流量分类方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(5): 1-10. |
| [3] | 陈梓彤, 贾鹏, 刘嘉勇. 基于Siamese架构的恶意软件隐藏函数识别方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(5): 62-75. |
| [4] | 赵彩丹, 陈璟乾, 吴志强. 基于多通道联合学习的自动调制识别网络[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(4): 20-29. |
| [5] | 张玉健, 刘代富, 童飞. 基于局部图匹配的智能合约重入漏洞检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(8): 1-7. |
| [6] | 刘光杰, 段锟, 翟江涛, 秦佳禹. 基于多特征融合的移动流量应用识别[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(7): 18-26. |
| [7] | 王浩洋, 李伟, 彭思维, 秦元庆. 一种基于集成学习的列车控制系统入侵检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(5): 46-53. |
| [8] | 胡卫, 赵文龙, 陈璐, 付伟. 基于Logits向量的JSMA对抗样本攻击改进算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(3): 62-69. |
| [9] | 郑耀昊, 王利明, 杨婧. 基于网络结构自动搜索的对抗样本防御方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(3): 70-77. |
| [10] | 刘峰, 杨成意, 於欣澄, 齐佳音. 面向去中心化双重差分隐私的谱图卷积神经网络[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(2): 39-46. |
| [11] | 夏强, 何沛松, 罗杰, 刘嘉勇. 基于普遍对抗噪声的高效载体图像增强算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(2): 64-75. |
| [12] | 林发鑫, 张健. 虚拟化平台异常行为检测系统的设计与实现[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(11): 62-67. |
| [13] | 仝鑫, 金波, 王靖亚, 杨莹. 一种面向Android恶意软件的多视角多任务学习检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 1-7. |
| [14] | 张郅, 李欣, 叶乃夫, 胡凯茜. 融合多重风格迁移和对抗样本技术的验证码安全性增强方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 129-135. |
| [15] | 高昌锋, 肖延辉, 田华伟. 基于多阶段渐进式神经网络的图像相机指纹提取算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(10): 15-23. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||