信息网络安全 ›› 2023, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (6): 91-103.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2023.06.009
威胁情报驱动的动态威胁狩猎方法
吴尚远1,2, 申国伟1,2( ), 郭春1,2, 陈意1,2
), 郭春1,2, 陈意1,2
- 1.贵州大学文本计算与认知智能教育部工程研究中心,贵阳 550025
2.贵州大学省部共建公共大数据国家重点实验室,贵阳 550025
-
收稿日期:2023-04-28出版日期:2023-06-10发布日期:2023-06-20 -
通讯作者:申国伟gwshen@gzu.edu.cn -
作者简介:吴尚远(1997—),男,广西,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为威胁狩猎|申国伟(1986—),男,湖南,教授,博士,主要研究方向为网络与信息安全、大数据、高性能网络和体系建模仿真|郭春(1986—),男,贵州,教授,博士,主要研究方向为恶意软件分析、入侵检测和数据挖掘|陈意(1991—),男,贵州,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为信息隐藏和数字水印 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(62062022);贵州省省级科技计划(黔科合基础-ZK[2023]重点011)
Threat Intelligence-Driven Dynamic Threat Hunting Method
WU Shangyuan1,2, SHEN Guowei1,2( ), GUO Chun1,2, CHEN Yi1,2
), GUO Chun1,2, CHEN Yi1,2
- 1. Engineering Research Center for Text Computing and Cognitive Intelligence, Ministry of Education, Guizhou University, Guiyang 550025, China
2. State Key Laboratory of Public Big Data, Guizhou University, Guiyang 550025, China
-
Received:2023-04-28Online:2023-06-10Published:2023-06-20
摘要:
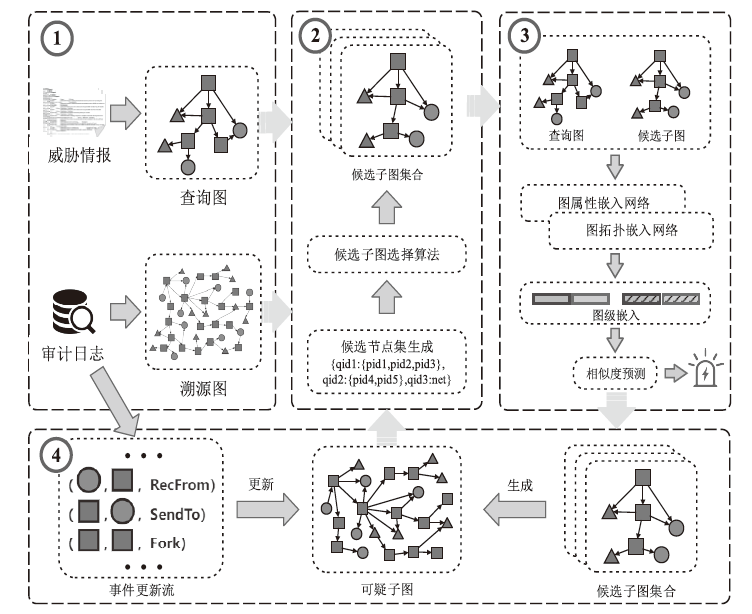
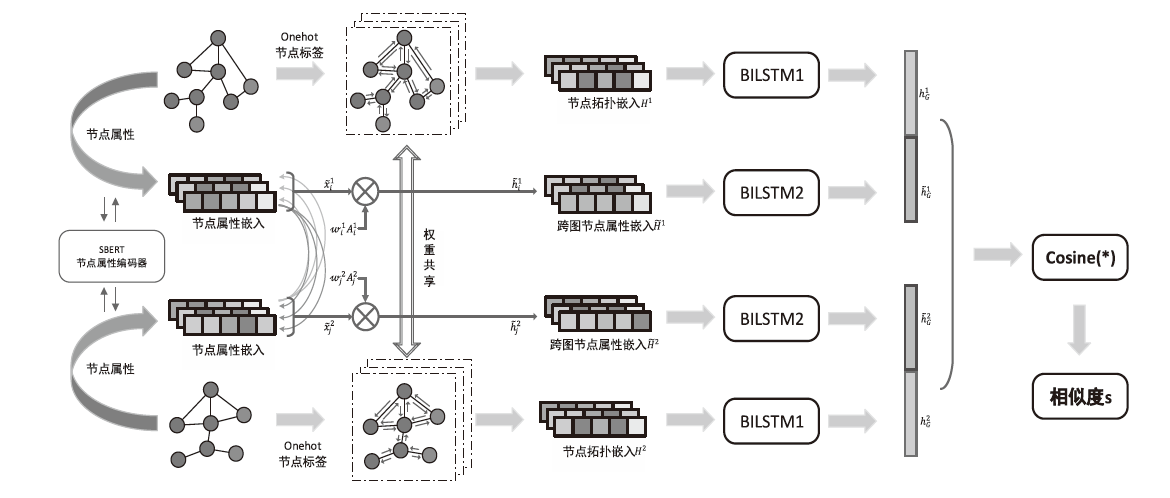
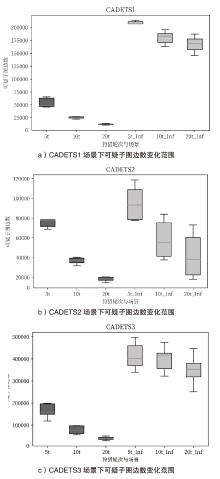
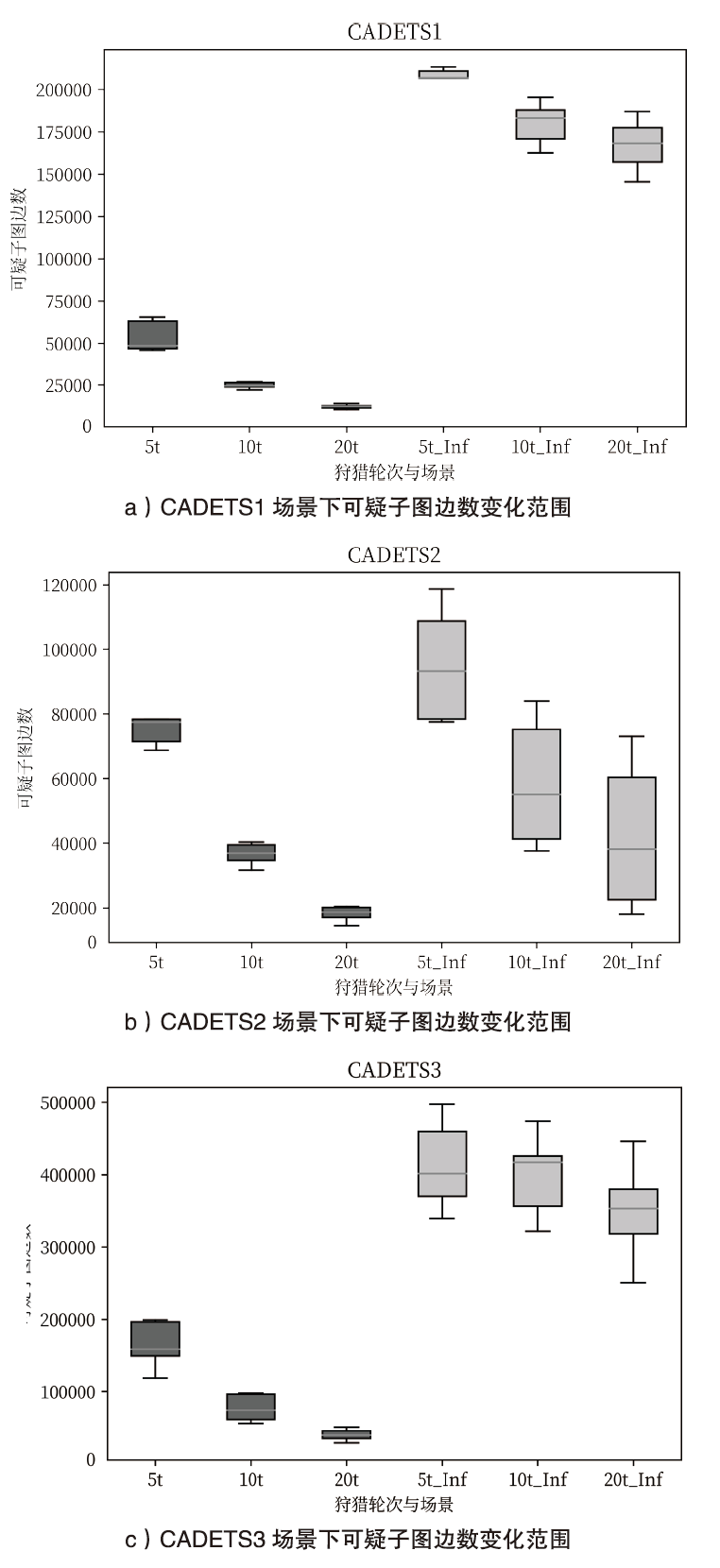
近年来,随着开源威胁情报自动化提取技术的发展,在威胁情报驱动下对溯源图(Provenance Graph)进行威胁狩猎有着无需专家知识且能提供完整攻击场景的优势,是一种有效的威胁检测手段。然而,现有的威胁狩猎方法仍存在以下不足:一方面,现有方法依赖威胁指标(Indicators of Compromise,IOC)进行威胁搜索,难以在攻击逃避检测的情况下对威胁进行有效检测;另一方面,现有方法鲜有考虑持续狩猎的应用场景,忽视了持续狩猎导致的高开销。为解决以上问题,文章提出一种威胁情报驱动的动态威胁狩猎方法(Threat Intelligence-Driven Dynamic Threat Hunting Method,DyHunter),可以在攻击逃避检测导致威胁情报与真实攻击不一致的情况下进行持续的威胁狩猎。DyHunter使用复合的候选子图选择算法避免攻击节点与攻击子图被遗漏,使用一种多层图相似性学习方法分别对拓扑结构相似性与节点属性相似性进行学习以提高模型鲁棒性,生成并维护一个可疑子图以减少持续狩猎的开销。实验结果表明,与已有方法相比,DyHunter可以有效保证在攻击逃避检测的情况下的高准确性,并在持续狩猎过程中减少94.1%以上的空间开销。
中图分类号:
引用本文
吴尚远, 申国伟, 郭春, 陈意. 威胁情报驱动的动态威胁狩猎方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(6): 91-103.
WU Shangyuan, SHEN Guowei, GUO Chun, CHEN Yi. Threat Intelligence-Driven Dynamic Threat Hunting Method[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(6): 91-103.
表6
不同大小的GCN/BILSTM隐藏层下AUC值
| GCN/BILSTM | CADETS1 | CADETS2 | CADETS3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NoInf | Inf | NoInf | Inf | NoInf | Inf | |
| 100/100 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.9926 | 1 | 0.9841 |
| 100/50 | 1 | 0.7589 | 1 | 0.1881 | 1 | 0.5784 |
| 100/200 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.9955 | 1 | 0.9802 |
| 50/50 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.8040 | 1 | 0.7345 |
| 50/100 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.9303 | 1 | 0.9089 |
| 200/200 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.8956 | 1 | 0.8524 |
| 200/100 | 1 | 0.9985 | 0.625 | 0.9941 | 0.7640 | 0.9824 |
| [1] |
LENG Tao, CAI Lijun, YU Aimin, et al. Review of Threat Discovery and Forensic Analysis Based on System Provenance Graph[J]. Journal on Communications, 2022. 43(7): 172-188.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022105 |
|
冷涛, 蔡利君, 于爱民, 等. 基于系统溯源图的威胁发现与取证分析综述[J]. 通信学报, 2022, 43(7): 172-188.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022105 |
|
| [2] | ZIPPERLE M, GOTTWALT F, CHANG E, et al. Provenance-Based Intrusion Detection Systems: A Survey[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2022, 55(7): 1-36. |
| [3] | MANZOOR E, MILAJERDI S M, AKOGLU L. Fast Memory-Efficient Anomaly Detection in Streaming Heterogeneous Gphs[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2016: 1035-1044. |
| [4] |
HAN Xueyuan, PASQUIER T, BATES A, et al. UNICORN: Runtime Provenance-Based Detector for Advanced Persistent Threats[EB/OL]. (2020-01-14)[2023-04-20]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2001.01525.
doi: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2001.01525 |
| [5] | WANG Qi, HASSAN W U, LI Ding, et al. You are What You Do: Hunting Stealthy Malware via Data Provenance Analysis[EB/OL]. (2020-01-01)[2023—04-20]. https://www.ndss-symposium.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/24167-paper.pdf. |
| [6] |
HAN Xueyuan, YU Xiao, PASQUIER T, et al. SIGL: Securing Software Installations Through Deep Graph Learning[EB/OL]. (2021-06-22)[2023-04-20]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2008.11533.
doi: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2008.11533 |
| [7] |
XIE Yulai, FENG Dan, HU Yuchong, et al. Pagoda: A Hybrid Approach to Enable Efficient Real-Time Provenance Based Intrusion Eetection in Big Data Environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2018, 17(6): 1283-1296.
doi: 10.1109/TDSC.8858 URL |
| [8] | MILAJERDI S M, GJOMEMO R, ESHETE B, et al. HOLMES: Real-Time APT Detection Through Correlation of Suspicious Information Flows[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York:IEEE, 2019: 1137-1152. |
| [9] | HOSSAIN M N, MILAJERDI S M, WANG Junao, et al. SLEUTH: Real-Time Attack Scenario Reconstruction from COTS Audit Data[C]// USENIX Association. 26th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 17). New York:Red Hook, 2017: 487-504. |
| [10] |
SUN Xiaoyan, DAI Jun, LIU Peng, et al. Using Bayesian Networks for Probabilistic Identification of Zero-Day Attack Paths[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2018, 13(10): 2506-2521.
doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2018.2821095 URL |
| [11] | HASSAN W U, BATES A, MARINO D. Tactical Provenance Analysis for Endpoint Detection and Response Systems[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York:IEEE, 2020: 1172-1189. |
| [12] | ALSAHEEL A, NAN Yuhong, MA Shiqing, et al. ATLAS: A Sequence-Based Learning Approach for Attack Investigation[C]// USENIX Association. Proceedings of the 30th USENIX Security Symposium. New York: Red Hook, 2021: 3005-3022. |
| [13] |
GOYAL A, HAN Xueyuan, WANG Gang, et al. Sometimes, You Aren’t What You Do: Mimicry Attacks Against Provenance Graph Host Intrusion Detection Systems[EB/OL]. (2023-03-03)[2023-04-20]. https://dx.doi.org/10.14722/ndss.2023.24207.
doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.14722/ndss.2023.24207 |
| [14] | GAO Peng, SHAO Fei, LIU Xiaoyuan, et al. Enabling Efficient Cyber Threat Hunting with Cyber Threat Intelligence[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE 37th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE). New York:IEEE, 2021: 193-204. |
| [15] | SATVAT K, GJOMEMO R, VENKATAKRISHNAN V N. EXTRACTOR: Extracting Attack Behavior from Threat Reports[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy (EuroS&P). New York:IEEE, 2021: 598-615. |
| [16] |
ZHANG Huixia, SHEN Guowei, GUO Chun, et al. EX-Action: Automatically Extracting Threat Actions from Cyber Threat Intelligence Report Based on Multimodal Learning[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2021, 1: 1-12.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1939-0122 URL |
| [17] | MILAJERDI S M, ESHETE B, GJOMEMO R, et al. Poirot: Aligning Attack BehAvior with Kernel Audit Records for Cyber Treat Hunting[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 2019 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Co-mputer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2019: 1795-1812. |
| [18] | WEI Renzheng, CAI Lijun, ZHAO Lixin, et al. Deephunter: A Graph Neural Network Based Approach for Robust Cyber Threat Hunting[C]// Springer. International Conference on Security and Privacy in Communication Systems. Berlin:Springer, 2021: 3-24. |
| [19] |
LIU Chen, LI Bo, ZHAO Jun, et al. MG-DVD: A Real-Time Framework for Malware Variant Detection Based on Dynamic Heterogeneous Graph Larning[EB/OL]. (2021-06-24)[2023-04-20]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2106.12288.
doi: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2106.12288 |
| [20] | REIMERS N, GUREVYCH I. Sentence-BERT: Sentence Embeddings Using Siamese BERT-Networks[C]// ACL. Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP). Stroudsburg:ACL, 2019: 3982-3992. |
| [21] | STRNAD A, MESSITER Q, WATSON R, et al. Casual, Adaptive, Distributed, and Efficient Tracing System (cadets)[R]. BAE Systems, 2019. |
| [22] | BAI Yunsheng, DING Hao, BIAN Song, et al. Simgnn: A Neural Network Approach to Fast Graph Ssimilarity Computation[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the Twelfth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2019: 384-392. |
| [23] |
LING Xiang, WU Lingfei, WANG Saizhuo, et al. Multilevel Graph Matching Networks for Deep Graph Similarity Learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(2), 799-813.
doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3102234 URL |
| [24] | QURESHI R J, RAMEL J Y, CARDOT H. Graph Based Shapes Representation and Recognition[C]// Springer. Graph-Based Representations in Pattern Recognition:6th IAPR-TC-15 International Workshop. Berlin:Springer, 2007: 49-60. |
| [1] | 冯景瑜, 张琪, 黄文华, 韩刚. 基于跨链交互的网络安全威胁情报共享方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(5): 21-29. |
| [2] | 程顺航, 李志华. 基于MRC的威胁情报实体识别方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(10): 76-82. |
| [3] | 张永生, 王志, 武艺杰, 杜振华. 基于Conformal Prediction的威胁情报繁殖方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(6): 90-95. |
| [4] | 王长杰, 李志华, 张叶. 一种针对恶意软件家族的威胁情报生成方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(12): 83-90. |
| [5] | 管磊, 胡光俊, 王专. 基于大数据的网络安全态势感知技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2016, 16(9): 45-50. |
| [6] | 徐丽萍, 郝文江. 美国政企网络威胁情报现状及对我国的启示[J]. 信息网络安全, 2016, 16(9): 278-284. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||