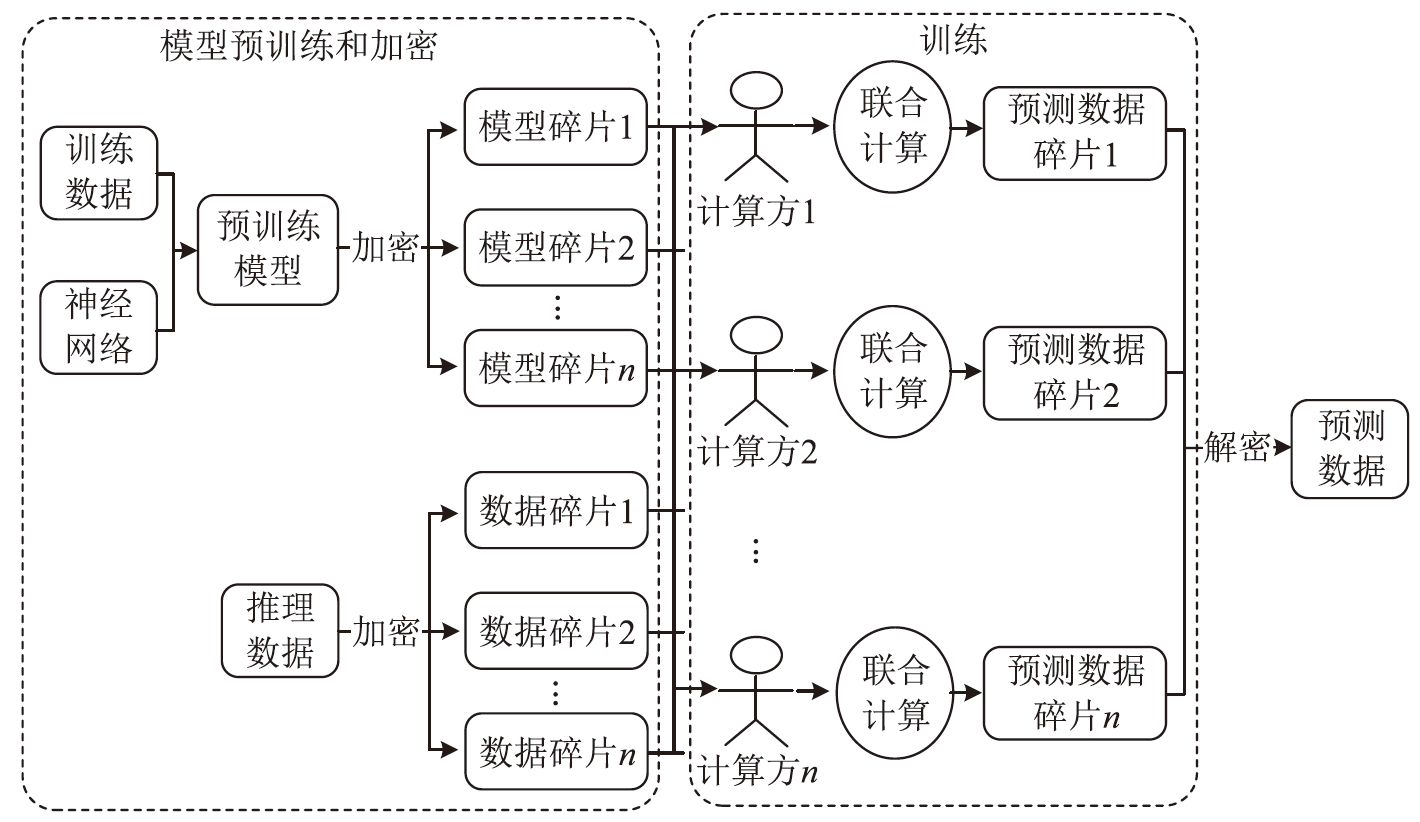
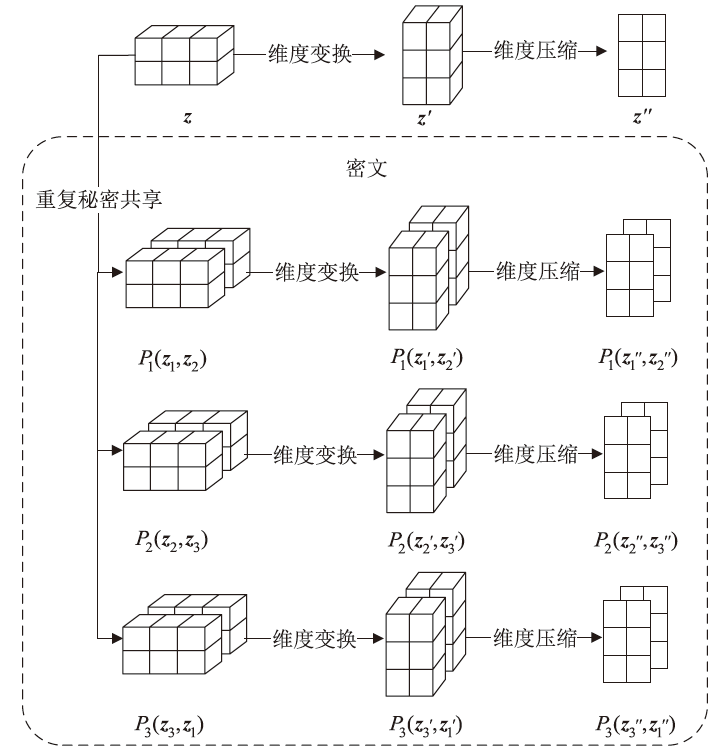
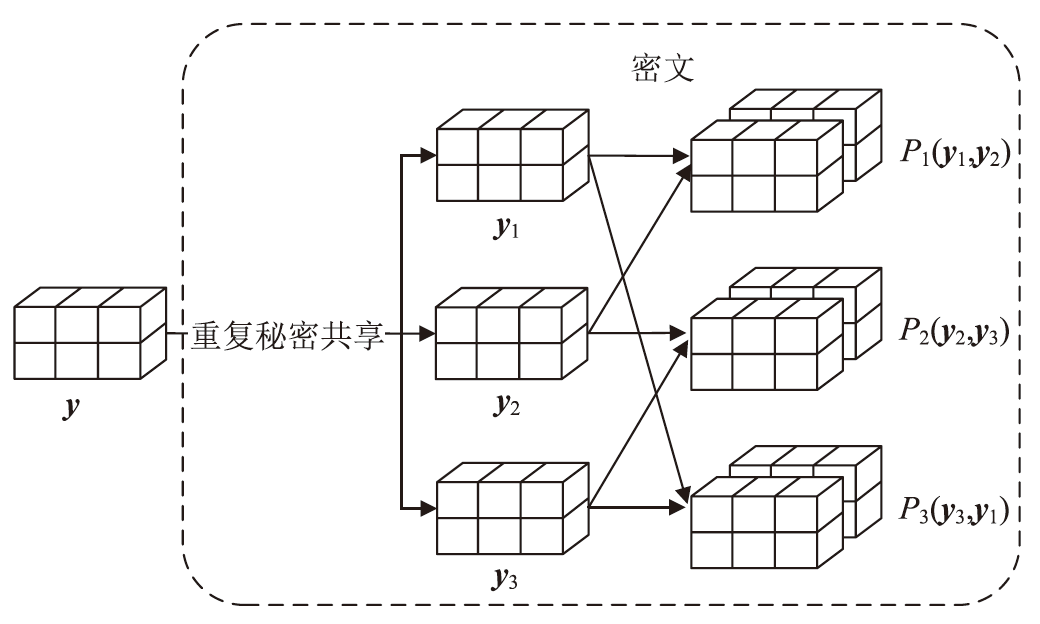
| [1] |
WANG Fei. Application Analysis of Privacy Computing in the Field of Public Security[J]. Netinfo Security, 2021, 21(S1): 70-73.
|
|
王飞. 隐私计算在公安领域的应用分析[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(S1):70-73.
|
| [2] |
YAO C C. Protocols for Secure Computations[C]// IEEE. 23rd Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science. New York: IEEE, 1982: 160-164.
|
| [3] |
YAO C C. How to Generate and Exchange Secrets[C]// IEEE. 27th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science. New York: IEEE, 1986: 162-167.
|
| [4] |
CHAUM D, CRÉPEAU C, DAMGARD I. Multiparty Unconditionally Secure Protocols[C]// ACM. 20th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing. New York: ACM, 1988: 11-19.
|
| [5] |
SHAMIR A. How to Share a Secret[J]. Communications of the ACM, 1979, 22(11): 612-613.
doi: 10.1145/359168.359176
URL
|
| [6] |
BLAKLEY G R. Safeguarding Cryptographic Keys[C]// IEEE. Managing Requirements Knowledge, International Workshop on IEEE Computer Society. New York: IEEE, 1979: 313-318.
|
| [7] |
GOLDREICH O. How to Play Any Mental Game[C]// ACM. 19th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing. New York: ACM, 1987: 218-229.
|
| [8] |
BEAVER D. Efficient Multiparty Protocols Using Circuit Randomization[C]// Springer. 11th Annual International Cryptology Conference on Advances in Cryptology. Heidelberg: Springer, 1991: 420-432.
|
| [9] |
PEI Bei, ZHANG Shuihai, LYU Chunli. A Proactive Multi-Secret Sharing Scheme for Cloud Storage[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(5): 95-104.
|
|
裴蓓, 张水海, 吕春利. 用于云存储的主动秘密共享方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(5):95-104.
|
| [10] |
ARAKI T, FURUKAWA J, LINDELL Y, et al. High-Throughput Semi-Honest Secure Three-Party Computation with an Honest Majority[C]// ACM. 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2016: 805-817.
|
| [11] |
MOHASSEL P, RINDAL P. ABY3: A Mixed Protocol Framework for Machine Learning[C]// ACM. 2018 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2018: 35-52.
|
| [12] |
WAGH S, TOPLE S, BENHAMOUDA F, et al. Falcon: Honest-Majority Maliciously Secure Framework for Private Deep Learning[J]. Privacy Enhancing Technologies, 2021(1): 188-208.
|
| [13] |
WAGH S, GUPTA D, CHANDRAN N. SecureNN: 3-Party Secure Computation for Neural Network Training[J]. Privacy Enhancing Technologies, 2019(3): 26-49.
|
| [14] |
LECUN Y, BOTTOU L. Gradient-Based Learning Applied to Document Recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324.
doi: 10.1109/5.726791
URL
|
| [15] |
KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks[J]. Communications of The ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84-90.
doi: 10.1145/3065386
URL
|
| [16] |
SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition[EB/OL]. (2014-09-04)[2023-07-27]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1409.1556.
|
| [17] |
SZEGEDY C, LIU Wei, JIA Yangqing, et al. Going Deeper with Convolutions[C]// IEEE. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2015: 1-9.
|
| [18] |
HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition[C]// IEEE. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2016: 770-778.
|
| [19] |
HARALAMPIEVA V, RUECKERT D, PASSERAT-PALMBACH J. A Systematic Comparison of Encrypted Machine Learning Solutions for Image Classification[C]// ACM. 2020 Workshop on Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning in Practice. New York: ACM, 2020: 55-59.
|
| [20] |
BAIDU. Instructions for PaddleFL-MPC Model Encryption Demo[EB/OL]. (2021-06-07)[2023-07-27]. https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleFL/tree/master/python/paddle_fl/mpc/examples/model_encryption.
|
| [21] |
DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An Image is Worth 16×16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale[EB/OL]. (2020-10-22)[2023-07-27]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929v2.
|
| [22] |
MOHASSEL P, ZHANG Yupeng. SecureML: A System for Scalable Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning[C]// IEEE. Security and Privacy(SP). New York: IEEE, 2017: 19-38.
|
| [23] |
RIAZI M S, WEINERT C, TKACHENKO O, et al. Chameleon: A Hybrid Secure Computation Framework for Machine Learning Applications[C]// ACM. 2018 Asia Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2018: 707-721.
|
| [24] |
KNOTT B, VENKATARAMAN S, HANNUN A, et al. CrypTen: Secure Multi-Party Computation Meets Machine Learning[EB/OL]. (2021-09-02)[2023-07-27]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.00984.
|
| [25] |
LEÓN MD, MORENO-BÁEZ A, MAGALLANES-QUINTANAR R, et al. Assessment in Subsets of MNIST Handwritten Digits and Their Effect in the Recognition Rate[J]. Journal of Pattern Recognition Research, 2011, 2(2): 244-252.
|
| [26] |
XIAO Han, RASUL K, VOLLGRAF R. Fashion-MNIST: A Novel Image Dataset for Benchmarking Machine Learning Algorithms[EB/OL]. (2017-09-15)[2023-07-27]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.07747.
|
| [27] |
LI Hongmin, LIU Hanchao, JI Xiangyang, et al. CIFAR10-DVS: An Event-Stream Dataset for Object Classification[J]. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2017, 11: 309-319.
doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00309
pmid: 28611582
|
 ), SONG Zewen1,2, ZHU Weiguo1,2, ZHAO Sicong3
), SONG Zewen1,2, ZHU Weiguo1,2, ZHAO Sicong3