Netinfo Security ›› 2023, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (6): 91-103.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2023.06.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
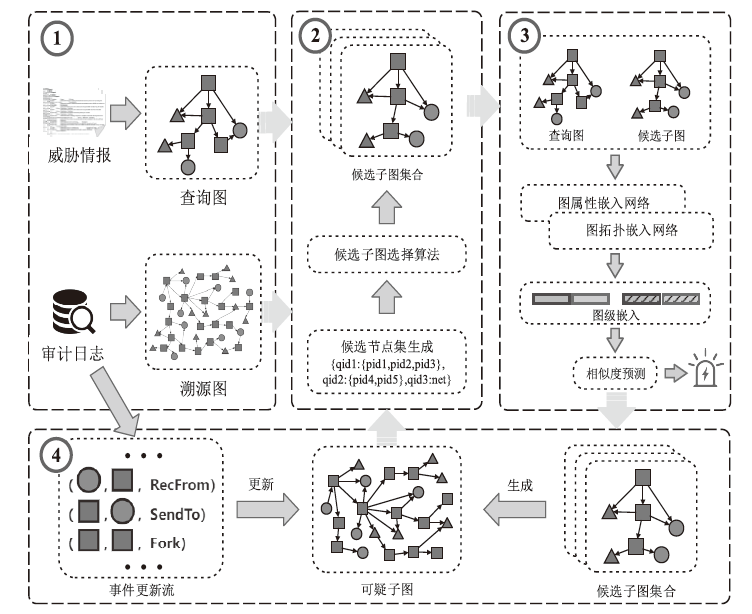
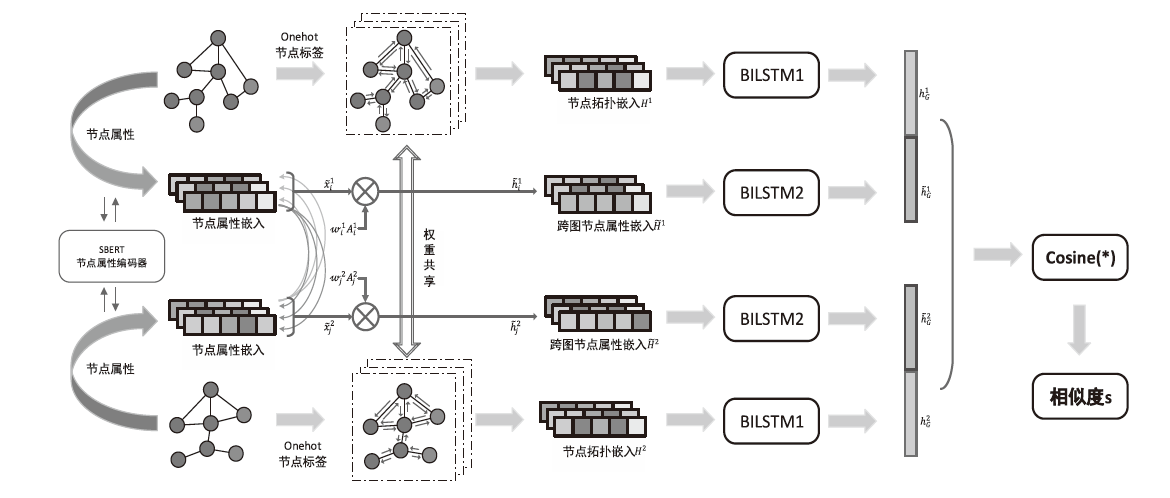
Threat Intelligence-Driven Dynamic Threat Hunting Method
WU Shangyuan1,2, SHEN Guowei1,2( ), GUO Chun1,2, CHEN Yi1,2
), GUO Chun1,2, CHEN Yi1,2
- 1. Engineering Research Center for Text Computing and Cognitive Intelligence, Ministry of Education, Guizhou University, Guiyang 550025, China
2. State Key Laboratory of Public Big Data, Guizhou University, Guiyang 550025, China
-
Received:2023-04-28Online:2023-06-10Published:2023-06-20
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WU Shangyuan, SHEN Guowei, GUO Chun, CHEN Yi. Threat Intelligence-Driven Dynamic Threat Hunting Method[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(6): 91-103.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://netinfo-security.org/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2023.06.009
| [1] |
LENG Tao, CAI Lijun, YU Aimin, et al. Review of Threat Discovery and Forensic Analysis Based on System Provenance Graph[J]. Journal on Communications, 2022. 43(7): 172-188.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022105 |
|
冷涛, 蔡利君, 于爱民, 等. 基于系统溯源图的威胁发现与取证分析综述[J]. 通信学报, 2022, 43(7): 172-188.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022105 |
|
| [2] | ZIPPERLE M, GOTTWALT F, CHANG E, et al. Provenance-Based Intrusion Detection Systems: A Survey[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2022, 55(7): 1-36. |
| [3] | MANZOOR E, MILAJERDI S M, AKOGLU L. Fast Memory-Efficient Anomaly Detection in Streaming Heterogeneous Gphs[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2016: 1035-1044. |
| [4] |
HAN Xueyuan, PASQUIER T, BATES A, et al. UNICORN: Runtime Provenance-Based Detector for Advanced Persistent Threats[EB/OL]. (2020-01-14)[2023-04-20]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2001.01525.
doi: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2001.01525 |
| [5] | WANG Qi, HASSAN W U, LI Ding, et al. You are What You Do: Hunting Stealthy Malware via Data Provenance Analysis[EB/OL]. (2020-01-01)[2023—04-20]. https://www.ndss-symposium.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/24167-paper.pdf. |
| [6] |
HAN Xueyuan, YU Xiao, PASQUIER T, et al. SIGL: Securing Software Installations Through Deep Graph Learning[EB/OL]. (2021-06-22)[2023-04-20]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2008.11533.
doi: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2008.11533 |
| [7] |
XIE Yulai, FENG Dan, HU Yuchong, et al. Pagoda: A Hybrid Approach to Enable Efficient Real-Time Provenance Based Intrusion Eetection in Big Data Environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2018, 17(6): 1283-1296.
doi: 10.1109/TDSC.8858 URL |
| [8] | MILAJERDI S M, GJOMEMO R, ESHETE B, et al. HOLMES: Real-Time APT Detection Through Correlation of Suspicious Information Flows[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York:IEEE, 2019: 1137-1152. |
| [9] | HOSSAIN M N, MILAJERDI S M, WANG Junao, et al. SLEUTH: Real-Time Attack Scenario Reconstruction from COTS Audit Data[C]// USENIX Association. 26th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 17). New York:Red Hook, 2017: 487-504. |
| [10] |
SUN Xiaoyan, DAI Jun, LIU Peng, et al. Using Bayesian Networks for Probabilistic Identification of Zero-Day Attack Paths[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2018, 13(10): 2506-2521.
doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2018.2821095 URL |
| [11] | HASSAN W U, BATES A, MARINO D. Tactical Provenance Analysis for Endpoint Detection and Response Systems[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York:IEEE, 2020: 1172-1189. |
| [12] | ALSAHEEL A, NAN Yuhong, MA Shiqing, et al. ATLAS: A Sequence-Based Learning Approach for Attack Investigation[C]// USENIX Association. Proceedings of the 30th USENIX Security Symposium. New York: Red Hook, 2021: 3005-3022. |
| [13] |
GOYAL A, HAN Xueyuan, WANG Gang, et al. Sometimes, You Aren’t What You Do: Mimicry Attacks Against Provenance Graph Host Intrusion Detection Systems[EB/OL]. (2023-03-03)[2023-04-20]. https://dx.doi.org/10.14722/ndss.2023.24207.
doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.14722/ndss.2023.24207 |
| [14] | GAO Peng, SHAO Fei, LIU Xiaoyuan, et al. Enabling Efficient Cyber Threat Hunting with Cyber Threat Intelligence[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE 37th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE). New York:IEEE, 2021: 193-204. |
| [15] | SATVAT K, GJOMEMO R, VENKATAKRISHNAN V N. EXTRACTOR: Extracting Attack Behavior from Threat Reports[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy (EuroS&P). New York:IEEE, 2021: 598-615. |
| [16] |
ZHANG Huixia, SHEN Guowei, GUO Chun, et al. EX-Action: Automatically Extracting Threat Actions from Cyber Threat Intelligence Report Based on Multimodal Learning[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2021, 1: 1-12.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1939-0122 URL |
| [17] | MILAJERDI S M, ESHETE B, GJOMEMO R, et al. Poirot: Aligning Attack BehAvior with Kernel Audit Records for Cyber Treat Hunting[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 2019 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Co-mputer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2019: 1795-1812. |
| [18] | WEI Renzheng, CAI Lijun, ZHAO Lixin, et al. Deephunter: A Graph Neural Network Based Approach for Robust Cyber Threat Hunting[C]// Springer. International Conference on Security and Privacy in Communication Systems. Berlin:Springer, 2021: 3-24. |
| [19] |
LIU Chen, LI Bo, ZHAO Jun, et al. MG-DVD: A Real-Time Framework for Malware Variant Detection Based on Dynamic Heterogeneous Graph Larning[EB/OL]. (2021-06-24)[2023-04-20]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2106.12288.
doi: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2106.12288 |
| [20] | REIMERS N, GUREVYCH I. Sentence-BERT: Sentence Embeddings Using Siamese BERT-Networks[C]// ACL. Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP). Stroudsburg:ACL, 2019: 3982-3992. |
| [21] | STRNAD A, MESSITER Q, WATSON R, et al. Casual, Adaptive, Distributed, and Efficient Tracing System (cadets)[R]. BAE Systems, 2019. |
| [22] | BAI Yunsheng, DING Hao, BIAN Song, et al. Simgnn: A Neural Network Approach to Fast Graph Ssimilarity Computation[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the Twelfth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2019: 384-392. |
| [23] |
LING Xiang, WU Lingfei, WANG Saizhuo, et al. Multilevel Graph Matching Networks for Deep Graph Similarity Learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(2), 799-813.
doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3102234 URL |
| [24] | QURESHI R J, RAMEL J Y, CARDOT H. Graph Based Shapes Representation and Recognition[C]// Springer. Graph-Based Representations in Pattern Recognition:6th IAPR-TC-15 International Workshop. Berlin:Springer, 2007: 49-60. |
| [1] | FENG Jingyu, ZHANG Qi, HUANG Wenhua, HAN Gang. A Cyber Threat Intelligence Sharing Scheme Based on Cross-Chain Interaction [J]. Netinfo Security, 2022, 22(5): 21-29. |
| [2] | CHENG Shunhang, LI Zhihua. Research on Threat Intelligence Entity Recognition Method Based on MRC [J]. Netinfo Security, 2021, 21(10): 76-82. |
| [3] | ZHANG Yongsheng, WANG Zhi, WU Yijie, DU Zhenhua. Cyber Threat Intelligence Propagation Based on Conformal Prediction [J]. Netinfo Security, 2020, 20(6): 90-95. |
| [4] | WANG Changjie, LI Zhihua, ZHANG Ye. A Threat Intelligence Generation Method for Malware Family [J]. Netinfo Security, 2020, 20(12): 83-90. |
| [5] | Lei GUAN, Guangjun HU, Zhuan WANG. Research on Network Security Situational Awareness Technology Based on Big Data [J]. Netinfo Security, 2016, 16(9): 45-50. |
| [6] | Liping XU, Wenjiang HAO. Analysis and Enlightenment of US Government and Enterprise Cyber Threat Intelligence [J]. Netinfo Security, 2016, 16(9): 278-284. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||