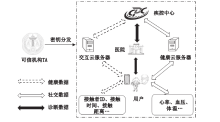
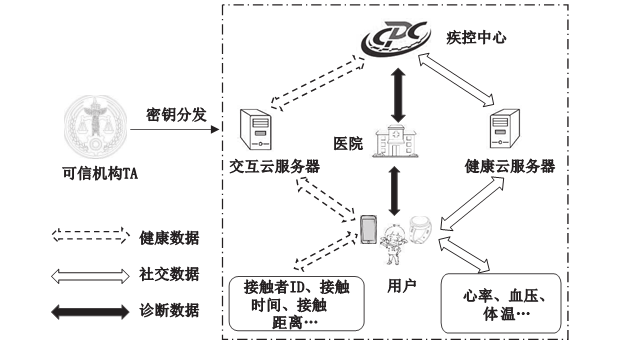
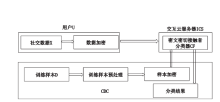
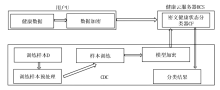
| [1] |
ZHANG Nan, CHEN Wenzhao, CHAN P T, et al. Close Contact Behavior in Indoor Environment and Transmission of Respiratory Infection[J]. Indoor Air, 2020, 30(4): 645-661.
doi: 10.1111/ina.12673
pmid: 32259319
|
| [2] |
LIANG Di, CUI Jing, LI Xiang. A Review of Offline Interaction in Dynamic Social Networks: Challenge and Prospect[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2018, 41(7): 1598-1618.
|
|
梁迪, 崔靖, 李翔. 线下交互的动态社交网络研究进展:挑战与展望[J]. 计算机学报, 2018, 41(7): 1598-1618.
|
| [3] |
SMIESZEK T, BURRI E U, SCHERZINGER R, et al. Collecting Close-Contact Social Mixing Data with Contact Diaries: Reporting Errors and Biases[J]. Epidemiology & Infection, 2012, 140(4): 744-752.
|
| [4] |
TAN Weijun, LIU Jingfeng. Application of Face Recognition in Tracing COVID-19 Fever Patients and Close Contacts[C]// IEEE. 19th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA). New York: IEEE, 2020: 1112-1116.
|
| [5] |
PDNN S, NOORDEEN F, KURUKULASURIYA H, et al. Effect of Climatic Factors and Population Density on the Distribution of Dengue in Sri Lanka: A GIS Based Evaluation for Prediction of Outbreaks[EB/OL]. (2017-07-09)[2022-12-12]. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0166806.
|
| [6] |
LI Qiaoxuan, CAO Wei, REN Hongyan, et al. Spatiotemporal Responses of Dengue Fever Transmission to the Road Network in an Urban Area[J]. Acta tropica, 2018, 183: 8-13.
doi: S0001-706X(17)31129-4
pmid: 29608873
|
| [7] |
HO T S, WENG T C, WANG J D, et al. Comparing Machine Learning with Case-Control Models to Identify Confirmed Dengue Cases[EB/OL]. (2020-10-10)[2022-12-20]. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0008843.
|
| [8] |
WENG S F, REPS J, KAI J, et al. Can Machine-Learning Improve Cardiovascular Risk Prediction Using Routine Clinical Data?[EB/OL]. (2017-04-04)[2022-12-06]. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0174944.
|
| [9] |
AN C, LIM H, KIM D-W, et al. Machine Learning Prediction for Mortality of Patients Diagnosed with COVID-19: A Nationwide Korean Cohort Study[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 1-11.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56847-4
|
| [10] |
BANOEI M M, DINPARASTISALEH R, ZADEH A V, et al. Machine-Learning-Based COVID-19 Mortality Prediction Model and Identification of Patients at Low and High Risk of Dying[J]. Critical Care, 2021, 25(1): 1-14.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03448-7
|
| [11] |
GAO Y, CAI G Y, FANG W, et al. Machine Learning Based Early Warning System Enables Accurate Mortality Risk Prediction for COVID-19[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 1-10.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13993-7
|
| [12] |
CHAE S, KWON S, LEE D. Predicting Infectious Disease Using Deep Learning and Big Data[EB/OL]. (2018-07-27) [2022-11-15] https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15081596.
|
| [13] |
YANG Xu, SHI Chenqi, LI Peihao, et al. Toward COVID-19 Contact Tracing Though Wi-Fi Probes[EB/OL]. (2022-03-14) [2022-11-30] https://doi.org/10.3390/s22062255.
|
| [14] |
WALRAVE M, WAETERLOOS C, PONNET K. Adoption of a Contact Tracing App for Containing COVID-19: A Health Belief Model Approach[J]. Jmir Public Health and Surveillance, 2020, 6(3): 488-497.
|
| [15] |
HINCH R, PROBERT W, NURTAY A, et al. Effective Configurations of a Digital Contact Tracing App: A Report to NHSX[EB/OL]. (2020-04-15) [2022-12-12] https://github.com/BDIpathogens/covid-19_instant_tracing/blob/master/Report.
|
| [16] |
DIAS D, CUNHA J P S. Wearable Health Devices-Vital Sign Monitoring, Systems and Technologies[EB/OL]. (2018-07-25) [2022-12-20] https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082414.
|
| [17] |
KAISSIS G A, MAKOWSKI M R, RUCKERT D, et al. Secure, Privacy-Preserving and Federated Machine Learning in Medical Imaging[J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2020, 2(6): 305-311.
doi: 10.1038/s42256-020-0186-1
|
| [18] |
MUNJAL K, BHATIA R. A Systematic Review of Homomorphic Encryption and its Contributions in Healthcare Industry[EB/OL]. (2022-05-03) [2022-11-16] https://10.1007/s40747-022-00756-z.
|
| [19] |
JAGADEESH K A, WU D J, BIRGMEIER J A, et al. Deriving Genomic Diagnoses Without Revealing Patient Genomes[J]. Science, 2017, 357: 692-695.
doi: 10.1126/science.aam9710
pmid: 28818945
|
| [20] |
ZHOU Yicong, PANETTA K, AGAIAN S. A Lossless Encryption Method for Medical Images Using Edge Maps[C]// IEEE. 31st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. New York: IEEE, 2009: 3707-3710.
|
| [21] |
VENGADAPURVAJA A, NISHA G, AARTHY R, et al. An Efficient Homomorphic Medical Image Encryption Algorithm for Cloud Storage Security[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2017, 115: 643-650.
doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2017.09.150
URL
|
| [22] |
CAUCHEMEZ S, BHATTARAI A, MARCHBANKS T L, et al. Role of Social Networks in Shaping Disease Transmission During a Community Outbreak of 2009 H1N1 Pandemic Influenza[J]. National Academy of Sciences, 2011, 108(7): 2825-2830.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1008895108
URL
|
| [23] |
CHEN Yi, WANG Aihong, YI Bo, et al. Epidemiological Characteristics of Infection in COVID-19 Close Contacts in Ningbo City[J]. Chinese Journal of Epidemiology, 2020, 41(5): 667-671.
|
|
陈奕, 王爱红, 易波, 等. 宁波市新型冠状病毒肺炎密切接触者感染流行病学特征分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2020, 41(5): 667-671.
|
| [24] |
THARAKAN S, NOMOTO K, MIYASHITA S, et al. Body Temperature Correlates with Mortality in COVID-19 Patients[J]. Critical Care, 2020, 24(1): 1-3.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-019-2683-3
|
| [25] |
XIE Yan, XU E, BOWE B, et al. Long-Term Cardiovascular Outcomes of COVID-19[J]. Nature Medicine, 2022, 28(3): 583-590.
doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-01689-3
|
 ), LI Kai3, XU Jian2,4
), LI Kai3, XU Jian2,4