Netinfo Security ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (3): 438-450.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.03.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
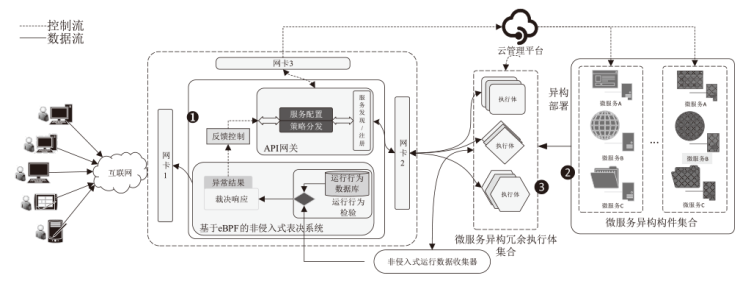
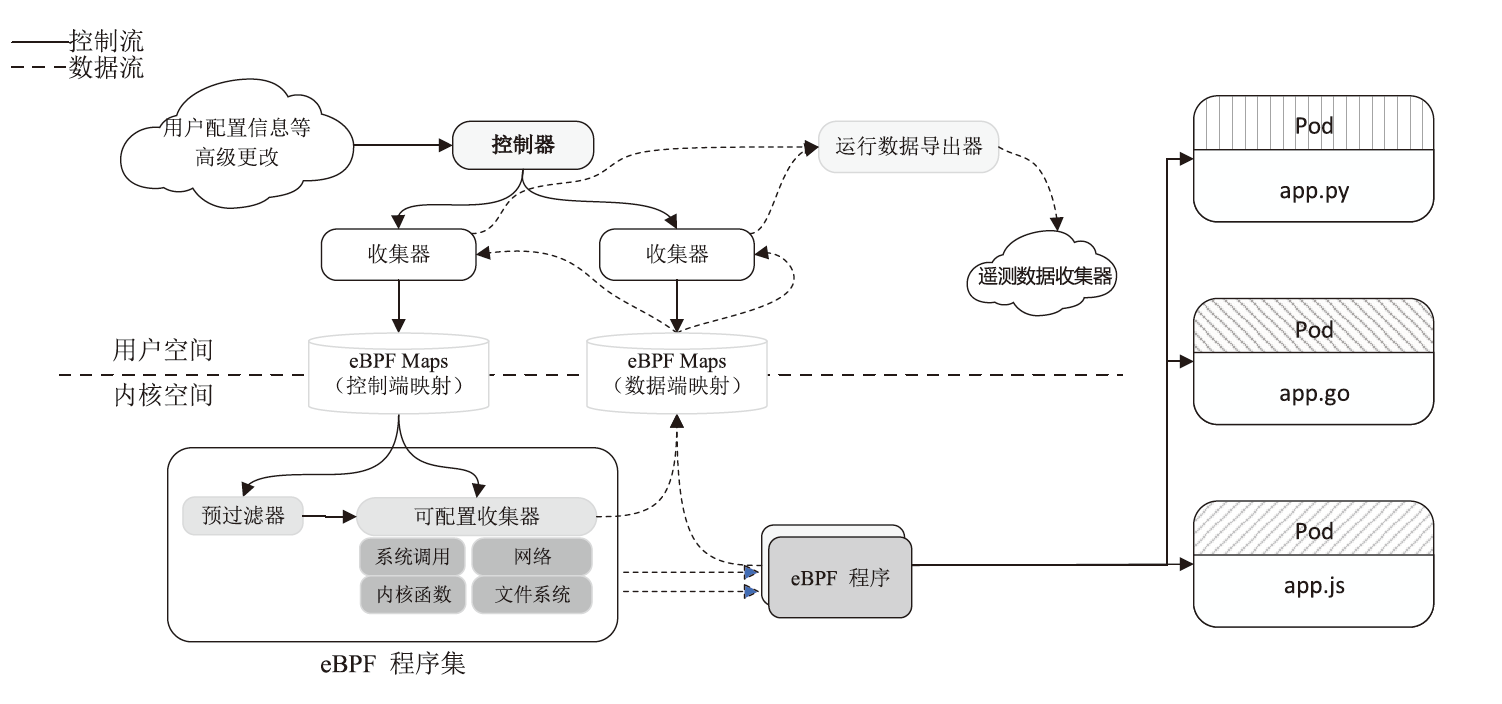
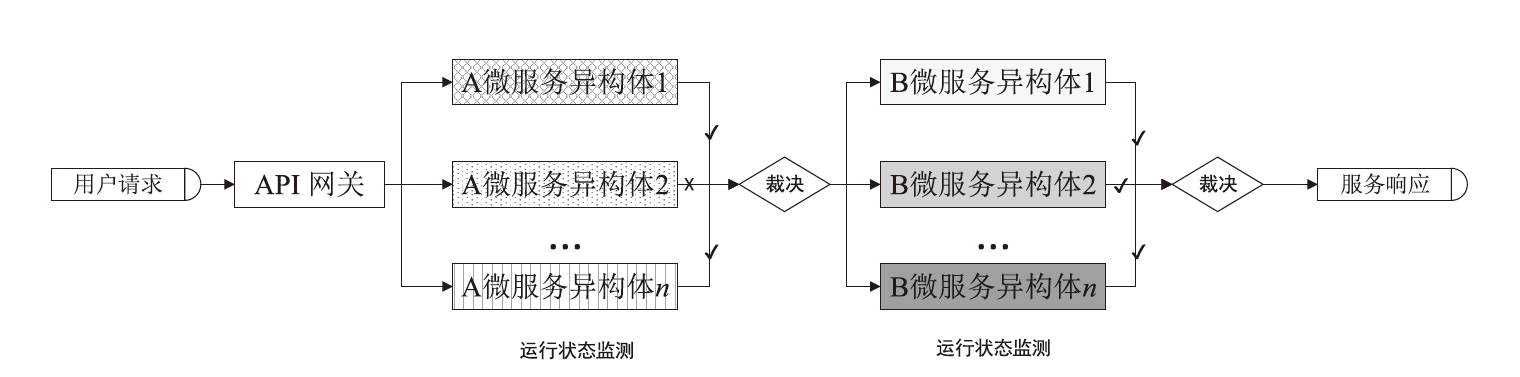
Research on Non-Intrusive Endogenous Security Microservice Model Based on Dynamic Heterogeneous Redundancy
SHI Lei1,2, LI Shibo1, CHENG Guozhen2,3, GAO Yufei1,2( )
)
- 1. School of Cyber Science and Engineering, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450002, China
2. Songshan Laboratory, Zhengzhou 450052, China
3. Institute of Information Technology, Information Engineering University, Zhengzhou 450007, China
-
Received:2024-12-30Online:2025-03-10Published:2025-03-26 -
Contact:GAO Yufei E-mail:yfgao@zzu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
SHI Lei, LI Shibo, CHENG Guozhen, GAO Yufei. Research on Non-Intrusive Endogenous Security Microservice Model Based on Dynamic Heterogeneous Redundancy[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(3): 438-450.
share this article
| 实验组 | 异构微服务软件配置 | 实验拓扑 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPU | 基础镜像操作系统 | 容器运行时 | ||
| K8s ingress + Microservice Executor 1 | Intel i5-10500(Intel x86_64) | Ubuntu | Docker 24.0.5 | |
| K8s ingress + Microservice Executor 2 | Intel i5-10500(Intel x86_64) | Ubuntu 22.04 | Containerd 1.7.11 | |
| K8s ingress + Microservice Executor 3 | AMD 7735H(AMD x86_64) | Arch Linux | Docker 24.0.5 | |
| EnSecDHR + Microservice Executor 1,2,3 | BCM2711(ARM64) | Armbian 23.11.1 | Containerd 1.7.11 | |
| [1] | THONES J. Microservices[J]. IEEE Software, 2015, 32(1): 116-125. |
| [2] | THONES E, ZAIGHAM M, RICARDO P. Cloud Computing: Concepts, Technology & Architecture[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2014. |
| [3] | WANG Haogang. The Design and Implementation of Declarative Universal Kubernetes Operator[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2021. |
| 汪浩港. 声明式的通用Kubernetes Operator的设计与实现[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2021. | |
| [4] |
WAN Xiaolan, LI Jinglin, LIU Kebin. Cloud Native Network Creating New Era of Intelligent Application[J]. Telecommunications Science, 2022, 38(6): 31-41.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-0801.2022130 |
|
万晓兰, 李晶林, 刘克彬. 云原生网络开创智能应用新时代[J]. 电信科学, 2022, 38(6):31-41.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-0801.2022130 |
|
| [5] | WANG Jiannan. Analysis and Countermeasures of Cloud-Native Security Risks[J]. Network Security Technology & Application, 2024(1): 79-81. |
| 王剑楠. 云原生安全风险分析与对策探讨[J]. 网络安全技术与应用, 2024(1):79-81. | |
| [6] | WU Shenglin, LIU Wanggen, YAN Ming, et al. A Real-Time Anomaly Detection System for Container Clouds Based on Unsupervised System Call Rule Generation[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(12): 91-102. |
| 吴圣麟, 刘汪根, 严明, 等. 基于无监督系统调用规则生成的容器云实时异常检测系统[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(12):91-102. | |
| [7] |
ZHANG Yuntao, FANG Binxing, DU Chunlai, et al. Container Escape Detection Method Based on Heterogeneous Observation Chain[J]. Journal on Communications, 2023, 44(1): 49-63.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2023008 |
|
张云涛, 方滨兴, 杜春来, 等. 基于异构观测链的容器逃逸检测方法[J]. 通信学报, 2023, 44(1):49-63.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2023008 |
|
| [8] | LADISA P, PLATE H, MARTINEZ M, et al. Sok: Taxonomy of Attacks on Open-Source Software Supply Chains[C]// IEEE. 2023 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York: IEEE, 2023: 1509-1526. |
| [9] | JI Shouling, WANG Qinying, CHEN Anying, et al. Survey on Open-Source Software Supply Chain Security[J]. Journal of Software, 2023, 34(3): 1330-1364. |
| 纪守领, 王琴应, 陈安莹, 等. 开源软件供应链安全研究综述[J]. 软件学报, 2023, 34(3):1330-1364. | |
| [10] | PARAST F K, SINDHAV C, NIKAM S, et al. Cloud Computing Security: A Survey of Service-Based Models[EB/OL]. (2022-03-14)[2024-07-24]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0167404821003977. |
| [11] | GUO Junli, XU Mingyang, YUAN Haoyu, et al. Introduction of Endogenous Security in Zero Trust Model[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 2022(6): 51-58. |
| 郭军利, 许明洋, 原浩宇, 等. 引入内生安全的零信任模型[J]. 郑州大学学报(理学版), 2022(6): 51-58. | |
| [12] | LU Guanhong. Application Security Research Based on API Gateway[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University, 2023. |
| 卢冠宏. 基于API网关的应用安全研究[D]. 广州: 广州大学, 2023. | |
| [13] | SALAMERO J. Kubernetes Runtime Security with Falco and Sysdig[EB/OL]. (2019-10-02)[2024-07-24]. https://www.cncf.io/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/Kubernetes-Runtime-Security-with-Falco-and-Sysdig.pdf. |
| [14] | WU Jiangxing. Research on Cyber Mimic Defense[J]. Journal of Cyber Security, 2016, 1(4): 1-10. |
| 邬江兴. 网络空间拟态防御研究[J]. 信息安全学报, 2016, 1(4):1-10. | |
| [15] | HAMMI B, ZEADALLY S, NEBHEN J. Security Threats, Countermeasures, and Challenges of Digital Supply Chains[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2023, 55(14s): 1-40. |
| [16] |
WU Jiangxing, ZOU Hong, XUE Xiangyang, et al. Cyber Resilience Enabled by Endogenous Security and Safety: Vision, Techniques, and Strategies[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2023, 25(6): 106-115.
doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2023.06.018 |
|
邬江兴, 邹宏, 薛向阳, 等. 内生安全赋能网络弹性的构想、方法与策略[J]. 中国工程科学, 2023, 25(6):106-115.
doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2023.06.018 |
|
| [17] |
SONG Ke, LIU Qinrang, WEI Shuai, et al. Endogenous Security Architecture of Ethernet Switch Based on Mimic Defense[J]. Journal on Communications, 2020, 41(5): 18-26.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020098 |
|
宋克, 刘勤让, 魏帅, 等. 基于拟态防御的以太网交换机内生安全体系结构[J]. 通信学报, 2020, 41(5):18-26.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020098 |
|
| [18] | ZHU Xuquan, JIANG Yiming, MA Hailong, et al. Research and Analysis of OSPF Protocol in Mimic Defense System[J]. Computer Engineering & Science, 2023, 45(2): 204-214. |
| 朱绪全, 江逸茗, 马海龙, 等. 拟态防御体系 OSPF 协议研究及分析[J]. 计算机工程与科学, 2023, 45(2):204-214. | |
| [19] | PU Liming, WEI Hongquan, LI Xing, et al. Mimic Cloud Service Architecture for Cloud Applications[J]. Chinese Journal of Network and Information Security, 2021, 7(1): 101-112. |
| 普黎明, 卫红权, 李星, 等. 面向云应用的拟态云服务架构[J]. 网络与信息安全学报, 2021, 7(1):101-112. | |
| [20] | GAO Zhenbin, JIA Guangrui, ZHANG Wenjian, et al. Mimic Ruling Optimization Method Based on Executive Outliers[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2021, 38(7): 2066-2071. |
| 高振斌, 贾广瑞, 张文建, 等. 基于异常值的拟态裁决优化方法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2021, 38(7):2066-2071. | |
| [21] | CHEN Fucai, ZHOU Mengli, LIU Wenyan, et al. Feedback Control Method for Mimic Defense in Cloud Environment[J]. Netinfo Security, 2021, 21(1): 49-56. |
| 陈福才, 周梦丽, 刘文彦, 等. 云环境下面向拟态防御的反馈控制方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(1):49-56. | |
| [22] | LIU Daoqing, HU Hongchao, HUO Shumin. Research on Persistent Storage-Oriented Mimic Defense Technology in Container Clouds[J]. Computer Engineering, 2024, 50(2): 1-19. |
| 刘道清, 扈红超, 霍树民. 容器云中面向持久化存储的拟态防御技术研究[J]. 计算机工程, 2024, 50(2):1-19. | |
| [23] | MAGNANI S, RISSO F, SIRACUSA D. A Control Plane Enabling Automated and Fully Adaptive Network Traffic Monitoring with eBPF[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 90778-90791. |
| [24] | SADIQ A, SYED H J, ANSARI A A, et al. Detection of Denial of Service Attack in Cloud Based Kubernetes Using eBPF[EB/OL]. (2023-04-15)[2024-07-24]. https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=1g470ry0636302501k5u02e0a5266699&site=xueshu_se. |
| [25] | SHARAF, AHMAD H A, DIMITRIOU I A, et al. Extended Berkeley Packet Filter: An Application Perspective[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 126370-126393. |
| [26] | LEITE L, ROCHA C, MILOJICIC D, et al. A Survey of DevOps Concepts and Challenges[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2019, 52(6): 1-35. |
| [27] | HANIF H, NASIR M, RAZAK M, et al. The Rise of Software Vulnerability: Taxonomy of Software Vulnerabilities Detection and Machine Learning Approaches[EB/OL]. (2021-02-01)[2024-07-24]. https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=1k6v0gx0hp6j0ac0c8430ga0yf777336&site=xueshu_se. |
| [28] |
PAN Chuanxing, ZHANG Zheng, MA Bolin, et al. Method against Process Control-Flow Hijacking Based on Mimic Defense[J]. Journal on Communications, 2021, 42(1): 37-47.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021013 |
|
潘传幸, 张铮, 马博林, 等. 面向进程控制流劫持攻击的拟态防御方法[J]. 通信学报, 2021, 42(1):37-47.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021013 |
| [1] | ZHOU Shucheng, LI Yang, LI Chuanrong, GUO Lulu, JIA Xinhong, YANG Xinghua. Context-Based Abnormal Root Cause Algorithm [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(7): 1062-1075. |
| [2] | SHI Yuan, LI Yang, ZHAN Mengqi. A Multi-Dimensional Root Cause Localization Algorithm for Microservices [J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(3): 73-83. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||