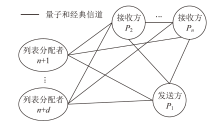
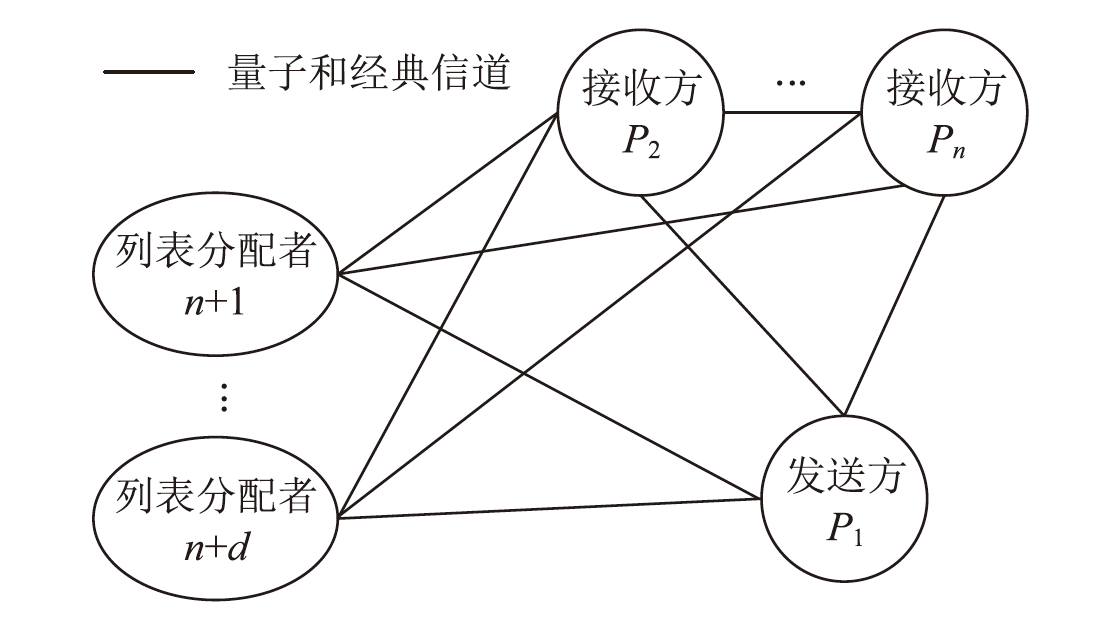
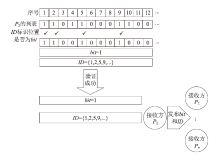
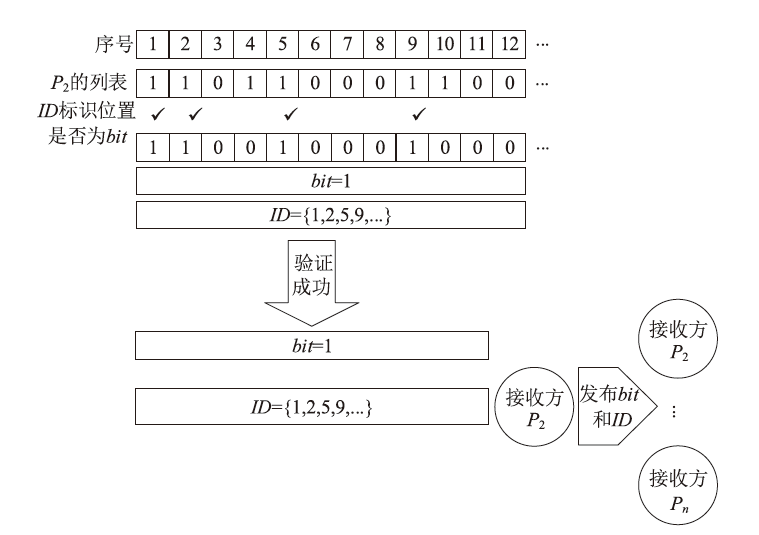
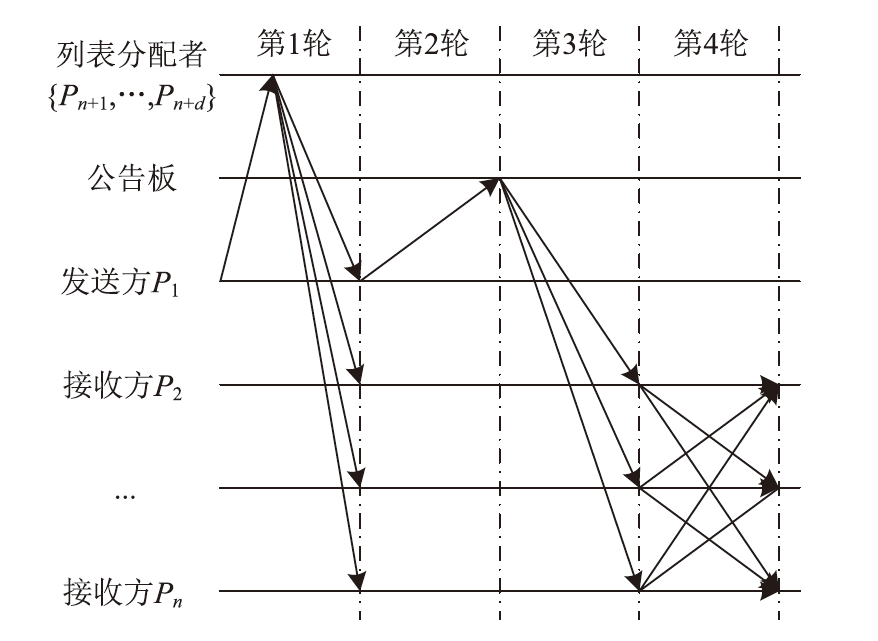
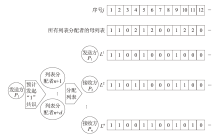
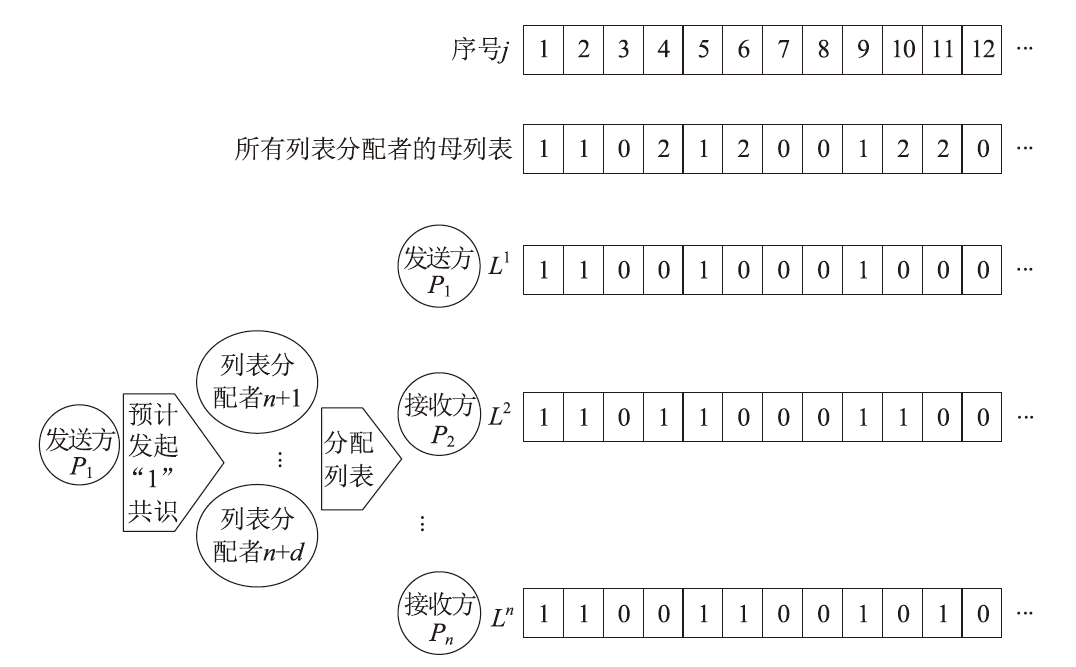
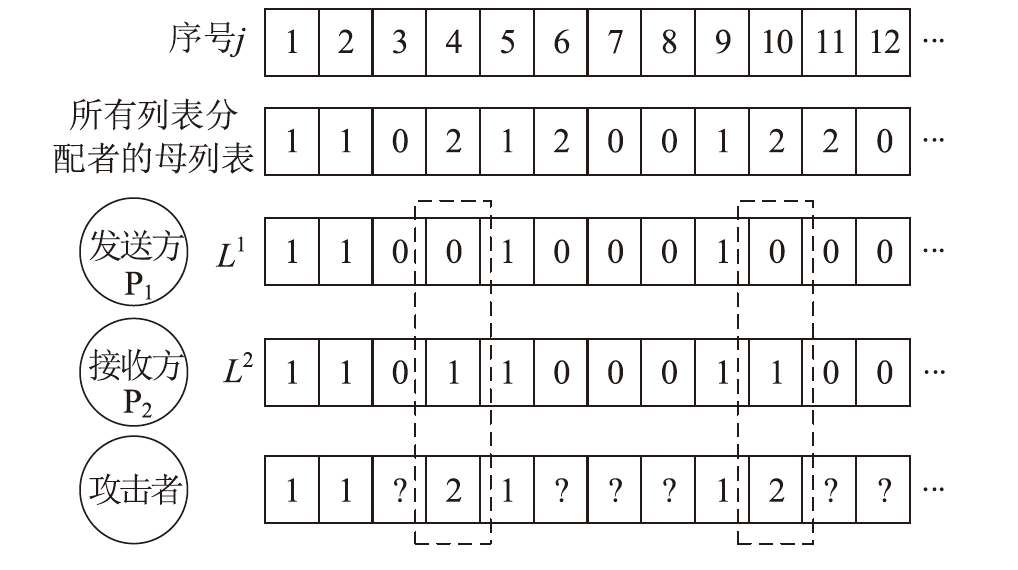
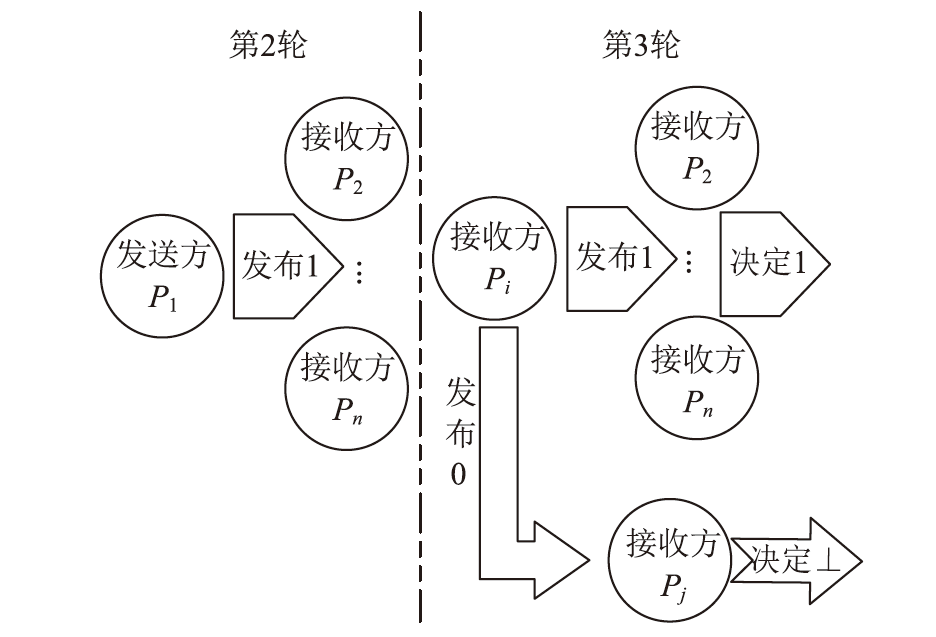
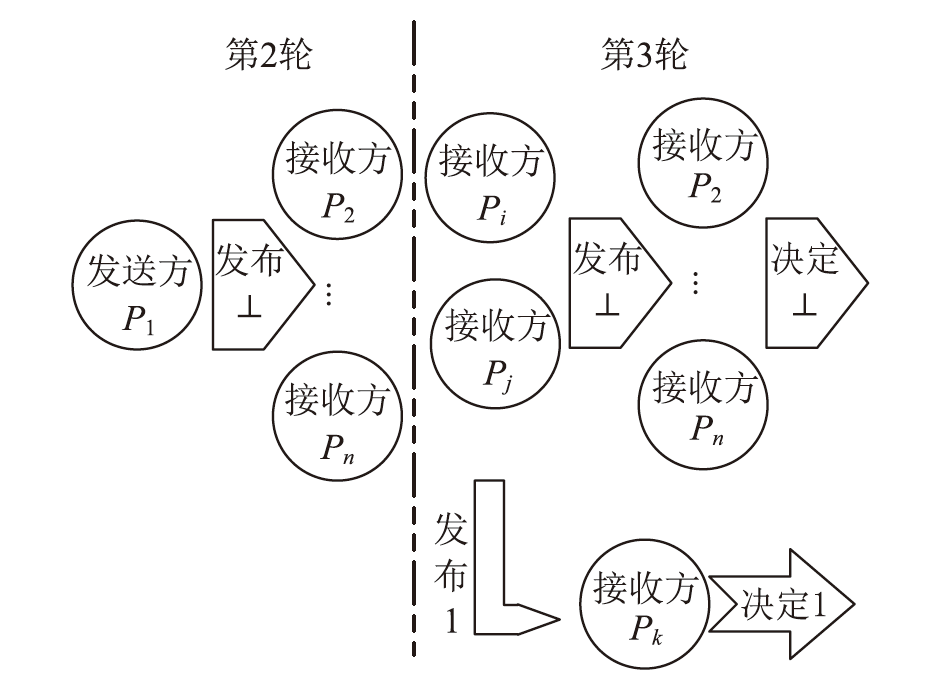
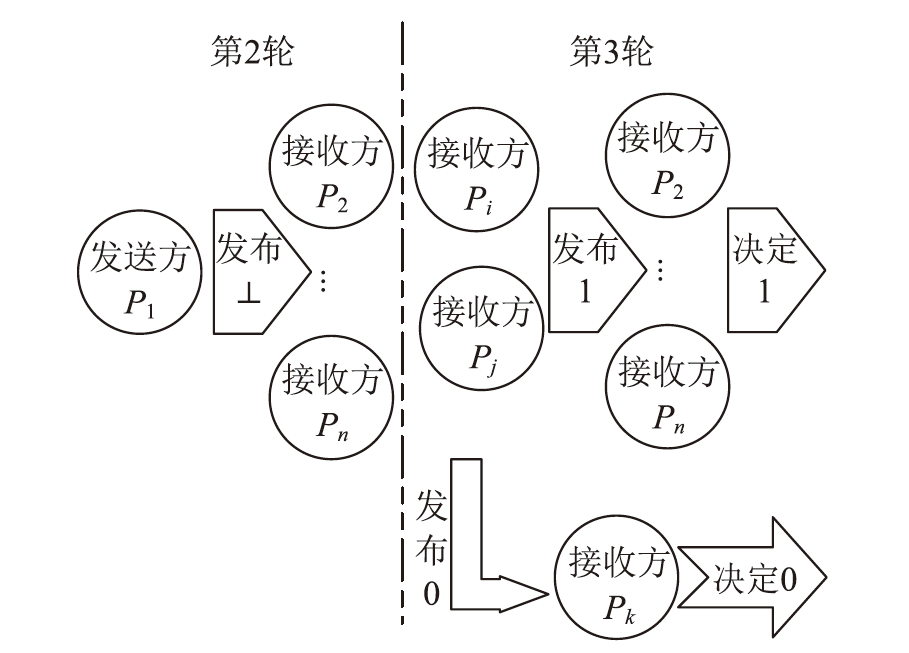
| [1] |
LAMPORT L, SHOSTAK R, PEASE M. The Byzantine Generals Problem[J]. ACM Transactions on Programming Languages and Systems, 1982, 4(3): 382-401.
doi: 10.1145/357172.357176
URL
|
| [2] |
CASTRO M, LISKOV B. Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance[C]// USENIX. 3rd Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation. Berkeley: USENIX, 1999: 173-186.
|
| [3] |
NAKAMOTO S. Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System[EB/OL]. (2008-08-21)[2023-04-02]. http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3440802.
|
| [4] |
YIN Maofang, MALKHI D, REITER M K, et al. HotStuff:BFT Consensus with Linearity and Responsiveness[C]//ACM. PODC’19:ACM Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing. New York: ACM, 2019: 347-356.
|
| [5] |
CHEN Kaijie, XIONG Yan, HUANG Wenchao, et al. A Formal Analysis Method of PoS Consensus Protocol Based on Byzantine Fault Tolerance[J]. Netinfo Security, 2021, 21(8): 35-42.
|
|
陈凯杰, 熊焰, 黄文超, 等. 一种基于拜占庭容错的PoS共识协议形式化分析方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(8):35-42.
|
| [6] |
KIKTENKO E O, POZHAR N O, ANUFRIEV M N, et al. Quantum-Secured Blockchain[EB/OL]. (2018-04-10)[2023-04-02]. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/2058-9565/aabc6b/meta.
|
| [7] |
PEASE M, SHOSTAK R, LAMPORT L. Reaching Agreement in the Presence of Faults[J]. Journal of the ACM, 1980, 27(2): 228-234.
doi: 10.1145/322186.322188
URL
|
| [8] |
FITZI M, GISIN N, MAURER U. Quantum Solution to the Byzantine Agreement Problem[EB/OL]. (2001-11-01)[2023-04-02]. https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevLett.87.217901.
|
| [9] |
FENG Ronghua, SHI Ronghua, ZHOU Jian, et al. Quantum Byzantine Agreement with Tripartite Entangled States[J]. International Journal of Theoretical Physics, 2019, 58: 1482-1498.
doi: 10.1007/s10773-019-04035-5
|
| [10] |
IBLISDIR S, GISIN N. Byzantine Agreement with Two Quantum-Key-Distribution Setups[EB/OL]. (2004-09-29)[2023-04-02]. https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevA.
|
| [11] |
BENNETT C H. Quantum Cryptography: Public Key Distribution and Coin Tossing[J]. Theoretical Computer Science, 2014, 560(1): 7-11.
doi: 10.1016/j.tcs.2014.05.025
URL
|
| [12] |
ZHANG Xue, GAO Fei, QIN Sujuan, et al. Current Status and Future Development of Quantum Cryptographic Protocols[J]. Strategic Study of Chinese Academy of Engineering, 2022, 24(4): 145-155.
|
|
张雪, 高飞, 秦素娟, 等. 量子密码协议研究现状与未来发展[J]. 中国工程科学, 2022, 24(4):145-155.
|
| [13] |
BOURENNANE M, CABELLO A, ZUKOWSKI M. Quantum Byzantine Agreement with a Single Qutrit[EB/OL]. (2010-01-12)[2023-04-02]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1001.1947.
|
| [14] |
BEN-OR M, HASSIDIM A. Fast Quantum Byzantine Agreement[C]//ACM. 37th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing. New York: ACM, 2005: 481-485.
|
| [15] |
TAVAKOLI A, CABELLO A, ŻUKOWSKI M, et al. Quantum Clock Synchronization with a Single Qudit[EB/OL]. (2015-01-23)[2023-04-02]. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep07982.
|
| [16] |
LUO Qingbin, FENG Kaiyuan, ZHENG Minghui. Quantum Multi-Valued Byzantine Agreement Based on D-Dimensional Entangled States[J]. International Journal of Theoretical Physics, 2019, 58(12): 4025-4032.
doi: 10.1007/s10773-019-04269-3
|
| [17] |
XUE Lide, CHEN Bingren, YANG Wei, et al. Practical Quantum Byzantine Protocol via Nearly Optimal Entanglement Resources[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2019, 18: 1-13.
doi: 10.1007/s11128-018-2112-6
|
| [18] |
CHOLVI V. Detectable Quantum Byzantine Agreement for Any Arbitrary Number of Dishonest Parties[EB/OL]. (2021-12-17)[2023-04-02]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2112.09437.
|
| [19] |
SUN Xin, KULICKI P, SOPEK M. Multi-Party Quantum Byzantine Agreement without Entanglement[EB/OL]. (2020-09-04)[2023-04-02]. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22101152.
|
| [20] |
FITZI M, GOTTESMAN D, HIRT M, et al. Detectable Byzantine Agreement Secure against Faulty Majorities[C]//ACM. Twenty-First Annual ACM Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing(PODC 2002). New York: ACM, 2002: 118-126.
|
| [21] |
AMIRI R, ANDERSSON E. Unconditionally Secure Quantum Signatures[J]. Entropy, 2015, 17(8): 5635-5659.
doi: 10.3390/e17085635
URL
|
| [22] |
AMIRI R, ABIDIN A, WALLDEN P, et al. Efficient Unconditionally Secure Signatures Using Universal Hashing[C]//Springer. Applied Cryptography and Network Security:16th International Conference. Heidelberg: Springer, 2018: 143-162.
|
| [23] |
XUE Lide. Research of Blockchain Consensus Algorithm and Its Application[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2021.
|
|
薛立德. 区块链共识算法及其应用研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2021.
|
| [24] |
CHAUM D, ROIJAKKERS S. Unconditionally-Secure Digital Signatures[C]//Springer. Advances in Cryptology-CRYPTO’90. Heidelberg: Springer, 1991: 206-214.
|
| [25] |
LI Binghong, XIE Yuanmei, CAO Xiaoyu, et al. One-Time Universal Hashing Quantum Digital Signatures without Perfect Keys[EB/OL]. [2023-04-02]. http://export.arxiv.org/abs/2301.01132.
|
| [26] |
KIKTENKO E O, ZELENETSKY A S, FEDOROV A K. Practical Quantum Multiparty Signatures Using Quantum-Key-Distribution Networks[EB/OL]. (2022-01-04)[2023-04-02]. https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevA.105.012408.
|
| [27] |
REN Chang, ZHAO Hong, JIANG Hua. Quantum Secured-Byzantine Fault Tolerance Blockchain Consensus Mechanism[J]. Computer Science, 2022, 49(5): 333-340.
doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.210400154
|
|
任畅, 赵洪, 蒋华. 一种量子安全拜占庭容错共识机制[J]. 计算机科学, 2022, 49(5):333-340.
doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.210400154
|
| [28] |
WALLDEN P, DUNJKO V, KENT A, et al. Quantum Digital Signatures with Quantum-Key-Distribution Components[EB/OL]. (2015-04-07)[2023-04-02]. https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevA.91.042304.
|
| [29] |
CARTER J L, WEGMAN M N. Universal Classes of Hash Functions[C]//ACM. 9th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing. New York: ACM, 1977: 106-112.
|
| [30] |
YIN Hualei, FU Yao, LI Chenlong, et al. Experimental Quantum Secure Network with Digital Signatures and Encryption[EB/OL]. (2022-10-22)[2023-04-02]. https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwac228.
|
| [31] |
QIN Huawang, XU Hao, TANG W K S. Public-Key Quantum Signature Based on Phase Shift Operation[EB/OL]. (2020-01-31)[2023-04-02]. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217984920500840.
|
| [32] |
GISIN N, RIBORDY G, TITTEL W, et al. Quantum Cryptography[EB/OL]. (2020-03-08)[2023-04-02]. https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.74.145.
|
| [33] |
GYONGYOSI L, IMRE S, NGUYEN H V. A Survey on Quantum Channel Capacities[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 20(2): 1149-1205.
|
 ), GONG Pengfei2
), GONG Pengfei2