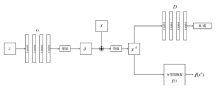
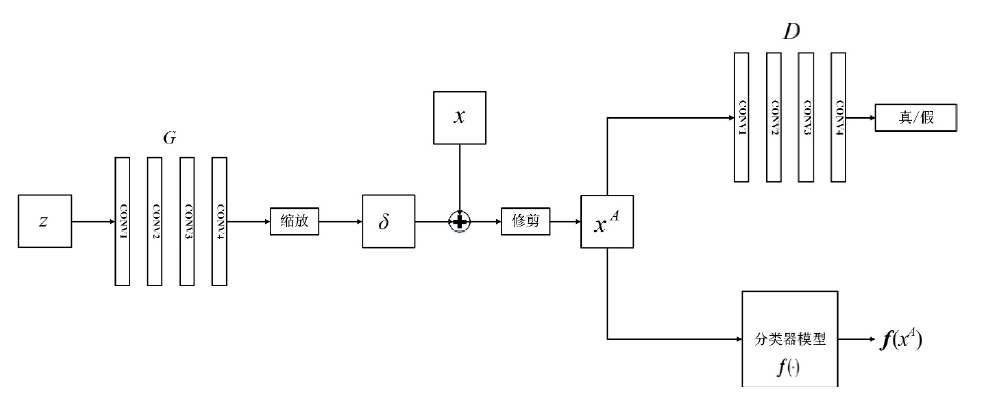
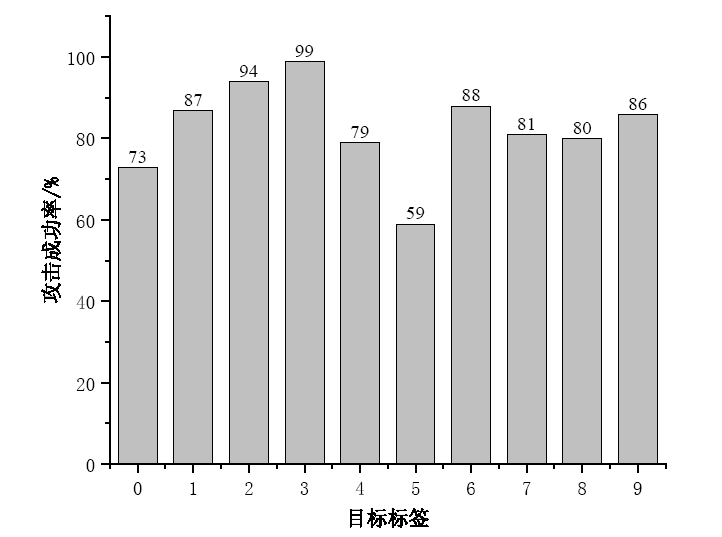
| [1] |
HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing , et al. Identity Mappings in Deep Residual Networks[M] //Springer. Computer Vision- ECCV 2016. Cham: Springer, 2016: 630-645.
|
| [2] |
DURAND T, MEHRASA N, MORI G . Learning a Deep ConvNet for Multi-label Classification with Partial Labels[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.09720v1, 2020-3-20.
|
| [3] |
ALOM M Z, ASPIRAS T, TAHA T M , et al. Skin Cancer Segmentation and Classification with NABLA-N and Inception Recurrent Residual Convolutional Networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.1112, 2020-3-20.
|
| [4] |
ISLAM J, ZHANG Yanqing . Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease: A Neuroimaging Study with Deep Learning Architectures[EB/OL]. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/329751271_Early_Diagnosis_of_Alzheimer's_Disease_A_Neuroimaging_Study_with_Deep_Learning_Architectures, 2020-3-20.
|
| [5] |
ANTON S D, KANOOR S, FRAUNHOLZ D , et al. Evaluation of Machine Learning-based Anomaly Detection Algorithms on an Industrial Modbus/tcp Data Set[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.11757v1, 2020-3-20.
|
| [6] |
YAN Weizhong, YU Lijie . On Accurate and Reliable Anomaly Detection for Gas Turbine Combustors: A Deep Learning Approach[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.09238, 2020-3-20.
|
| [7] |
SZEGEDY C, ZAREMBA W, SUTSKEVER I , et al. Intriguing Properties of Neural Networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.6199, 2020-3-20.
|
| [8] |
MOOSAVI-DEZFOOLI S M, FAWZI A, FAWZI O , et al. Universal Adversarial Perturbations [C]//IEEE. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), July 21-26, 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA. NJ: IEEE, 2017: 1765-1773.
|
| [9] |
CARLINI N, WAGNER D . Towards Evaluating the Robustness of Neural Networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1608.04644v1, 2020-3-20.
|
| [10] |
GOODFELLOW I, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M , et al. Generative Adversarial Nets[EB/OL]. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.747.1316&rep=rep1&type=pdf, 2020-3-20.
|
| [11] |
RADFORD A, METZ L, CHINTALA S . Unsupervised Representation Learning with Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.06434, 2020-3-20.
|
| [12] |
GOODFELLOW I J, SHLENS J, SZEGEDY C . Explaining and Harnessing Adversarial Examples[EB/OL]. http://de.arxiv.org/pdf/1412.6572, 2020-3-20.
|
| [13] |
TRAMÈR F, KURAKIN A, PAPERNOT N , et al. Ensemble Adversarial Training: Attacks and Defenses[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.07204, 2020-3-20.
|
| [14] |
DONG Yinpeng, LIAO Fangzhou, PANG Tianyu , et al. Boosting Adversarial Attacks with Momentum[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1710.06081, 2020-3-20.
|
| [15] |
CHEN Jianbo, JORDAN M I, WAINWRIGHT M J . Hopskipjumpattack: A Query-efficient Decision-based Attack[EB/OL]. , 2020-3-20.
|
| [16] |
MOPURI K R, GARG U, BABU R V . Fast Feature Fool: A Data Independent Approach to Universal Adversarial Perturbations[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.05572, 2020-3-20.
|
| [17] |
HAYES J, DANEZIS G . Learning Universal Adversarial Perturbations with Generative Models[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.05207?context=stat, 2020-3-20.
|
| [18] |
POURSAEED O, KATSMAN I, GAO Bicheng , et al. Generative Adversarial Perturbations[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.02328, 2020-3-20.
|
| [19] |
SHAFAHI A, NAJIBI M, XU Zheng , et al. Universal Adversarial Training[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1811.11304, 2020-3-20.
|
| [20] |
KRIZHEVSKY A . Learning Multiple Layers of Features from Tiny Images[EB/OL]. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.222.9220, 2020-3-20.
|
| [21] |
SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A . Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-scale Image Recognition[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556, 2020-3-20.
|
| [22] |
HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing , et al. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385, 2020-3-20.
|
| [23] |
HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN DER MAATEN L , et al. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1608.06993, 2020-3-20.
|
 )
)