信息网络安全 ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (6): 843-858.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.06.001
基于威胁传播的网络安全态势评估方法
- 1.武汉大学国家网络安全学院,武汉 430072
2.空天信息安全与可信计算教育部重点实验室,武汉 430072
-
收稿日期:2025-01-23出版日期:2025-06-10发布日期:2025-07-11 -
通讯作者:赵波 E-mail:zhaobo@whu.edu.cn -
作者简介:赵波(1972—),男,山东,教授,博士,CCF高级会员,主要研究方向为信息系统安全、嵌入式系统、可信计算|彭君茹(2000—),女,宁夏,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为网络安全、软件安全|王一琁(1994—),男,江苏,博士研究生,主要研究方向为网络安全、知识图谱 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(U1936122);湖北省重点研发计划(2020BAB101)
Network Security Situation Assessment Method Based on Threat Propagation
ZHAO Bo1,2( ), PENG Junru1,2, WANG Yixuan1,2
), PENG Junru1,2, WANG Yixuan1,2
- 1. School of Cyber Science and Engineering, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China
2. Key Laboratory of Aerospace Information Security and Trusted Computing, Ministry of Education, Wuhan 430072, China
-
Received:2025-01-23Online:2025-06-10Published:2025-07-11 -
Contact:ZHAO Bo E-mail:zhaobo@whu.edu.cn
摘要:
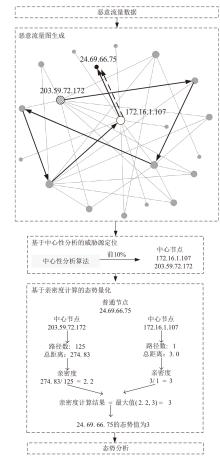
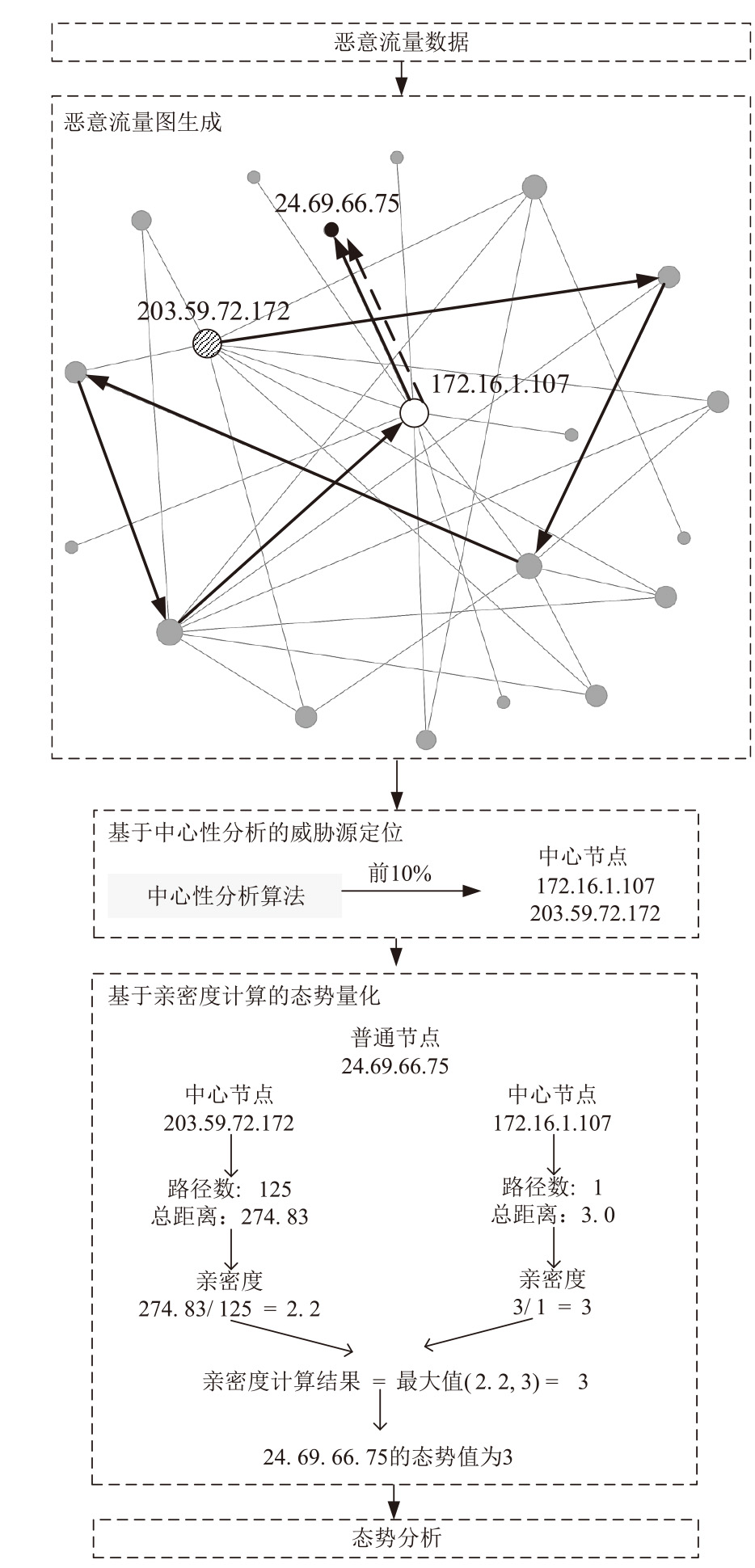
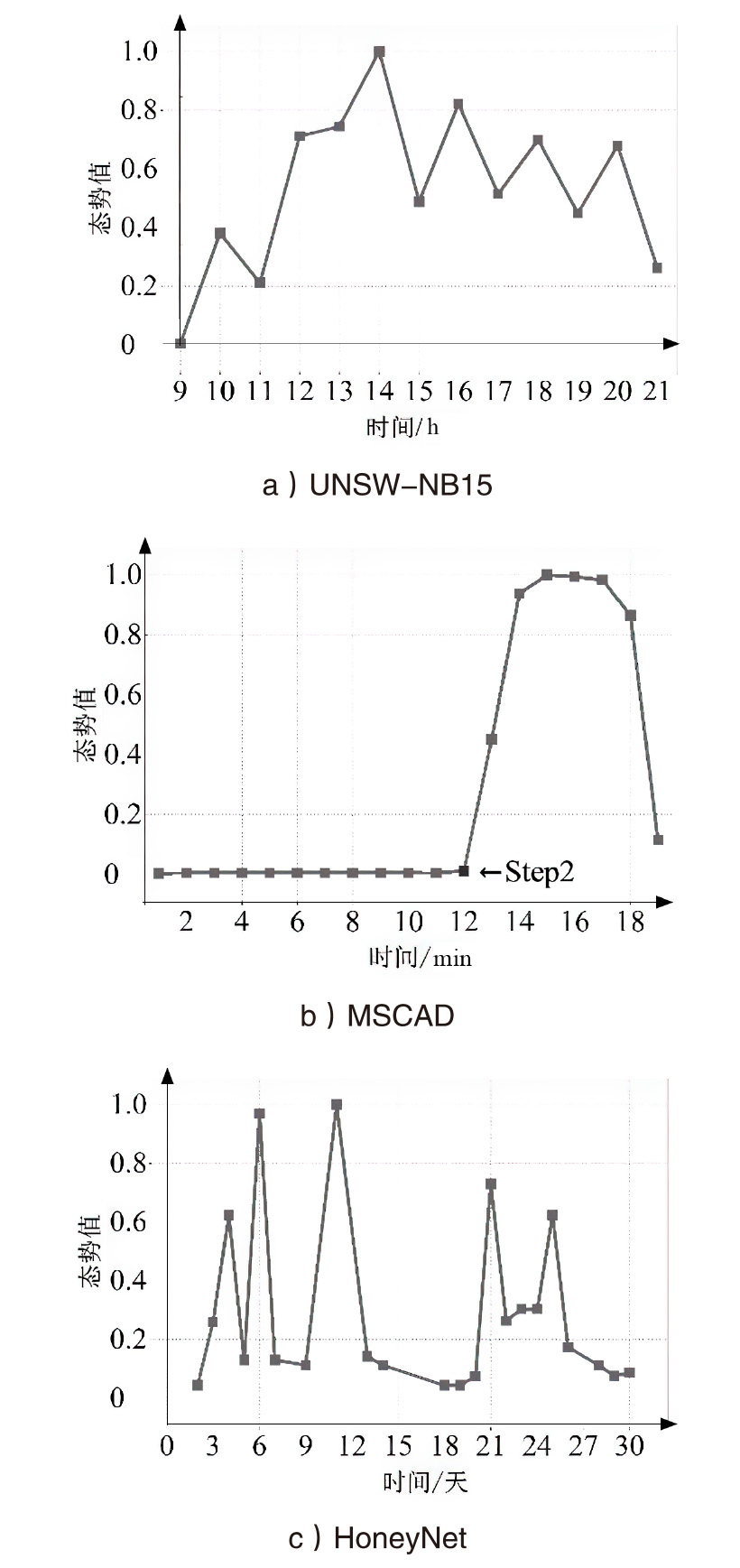
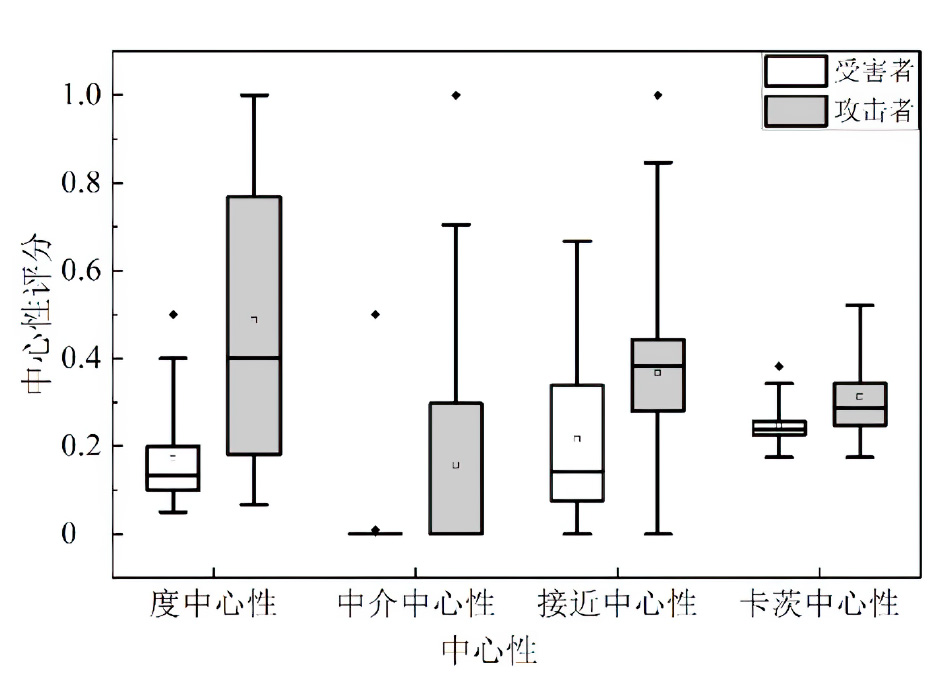
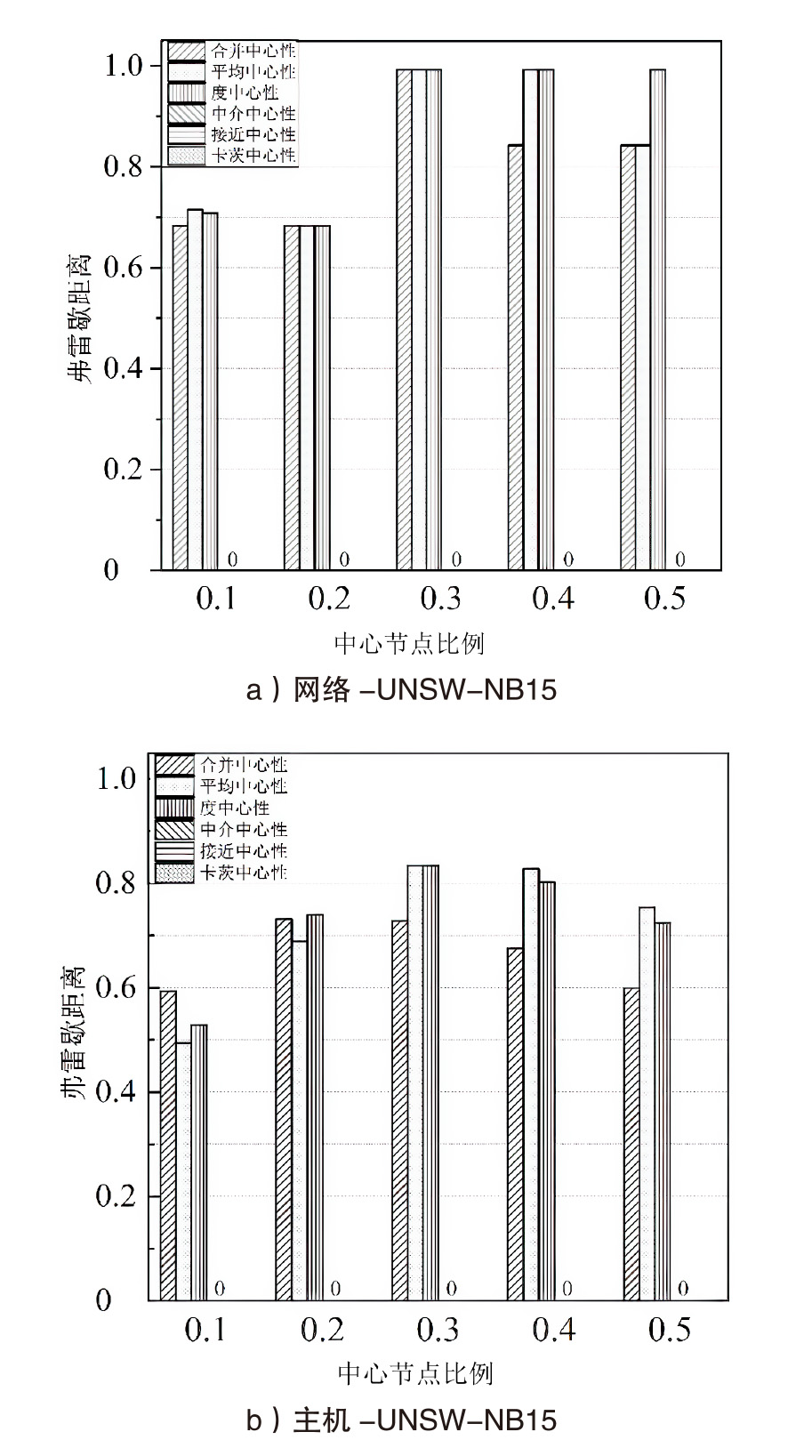
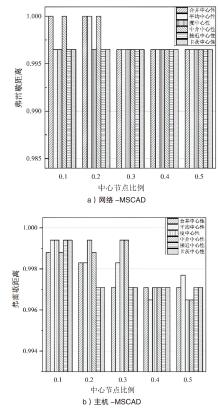
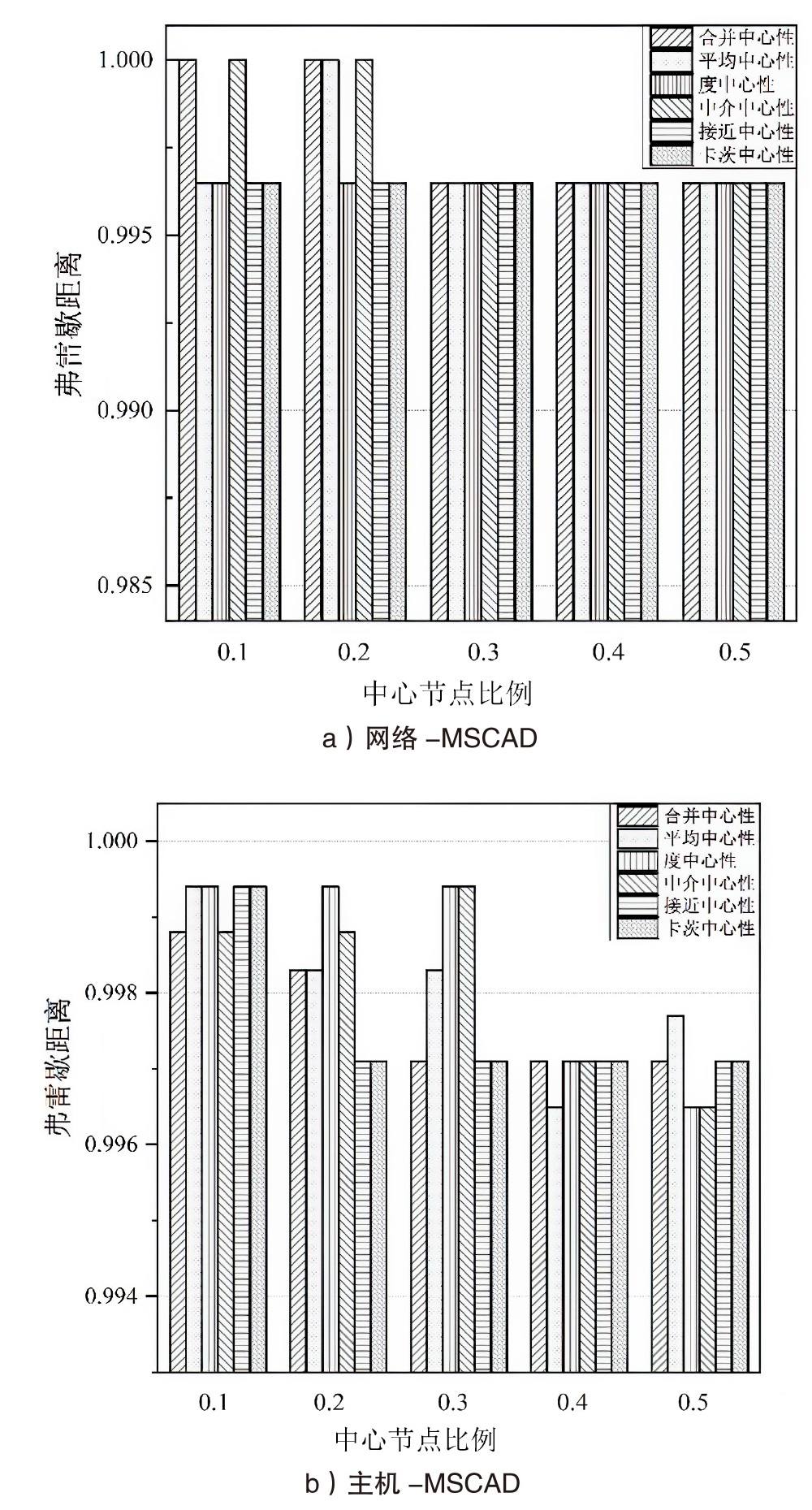
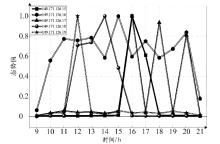
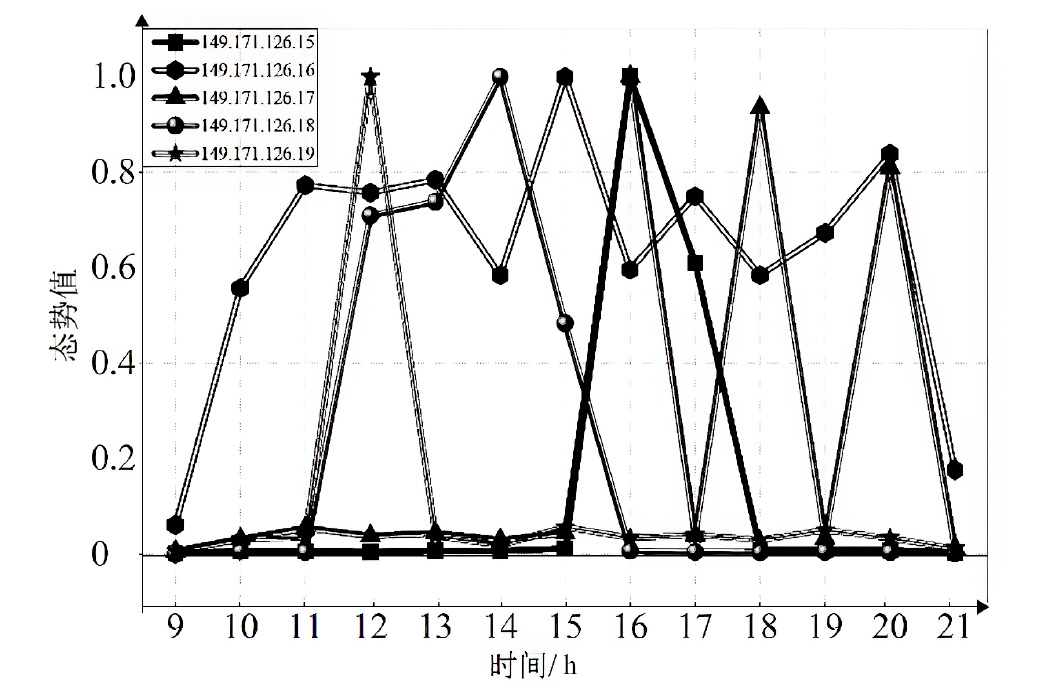
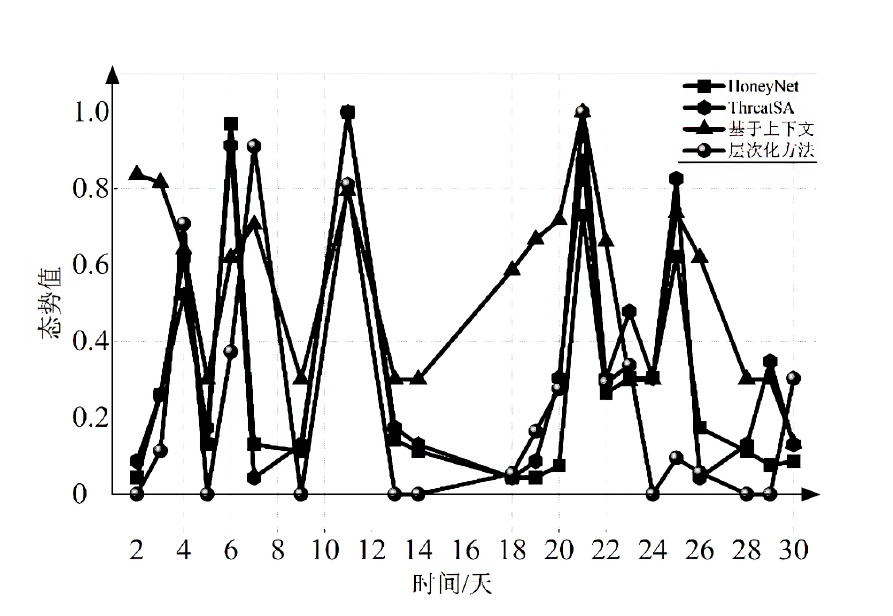
网络安全态势评估是态势感知领域中的一项重要研究。目前,已有许多网络安全态势评估方法,但以往的研究通常缺乏可迁移性或依赖专家经验,导致评估过程不够灵活,评估结果也带有一定的主观性。通过分析恶意流量图,发现攻击者通常表现出较高的中心性特征,而这种特征与社交网络中个体之间的互动和影响力传播有相似之处。在社交网络中,中心性分析用于识别关键节点并揭示其传播路径,类似地,恶意流量图中的中心性分析有助于识别攻击源和传播节点。通过这种结构上的相似性,社交网络分析方法得以迁移到恶意流量图,进一步增强了态势评估的可迁移性。为克服传统方法的迁移性问题,文章提出一种新颖的网络安全态势评估方法(ThreatSA),与传统的静态分析方法不同,ThreatSA将恶意流量转化为图结构,并通过中心性分析量化节点的重要性,识别出攻击者或传播节点。随后,利用亲密度分析衡量这些节点与其他节点之间的关系强度,从而动态反映主机的安全态势。ThreatSA仅依赖恶意流量数据,且适用于信息不完整的网络环境。通过对3个公开的网络攻击数据集进行实验评估,结果表明,ThreatSA能够实时评估网络态势,并达到99.32%、99.65%和99.74%的相似度。与当前具有代表性的两种方法相比,ThreatSA在网络安全态势评估中取得了卓越的表现。
中图分类号:
引用本文
赵波, 彭君茹, 王一琁. 基于威胁传播的网络安全态势评估方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(6): 843-858.
ZHAO Bo, PENG Junru, WANG Yixuan. Network Security Situation Assessment Method Based on Threat Propagation[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(6): 843-858.
| [1] | ALAVIZADEH H, JANG-JACCARD J, ENOCH S Y, et al. A Survey on Cyber Situation-Awareness Systems: Framework, Techniques, and Insights[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2023, 55(5): 1-37. |
| [2] | CHEN Xiuzhen, ZHENG Qinghua, GUAN Xiaohong, et al. Quantitative Hierarchical Threat Evaluation Model for Network Security[J]. Journal of Software, 2006, 17(4): 885-897. |
| 陈秀真, 郑庆华, 管晓宏, 等. 层次化网络安全威胁态势量化评估方法[J]. 软件学报, 2006, 17(4): 885-897. | |
| [3] | JIA Yiyang, WU Hanyan, JIANG Dongxing. A Hierarchical Framework of Security Situation Assessment for Information System[C]// IEEE. 2015 International Conference on Cyber-Enabled Distributed Computing and Knowledge Discovery. New York: IEEE, 2015: 23-28. |
| [4] | XIE Lixia, NI Huiyu, YANG Hongyu, et al. A Key Business Node Identification Model for Internet of Things Security[EB/OL]. (2020-12-12)[2024-12-15]. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/6654283. |
| [5] | ALALI M, ALMOGREN A, HASSAN M M, et al. Improving Risk Assessment Model of Cyber Security Using Fuzzy Logic Inference System[J]. Computers & Security, 2018, 74: 323-339. |
| [6] | BODE M A, OLUWADARE S A, ALESE B K, et al. Risk Analysis in Cyber Situation Awareness Using Bayesian Approach[C]// IEEE. 2015 International Conference on Cyber Situational Awareness, Data Analytics and Assessment (CyberSA). New York: IEEE, 2015: 1-12. |
| [7] | XI Rongrong, YUN Xiaochun, ZHANG Yongzheng. Quantitative Threat Situational Assessment Based on Contextual Information[J]. Journal of Software, 2015, 26(7): 1638-1649. |
| 席荣荣, 云晓春, 张永铮. 基于环境属性的网络威胁态势量化评估方法[J]. 软件学报, 2015, 26(7): 1638-1649. | |
| [8] | POOLSAPPASIT N, DEWRI R, RAY I. Dynamic Security Risk Management Using Bayesian Attack Graphs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2012, 9(1): 61-74. |
| [9] | LI Cheng, LI Xingming. Cyber Performance Situation Awareness on Fuzzy Correlation Analysis[C]// IEEE. 2017 3rd IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC). New York: IEEE, 2017: 424-428. |
| [10] | ZHANG Lin, ZHU Yian, SHI Xianchen, et al. A Situation Assessment Method with an Improved Fuzzy Deep Neural Network for Multiple UAVs[EB/OL]. (2020-04-04)[2024-12-15]. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11040194. |
| [11] | ZHAO Yuyu, CHENG Guang, DUAN Yu, et al. Secure IoT Edge: Threat Situation Awareness Based on Network Traffic[EB/OL]. (2021-11-06)[2024-12-15]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2021.108525. |
| [12] | TANG Xiangyan, CHEN Meizhu, CHENG Jieren, et al. A Security Situation Assessment Method Based on Neural Network[EB/OL]. (2020-01-03)[2024-12-15]. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-37352-8_52. |
| [13] | LI Yan, HUANG Guangqiu, WANG Chunzi, et al. Analysis Framework of Network Security Situational Awareness and Comparison of Implementation Methods[EB/OL]. (2019-08-13)[2024-12-15]. https://jwcn-eurasipjournals.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s13638-019-1506-1. |
| [14] | KUMARI A, GUPTA D, UPPAL M. Enhanced Security Measures for Government and Military: ANN and Decision Tree Approach to Counter VPN Malicious Transmission[C]// IEEE. 2024 IEEE 3rd World Conference on Applied Intelligence and Computing (AIC). New York: IEEE, 2024: 1367-1372. |
| [15] | GOMES J E C, EHLERT R R, BOESCHE R M, et al. Surveying Emerging Network Approaches for Military Command and Control Systems[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2024, 56(6): 1-38. |
| [16] | UPADHYAY D, MANERO J, ZAMAN M, et al. Intrusion Detection in SCADA Based Power Grids: Recursive Feature Elimination Model with Majority Vote Ensemble Algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2021, 8(3): 2559-2574. |
| [17] | VERMA P, BHAROT N, BRESLIN J G, et al. Uncovering Collateral Damages and Advanced Defense Strategies in Cloud Environments against DDoS Attacks: A Comprehensive Review[EB/OL]. (2020-04-04)[2024-12-15]. https://doi.org/10.1002/ett.4934. |
| [18] | ESFANDIARI S, FAKHRAHMAD M. Predicting Node Influence in Complex Networks by the K-Shell Entropy and Degree Centrality[C]// ACM. Companion Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2024. New York: ACM, 2024: 629-632. |
| [19] | LEE Y G, PARK M J, KWON O M. Betweenness-Centrality-Based-Pinning Control Approach to Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2024, 71(3): 1216-1220. |
| [20] | LIU Zhenfang, YE Jianxiong, ZOU Zhaonian. Closeness Centrality on Uncertain Graphs[J]. ACM Transactions on the Web, 2023, 17(4): 1-29. |
| [21] | ZHANG Tianming, FANG Junkai, YANG Zhengyi, et al. TATKC: A Temporal Graph Neural Network for Fast Approximate Temporal Katz Centrality Ranking[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2024. New York: ACM, 2024: 527-538. |
| [22] | ZOU Deqing, WU Yueming, YANG Siru, et al. IntDroid: Android Malware Detection Based on API Intimacy Analysis[J]. ACM Transactions on Software Engineering and Methodology, 2021, 30(3): 1-32. |
| [23] |
BRINGMANN L F, ELMER T, EPSKAMP S, et al. What Do Centrality Measures Measure in Psychological Networks?[J]. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 2019, 128(8): 892-903.
doi: 10.1037/abn0000446 pmid: 31318245 |
| [24] | MOUSTAFA N, SLAY J. UNSW-NB15: A Comprehensive Data Set for Network Intrusion Detection Systems (UNSW-NB15 Network Data Set)[C]// IEEE. 2015 Military Communications and Information Systems Conference (MilCIS). New York: IEEE, 2015: 1-6. |
| [25] | ALMSEIDIN M, AL-SAWWA J, ALKASASSBEH M. Generating a Benchmark Multi-Step Cyber Attacks Dataset for Intrusion Detection[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, 2022, 43(3): 3679-3694. |
| [26] | KOUR K, GOSWAMI S, SHARMA D M, et al. Honeynet Implementation in Cyber Security Attack Prevention with Data Monitoring System Using AI Technique and IoT 4G Networks[J]. International Journal of Communication Networks and Information Security (IJCNIS), 2022, 14(3): 163-175. |
| [27] | SUN Jingchun, DENG Fei, DU Boya. Research on Whole-Link Risk Situational Awareness Index System and Dynamic Risk Pool Supervision[C]// ACM. The 2022 11th International Conference on Networks, Communication and Computing. New York: ACM, 2022: 190-197. |
| [28] | WANG Juan, ZHANG Fengli, FU Chong, et al. Study on Index System in Network Situation Awareness[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2007, 27(8): 1907-1909. |
| 王娟, 张凤荔, 傅翀, 等. 网络态势感知中的指标体系研究[J]. 计算机应用, 2007, 27(8): 1907-1909. | |
| [29] | WU Guo, CHEN Lei, SI Zhigang, et al. An Index Optimization Model for Network Security Situation Evaluation[J]. Computer Engineering & Science, 2017, 39(5): 861-869. |
| 吴果, 陈雷, 司志刚, 等. 网络安全态势评估指标体系优化模型研究[J]. 计算机工程与科学, 2017, 39(5): 861-869. | |
| [30] | CONRADI J, DRIEMEL A. On Computing Thek-Shortcut Fréchet Distance[J]. ACM Transactions on Algorithms, 2024, 20(4): 1-37. |
| [31] | ZHANG Ruiqing, XIA Jingkang, MA Junjie, et al. Human-Robot Interactive Skill Learning and Correction for Polishing Based on Dynamic Time Warping Iterative Learning Control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2024, 32(6): 2310-2320. |
| [32] | SHI Zhanhui, XIAO Jie, JIANG Jianhui, et al. Identifying Reliability High-Correlated Gates of Logic Circuits with Pearson Correlation Coefficient[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2024, 71(4): 2319-2323. |
| [33] | WALEED A, JAMALI A F, MASOOD A. Which Open-Source IDS? Snort, Suricata or Zeek[EB/OL]. (2022-06-22)[2024-12-15]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2022.109116. |
| [1] | 石乐义, 徐兴华, 刘祎豪, 刘佳. 一种改进概率神经网络的工业控制系统安全态势评估方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(3): 15-25. |
| [2] | 余晴, 郑崇辉, 杜晔. 面向云平台虚拟层的安全态势评估关键技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(7): 53-59. |
| [3] | 赵志岩, 纪小默. 智能化网络安全威胁感知融合模型研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(4): 87-93. |
| [4] | 范渊, 刘志乐, 王吉文. 一种基于模糊粗糙集的网络态势评估方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2015, 15(9): 58-61. |
| [5] | 陈敏欣;谢冬青;黄海. 环境监测有害成分的数据融合及其水质状况评价[J]. , 2014, 14(2): 0-0. |
| [6] | . 环境监测有害成分的数据融合及其水质状况评价[J]. , 2014, 14(2): 63-. |
| [7] | 张静;陈冠直;赵玉洁;闻楠. 石油石化系统信息安全态势评估指标体系研究[J]. , 2012, 12(3): 0-0. |
| [8] | 张勇;丁建林. 赛博空间态势感知技术研究[J]. , 2012, 12(3): 0-0. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||