信息网络安全 ›› 2024, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (11): 1632-1642.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2024.11.003
民航空管信息系统用户多因子持续身份可信认证方法研究
- 1.清华大学自动化系,北京 100084
2.中国人民公安大学交通管理学院,北京 100038
-
收稿日期:2024-08-10出版日期:2024-11-10发布日期:2024-11-21 -
通讯作者:晏松ys1133@126.com -
作者简介:陈宝刚(1975—),男,山东,高级工程师,硕士,主要研究方向为民航网络和数据安全、机器学习、大数据应用、神经网络|张毅(1964—),男,四川,教授,博士,主要研究方向为智能交通系统工程、交通大数据分析、交通群体协同控制|晏松(1990—),男,云南,讲师,博士,主要研究方向为智能交通、交通仿真与控制、交通大数据分析
Research on Multi-Factor Continuous Trustworthy Identity Authentication for Users in Civil Aviation Air Traffic Control Operational Information Systems
CHEN Baogang1, ZHANG Yi1, YAN Song2( )
)
- 1. Department of Automation, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
2. School of Traffic Management, People’s Public Security University of China, Beijing 100038, China
-
Received:2024-08-10Online:2024-11-10Published:2024-11-21
摘要:
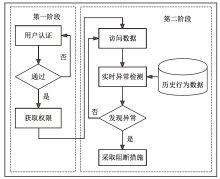
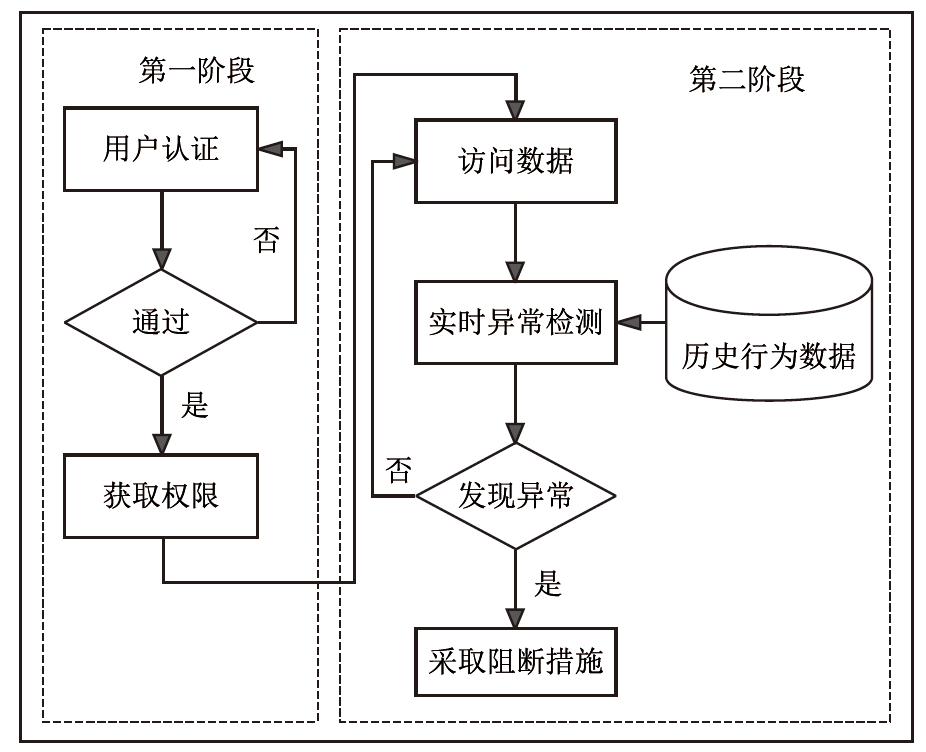
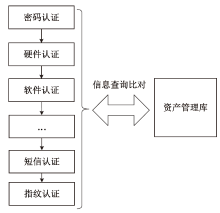
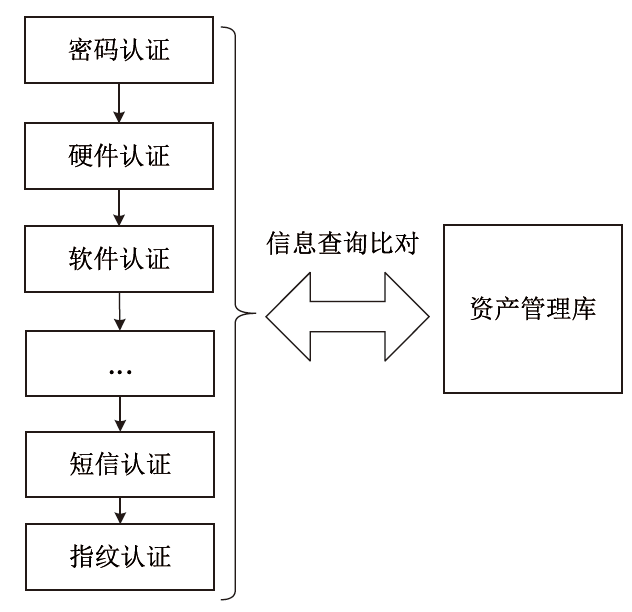
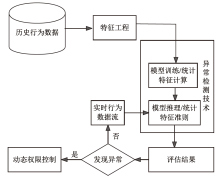
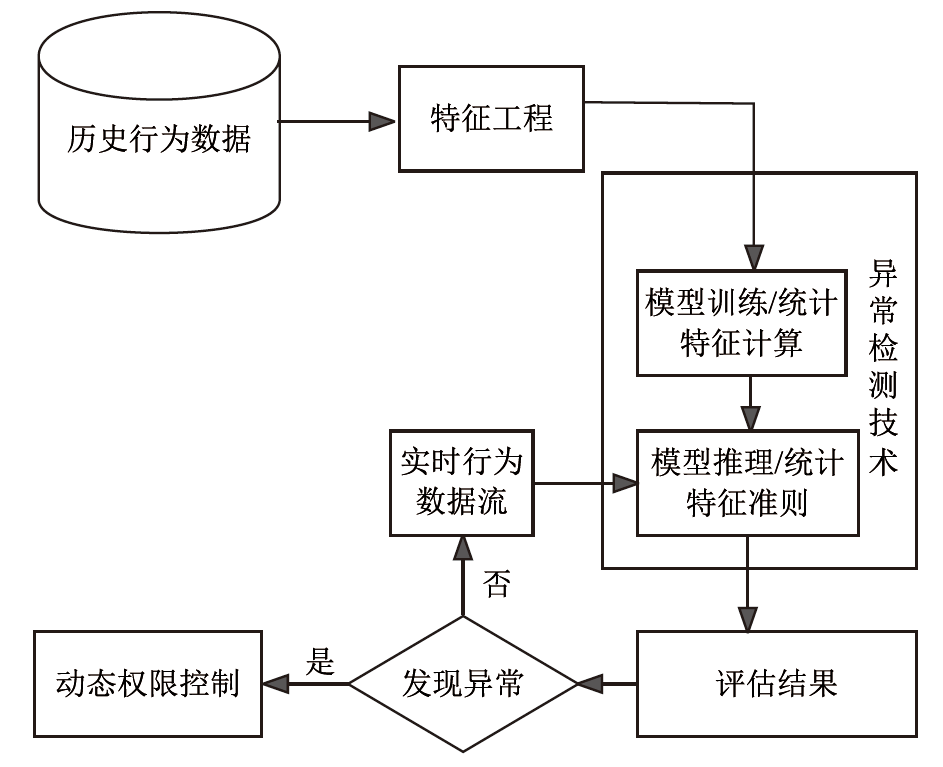
随着网络安全威胁不断演变,传统身份认证方法面临着日益严峻的挑战。文章以民航空管信息系统为应用背景,提出一种多因子身份可信持续认证方法。该方法包含两个阶段,第一阶段为登录时多因子身份可信认证,第二阶段为登录后多因子行为特征持续身份可信认证。在第二阶段持续认证中采用统计特征法和机器学习模型,增强对用户行为模式的实时监测和分析能力,提高异常行为检测的准确性。文章通过实验验证了多因子行为特征持续身份可信认证在单点异常和上下文异常场景下的有效性,证明了其在身份认证领域的可靠性和实用性。实验结果表明,该方法在提高系统安全性和降低被破解风险方面具有一定的优势。
中图分类号:
引用本文
陈宝刚, 张毅, 晏松. 民航空管信息系统用户多因子持续身份可信认证方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(11): 1632-1642.
CHEN Baogang, ZHANG Yi, YAN Song. Research on Multi-Factor Continuous Trustworthy Identity Authentication for Users in Civil Aviation Air Traffic Control Operational Information Systems[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(11): 1632-1642.
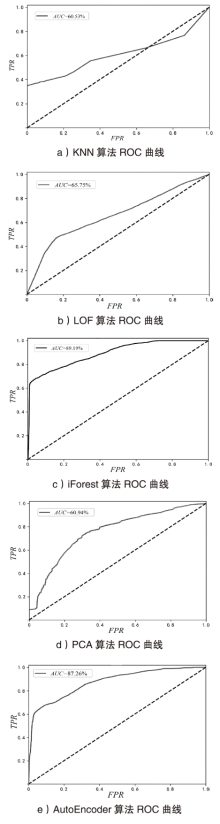
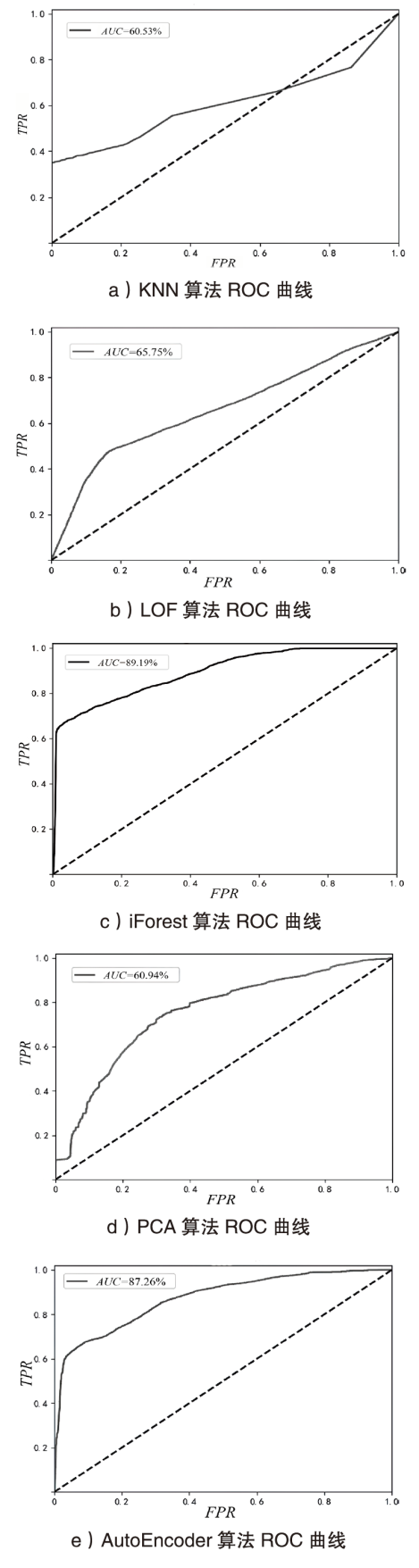
表4
采用流量分组策略后机器学习法性能
| 方法 | 流量分组 | 超参数 | 异常识别率 | 异常误报率 | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KNN | 全流量 | 邻近点 | 10 | 35.57% | 8.67% | 60.21% |
| 30 | 31.27% | 9.20% | 59.46% | |||
| 50 | 29.82% | 9.12% | 58.61% | |||
| 70 | 29.59% | 8.96% | 58.11% | |||
| 90 | 29.81% | 9.14% | 58.40% | |||
| 分组流量 | 10 | 39.57% | 5.21% | 60.53% | ||
| 30 | 39.12% | 5.44% | 60.23% | |||
| 50 | 40.51% | 6.83% | 58.90% | |||
| 70 | 40.11% | 6.61% | 57.98% | |||
| 90 | 39.97% | 7.14% | 57.97% | |||
| LOF | 全流量 | 250 | 26.70% | 9.39% | 61.50% | |
| 500 | 32.63% | 9.17% | 65.75% | |||
| 1000 | 32.28% | 9.19% | 65.09% | |||
| 1500 | 32.28% | 9.19% | 64.70% | |||
| 2000 | 32.47% | 9.18% | 64.48% | |||
| 分组流量 | 250 | 32.13% | 9.19% | 64.50% | ||
| 500 | 31.50% | 9.22% | 63.67% | |||
| 1000 | 28.04% | 9.34% | 61.20% | |||
| 1500 | 23.62% | 9.50% | 56.90% | |||
| 2000 | 22.77% | 9.53% | 58.73% | |||
| iForest | 全流量 | 决策树数量 | 50 | 52.01% | 8.43% | 84.83% |
| 100 | 48.95% | 8.50% | 83.16% | |||
| 150 | 56.19% | 8.30% | 84.53% | |||
| 200 | 58.20% | 8.22% | 85.32% | |||
| 250 | 57.21% | 8.27% | 84.37% | |||
| 分组流量 | 50 | 64.67% | 7.52% | 88.13% | ||
| 100 | 64.70% | 7.84% | 88.66% | |||
| 150 | 64.19% | 7.77% | 88.34% | |||
| 200 | 64.49% | 7.71% | 89.19% | |||
| 250 | 64.68% | 7.74% | 88.92% | |||
| PCA | 全流量 | — | 31.97% | 9.20% | 75.26% | |
| 分组流量 | — | 47.23% | 8.62% | 60.94% | ||
| AutoEncoder | 全流量 | — | 29.03% | 9.31% | 76.20% | |
| 分组流量 | — | 43.22% | 8.63% | 87.26% | ||
表7
特征工程策略下模型性能比较
| 算法 | 特征工程 | 异常识别率 | 异常误报率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| KNN | 聚合数据 | 56.03% | 11.22% |
| 聚合数据+时段分组 | 82.17% | 4.04% | |
| 随机森林 | 聚合数据 | 91.60% | 2.64% |
| 聚合数据+时段分组 | 91.80% | 2.76% | |
| GBDT | 聚合数据 | 90.53% | 2.26% |
| 聚合数据+时段分组 | 88.87% | 1.00% | |
| ExtraTrees | 聚合数据 | 88.60% | 0.84% |
| 聚合数据+时段分组 | 88.60% | 0.84% | |
| Adaboost | 聚合数据 | 19.80% | 4.18% |
| 聚合数据+时段分组 | 91.37% | 2.50% | |
| GaussianNB | 聚合数据 | 9.99% | 5.59% |
| 聚合数据+时段分组 | 91.83% | 8.04% | |
| CategoricalNB | 聚合数据 | 16.33% | 6.00% |
| 聚合数据+时段分组 | 86.80% | 0.60% |
| [1] | International Civil Aviation Organization. CYBERSECURITY ACTION PLAN-Second Edition[EB/OL]. [2024-05-11]. https://www.icao.int/aviationcybersecurity/Documents/CYBERSECURITY ACTION PLAN-Second edition.EN.pdf. |
| [2] | XU Dandan, LI Peiyu, ZHANG Shiqian, et al. Research on Multi-Factor Authentication Method in Unified Identity Authentication System[J]. Journal of Fuzhou University(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(5): 616-620. |
| 许丹丹, 李沛谕, 张世倩, 等. 统一身份认证系统中的多因子身份认证方法[J]. 福州大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 51(5):616-620. | |
| [3] | OMETOV A, BEZZATEEV S, MÄKITALO N, et al. Multi-Factor Authentication: A Survey[J]. Cryptography, 2018, 2(1): 1-31. |
| [4] | ZHANG Meng, YIN Qiqi. Research Progress of Static Password Authentication Technology[J]. Cyberspace Security, 2018, 9(7): 11-14. |
| 张猛, 尹其其. 静态口令认证技术研究进展[J]. 网络空间安全, 2018, 9(7):11-14. | |
| [5] | ZHAO Zhihui, LI Xinshe. Research on Password-Based Identity Authentication System[J]. Network Security Technology & Application, 2009(4): 18-19. |
| 赵志辉, 李新社. 基于口令的身份认证系统研究[J]. 网络安全技术与应用, 2009(4):18-19. | |
| [6] | YOU Lin. A Survey on Biometric Cryptographic Technology[J]. Journal of Hangzhou Dianzi University(Natural Sciences), 2015, 35(3): 1-17. |
| 游林. 生物特征密码技术综述[J]. 杭州电子科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 35(3):1-17. | |
| [7] |
LI Fujuan, MA Zhuo, WANG Qun. Survey on Identity Management in Blockchain Systems[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2024, 60(1): 57-73.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2302-0189 |
|
李馥娟, 马卓, 王群. 区块链系统身份管理机制研究综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2024, 60(1):57-73.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2302-0189 |
|
| [8] | ZHAO Liang, MAO Bing, XIE Li. Survey of Acess Control[J]. Computer Engineering, 2004, 30(2): 1-2. |
| 赵亮, 茅兵, 谢立. 访问控制研究综述[J]. 计算机工程, 2004, 30(2):1-2. | |
| [9] | LIU Long, CHEN Jianbin, XUE Ruisi. Research and Design of Data Permission Management[J]. Value Engineering, 2013, 32(31): 215-216. |
| 刘龙, 陈建斌, 薛锐思. 数据权限管理的研究和设计[J]. 价值工程, 2013, 32(31):215-216. | |
| [10] | POTTIER F, SKALKA C, SMITH S. A Systematic Approach to Static Access Control[J]. ACM Transactions on Programming Languages and Systems, 2005, 27(2): 344-382. |
| [11] | CHEN T S, CHUNG J Y, TIAN Changsi, et al. A Novel Key Management Scheme for Dynamic Access Control in a User Hierarchy[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2005, 162(1): 339-351. |
| [12] | YU Jiang, SU Jinhai, ZHANG Yongfu. Design and Analysis of USB-Key Based Strong Password Authentication Scheme[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2011, 31(2): 511-513. |
| 于江, 苏锦海, 张永福. 基于USB-Key的强口令认证方案设计与分析[J]. 计算机应用, 2011, 31(2):511-513. | |
| [13] | KRIEGEL H P, KRÖGER P, ZIMEK A. Outlier Detection Techniques[J]. Tutorial at KDD, 2010, 10: 1-76. |
| [14] | LAI K H, ZHA Daochen, WANG Guanchu, et al. TODS: An Automated Time Series Outlier Detection System[EB/OL]. [2024-05-22]. https://www.xueshufan.com/publication/3175611124. |
| [15] | SIEGMUND D. Error Probabilities and Average Sample Number of the Sequential Probability Ratio Test[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B: Statistical Methodology, 1975, 37(3): 394-401. |
| [16] | GOLDSTEIN M, DENGEL A. Histogram-Based Outlier Score(hbos): A Fast Unsupervised Anomaly Detection Algorithm[J]. KI-2012: Poster and Demo Track, 2012, 1: 59-63. |
| [17] | BOUKERCHE A, ZHENG Lining, ALFANDI O. Outlier Detection: Methods, Models, and Classification[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2020, 53(3): 1-37. |
| [18] | WALFISH S. A Review of Statistical Outlier Methods[J]. Pharmaceutical Technology, 2006, 30(11): 82-86. |
| [19] | GU Xiaoyi, AKOGLU L, RINALDO A. Statistical Analysis of Nearest Neighbor Methods for Anomaly Detection[EB/OL]. (2019-07-08)[2024-05-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.03813v1. |
| [20] | BREUNIG M M, KRIEGEL H P, NG R T, et al. LOF: Identifying Density-Based Local Outliers[C]//ACM. The 2000 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data. New York: ACM, 2000: 93-104. |
| [21] | LIU F T, TINGKaiming, ZHOU Zhihua. Isolation Forest[C]//IEEE. 2008 8th IEEE International Conference on Data Mining. New York: IEEE, 2008: 413-422. |
| [22] | SHYU M L, CHEN S C, SARINNAPAKORN K, et al. A Novel Anomaly Detection Scheme Based on Principal Component Classifier[C]//IEEE. The IEEE Foundations and New Directions of Data Mining Workshop. New York: IEEE, 2003: 172-179. |
| [23] | RUMELHART D E, HINTON G E, WILLIAMS R J. Learning Representations by Back-Propagating Errors[J]. Nature, 1986, 323: 533-536. |
| [24] |
HINTON G E, OSINDERO S, TEH Y W. A Fast Learning Algorithm for Deep Belief Nets[J]. Neural Computation, 2006, 18(7): 1527-1554.
doi: 10.1162/neco.2006.18.7.1527 pmid: 16764513 |
| [25] | BREIMAN L. Random Forests[J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45: 5-32. |
| [26] | FRIEDMAN J H. Greedy Function Approximation: A Gradient Boosting Machine[J]. The Annals of Statistics, 2001, 29(5): 1189-1232. |
| [27] | GEURTS P, ERNST D, WEHENKEL L. Extremely Randomized Trees[J]. Machine Learning, 2006, 63(1): 3-42. |
| [28] | FREUND Y, SCHAPIRE R E. Experiments with a New Boosting Algorithm[C]//ACM. 13th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 1996: 148-156. |
| [29] | ZHANG H. The Optimality of Naive Bayes[EB/OL]. [2024-05-22]. https://aaai.org/papers/flairs-2004-097/. |
| [30] | RENNIE J D M, SHIH L, TEEVAN J, et al. Tackling the Poor Assumptions of Naive Bayes Text Classifiers[EB/OL]. [2024-05-22]. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Tackling-the-Poor-Assumptions-of-Naive-Bayes-Text-Rennie-Shih/b7fab2f72ebbf4e98def1daf8c29ffcfe91183bf. |
| [31] | MANNING C D, RAGHAVAN P, SCHÜTZE H. Introduction to Information Retrieval[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2008. |
| [32] | METSIS V, ANDROUTSOPOULOS I, PALIOURAS G. Spam Filtering with Naive Bayes-which Naive Bayes?[EB/OL]. [2024-05-22]. http://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/39a8/0339844a27e63a2b82ae4f8eb964da787172.pdf. |
| [1] | 周书丞, 李杨, 李传荣, 郭璐璐, 贾辛洪, 杨兴华. 基于上下文的异常根因算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(7): 1062-1075. |
| [2] | 张浩, 谢大智, 胡云晟, 叶骏威. 基于半监督学习的网络异常检测研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(4): 491-508. |
| [3] | 王健, 陈琳, 王凯崙, 刘吉强. 基于时空图神经网络的应用层DDoS攻击检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(4): 509-519. |
| [4] | 戚晗, 王敬童, 拱长青. 基于随机量子层的变分量子卷积神经网络鲁棒性研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 363-373. |
| [5] | 江荣, 刘海天, 刘聪. 基于集成学习的无监督网络入侵检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 411-426. |
| [6] | 冯光升, 蒋舜鹏, 胡先浪, 马明宇. 面向物联网的入侵检测技术研究新进展[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 167-178. |
| [7] | 印杰, 陈浦, 杨桂年, 谢文伟, 梁广俊. 基于人工智能的物联网DDoS攻击检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(11): 1615-1623. |
| [8] | 兰浩良, 王群, 徐杰, 薛益时, 张勃. 基于区块链的联邦学习研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(11): 1643-1654. |
| [9] | 王南, 袁也, 杨浩然, 文周之, 苏明, 刘晓光. 环保大数据在区块链中的隐私计算[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(10): 1515-1527. |
| [10] | 张子涵, 赖清楠, 周昌令. 深度学习框架模糊测试研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(10): 1528-1536. |
| [11] | 萨其瑞, 尤玮婧, 张逸飞, 邱伟杨, 马存庆. 联邦学习模型所有权保护方案综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(10): 1553-1561. |
| [12] | 宋玉涵, 祝跃飞, 魏福山. 一种基于AdaBoost模型的区块链异常交易检测方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1): 24-35. |
| [13] | 秦中元, 马楠, 余亚聪, 陈立全. 基于双重图神经网络和自编码器的网络异常检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(9): 1-11. |
| [14] | 薛羽, 张逸轩. 深层神经网络架构搜索综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(9): 58-74. |
| [15] | 王鹃, 张冲, 龚家新, 李俊娥. 基于机器学习的模糊测试研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(8): 1-16. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||