信息网络安全 ›› 2024, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (9): 1386-1395.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2024.09.007
面向骨骼动作识别的优化梯度感知对抗攻击方法
- 1.安徽大学互联网学院,合肥 230039
2.合肥工业大学计算机与信息学院,合肥 230009
-
收稿日期:2023-10-30出版日期:2024-09-10发布日期:2024-09-27 -
通讯作者:刁云峰diaoyunfeng@hfut.edu.cn -
作者简介:陈晓静(1990—),女,安徽,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为计算机视觉、量子通信|陶杨(1998—),女,安徽,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为计算机视觉、人工智能安全|吴柏祺(2003—),男,安徽,主要研究方向为人工智能安全、数据安全及隐私保护|刁云峰(1993—),男,山东,讲师,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为人工智能安全、计算机视觉 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(12001002);国家自然科学基金(62302139);中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金(JZ2023HGQA0101);中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金(JZ2023HGTA0202)
Optimization Gradient Perception Adversarial Attack for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition
CHEN Xiaojing1, TAO Yang1, WU Baiqi2, DIAO Yunfeng2( )
)
- 1. School of Internet, Anhui University, Hefei 230039, China
2. School of Computer Science and Information Engineering, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei 230009, China
-
Received:2023-10-30Online:2024-09-10Published:2024-09-27
摘要:
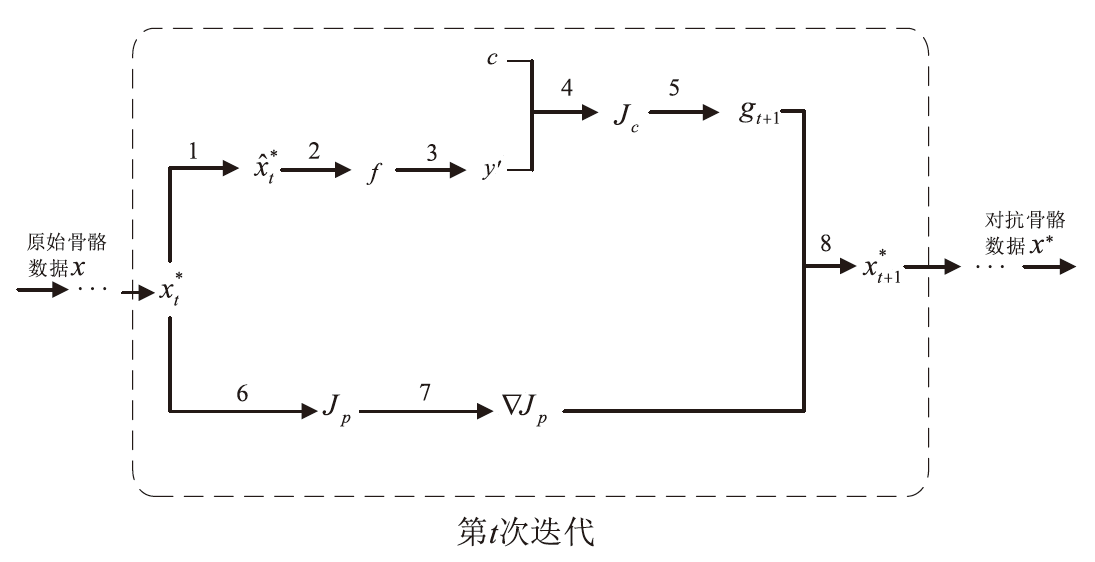
基于骨骼的动作识别模型被广泛应用于自动驾驶、行为监测和动作分析等领域。一些研究表明,这些模型容易受到对抗攻击,引发了一系列安全漏洞和隐私问题。虽然现有攻击方法在白盒攻击下能够取得较高的成功率,但是这些方法都需要攻击者获得模型的全部参数,这在现实场景中不易实现,且在黑盒攻击下的可迁移性较差。为了解决上述问题,文章提出一种面向骨骼动作识别的优化梯度感知对抗攻击方法NAG-PA。该方法在梯度计算的每次迭代中都优先估计下一步参数更新后的值,并在更新后的位置进行梯度累积。同时,对当前位置进行修正,避免落入局部极值,从而提高对抗样本的可迁移性。此外,文章所提方法还使用了感知损失以确保迁移攻击具有不可感知性。在现有公开数据集和骨骼动作识别模型上的实验结果表明,文章所提方法可以显著提高对抗攻击的可迁移性。
中图分类号:
引用本文
陈晓静, 陶杨, 吴柏祺, 刁云峰. 面向骨骼动作识别的优化梯度感知对抗攻击方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(9): 1386-1395.
CHEN Xiaojing, TAO Yang, WU Baiqi, DIAO Yunfeng. Optimization Gradient Perception Adversarial Attack for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(9): 1386-1395.
表2
衰减因子μ对迁移攻击成功率的影响
| 代理模型 | 目标模型 | μ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 | ||
| 2s-AGCN | STGCN | 33.49% | 34.38% | 33.04% | 33.71% | 33.71% |
| CTRGCN | 16.52% | 15.18% | 15.85% | 15.63% | 16.97% | |
| MSG3D | 45.54% | 44.87% | 44.64% | 45.09% | 45.98% | |
| FR-HEAD | 11.84% | 9.60% | 11.39% | 11.39% | 10.72% | |
| STGCN | 2s-AGCN | 9.15% | 9.60% | 10.04% | 10.49% | 10.27% |
| CTRGCN | 16.75% | 17.86% | 17.19% | 17.19% | 16.30% | |
| MSG3D | 26.11% | 29.69% | 29.01% | 29.69% | 29.69% | |
| FR-HEAD | 11.61% | 12.28% | 11.39% | 10.27% | 11.17% | |
| MSG3D | STGCN | 41.52% | 40.85% | 40.18% | 39.51% | 39.74% |
| 2s-AGCN | 21.65% | 21.21% | 21.88% | 20.76% | 21.21% | |
| CTRGCN | 18.75% | 18.98% | 19.87% | 18.75% | 21.21% | |
| FR-HEAD | 10.50% | 9.83% | 10.27% | 9.83% | 10.27% | |
表3
感知损失对对抗骨骼动作样本质量的影响
| 数据集 | 模型 | l | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDM05 | STGCN | P | 0.140 | 0.002 | 0.610% |
| NP | 0.310 | 0.026 | 1.320% | ||
| 2s-AGCN | P | 0.210 | 0.003 | 1.960% | |
| NP | 0.320 | 0.026 | 2.760% | ||
| MSG3D | P | 0.180 | 0.004 | 1.440% | |
| NP | 0.300 | 0.052 | 2.410% | ||
| NTU60 | STGCN | P | 0.040 | 0.011 | 6.960% |
| NP | 0.050 | 0.025 | 7.490% | ||
| 2s-AGCN | P | 0.020 | 0.005 | 3.570% | |
| NP | 0.020 | 0.010 | 3.520% | ||
| CTRGCN | P | 0.030 | 0.012 | 6.580% | |
| NP | 0.060 | 0.028 | 8.320% | ||
| MSG3D | P | 0.020 | 0.005 | 3.660% | |
| NP | 0.020 | 0.011 | 3.880% | ||
| FR-HEAD | P | 0.010 | 0.005 | 3.050% | |
| NP | 0.020 | 0.013 | 3.680% | ||
| DGNN | P | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.700% | |
| NP | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.790% |
表4
NAG-PA与SMART的迁移攻击成功率比较
| 代理 模型 | 攻击 方法 | 目标模型 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STGCN | 2s-AGCN | MSG3D | DGNN | CTRGCN | SGN | FR-HEAD | ||
| STGCN | SMART | — | 5.39% | 2.97% | 8.36% | 7.58% | 97.11% | 8.60% |
| NAG-PA | — | 17.03% | 12.73% | 21.02% | 14.22% | 98.21% | 24.69% | |
| 2s-AGCN | SMART | 14.61% | — | 2.97% | 8.59% | 8.91% | 98.13% | 9.85% |
| NAG-PA | 18.91% | — | 12.97% | 25.23% | 11.25% | 97.74% | 15.55% | |
| MSG3D | SMART | 17.35% | 9.30% | — | 12.27% | 11.41% | 97.27% | 12.35% |
| NAG-PA | 20.71% | 17.89% | — | 26.25% | 15.61% | 97.58% | 18.83% | |
| DGNN | SMART | 14.38% | 6.48% | 3.20% | — | 7.19% | 97.66% | 7.66% |
| NAG-PA | 15.16% | 7.03% | 3.51% | — | 9.15% | 98.36% | 8.91% | |
| CTRGCN | SMART | 17.04% | 8.05% | 5.00% | 10.23% | — | 97.19% | 12.90% |
| NAG-PA | 25.24% | 15.70% | 10.47% | 20.55% | — | 97.74% | 41.80% | |
| FR-HEAD | SMART | 16.10% | 7.03% | 3.20% | 9.22% | 8.75% | 97.90% | — |
| NAG-PA | 19.77% | 9.68% | 8.13% | 17.27% | 17.90% | 98.05% | — | |
| [1] | SZEGEDY C, ZAREMBA W, SUTSKEVER I, et al. Intriguing Properties of Neural Networks[EB/OL]. (2014-02-19)[2023-09-23]. |
| [2] | WEI Xingxing, ZHU Jun, YUAN Sha, et al. Sparse Adversarial Perturbations for Videos[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 33(1): 8973-8980. |
| [3] | REN Bin, LIU Mengyuan, DING Runwei, et al. A Survey on 3D Skeleton-Based Action Recognition Using Learning Method[EB/OL]. (2020-02-14)[2023-09-23]. |
| [4] | WANG He, HE Feixiang, PENG Zhexi, et al. Understanding the Robustness of Skeleton-Based Action Recognition under Adversarial Attack[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2021: 14651-14660. |
| [5] | TANAKA N, KERA H, KAWAMOTO K. Adversarial Bone Length Attack on Action Recognition[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2022, 36(2): 2335-2343. |
| [6] | GOODFELLOW I J, SHLENS J, SZEGEDY C. Explaining and Harnessing Adversarial Examples[EB/OL]. (2015-03-20)[2023-09-23]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6572. |
| [7] | DONG Yinpeng, LIAO Fangzhou, PANG Tianyu, et al. Boosting Adversarial Attacks with Momentum[C]// IEEE. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2018: 9185-9193. |
| [8] | WANG Xiaosen, HE Kun. Enhancing the Transferability of Adversarial Attacks through Variance Tuning[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2021: 1924-1933. |
| [9] | CHEN Huanran, ZHANG Yichi, DONG Yinpeng, et al. Rethinking Model Ensemble in Transfer-Based Adversarial Attacks[EB/OL]. (2023-03-16)[2023-09-23]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.09105. |
| [10] | LI Chenwei, ZHANG Hengwei, GAO Wei, et al. Transferable Image Adversarial Attack Method with AdaN Adaptive Gradient Optimizer[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(7): 64-73. |
| 李晨蔚, 张恒巍, 高伟, 等. 基于AdaN自适应梯度优化的图像对抗迁移攻击方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(7): 64-73. | |
| [11] | MÜLLER M, RÖDER T, CLAUSEN M, et al. Documentation Mocap Database HDM05[R]. Bonn: University Bonn, No. CG-2007-2, ISSN 1610-8892, 2007. |
| [12] | SHAHROUDY A, LIU Jun, NG T T, et al. NTU RGB D: A Large Scale Dataset for 3D Human Activity Analysis[C]// IEEE. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2016: 1010-1019. |
| [13] | LU Zhengzhi, WANG He, CHANG Ziyi, et al. Hard No-Box Adversarial Attack on Skeleton-Based Human Action Recognition with Skeleton-Motion-Informed Gradient[EB/OL]. (2023-08-18)[2023-09-23]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.05681. |
| [14] | MEHTA D, SRIDHAR S, SOTNYCHENKO O, et al. VNect: Real-Time 3D Human Pose Estimation with a Single RGB Camera[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2017, 36(4): 1-14. |
| [15] | DU Yong, WANG Wei, WANG Liang. Hierarchical Recurrent Neural Network for Skeleton Based Action Recognition[C]// IEEE. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2015: 1110-1118. |
| [16] |
ZHANG Pengfei, LAN Cuiling, XING Junliang, et al. View Adaptive Neural Networks for High Performance Skeleton-Based Human Action Recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(8): 1963-1978.
doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2896631 pmid: 30714909 |
| [17] | DU Yong, FU Yun, WANG Liang. Skeleton Based Action Recognition with Convolutional Neural Network[C]// IEEE. 2015 3rd IAPR Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition (ACPR). New York: IEEE, 2015: 579-583. |
| [18] | LIU Mengyuan, LIU Hong, CHEN Chen. Enhanced Skeleton Visualization for View Invariant Human Action Recognition[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 68: 346-362. |
| [19] | YAN Sijie, XIONG Yuanjun, LIN Dahua. Spatial Temporal Graph Convolutional Networks for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2018, 32(1): 7444-7452. |
| [20] | SHI Lei, ZHANG Yifan, CHENG Jian, et al. Two-Stream Adaptive Graph Convolutional Networks for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2019: 12018-12027. |
| [21] | LIU Ziyu, ZHANG Hongwen, CHEN Zhenghao, et al. Disentangling and Unifying Graph Convolutions for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2020: 140-149. |
| [22] | TANG Yansong, TIAN Yi, LU Jiwen, et al. Deep Progressive Reinforcement Learning for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition[C]// IEEE. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2018: 5323-5332. |
| [23] | KURAKIN A, GOODFELLOW J I, BENGIO S. Adversarial Examples in the Physical World[EB/OL]. (2017-02-11)[2023-09-23]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.02533. |
| [24] | HU Wei, ZHAO Wenlong, CHEN Lu, et al. An Improved JSMA Algorithm against Sample Attack Based on Logits Vector[J]. Netinfo Security, 2022, 22(3): 62-69. |
| 胡卫, 赵文龙, 陈璐, 等. 基于Logits向量的JSMA对抗样本攻击改进算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(3): 62-69. | |
| [25] | LIU Jian, AKHTAR N, MIAN A. Adversarial Attack on Skeleton-Based Human Action Recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(4): 1609-1622. |
| [26] | DIAO Yunfeng, SHAO Tianjia, YANG Yongliang, et al. BASAR: Black-Box Attack on Skeletal Action Recognition[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2021: 7593-7603. |
| [27] | LIN Jiadong, SONG Chuanbiao, HE Kun, et al. Nesterov Accelerated Gradient and Scale Invariance for Adversarial Attacks[EB/OL]. (2020-02-03)[2023-09-23]. https://arxiv.linfen3.top/abs/1908.06281. |
| [28] | NESTEROV Y. A Method for Unconstrained Convex Minimization Problem with the Rate of Convergence O(1/k^2)[J]. Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR, 1983, 269(3): 543-547. |
| [29] | ZHANG Pengfei, LAN Cuiling, ZENG Wenjun, et al. Semantics-Guided Neural Networks for Efficient Skeleton-Based Human Action Recognition[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2020: 1109-1118. |
| [30] | SHI Lei, ZHANG Yifan, CHENG Jian, et al. Skeleton-Based Action Recognition with Directed Graph Neural Networks[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2019: 7904-7913. |
| [31] | CHEN Yuxin, ZHANG Ziqi, YUAN Chunfeng, et al. Channel-Wise Topology Refinement Graph Convolution for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). New York: IEEE, 2021: 13339-13348. |
| [32] | ZHOU Huanyu, LIU Qingjie, WANG Yunhong. Learning Discriminative Representations for Skeleton Based Action Recognition[C]// IEEE. 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2023: 10608-10617. |
| [33] | WANG He, DIAO Yunfeng, TAN Zichang, et al. Defending Black-Box Skeleton-Based Human Activity Classifiers[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2023, 37(2): 2546-2554. |
| [1] | 徐茹枝, 张凝, 李敏, 李梓轩. 针对恶意软件的高鲁棒性检测模型研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1184-1195. |
| [2] | 田钊, 牛亚杰, 佘维, 刘炜. 面向车联网的车辆节点信誉评估方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(5): 719-731. |
| [3] | 张光华, 刘亦纯, 王鹤, 胡勃宁. 基于JSMA对抗攻击的去除深度神经网络后门防御方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(4): 545-554. |
| [4] | 徐子荣, 郭焱平, 闫巧. 基于特征恶意度排序的恶意软件对抗防御模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(4): 640-649. |
| [5] | 杨志鹏, 刘代东, 袁军翼, 魏松杰. 基于自注意力机制的网络局域安全态势融合方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 398-410. |
| [6] | 江荣, 刘海天, 刘聪. 基于集成学习的无监督网络入侵检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 411-426. |
| [7] | 冯光升, 蒋舜鹏, 胡先浪, 马明宇. 面向物联网的入侵检测技术研究新进展[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 167-178. |
| [8] | 赵鹏程, 于俊清, 李冬. 一种基于深度学习的SRv6网络流量调度优化算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 272-281. |
| [9] | 金志刚, 丁禹, 武晓栋. 融合梯度差分的双边校正联邦入侵检测算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 293-302. |
| [10] | 魏金侠, 黄玺章, 付豫豪, 李婧, 龙春. 基于全局特征学习的挖矿流量检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(10): 1506-1514. |
| [11] | 张子涵, 赖清楠, 周昌令. 深度学习框架模糊测试研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(10): 1528-1536. |
| [12] | 芦效峰, 程天泽, 龙承念. 基于随机游走的图神经网络黑盒对抗攻击[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(10): 1570-1577. |
| [13] | 薛羽, 张逸轩. 深层神经网络架构搜索综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(9): 58-74. |
| [14] | 刘宇啸, 陈伟, 张天月, 吴礼发. 基于稀疏自动编码器的可解释性异常流量检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(7): 74-85. |
| [15] | 蒋英肇, 陈雷, 闫巧. 基于双通道特征融合的分布式拒绝服务攻击检测算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(7): 86-97. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||