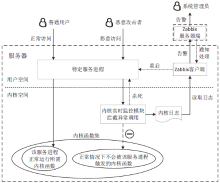
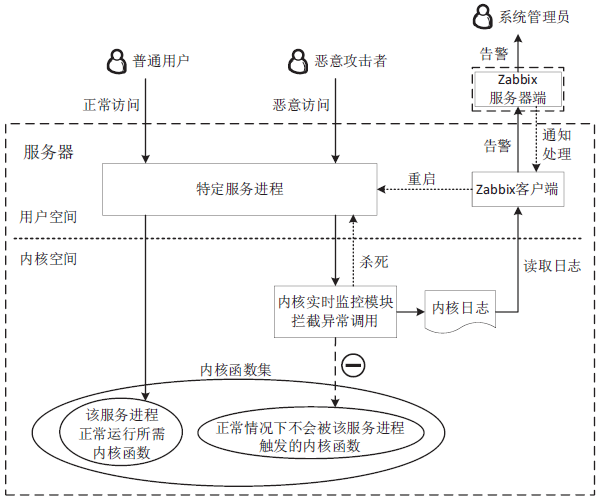
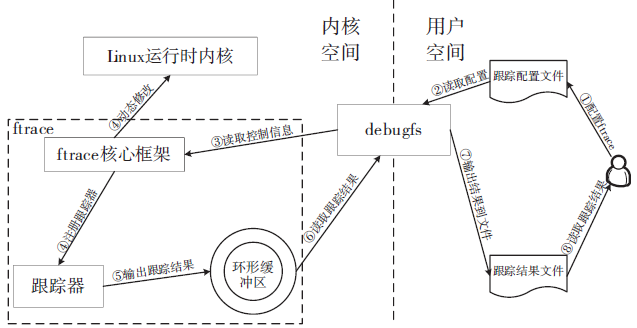
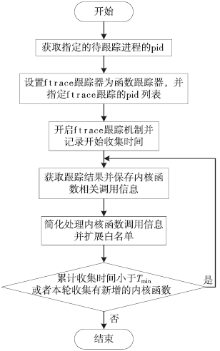
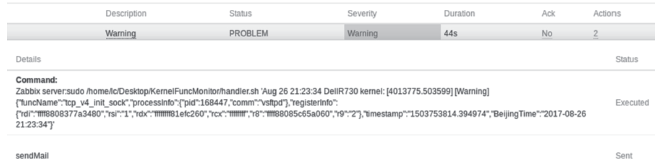
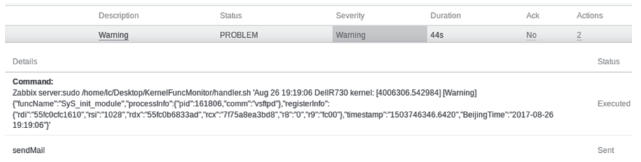
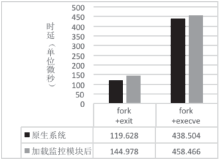
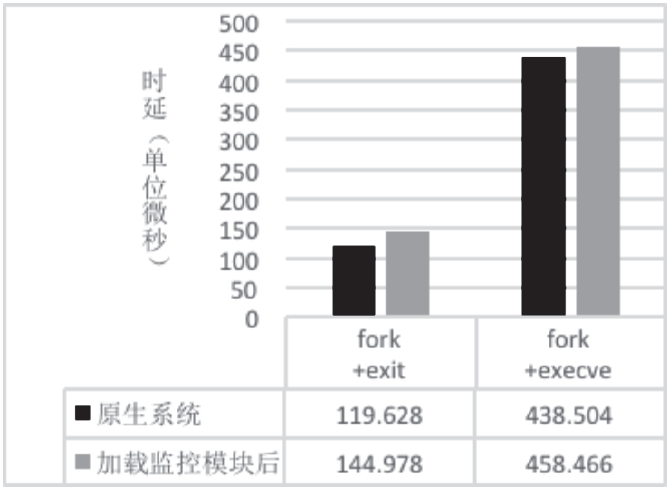
| [1] |
Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures [EB/OL]. .
|
| [2] |
STEVEN A, HOFMEYR, STEPHANIE F,et al.Intrusion Detection Using Sequences of System Calls[J]. Journal of Computer Security, 1998(6):151-180.
|
| [3] |
卿斯汉,程伟,杜超. Windows操作系统的安全风险可控性分析[J]. 信息网络安全,2015(4):5-12.
|
| [4] |
MURTAZA S S, KHREICH W, HAMOU-LHADJA B, et al.A Host-based Anomaly Detection Approach by Representing System Calls as States of Kernel Modules[C] // IEEE Computer Society. 2013 24th IEEE International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering (ISSRE 2013), November 4-7, 2013, Pasadena, CA, United states. Washington DC: IEEE Computer Society, 2013: 431-440.
|
| [5] |
黄飞. 基于进程行为的主机异常检测系统[D]. 扬州:扬州大学, 2008.
|
| [6] |
李汶洋. Android操作系统恶意软件检测技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全,2015(9):62-65.
|
| [7] |
GIDEON C, HU Jiankun.A Semantic Approach to Host-based Intrusion Detection Systems Using Contiguous and Discontiguous System Call Patterns[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2014, 63(4):807-819.
|
| [8] |
MA W, DUAN P, LIU S, et al.Shadow Attacks: Automatically Evading System-call-behavior Based Malware Detection[J]. Journal in Computer Virology, 2012, 8(1-2):1-13.
|
| [9] |
宋新龙,郑东,杨中皇. 基于AOSP与SELinux的移动设备管理系统[J]. 信息网络安全,2017(9):103-106.
|
| [10] |
赵旭,陈丹敏,颜学雄,等. 沙箱技术研究综述[J]. 中原工学院学报,2014,25(4):1-5.
|
| [11] |
程香鹏,陈莉君. 基于LSM的沙箱模块设计与实现[J]. 计算机与数字工程,2014,42(8):1521-1525.
|
| [12] |
黄义文. Linux操作系统内核裁剪的分析[J]. 中国民航飞行学院学报, 2010, 21(3):56-59.
|
| [13] |
徐晨辉. 嵌入式Linux内核裁剪及移植的研究与实现[D]. 上海:东华大学, 2009.
|
| [14] |
KURMUS A, SORNIOTTI A, KAPITZA R.Attack Surface Reduction for Commodity OS Kernels: Trimmed Garden Plants May Attract Less Bugs[C] // ACM Special Interest Group on Operating Systems (SIGOPS). 4th Workshop on European Workshop on System Security (EUROSEC'11), April 10, 2011, Salzburg, Austria.New York: Association for Computing Machinery, 2011: 168-192.
|
| [15] |
KURMUS A, DECHAND S, KAPITZA R.Quantifiable Run-time Kernel Attack Surface Reduction[C] // Nominet, Kaspersky Lab, Huawei, HP Labs Bristol, GCHQ, et al. 11th International Conference on Detection of Intrusions and Malware, and Vulnerability Assessment (DIMVA 2014), July 10-11, 2014, Egham, United kingdom. New York: Springer Verlag, 2014:212-234.
|
| [16] |
武成岗,李建军. 控制流完整性的发展历程[J]. 中国教育网络, 2016(4):52-55.
|
| [17] |
RAFIK F, MICHEL D.Efficient Conditional Tracepoints in Kernel Space[J]. The Open Cybernetics &Systemics Journal,2012, 6(1):11-25.
|
| [18] |
JIM K, PRASANNA S P, MASAMI H. Kernel Probes (Kprobes) [EB/OL]., 2017-7-15.
|
| [19] |
黄杰,翟高寿. 针对内核非控制数据攻击的在线监测方法研究[J]. 计算机应用与软件,2017,34(2):325-333.
|
| [20] |
Zabbix-百度百科[EB/OL]. .
|
| [21] |
蒋卫华,李伟华,杜君. 缓冲区溢出攻击:原理,防御及检测[J]. 计算机工程, 2003,29(10):5-7.
|
| [22] |
黄志军,郑滔. 基于Return-Oriented Programming的程序攻击与防护[J]. 计算机科学,2012,39(6):1-5.
|
| [23] |
CVE. CVE-2015-8660 [EB/OL]. , 2015-12-23.
|
| [24] |
CVE. CVE-2016-8655 [EB/OL]. , 2016-10-12.
|
 ), Chen LIU1, Yong XIANG2
), Chen LIU1, Yong XIANG2