信息网络安全 ›› 2024, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (8): 1241-1251.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2024.08.010
基于随机博弈网的窃密木马诱导式博弈模型
- 1.贵州大学计算机科学与技术学院,贵阳 550025
2.文本计算与认知智能教育部工程研究中心,贵阳 550025
-
收稿日期:2024-05-13出版日期:2024-08-10发布日期:2024-08-22 -
通讯作者:郭春gc_gzedu@163.com -
作者简介:郭钰铮(2000—),女,河南,硕士研究生,CCF学生会员,主要研究方向为恶意软件分析|郭春(1986—),男,贵州,教授,博士,CCF高级会员,主要研究方向为恶意软件分析、入侵检测和数据挖掘|崔允贺(1987—),男,山东,副教授,博士,CCF专业会员,主要研究方向为软件定义网络、边缘计算和云计算|李显超(1979—),男,河南,硕士,主要研究方向为数据中心、物联网和云计算 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(62162009);国家自然科学基金(62102111);贵州省高等学校大数据与网络安全创新团队(黔教技[2023]052);贵州省科技计划项目(黔科合平台人才 GHB[2023]001)
Inducement Game Model of Data-Stealing Trojan Based on Stochastic Game Nets
GUO Yuzheng1,2, GUO Chun1,2( ), CUI Yunhe1,2, LI Xianchao1
), CUI Yunhe1,2, LI Xianchao1
- 1. College of Computer Science and Technology, Guizhou University, Guiyang 550025, China
2. Engineering Research Center for Text Computing and Cognitive Intelligence, Ministry of Education, Guiyang 550025, China
-
Received:2024-05-13Online:2024-08-10Published:2024-08-22
摘要:
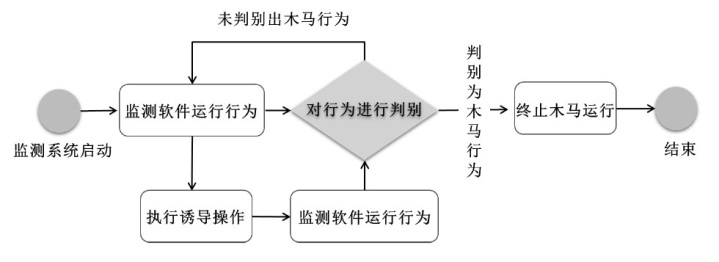
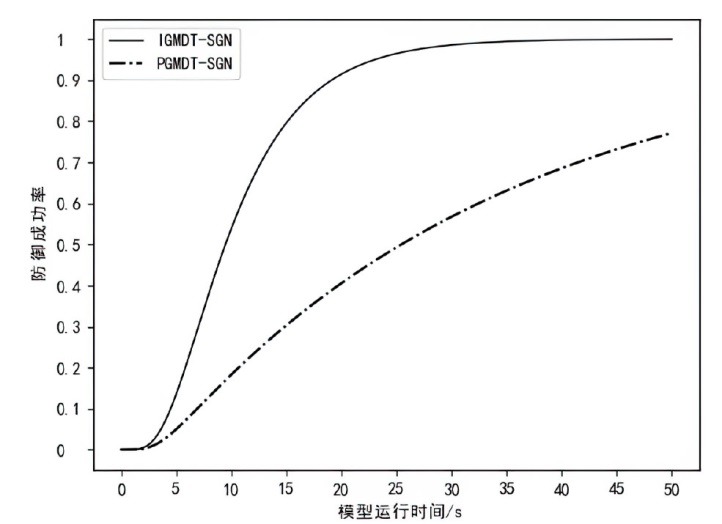
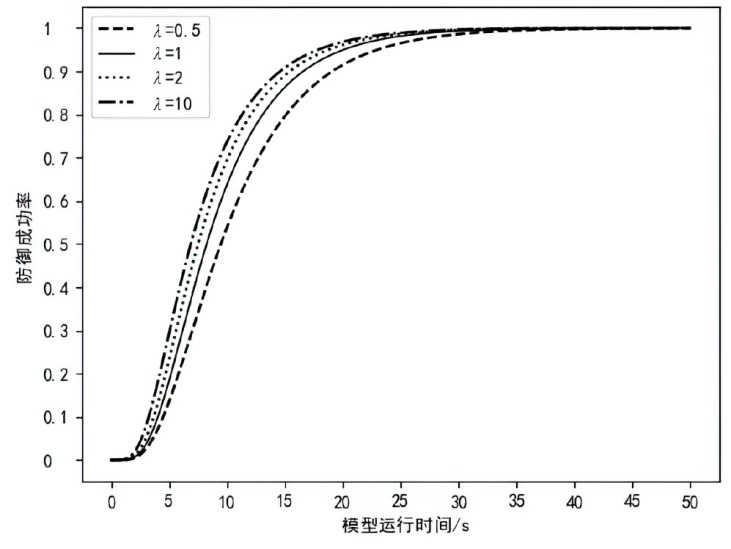
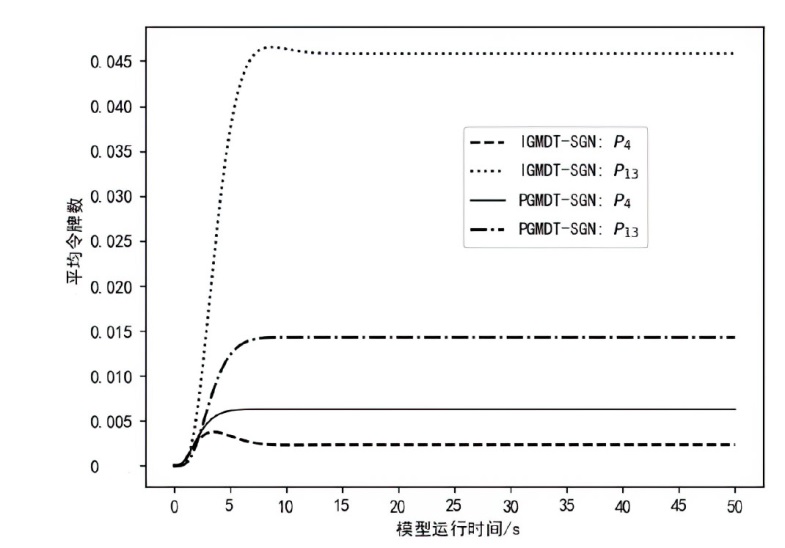
为实现长期窃取信息的目的,窃密木马通常采用触发执行策略来实施其恶意行为,使得其恶意行为的执行具有高隐蔽性和不确定性。主流的窃密木马防御模型采用被动监测窃密木马行为并加以检测的被动防御策略,容易出现漏报和检测不及时的情况。为了提升窃密木马防御模型的防御效果,文章引入诱导操作以构建窃密木马诱导式防御策略,并使用随机博弈网对窃密木马和防御方的攻防对抗过程进行建模分析,构建了IGMDT-SGN。IGMDT-SGN直观揭示了防御方运用诱导式防御策略来对抗窃密木马的策略性逻辑和时序关系。通过模型量化计算对IGMDT-SGN中诱导式防御策略的防御效果进行定量分析,结果表明,窃密木马诱导式防御策略在防御成功率、防御平均时间上优于窃密木马被动防御策略,可为窃密木马的防御提供有益参考。
中图分类号:
引用本文
郭钰铮, 郭春, 崔允贺, 李显超. 基于随机博弈网的窃密木马诱导式博弈模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1241-1251.
GUO Yuzheng, GUO Chun, CUI Yunhe, LI Xianchao. Inducement Game Model of Data-Stealing Trojan Based on Stochastic Game Nets[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(8): 1241-1251.
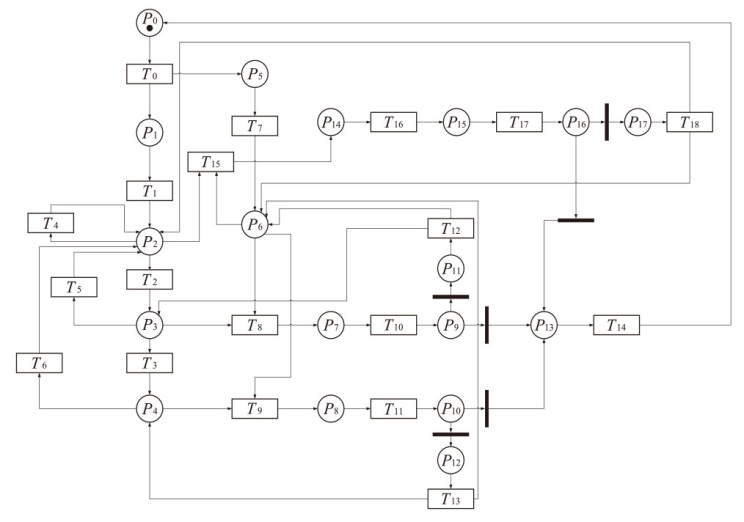
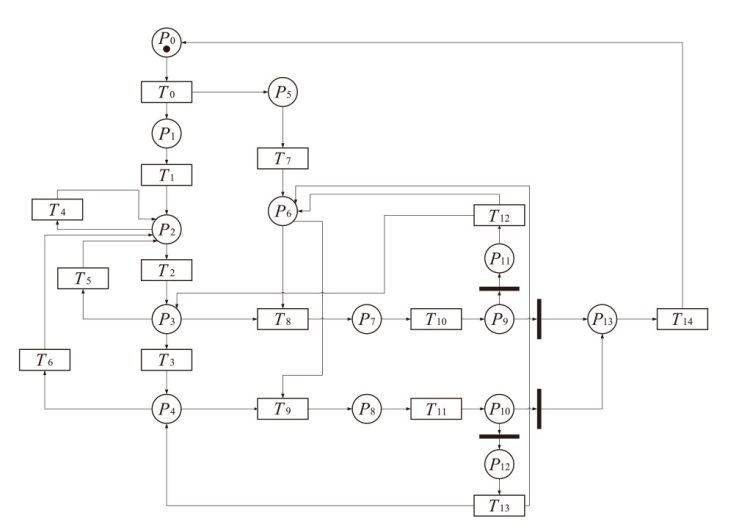
表2
IGMDT-SGN中位置和变迁的含义
| 位置 | 含义 | 变迁 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|---|
| P0 | 正常系统 | T0 | 木马启动 |
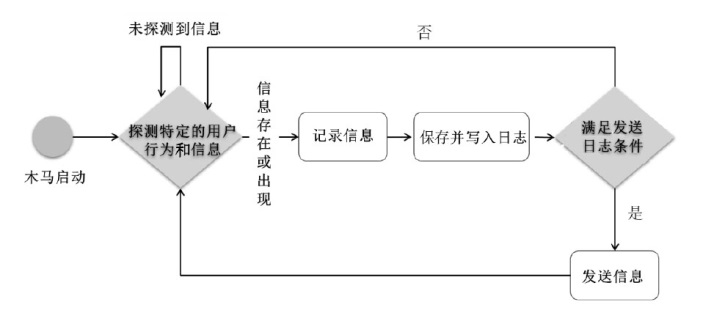
| P1 | 木马运行 | T1 | 木马探测特定的用户行为和信息 |
| P2 | 木马等待信息 | T2 | 木马将所记录信息写入日志 |
| P3 | 木马记录信息 | T3 | 木马发送日志 |
| P4 | 木马进行网络通信 | T4 | 木马探测特定的用户行为和信息 |
| P5 | 防御方开始防御 | T5 | 木马探测特定的用户行为和信息 |
| P6 | 监测木马运行行为 | T6 | 木马探测特定的用户行为和信息 |
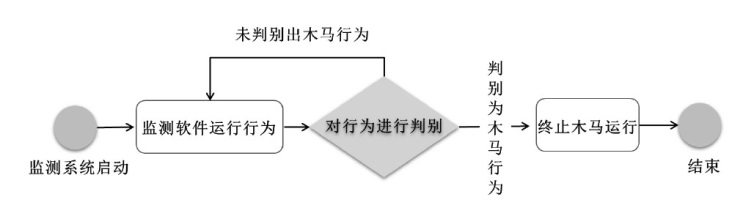
| P7 | 软件行为待判别 | T7 | 监测软件运行行为 |
| P8 | 软件行为待判别 | T8 | 监测系统对软件行为进行记录 |
| P9 | 判别结果 | T9 | 监测系统对软件行为进行记录 |
| P10 | 判别结果 | T10 | 判别木马行为 |
| P11 | 未判别出木马行为 | T11 | 判别木马行为 |
| P12 | 未判别出木马行为 | T12 | 监测软件运行行为 |
| P13 | 判别出木马行为 | T13 | 监测软件运行行为 |
| P14 | 木马行为被诱发 | T14 | 终止木马运行 |
| P15 | 软件行为待判别 | T15 | 执行诱导操作 |
| P16 | 判别结果 | T16 | 监测系统对软件行为进行记录 |
| P17 | 未判别出木马行为 | T17 | 判别木马行为 |
| - | - | T18 | 监测软件运行行为 |
表3
IGMDT-SGN的参数设置
| 参与者 | 序号 | 行为描述 | λ | π |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 窃密木马 | 木马自启动 | 1 | 1 | |
| 探测特定的用户行为和信息 | 3 | 0.5785 | ||
| 记录信息并写入日志 | 1.5 | 0.2479 | ||
| 发送日志 | 0.5 | 0.1736 | ||
| 防御方 | 监测软件运行行为 | 2 | 1 | |
| 监测系统对软件行为进行记录 | 0.8 | 0.3077 | ||
| 判别木马行为 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 执行诱导操作 | 0.5 | 0.6923 | ||
| 终止木马运行 | 2 | 1 |
| [1] | WOODHAMS S. Spyware: An Unregulated and Escalating Threat to Independent Media[M]. Washington: Center for International Media Assistance, 2021. |
| [2] | MARCZAK B, SCOTT-RAILTON J, BERDAN K, et al. Hooking Candiru: Another Mercenary Spyware Vendor Comes into Focus[R]. Toronto: University of Toronto, Citizen Lab Research Report No. 139, 2021. |
| [3] | MALWAREBYTE. 2022 Threat Review[EB/OL]. (2023-01-28)[2024-04-23]. https://www.malwarebytes.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2023/08/mwb_threatreview_2022_ss_v1.pdf. |
| [4] | ALSMADI T, ALQUDAH N. A Survey on Malware Detection Techniques[C]// IEEE. 2021 International Conference on Information Technology (ICIT). New York: IEEE, 2021: 371-376. |
| [5] | MANIRIHO P, MAHMOOD A N, CHOWDHURY M J M. A Study on Malicious Software Behaviour Analysis and Detection Techniques: Taxonomy, Current Trends and Challenges[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2022, 130: 1-18. |
| [6] | MAO Ting, CHE Shengbing, DENG Wei. Research on the Hidden Technology of Troy Trojan-Horse[C]// Atlantis Press. 2017 2nd International Conference on Modelling, Simulation and Applied Mathematics (MSAM2017). Paris: Atlantis Press, 2017: 304-307. |
| [7] | YANG Runqing, CHEN Xutong, XU Haitao, et al. RATScope: Recording and Reconstructing Missing RAT Semantic Behaviors for Forensic Analysis on Windows[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2022, 19(3): 1621-1638. |
| [8] | JAVAHERI D, HOSSEINZADEH M, RAHMANI A M. Detection and Elimination of Spyware and Ransomware by Intercepting Kernel-Level System Routines[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 78321-78332. |
| [9] | LYSENKO S, BOBROVNIKOVA K, POPOV P T, et al. Spyware Detection Technique Based on Reinforcement Learning[C]// RWTH Aachen University. CEUR Workshop Proceedings. Aachen: RWTH Aachen University. 2020: 307-316. |
| [10] | HU Guangjun, ZHU Ping. Research on Trojan Detection Strategy Based on Dynamic Game[C]// China Computer Federation Computer Security Professional Committee. Proceedings of the National Computer Security Academic Exchange Conference (Volume 24). China University of Science and Technology Press, 2009: 357-360. |
| 胡光俊, 朱平. 基于动态博弈的木马检测策略研究[C]// 中国计算机学会计算机安全专业委员会.全国计算机安全学术交流会论文集(第二十四卷).中国科学技术大学出版社, 2009: 357-360. | |
| [11] | GAO He, WANG Yuanzhuo, WANG Li, et al. Trojan Characteristics Analysis Based on Stochastic Petri Nets[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of 2011 IEEE International Conference on Intelligence and Security Informatics. New York: IEEE, 2011: 213-215. |
| [12] | FAN Lejun, WANG Yuanzhuo, CHENG Xueqi, et al. Privacy Theft Malware Multi-Process Collaboration Analysis[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2015, 8(1): 51-67. |
| [13] | YU Min, LIU Chao, QIU Xinliang, et al. Modeling and Analysis of Information Theft Trojan Based on Stochastic Game Nets[C]// IEEE. 2015 2nd International Conference on Information Science and Control Engineering. New York: IEEE, 2015: 318-322. |
| [14] | YAN Qing, SONG Lipeng. Modelling and Control of Trojan Propagation via Online Game Accelerators[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021, 2021(10): 1-10. |
| [15] | PENG Jiaxin, GUO Chun, PING Yuan, et al. SNDMI: Spyware Network Traffic Detection Method Based on Inducement Operations[EB/OL]. (2024-03-13)[2024-04-23]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S016740482400107X?via%3Dihub. |
| [16] | MI Yan, ZHANG Hengwei, HU Hao, et al. Optimal Network Defense Strategy Selection Method: A Stochastic Differential Game Model[EB/OL]. (2021-08-24)[2024-04-23]. https://www.xueshufan.com/publication/3195737479. |
| [17] | WANG Yuanzhuo, LIN Chuang, CHENG Xueqi, et al. Analysis for Network Attack-Defense Based on Stochastic Game Model[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2010, 33(9): 1748-1762. |
| 王元卓, 林闯, 程学旗, 等. 基于随机博弈模型的网络攻防量化分析方法[J]. 计算机学报, 2010, 33(9): 1748-1762. | |
| [18] | NOURREDINE O, MENOUAR B, CAMPO E, et al. A New Generalized Stochastic Petri Net Modeling for Energy-Harvesting-Wireless Sensor Network Assessment[J]. International Journal of Communication Systems, 2023, 36(11): 1-25. |
| [19] | LIU Shuanglei, LI Weijun, GAO Peng, et al. Modeling and Performance Analysis of Gas Leakage Emergency Disposal Process in Gas Transmission Station Based on Stochastic Petri Nets[EB/OL]. (2022-07-02)[2024-04-23]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0951832022003337?via%3Dihub. |
| [20] | WU Zenan, TIAN Liqin, CHEN Nan. Research on Quantitative Analysis of System Security Based on Stochastic Petri Net[J]. Netinfo Security, 2020, 20(9): 27-31. |
| 毋泽南, 田立勤, 陈楠. 基于随机Petri网的系统安全性量化分析研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(9): 27-31. | |
| [21] | HO E, RAJAGOPALAN A, SKVORTSOV A, et al. Game Theory in Defence Applications: A Review[EB/OL]. (2022-01-28)[2024-04-23]. tps://www.xueshufan.com/publication/3210652180. |
| [22] | ZIMMERMANN A. Modeling and Evaluation of Stochastic Petri Nets with TimeNET 4.1[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Performance Evaluation Methodologies and Tools. New York: IEEE, 2012: 54-63. |
| [23] | ZIMMERMANN A. Modelling and Performance Evaluation with TimeNET 4.4[C]// Springer. International Conference on Quantitative Evaluation of Systems. Heidelberg: Springer, 2017: 300-303. |
| [24] | SUN Xiaoyun, YU Zhenhua, GAO Hongxia, et al. Trustworthiness Analysis and Evaluation for Command and Control Cyber-Physical Systems Using Generalized Stochastic Petri Nets[EB/OL]. (2023-04-23)[2024-04-23]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S002002552300511X?via%3Dihub#preview-section-cited-by. |
| [25] | CHEN Xiaohui, HAO Zhiyu, LI Lun, et al. CruParamer: Learning on Parameter-Augmented API Sequences for Malware Detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2022, 17: 788-803. |
| [26] | LI Ce, LYU Qiujian, LI Ning, et al. A Novel Deep Framework for Dynamic Malware Detection Based on API Sequence Intrinsic Features[EB/OL]. (2022-03-08)[2024-04-23]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0167404822000840. |
| [1] | 金志刚, 王新建, 李根, 岳顺民. 融合攻击图和博弈模型的网络防御策略生成方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(1): 1-9. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||