信息网络安全 ›› 2023, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (11): 84-93.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2023.11.009
一种基于大语言模型的SQL注入攻击检测方法
- 国防科技大学电子科学学院,长沙 410073
-
收稿日期:2023-08-25出版日期:2023-11-10发布日期:2023-11-10 -
通讯作者:王剑jwang@nudt.edu.cn -
作者简介:黄恺杰(2000—),男,湖南,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为网络安全|王剑(1975—),男,湖南,教授,博士,主要研究方向为网络安全|陈炯峄(1993—),男,湖南,讲师,博士,主要研究方向为网络安全 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(62302508);教育部-中国移动科研基金(MCM20200103)
A Large Language Model Based SQL Injection Attack Detection Method
HUANG Kaijie, WANG Jian( ), CHEN Jiongyi
), CHEN Jiongyi
- College of Electronic Science and Technology, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
-
Received:2023-08-25Online:2023-11-10Published:2023-11-10
摘要:
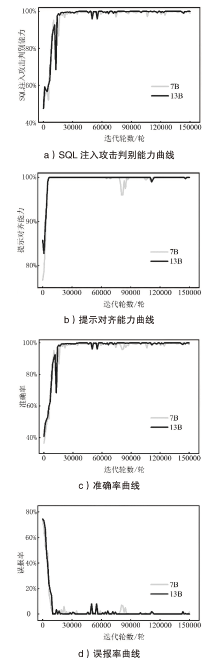
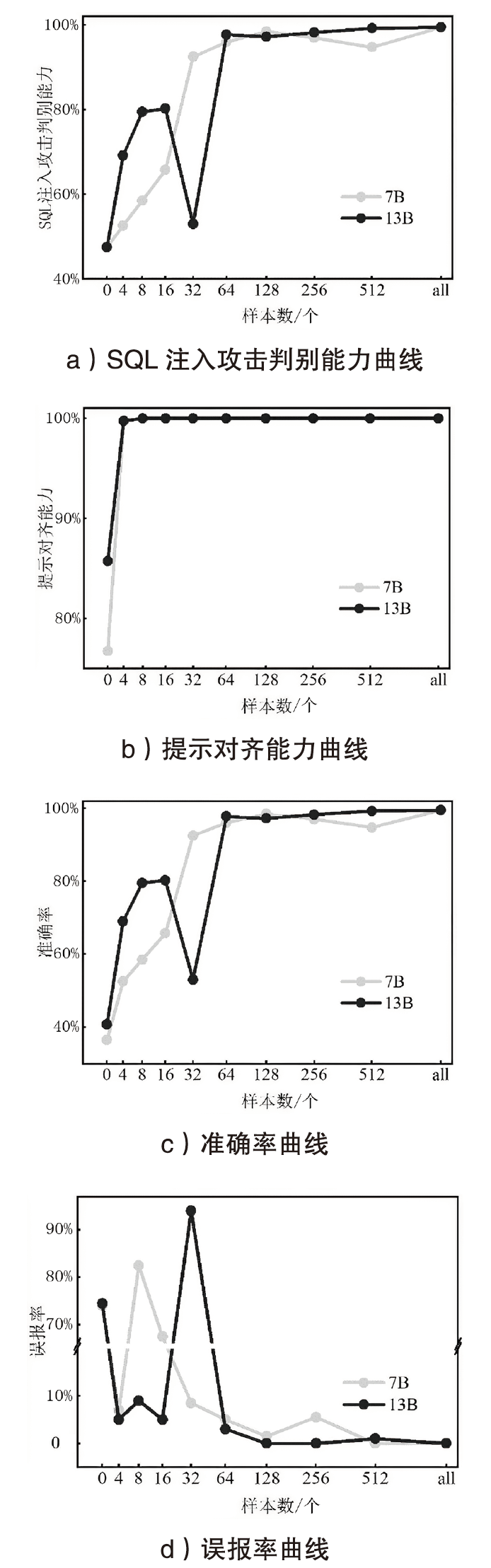
SQL注入攻击是一种被攻击者广泛使用的网络攻击手段,严重威胁网络空间安全。传统的SQL注入攻击检测方法主要有基于规则和基于机器学习两种,这些方法存在泛用性较差且误报率高的问题。文章提出一种基于大语言模型的SQL注入攻击检测方法,利用提示工程和指令微调技术,得到SQL注入攻击检测专用大语言模型;通过分析迭代轮数、微调样本数以及推理参数对模型性能的影响,探索提升大语言模型检测能力的途径;依托大语言模型强大的语义理解能力,降低检测误报率。对文章所提的SQL注入攻击检测专用大语言模型在Kaggle数据集上进行实验分析,结果表明其准确率达到99.85%以上,误报率低于0.2%,F1值达到0.999,相较于目前较先进的SQL注入攻击检测方法,在检测性能上有较大提升。
中图分类号:
引用本文
黄恺杰, 王剑, 陈炯峄. 一种基于大语言模型的SQL注入攻击检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 84-93.
HUANG Kaijie, WANG Jian, CHEN Jiongyi. A Large Language Model Based SQL Injection Attack Detection Method[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(11): 84-93.
| [1] |
LU Dongzhe, FEI Jinlong, LIU Long. A Semantic Learning-Based SQL Injection Attack Detection Technology[J]. Electronics, 2023, 12: 1344-1356.
doi: 10.3390/electronics12061344 URL |
| [2] | CLARKE J, FOWLER K, OFTEDAL E, et al. SQL Injection Attacks and Defense[M]. Ohio: Syngress, 2009. |
| [3] | OWASP. OWASP Top Ten[EB/OL]. (2023-05-25)[2023-08-12]. https://owasp.org/Top10/. |
| [4] | UWAGBOLE S O, BUCHANAN W J, FAN Lu. An Applied Pattern-Driven Corpus to Predictive Analytics in Mitigating SQL Injection Attack[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the 2017 Seventh International Conference on Emerging Security Technologies (EST). New York: IEEE, 2017: 12-17. |
| [5] | UWAGBOLE S O, BUCHANAN W J, FAN Lu. Applied Machine Learning Predictive Analytics to SQL Injection Attack Detection and Prevention[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the 2017 IFIP/IEEE Symposium on Integrated Network and Service Management (IM). New York: IEEE, 2017: 1087-1090. |
| [6] |
GU Haifeng, ZHANG Jianning, LIU Tian, et al. DIAVA: A Traffic-Based Framework for Detection of SQL Injection Attacks and Vulnerability Analysis of Leaked Data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2020, 69(1): 188-202.
doi: 10.1109/TR.24 URL |
| [7] | LIVSHITS V B, LAM M S. Finding Security Vulnerabilities in Java Applications with Static Analysis[C]// USENIX. Proceedings of the 14th Conference on USENIX Security Symposium. New York: USENIX Association, 2005: 18-29. |
| [8] |
PROKHORENKO V, CHOO K-K R, ASHMAN H. Web Application Protection Techniques: A Taxonomy[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2016, 60: 95-112.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2015.11.017 URL |
| [9] | HASAN M, BALBAHAITH Z, TARIQUE M. Detection of SQL Injection Attacks: A Machine Learning Approach[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Electrical and Computing Technologies and Applications (ICECTA). New York: IEEE, 2019: 1-6. |
| [10] | LI Hongling, ZOU Jianxin. Research of SQL Injection Detection Based on SVM and Text Feature Extraction[J]. Netinfo Security, 2017, 17(12): 40-46. |
| 李红灵, 邹建鑫. 基于SVM和文本特征向量提取的SQL注入检测研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2017, 17(12): 40-46. | |
| [11] | FAROOQ U. Ensemble Machine Learning Approaches for Detection of SQL Injection Attack[J]. Tehnicki Glasnik, 2021, 15(1): 112-120. |
| [12] |
GOWTHAM M, PRAMOD H B. Semantic Query-Featured Ensemble Learning Model for SQL-Injection Attack Detection in IoT-Ecosystems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2022, 71(2): 1057-1074.
doi: 10.1109/TR.2021.3124331 URL |
| [13] | TANG Peng, QIU Weidong, HUANG Zheng, et al. Detection of SQL Injection Based on Artificial Neural Network[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2020, 190: 1-12. |
| [14] | BROWN T B, MANN B, RYDER N, et al. Language Models are Few-Shot Learners[EB/OL]. (2020-05-01)[2023-08-12]. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2020arXiv200514165B. |
| [15] | RADFORD A, WU J, CHILD R, et al. Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners[EB/OL]. (2019-02-27)[2023-08-12]. https://cdn.openai.com/better-language-models/language_models_are_unsupervised_multitask_learners.pdf. |
| [16] | JIAO Wenxiang, WANG Wenxuan, HUANG J, et al. Is ChatGPT a Good Translator? Yes with GPT-4 as The Engine[EB/OL]. (2023-05-19)[2023-08-12]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.08745.pdf. |
| [17] | SANTIAGO E. AI in Content Creation: How Creators and Marketers are Using It Data[EB/OL]. (2023-04-17)[2023-08-12]. https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/ai-in-content-marketing. |
| [18] | KEARY T. 12 Practical Large Language Model (LLM) Applications[EB/OL]. (2023-07-14)[2023-08-12]. https://www.techopedia.com/12-practical-large-language-model-llm-applications. |
| [19] | LAMB A. A Brief Introduction to Generative Models[EB/OL]. (2021-02-27)[2023-08-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.00265. |
| [20] | WEI J, BOSMA M, ZHAO V, et al. Finetuned Language Models are Zero-Shot Learners[EB/OL]. (2022-02-08)[2023-08-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.01652. |
| [21] | SYED S. SQL Injection Dataset[EB/OL]. (2021-09-09)[2023-08-12]. https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/syedsaqlainhussain/sql-injection-dataset. |
| [22] | ZHANG Wei, LI Yueqin, LI Xiaofeng, et al. Deep Neural Network-Based SQL Injection Detection Method[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2022, 22: 1-9. |
| [23] | ROY P, KUMAR R, RANI P. SQL Injection Attack Detection by Machine Learning Classifier[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Applied Artificial Intelligence and Computing (ICAAIC). New York: IEEE, 2022: 394-400. |
| [24] | OpenAI. Completion-OpenAI API[EB/OL]. [2023-08-12]. https://beta.openai.com/docs/guides/completion/prompt-design. |
| [25] | TAORI R, GULRAJANI I, ISHAAN G, et al. Stanford Alpaca: An Instruction-Following LLaMA Model[EB/OL]. (2023-05-30)[2023-08-12]. https://github.com/tatsu-lab/stanford_alpaca. |
| [26] | CHEN M, TWOEK J, JUN H, et al. Evaluating Large Language Models Trained on Code[EB/OL]. (2021-07-14)[2023-08-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.03374. |
| [27] | HU E J, SHEN Yelong, WALLIS P, et al. LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models[EB/OL]. (2021-06-17)[2023-08-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.09685. |
| [28] | NEIL H, ANDREI G, STANISLAW J, et al. Parameter-Efficient Transfer Learning for NLP[EB/OL]. (2019-06-13)[2023-08-12]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.00751.pdf. |
| [29] | XIANG L L, PERCY L. Prefix-Tuning: Optimizing Continuous Prompts for Generation[EB/OL]. (2021-01-01)[2023-08-12]. https://browse.arxiv.org/pdf/2101.00190.pdf. |
| [30] | PEARCE H A, TAN B, AHMAD B, et al. Examining Zero-Shot Vulnerability Repair with Large Language Models[C]// IEEE. 44th IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. New York: IEEE, 2023: 2339-2356. |
| [31] | GRORGI G. Llama. cpp.[2023-08-12]. https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp. |
| [32] | CARLOS M, ADRIAN W, LUCA A, et al. Lightning-AI/lit-llama: Implementation of the LLaMA Language Model Based on NanoGPT[EB/OL]. (2023-07-19)[2023-08-12]. https://github.com/Lightning-AI/lit-llama. |
| [33] | RAFFEL C, SHAZEER N, ROBERTS A, et al. Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer[J]. Juornal of Machine Learning Research, 2020, 21(1): 1-53. |
| [34] | HUGO T, THUBAUT L, GATIER I, et al. LLaMA: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models[EB/OL]. (2023-02-27)[2023-08-12]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2302.13971.pdf. |
| [35] |
LI Qi, LI Weishi, WANG Junfeng, et al. A SQL Injection Detection Method Based on Adaptive Deep Forest[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 145385-145394.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2944951 |
| [36] | GUO Chun, CAI Wenyan, SHEN Guowei, et al. Research on SQL Injection Attacks Detection Method Based on the Truncated Key Payload[J]. Netinfo Security, 2021, 21(7): 43-53. |
| 郭春, 蔡文艳, 申国伟, 等. 基于关键载荷截取的SQL注入攻击检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(7): 43-53. |
| [1] | 张东鑫, 郎波, 严寒冰. 基于流量行为图的攻击检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(1): 72-79. |
| [2] | 陈良臣, 刘宝旭, 高曙. 网络攻击检测中流量数据抽样技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(8): 22-28. |
| [3] | 张雪博, 刘敬浩, 付晓梅. 基于改进Logistic回归算法的抗Web DDoS攻击模型的设计与实现[J]. 信息网络安全, 2017, 17(6): 62-67. |
| [4] | 李恒, 沈华伟, 程学旗, 翟永. 网络高流量分布式拒绝服务攻击防御机制研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2017, 17(5): 37-43. |
| [5] | 夏玉明, 胡绍勇, 朱少民, 刘丽丽. 基于卷积神经网络的网络攻击检测方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2017, 17(11): 32-36. |
| [6] | 刘文生, 乐德广, 刘伟. SQL注入攻击与防御技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2015, 15(9): 129-134. |
| [7] | 田玉杰, 赵泽茂, 王丽君, 连科. 基于分类的SQL注入攻击双层防御模型研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2015, 15(6): 1-6. |
| [8] | . 二阶 SQL 注入攻击防御模型[J]. , 2014, 14(11): 70-. |
| [9] | 田玉杰, 赵泽茂, 张海川, 李学双. 二阶SQL注入攻击防御模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2014, 15(11): 70-73. |
| [10] | 杨玉龙;彭长根;周洲. 基于同态加密的防止SQL注入攻击解决方案[J]. , 2014, 14(1): 0-0. |
| [11] | 张令通;罗森林. SQL盲注入快速攻击方法研究[J]. , 2013, 13(5): 0-0. |
| [12] | 魏为民;袁仲雄. 网络攻击与防御技术的研究与实践[J]. , 2012, 12(12): 0-0. |
| [13] | 颜浩;蒋巍;蒋天发. SQLI和XSS漏洞检测与防御技术研究[J]. , 2011, 11(12): 0-0. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||