信息网络安全 ›› 2023, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (4): 30-38.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2023.04.004
面向多畸变稳健性的图像归因算法
- 1.南京航空航天大学计算机科学与技术学院,南京 211106
2.哈尔滨工业大学(深圳)计算机科学与技术学院,深圳 518055
-
收稿日期:2022-10-20出版日期:2023-04-10发布日期:2023-04-18 -
通讯作者:张玉书 E-mail:yushu@nuaa.edu.cn -
作者简介:祁树仁(1994—),男,辽宁,博士研究生,主要研究方向为视觉表征、稳健模式识别和媒体内容安全|张玉书(1987—),男,甘肃,教授,博士,主要研究方向为多媒体安全与人工智能、区块链与物联网安全|薛明富(1986—),男,江苏,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为人工智能安全、硬件安全、硬件木马检测|花忠云(1989—),男,湖南,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为混沌理论及应用、多媒体安全、信息隐藏和图像处理。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(62072237);江苏省研究生科研与实践创新计划(KYCX22_0383)
Image Attribution Algorithm with Multi-Distortion Robustness
QI Shuren1, ZHANG Yushu1( ), XUE Mingfu1, HUA Zhongyun2
), XUE Mingfu1, HUA Zhongyun2
- 1. College of Computer Science and Technology, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing 211106, China
2. School of Computer Science and Technology, Harbin Institute of Technology(Shenzhen), Shenzhen 518055, China
-
Received:2022-10-20Online:2023-04-10Published:2023-04-18 -
Contact:ZHANG Yushu E-mail:yushu@nuaa.edu.cn
摘要:
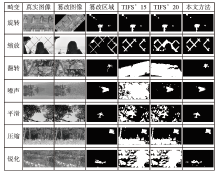
随着多媒体编辑软件和生成式神经网络的发展,数字图像的可信度正在不断削弱。作为一种新兴的溯源式取证技术,图像归因回溯需分析图像的可信源和可视化图像的编辑性改变,因而能够有效对抗恶意篡改并辅助群体和个人对图像信息形成正确判断。但是目前的图像归因方法对网络空间中常见的几何变形和信号压缩表现不够稳定,特别是对于图像同时包含多种畸变的情况。为此,文章提出一种多畸变稳健的图像归因方法,该方法基于一种正交且协变的图像局部表征策略,具有对多种几何变换和信号损失的稳健性,同时设计了面向稀疏域和稠密域表征任务的两种快速计算方案。由此形成的图像归因方法能够有效回溯可信数据库中的近重复图像源,矫正待分析图像的几何姿态,并可视化潜在的图像篡改区域。该方法对网络空间中的多种良性变换具有稳健性,同时保持对恶性内容篡改的敏感性。仿真结果表明,该方法具有更优的篡改检测稳健性和综合检测精度,同时具有更优的特征紧凑性和实现成本。
中图分类号:
引用本文
祁树仁, 张玉书, 薛明富, 花忠云. 面向多畸变稳健性的图像归因算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(4): 30-38.
QI Shuren, ZHANG Yushu, XUE Mingfu, HUA Zhongyun. Image Attribution Algorithm with Multi-Distortion Robustness[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(4): 30-38.
表1
单畸变下的图像归因稳健性评估
| 方法 | TIFS’15 | TIFS’20 | 本文方法 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 准确率 | 召回率 | F1指标 | 准确率 | 召回率 | F1指标 | 准确率 | 召回率 | F1指标 | |
| 无畸变 | 87.18% | 77.85% | 79.92% | 87.24% | 77.70% | 79.85% | 83.99% | 72.88% | 75.63% |
| 旋转20° | 86.50% | 67.37% | 72.25% | 86.28% | 67.28% | 72.06% | 83.48% | 62.70% | 68.14% |
| 旋转45° | 82.55% | 60.01% | 65.73% | 82.27% | 59.78% | 65.40% | 82.10% | 56.25% | 62.36% |
| 翻转列 | 45.03% | 49.09% | 41.40% | 64.63% | 66.70% | 59.76% | 82.89% | 69.99% | 73.45% |
| 翻转行 | 55.89% | 59.07% | 52.58% | 64.87% | 66.65% | 60.01% | 82.88% | 69.97% | 73.43% |
| 缩放0.8 | 84.72% | 75.48% | 76.80% | 81.34% | 75.24% | 74.12% | 82.75% | 70.60% | 73.64% |
| 缩放1.3 | 77.41% | 50.20% | 56.41% | 75.20% | 49.57% | 54.99% | 74.85% | 47.11% | 53.37% |
| 高斯噪声0.01 | 85.89% | 73.85% | 76.28% | 86.75% | 74.70% | 77.65% | 81.71% | 69.16% | 72.14% |
| 高斯噪声0.02 | 83.41% | 74.72% | 74.39% | 85.03% | 74.09% | 76.17% | 81.49% | 69.54% | 71.78% |
| 均值平滑 7×7 | 64.94% | 75.71% | 61.25% | 65.49% | 75.65% | 61.74% | 80.03% | 69.97% | 71.32% |
| 均值平滑14×14 | 54.90% | 74.75% | 52.85% | 55.36% | 74.90% | 53.39% | 73.70% | 66.03% | 65.03% |
| 高斯平滑 7×7 | 67.03% | 75.72% | 62.85% | 67.57% | 74.90% | 63.22% | 79.93% | 69.70% | 71.19% |
| 高斯平滑14×14 | 58.75% | 75.48% | 56.06% | 59.36% | 75.29% | 56.59% | 76.08% | 66.81% | 67.05% |
| 中值平滑 7×7 | 69.91% | 75.72% | 65.29% | 70.58% | 75.27% | 65.75% | 82.71% | 71.04% | 73.46% |
| 中值平滑14×14 | 59.91% | 74.73% | 57.10% | 60.57% | 74.79% | 57.81% | 77.49% | 69.09% | 68.63% |
| JPEG 压缩10 | 82.55% | 76.14% | 74.83% | 83.85% | 75.66% | 75.88% | 84.06% | 71.59% | 74.85% |
| JPEG 压缩5 | 75.95% | 75.51% | 68.90% | 76.47% | 75.18% | 69.33% | 82.09% | 69.38% | 72.21% |
| 拉普拉斯锐化 | 48.99% | 80.49% | 49.18% | 55.05% | 78.56% | 53.87% | 71.24% | 50.56% | 55.48% |
| 平均值↑ | 70.64% | 70.66% | 63.56% | 72.66% | 71.77% | 65.42% | 80.19% | 66.24% | 69.06% |
| 标准差↓ | 13.68% | 9.21% | 10.67% | 11.06% | 7.11% | 8.57% | 3.76% | 7.19% | 6.18% |
表2
多畸变下的图像归因稳健性评估
| 方法 | TIFS’15 | TIFS’20 | 本文方法 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 准确率 | 召回率 | F1指标 | 准确率 | 召回率 | F1指标 | 准确率 | 召回率 | F1指标 | |
| 旋转10°+缩放0.5+JPEG20 | 68.01% | 64.37% | 59.66% | 59.97% | 63.23% | 54.34% | 82.69% | 60.00% | 65.89% |
| 旋转-10°+缩放0.8+高斯噪声0.01 | 79.92% | 56.67% | 61.80% | 77.29% | 55.31% | 59.39% | 77.06% | 48.20% | 55.17% |
| 旋转15°+缩放1.2+高斯平滑5×5 | 66.95% | 58.30% | 54.43% | 65.41% | 56.52% | 52.97% | 81.79% | 54.25% | 60.90% |
| 旋转15°+翻转列+缩放1.2+高斯噪声0.01 | 10.38% | 25.02% | 10.54% | 15.65% | 31.38% | 14.70% | 80.93% | 53.69% | 60.18% |
| 旋转15°+翻转行+缩放1.3+JPEG 30 | 20.60% | 30.01% | 17.87% | 16.67% | 30.23% | 15.16% | 77.83% | 46.47% | 53.57% |
| 旋转-10°+翻转列+缩放0.8+高斯平滑5×5 | 6.13% | 18.37% | 7.10% | 12.46% | 33.19% | 13.90% | 82.09% | 64.08% | 67.75% |
| 旋转5°+翻转行+缩放0.8+ 锐化 | 15.36% | 35.95% | 16.33% | 7.34% | 29.21% | 9.19% | 76.24% | 55.23% | 59.64% |
| 平均值↑ | 38.19% | 41.24% | 32.53% | 36.40% | 42.73% | 31.38% | 79.80% | 54.56% | 60.44% |
| 标准差↓ | 29.49% | 16.92% | 22.93% | 27.53% | 13.77% | 21.10% | 2.47% | 5.70% | 4.77% |
| [1] |
VERDOLIVA L. Media Forensics and Deepfakes: An Overview[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2020, 14(5): 910-932.
doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2020.3002101 URL |
| [2] | LI Xurong, JI Shouling, WU Chunming, et al. Survey on Deepfakes and Detection[J]. Journal of Software, 2020, 32(2): 496-518. |
| 李旭嵘, 纪守领, 吴春明, 等. 深度伪造与检测技术综述[J]. 软件学报, 2020, 32(2): 496-518. | |
| [3] | NGUYEN E, BUI T, SWAMINATHAN V, et al. OSCAR-Net: Object-Centric Scene Graph Attention for Image Attribution[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision. New York: IEEE, 2021: 14499-14508. |
| [4] |
WANG Xiaofeng, PANG Kemu, ZHOU Xiaorui, et al. A Visual Model-Based Perceptual Image Hash for Content Authentication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2015, 10(7): 1336-1349.
doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2015.2407698 URL |
| [5] |
ZHENG Yue, CAO Yuan, CHANG C H. A PUF-Based Data-Device Hash for Tampered Image Detection and Source Camera Identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 15: 620-634.
doi: 10.1109/TIFS.10206 URL |
| [6] |
MORRA L, LAMBERTI F. Benchmarking Unsupervised Near-Duplicate Image Detection[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2019, 135: 313-326.
doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2019.05.002 |
| [7] | DU Ling, HO A T S, CONG Runming. Perceptual Hashing for Image Authentication: A Survey[EB/OL]. [2022-09-11]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0923596519301286?casa_token=-0e5whXRzlMAAAAA:FmzmPXwGobhIxJqrpIjEuyQquICm3J7lTNsuI4PaALvnTR1nHeB2hBr10NVoyC45kTb6sxH9I9Ql. |
| [8] | ROSENTHOL L, PARSONS A, SCOUTEN E, et al. Content Authenticity Initiative (CAI): Setting the Standard for Content Attribution[EB/OL]. [2022-10-11]. https://contentauthenticity.org/. |
| [9] | BLACK A, BUI T, JIN Hailin, et al. Deep Image Comparator: Learning to Visualize Editorial Change[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2021: 972-980. |
| [10] |
MOREIRA D, BHARATI A, BROGAN J, et al. Image Provenance Analysis at Scale[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(12): 6109-6123.
doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2865674 URL |
| [11] |
BHARATI A, MOREIRA D, FLYNN P J, et al. Transformation-Aware Embeddings for Image Provenance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2021, 16: 2493-2507.
doi: 10.1109/TIFS.10206 URL |
| [12] |
COZZOLINO D, VERDOLIVA L. Noiseprint: A CNN-Based Camera Model Fingerprint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2019, 15: 144-159.
doi: 10.1109/TIFS.10206 URL |
| [13] |
MATERN F, RIESS C, STAMMINGER M. Gradient-Based Illumination Description for Image Forgery Detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2019, 15: 1303-1317.
doi: 10.1109/TIFS.10206 URL |
| [14] | QI Hua, GUO Qing, JUEFEI-XU F, et al. Deeprhythm: Exposing Deepfakes with Attentional Visual Heartbeat Rhythms[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. New York: ACM, 2020: 4318-4327. |
| [15] | WU Jinhai, LIN Fuzong. Image Authentication Based on Digital Watermarking[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2004, 27(9): 1153-1161. |
| 吴金海, 林福宗. 基于数字水印的图像认证技术[J]. 计算机学报, 2004, 27(9): 1153-1161. | |
| [16] | ZHANG Rui, XUE Rui, LIU Ling. Security and Privacy on Blockchain[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2019, 52(3): 1-34. |
| [17] | HAO Qingying, LUO Licheng, JAN S T K, et al. It's Not What It Looks Like: Manipulating Perceptual Hashing Based Applications[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 2021 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2021: 69-85. |
| [18] |
LIANG Xiaoping, TANG Zhenjun, HUANG Ziqing, et al. Efficient Hashing Method Using 2D-2D PCA for Image Copy Detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2021, 35(4): 3765-3778.
doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2021.3131188 URL |
| [19] |
ZHOU Zhili, WANG Yunlong, WU Q M J, et al. Effective and Efficient Global Context Verification for Image Copy Detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2016, 12(1): 48-63.
doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2016.2601065 URL |
| [20] | LIANG Xiaoping, TANG Zhenjun, WU Jingli, et al. Robust Image Hashing with Isomap and Saliency Map for Copy Detection[EB/OL]. [2022-09-11]. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9665342. |
| [21] |
ZHANG Xuyao, LIU Chenglin, SUEN C Y. Towards Robust Pattern Recognition: A Review[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2020, 108(6): 894-922.
doi: 10.1109/PROC.5 URL |
| [22] | BALNTAS V, LENC K, VEDALDI A, et al. H-Patches: A Benchmark and Evaluation of Handcrafted and Learned Local Descriptors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(11): 2825-2841. |
| [23] | QI Shuren, ZHANG Yushu, WANG Chao, et al. A Principled Design of Image Representation: Towards Forensic Tasks[EB/OL]. [2022-09-11]. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9881995. |
| [24] | QI Shuren, ZHANG Yushu, WANG Chao, et al. A Survey of Orthogonal Moments for Image Representation: Theory, Implementation, and Evaluation[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2021, 55(1): 1-35. |
| [25] |
LOWE D G. Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant Keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91-110.
doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 URL |
| [26] |
XIE Lingxi, WANG Jingdong, ZHANG Bo, et al. Fine-Grained Image Search[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2015, 17(5): 636-647.
doi: 10.1109/TMM.2015.2408566 URL |
| [27] | VEMPALA S S. The Random Projection Method[M]. Providence, RhodeIsland, USA: American Mathematical Soc., 2005. |
| [28] |
DERRODE S, GHORBEL F. Robust and Efficient Fourier-Mellin Transform Approximations for Invariant Grey-Level Image Description and Reconstruction[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2001, 83(1): 57-78.
doi: 10.1006/cviu.2001.0922 URL |
| [29] |
YAP P T, JIANG Xudong, KOT A C. Two-Dimensional Polar Harmonic Transforms for Invariant Image Representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(7): 1259-1270.
doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2009.119 URL |
| [30] | KORUS P, HUANG Jiwu. Evaluation of Random Field Models in Multi-Modal Unsupervised Tampering Localization[C]// IEEE. 2016 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security (WIFS). New York: IEEE, 2016: 1-6. |
| [1] | 傅志彬, 祁树仁, 张玉书, 薛明富. 基于稠密连接的深度修复定位网络[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(7): 84-93. |
| [2] | 朱新同, 唐云祁, 耿鹏志. 基于特征融合的篡改与深度伪造图像检测算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(8): 70-81. |
| [3] | . 一种分块压缩感知观测值的图像篡改认证算法[J]. , 2014, 14(4): 35-. |
| [4] | 杨婧, 范梦迪, 高雄智, 任延珍. 一种改进的MP3被动篡改定位检测算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2014, 15(10): 7-10. |
| [5] | 康海燕;祈鑫;魏美荣. 中小型网站智能安全检测研究[J]. , 2014, 14(1): 0-0. |
| [6] | 杨婧;任延珍;汪肇翔;崔晓煜. 基于差异能量的监控视频篡改检测算法[J]. , 2013, 13(9): 0-0. |
| [7] | 李娇;王健;曹继文;陈彤. 基于感知哈希的在线发表论文版权保护系统[J]. , 2013, 13(11): 0-0. |
| [8] | 彭欢;蒋天发. 基于几何不变性的图像水印[J]. , 2009, 9(4): 0-0. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||