信息网络安全 ›› 2023, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (1): 44-56.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2023.01.006
基于社区发现的社交网络影响力阻断最大化算法
- 西北工业大学深圳研究院,深圳 518057
-
收稿日期:2022-08-16出版日期:2023-01-10发布日期:2023-01-19 -
通讯作者:李晓宇 E-mail:lixiaoyu@nwpu.edu.cn -
作者简介:慕志颖(1994—),女,山东,博士研究生,主要研究方向为数据挖掘和社交网络舆论对抗|许加全(1994—),男,福建,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为社交网络舆论对抗|李晓宇(1980—),男,河南,副研究员,博士,主要研究方向为社交网络舆论对抗和网络空间安全 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(62272389);深圳市基础研究资助项目(20210317191843003);陕西省重点研发计划(2021ZDLGY05-01)
Community-Detection-Based Influence Blocking Maximization Algorithm in Social Network
MU Zhiying, XU Jiaquan, LI Xiaoyu( )
)
- Research & Development Institute of Northwestern Polytechnical University in Shenzhen, Shenzhen 518057, China
-
Received:2022-08-16Online:2023-01-10Published:2023-01-19 -
Contact:LI Xiaoyu E-mail:lixiaoyu@nwpu.edu.cn
摘要:
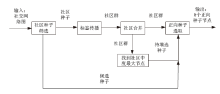
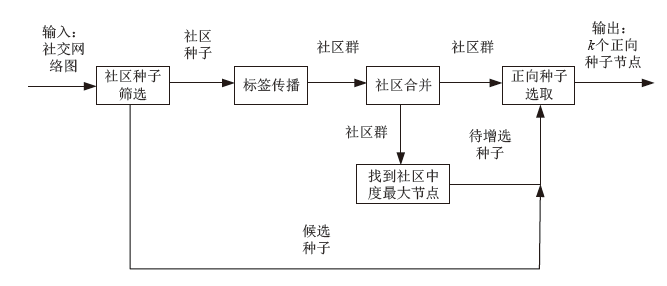
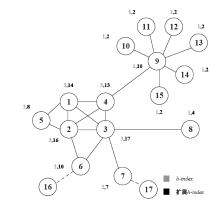
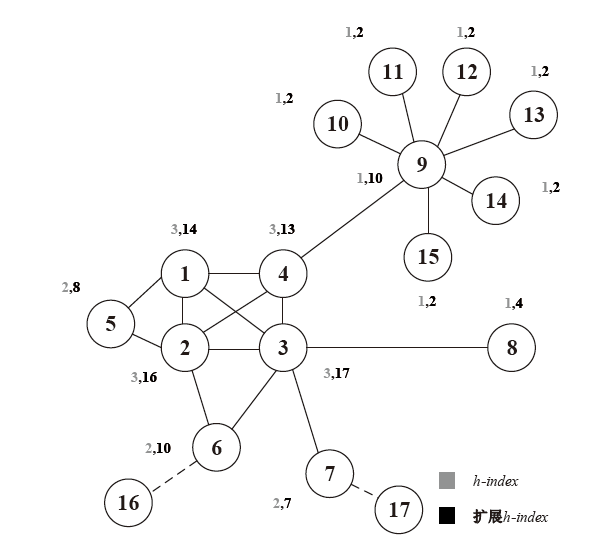
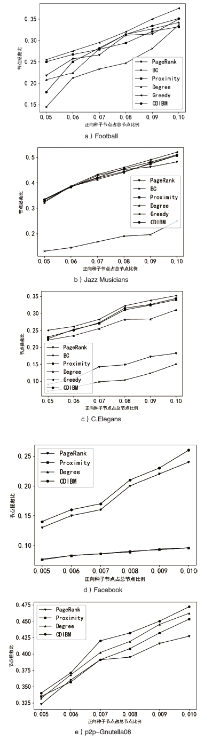
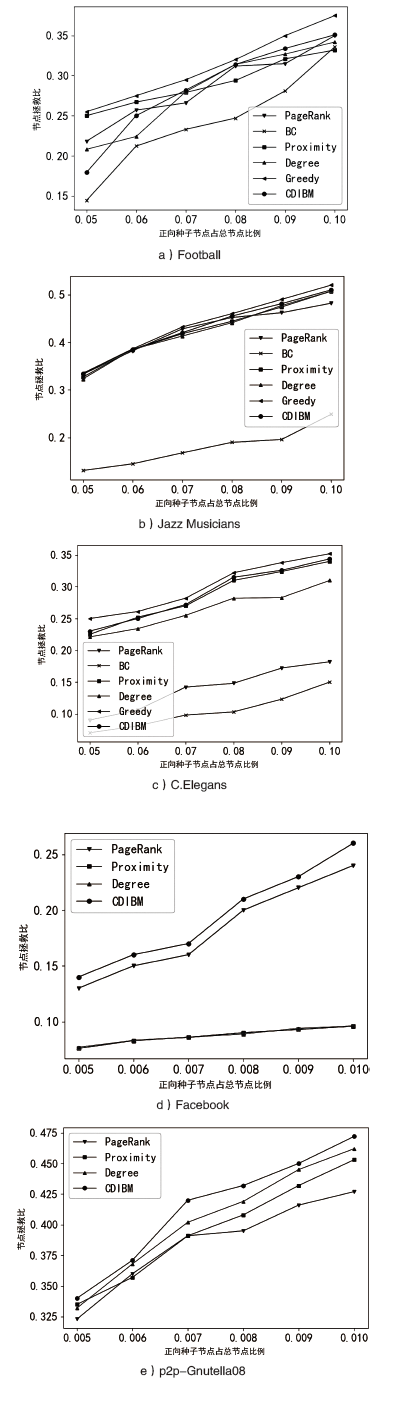
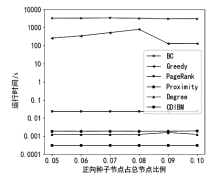
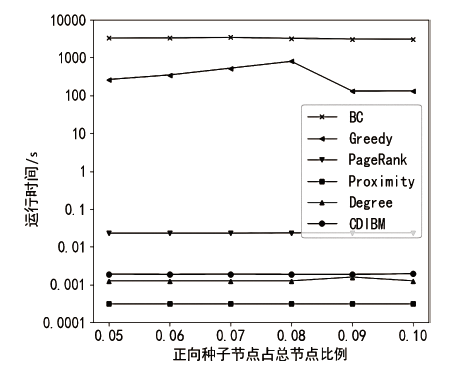
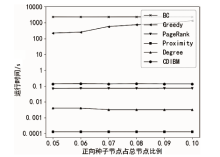
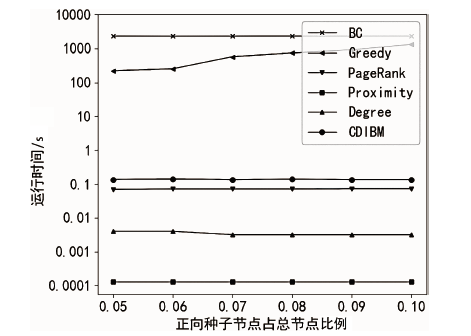
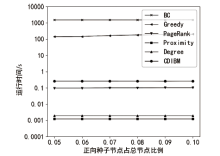
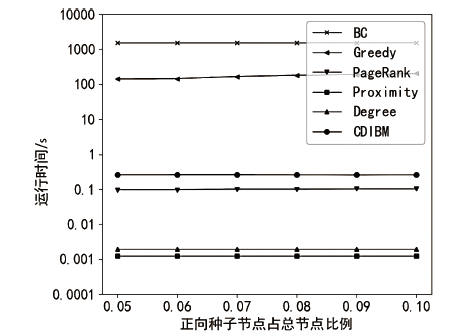
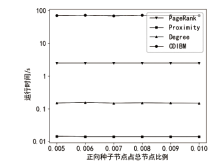
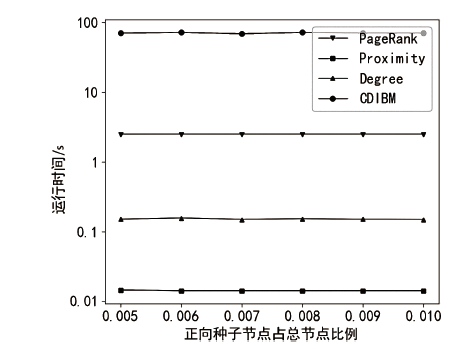
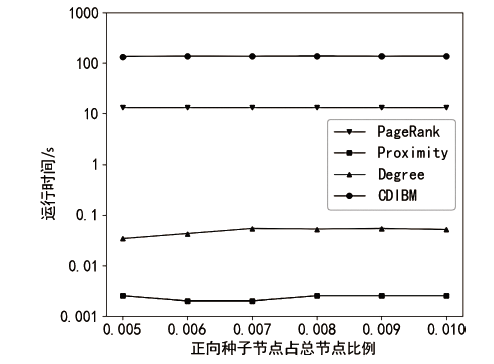
随着社交网络的日益普及,社交网络已经成为信息传播的主要平台之一。由于对社交网络内容监管相对困难,导致一些负面信息容易快速扩散并产生较大的不良影响。影响力阻断最大化问题旨在寻找需要采用正影响的节点集,使信息传播过程中被负向消息影响的节点数量最小化。针对现有社交网络影响力阻断算法运行时间复杂度较高的问题,文章提出了基于社区发现的影响力阻断最大化算法,该算法首先使用社交网络节点的扩展h指数中心性来选择候选种子节点;然后以这些种子节点为起点,利用标签传播算法发现社交网络中的社区;接着通过计算社交网络社区的关系矩阵及当前关系矩阵的模块度对社区进行合并;最后,计算初始种子节点的标签度量等级,选取前
中图分类号:
引用本文
慕志颖, 许加全, 李晓宇. 基于社区发现的社交网络影响力阻断最大化算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(1): 44-56.
MU Zhiying, XU Jiaquan, LI Xiaoyu. Community-Detection-Based Influence Blocking Maximization Algorithm in Social Network[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(1): 44-56.
| [1] | KEMPE D, KLEINBERG J, TARDOS É. Maximizing the Spread of Influence Through a Social Network[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the Ninth ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2003: 137-146. |
| [2] | HE X, SONG G, CHEN W, et al. Influence Blocking Maximization in Social Networks Under the Competitive Linear Threshold Model[C]// SIAM. Proceedings of the 2012 Siam International Conference on Data Mining. New York: SIAM, 2012: 463-474. |
| [3] | CHEN W, YUAN Y, ZHANG L. Scalable Influence Maximization in Social Networks Under the Linear Threshold Model[C]// IEEE. 2010 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining. New York: IEEE, 2010: 88-97. |
| [4] | BORGS C, BRAUTBAR M, CHAYES J, et al. Maximizing Social Influence in Nearly Optimal Time[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the Twenty-fifth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms. New York: ACM, 2014: 946-957. |
| [5] | TANG Y, XIAO X, SHI Y. Influence Maximization: Near-Optimal Time Complexity Meets Practical Efficiency[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 2014 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data. New York: ACM, 2014: 75-86. |
| [6] | NGUYEN H T, THAI M T, DINH T N. Stop-and-Stare: Optimal Sampling Algorithms for Viral Marketing in Billion-Scale Networks[EB/OL]. [2022-06-20]https://dblp.uni-trier.de/rec/journals/corr/NguyenTD16.html. |
| [7] |
BU Z, ZHANG C, XIA Z, et al. A Fast Parallel Modularity Optimization Algorithm (FPMQA) for Community Detection in Online Social Network[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2013, 50: 246-259.
doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2013.06.014 URL |
| [8] | DOMINGOS P, RICHARDSON M. Mining the Network Value of Customers[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the Seventh ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2001: 57-66. |
| [9] | CHEN W, LAKSHMANAN L V S, CASTILLO C. Information and Influence Propagation in Social Networks[J]. Synthesis Lectures on Data Management, 2013, 5(4): 170-177. |
| [10] | CHEN W, COLLINS A, CUMMINGS R, et al. Influence Maximization in Social Networks When Negative Opinions May Emerge and Propagate[C]// SIAM. Proceedings of the 2011 Siam International Conference on Data Mining. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics. New York: SIAM, 2011: 379-390. |
| [11] | CARNES T, NAGARAJAN C, WILD S M, et al. Maximizing Influence in a Competitive Social Network: A Follower’s Perspective[EB/OL]. [2022-06-25]. http://www.xueshufan.com/publication/2105509646. |
| [12] | GOMEZ-RODRIGUEZ M, BALDUZZI D, SCHÖLKOPF B. Uncovering the Temporal Dynamics of Diffusion Networks[EB/OL]. [2022-06-28]. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2011arXiv1105.0697G/abstract. |
| [13] | GOMEZ-RODRIGUEZ M, SCHOLKOPF B. Inf luence Maximization in Continuous Time Diffusion Networks[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2012: 313-320. |
| [14] |
DU N, SONG L, GOMEZ-RODRIGUEZ M, et al. Scalable Influence Estimation in Continuous-Time Diffusion Networks[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2013, 26: 3147-3155.
pmid: 26752940 |
| [15] | SAITO K, KIMURA M, OHARA K, et al. Selecting Information Diffusion Models over Social Networks for Behavioral Analysis[C]// Springer. Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases. Berlin: Springer, 2010: 180-195. |
| [16] | GOMEZ-RODRIGUEZ M, SONG L, DU N, et al. Influence Estimation and Maximization in Continuous-Time Diffusion Networks[J]. ACM Transactions on Information Systems (TOIS), 2016, 34(2): 1-33. |
| [17] | NEWMAN M E J. Spread of Epidemic Disease on Networks[J]. Physical Review E, 2002, 66(1): 180-195. |
| [18] | LI Y, CHEN W, WANG Y, et al. Influence Diffusion Dynamics and Influence Maximization in Social Networks with Friend and Foe Relationships[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the Sixth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2013: 657-666. |
| [19] | CLARK A, POOVENDRAN R. Maximizing Influence in Competitive Environments: A Game-Theoretic Approach[C]// Springer. International Conference on Decision and Game Theory for Security. Berlin: Springer, 2011: 151-162. |
| [20] |
WANG F, JIANG W, LI X, et al. Maximizing Positive Influence Spread in Online Social Networks via Fluid Dynamics[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2018, 86: 1491-1502.
doi: 10.1016/j.future.2017.05.050 URL |
| [21] | RAGHAVAN U N, ALBERT R, KUMARA S. Near Linear Time Algorithm to Detect Community Structures in Large-Scale Networks[J]. Physical Review E, 2007, 76(3): 106-117. |
| [22] |
ZHAO Y, LI S, JIN F. Identification of Influential Nodes in Social Networks with Community Structure Based on Label Propagation[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 210: 34-44.
doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.11.125 URL |
| [23] |
SALAVATI C, ABDOLLAHPOURI A, MANBARI Z. Ranking Nodes in Complex Networks Based on Local Structure and Improving Closeness Centrality[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 336: 36-45.
doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.04.086 URL |
| [24] |
BERAHMAND K, BOUYER A, SAMADI N. A New Local and Multidimensional Ranking Measure to Detect Spreaders in Social Networks[J]. Computing, 2019, 101(11): 1711-1733.
doi: 10.1007/s00607-018-0684-8 URL |
| [25] |
RUI X, MENG F, WANG Z, et al. A Reversed Node Ranking Approach for Influence Maximization in Social Networks[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2019, 49(7): 2684-2698.
doi: 10.1007/s10489-018-01398-w URL |
| [26] |
WEN T, DENG Y. Identification of Influencers in Complex Networks by Local Information Dimensionality[J]. Information Sciences, 2020, 512: 549-562.
doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.10.003 URL |
| [27] |
HUANG H, SHEN H, MENG Z, et al. Community-Based Influence Maximization for Viral Marketing[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2019, 49(6): 2137-2150.
doi: 10.1007/s10489-018-1387-8 |
| [28] | BHARATHI S, KEMPE D, SALEK M. Competitive Influence Maximization in Social Networks[C]// Springer. International Workshop on Web and Internet Economics. Berlin: Springer, 2007: 306-311. |
| [29] |
HIRSCH J E. An Index to Quantify an Individual's Scientific Research Output[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2005, 102(46): 16569-16572.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507655102 URL |
| [30] | LÜ L, ZHOU T, ZHANG Q M, et al. The H-Index of a Network Node and Its Relation to Degree and Coreness[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7(1): 1-7. |
| [31] |
LIU Q, ZHU Y X, JIA Y, et al. Leveraging Local H-Index to Identify and Rank Influential Spreaders in Networks[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2018, 512: 379-391.
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2018.08.053 URL |
| [32] |
ZAREIE A, SHEIKHAHMADI A. EHC: Extended H-Index Centrality Measure for Identification of Users’ Spreading Influence in Complex Networks[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2019, 514: 141-155.
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2018.09.064 URL |
| [33] |
RUI X, YANG X, FAN J, et al. A Neighbour Scale Fixed Approach for Influence Maximization in Social Networks[J]. Computing, 2020, 102(2): 427-449.
doi: 10.1007/s00607-019-00778-5 URL |
| [34] | LI X, ZHOU S, LIU J, et al. Communities Detection in Social Network Based on Local Edge Centrality[EB/OL]. [2022-06-25]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0378437119309173. |
| [35] |
NEWMAN M E. Modularity and Community Structure in Networks[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2006, 103(23): 8577-8582.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0601602103 URL |
| [36] | NGUYEN H T, THAI M T, DINH T N. Stop-and-Stare: Optimal Sampling Algorithms for Viral Marketing in Billion-Scale Networks[EB/OL]. [2022-06-29]. https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=cead64288e71fe041608ecc9cd3a6d8e. |
| [37] | ARAZKHANI N, MEYBODI M R, REZVANIAN A. Influence Blocking Maximization in Social Network Using Centrality Measures[C]// IEEE. 2019 5th Conference on Knowledge Based Engineering and Innovation (KBEI). New York: IEEE, 2019: 492-497. |
| [38] |
SU S, LI X, CHENG X, et al. Location-Aware Targeted Influence Maximization in Social Networks[J]. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 2018, 69(2): 229-241.
doi: 10.1002/asi.23931 URL |
| [39] | PAGE L, BRIN S, MOTWANI R, et al. The PageRank Citation Ranking: Bringing Order to the Web[M]. Stanford: Stanford InfoLab, 1999. |
| [1] | 马相军, 何泾沙, 吴铁军, 范敦球. 社交网络关键黑客节点识别方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(1): 57-65. |
| [2] | 周玉晶, 沈嘉荟, 邱海韬, 查达仁. 基于复杂网络的社交媒体内容安全可视化分析系统[J]. 信息网络安全, 2016, 16(9): 158-162. |
| [3] | 温俊伟. 面向Twitter的分析系统研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2016, 16(9): 234-239. |
| [4] | 许为, 林柏钢, 林思娟, 杨旸. 一种基于用户交互行为和相似度的社交网络社区发现方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2015, 15(7): 77-83. |
| [5] | . 社交网Twitter平台的人物关系网社区发现[J]. , 2014, 14(5): 32-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||