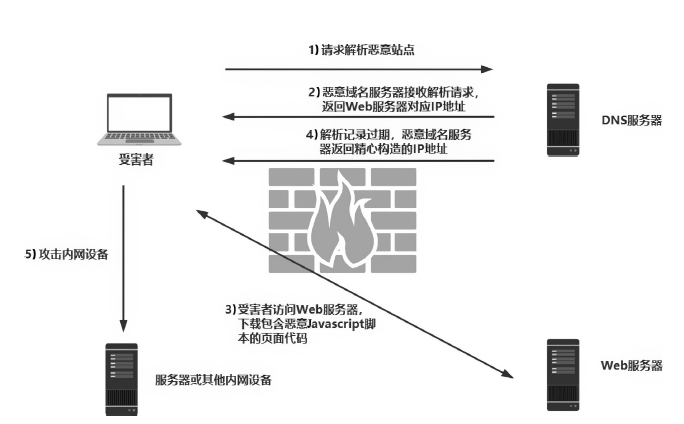
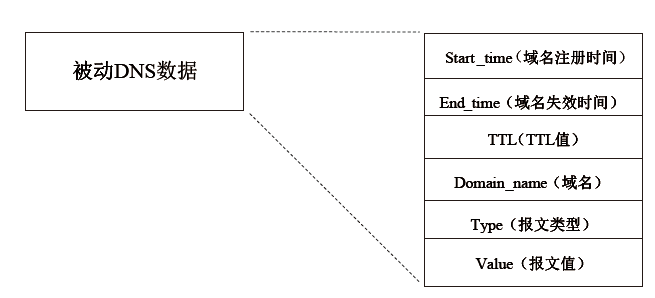
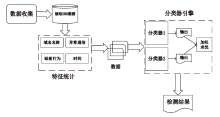
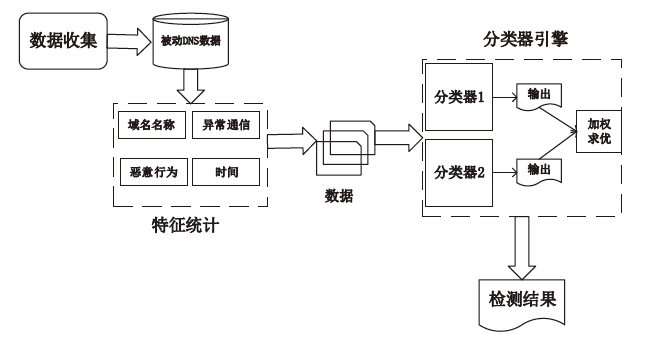
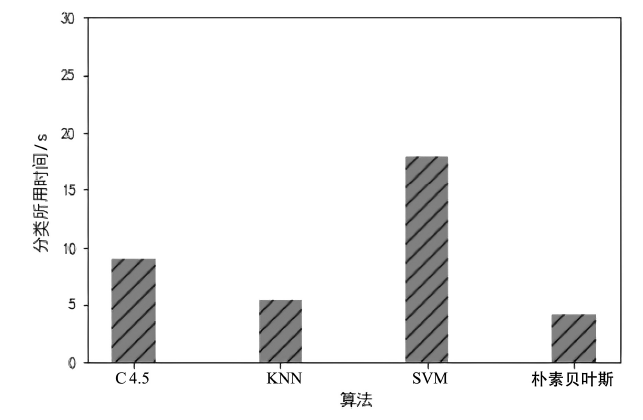
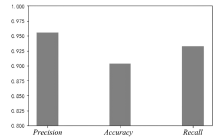
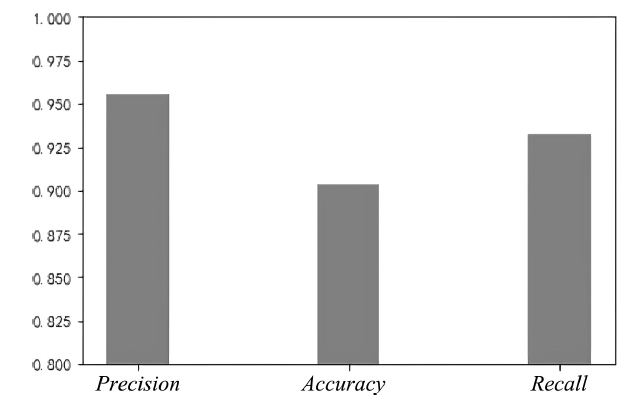
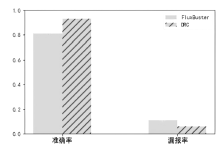
| [1] |
HONG Bo, GENG Guanggang, WANG Liming, et al. System to Discover Phishing Attacks Actively Based on DNS[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2013,30(12):3771-3774.
|
|
洪博, 耿光刚, 王利明, 等. 一种基于DNS主动检测钓鱼攻击的系统[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2013,30(12):3771-3774.
|
| [2] |
TATANG D, SUURLAND T, HOLZ T. Study of DNS Rebinding Attacks on Smart Home Devices[EB/OL]. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/335243263_Study_of_DNS_Re-bin-ding_At-tacks_on_Smart_Home_De-vices, 2020-01-20.
|
| [3] |
JACKSON C, BORTZ A, BONEH D, et al. Protecting Browser State from Web Privacy Attacks [C]//ACM. The 15th International Conference on World Wide Web, May 23-26, 2006, Edinburgh, Scotland, UK. New York: ACM, 2006: 737-744.
|
| [4] |
DAI Yunxing, RESIG R. FireDrill: Interactive DNS Rebinding [C]// USENIX. The 7th USENIX Conference on Offensive Technologies, August 13, 2013, Washington, DC, USA. Berkeley: USENIX Association, 2013: 2.
|
| [5] |
DORSEY B. Attacking Private Networks from the Internet with DNS Rebinding[EB/OL]. https://medium.com/@brannondorsey/attacking-private-networks-from-the-internet-with-dns-rebinding-ea7098a2d325, 2018-06-19.
|
| [6] |
Armis. DNS Rebinding Exposes Half a Billion Devices in the Enterprise[EB/OL]. https://www.armis.com/resources/iot-security-blog/dns-rebinding-exposes-half-a-billion-iot-devices-in-the-enterprise/, 2020-01-20.
|
| [7] |
F-Secure. Minikube RCE & VM Escape[EB/OL]. https://labs.f-secure.com/advisories/minikube-rce/, 2020-01-20.
|
| [8] |
ZHA Chengji. Analysis of Mobile Internet Based on DNS Log[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2014.
|
|
查诚吉. 基于DNS日志的移动互联网分析[D]. 北京:北京邮电大学, 2014.
|
| [9] |
TIAN Shiqi. Implementation and Traffic Analysis of DNS Traffic Collection System[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2018.
|
|
田世奇. DNS流量采集系统的实现与流量分析[D]. 北京:北京邮电大学, 2018.
|
| [10] |
ANTONAKAKIS M, PERDISCI R, DAGON D, et al. Building a Dynamic Reputation System for DNS [C]// USENIX. The 19th USENIX Conference on Security, August 11-13, 2010, Washington, DC, USA. Berkeley: USENIX Association, 2010: 18.
|
| [11] |
BILGE L, SEN S, BALZAROTTI D, et al. Exposure: A Passive DNS Analysis Service to Detect and Report Malicious Domains[J]. ACM Transactions on Information and System Security, 2014,16(4):1-28.
|
| [12] |
RAHBARINIA B, PERDISCI R, et al. Efficient and Accurate Behavior-based Tracking of Malware-control Domains in Large ISP Networks[J]. ACM Transactions on Privacy and Security, 2016,2016(19):1-31.
|
| [13] |
PERDISCI R, CORONA I, GIACINTO G. Early Detection of Malicious Flux Networks via Large-scale Passive DNS Traffic Analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2012,9(5):714-726.
|
| [14] |
ZHANG Weiwei, GONG Jian, LIU Shangdong, et al. DNS Surveillance on Backbone[J]. Journal of Software, 2017,28(9):2370-2387.
|
|
张维维, 龚俭, 刘尚东, 等. 面向主干网的DNS流量监测[J]. 软件学报, 2017,28(9):2370-2387.
|
| [15] |
WEIMER F. Passive DNS Replication[EB/OL]. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/265577184_Passive_DNS_Replication, 2020-01-20.
|
| [16] |
FARID D M, ZHANG Li, RAHMAN C M, et al. Hybrid Decision Tree and Naive Bayes Classifiers for Multi-class Classification Tasks[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2014,41(4):1937-1946.
|
| [17] |
RISKIQ. RiskIQ PassiveTotal[EB/OL]. https://www.riskiq.com/products/passivetotal/, 2020-01-20.
|
| [18] |
circl. lu. CIRCL Passive DNS[EB/OL]. https://www.circl.lu/services/passive-dns/, 2020-01-20.
|
| [19] |
ZHOU Changling, CHEN Kai, GONG Xuxiao, et al. Detection of Fast-flux Domains Based on Passive DNS Analysis[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2016,52(3):396-402.
|
|
周昌令, 陈恺, 公绪晓, 等. 基于Passive DNS的速变域名检测[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2016,52(3):396-402.
|
| [20] |
Alexa. The Top 500 Sites on the Web[EB/OL]. https://www.alexa.com/topsites, 2020-01-20.
|
 ), 潘祖烈1,2, 沈毅1,2, 陈远超1,2
), 潘祖烈1,2, 沈毅1,2, 陈远超1,2
 ), PAN Zulie1,2, SHEN Yi1,2, CHEN Yuanchao1,2
), PAN Zulie1,2, SHEN Yi1,2, CHEN Yuanchao1,2