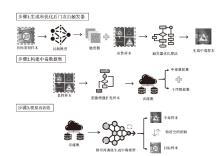
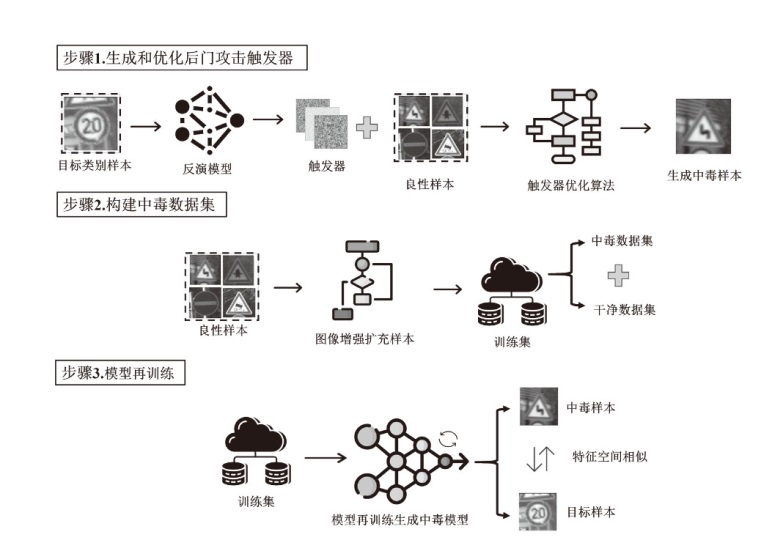
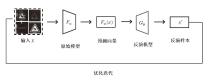
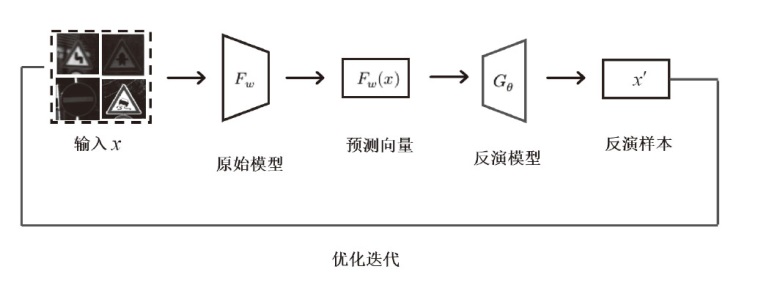
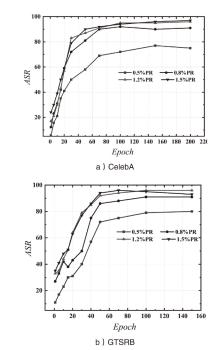
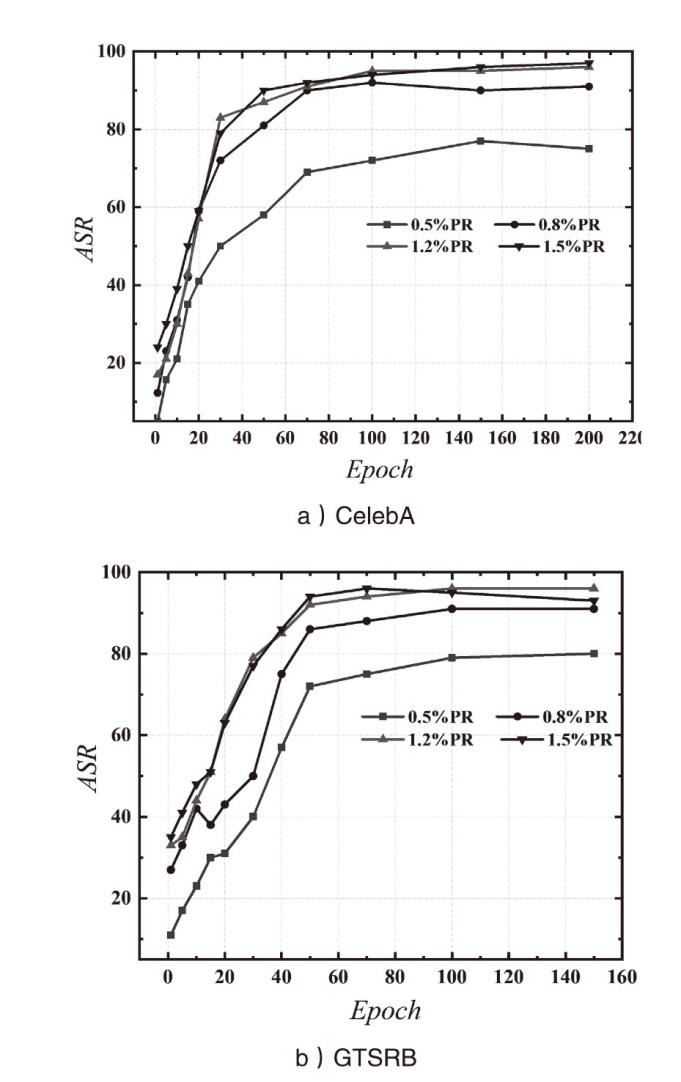
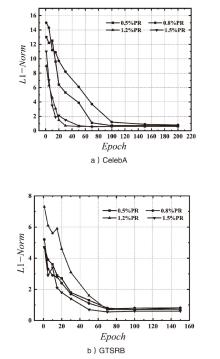
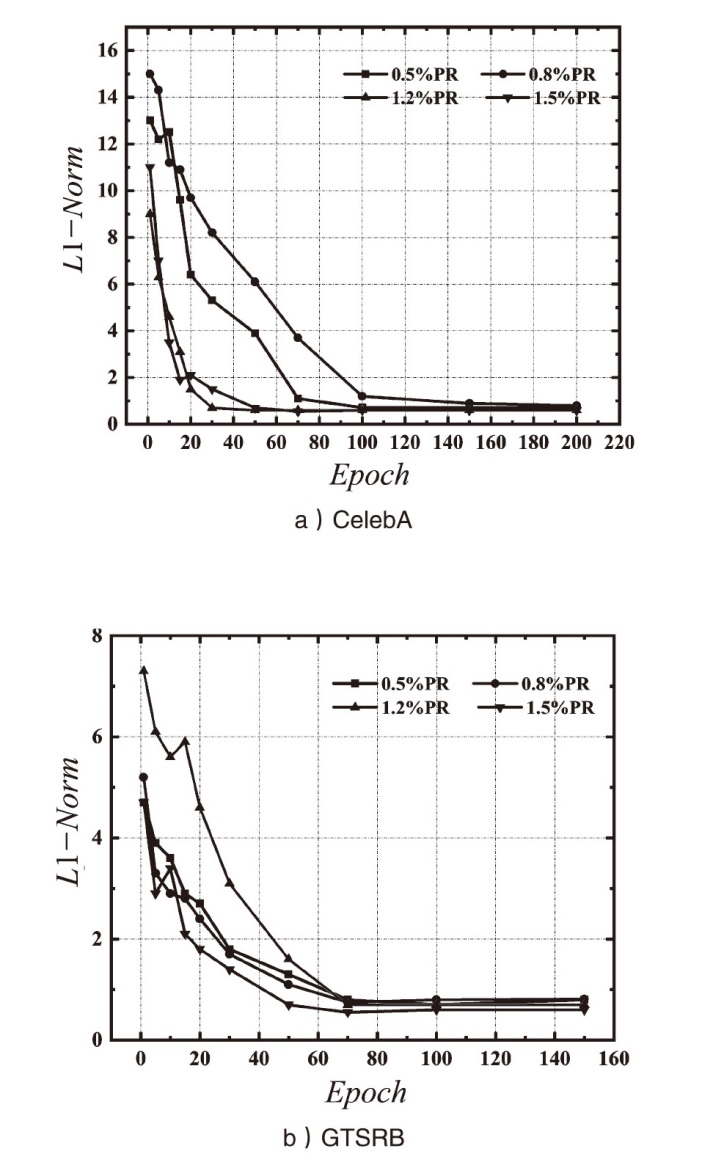
| [1] |
SARKER I H, KHAN A I, ABUSHARK Y B, et al. Internet of Things (IoT) Security Intelligence: A Comprehensive Overview, Machine Learning Solutions and Research Directions[J]. Mobile Networks and Applications, 2023, 28(1): 296-312.
|
| [2] |
FANG W, DING L. Computer Vision and Deep Learning to Manage Safety in Construction: Matching Images of Unsafe Behavior and Semantic Rules[J]. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 2021, 70(12): 4120-4132.
|
| [3] |
WENGER E, PASSANANTI J, BHAGOJI A N, et al. Backdoor Attacks against Deep Learning Systems in the Physical World[C]// IEEE.Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2021: 6206-6215.
|
| [4] |
BANSAL H, SINGHI N, YANG Y, et al. Cleanclip: Mitigating Data Poisoning Attacks in Multimodal Contrastive Learning[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. New York: IEEE, 2023: 112-123.
|
| [5] |
ZENG Y, PARK W, MAO Z M, et al. Rethinking the Backdoor Attacks’ Triggers: A Frequency Perspective[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. New York: IEEE, 2021: 16473-16481.
|
| [6] |
DUMFORD J, SCHEIRER W. Backdooring Convolutional Neural Networks via Targeted Weight Perturbations[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB). New York: IEEE, 2020: 1-9.
|
| [7] |
LI Yuanchun, HUA Jiayi, WANG Haoyu, et al. Deeppayload: Black-Box Backdoor Attack on Deep Learning Models through Neural Payload Injection[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE/ACM 43rd International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE). New York: IEEE, 2021: 263-274.
|
| [8] |
RAKIN A S, HE Z, FAN D. Targeted Neural Network Attack with Bit Trojan[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2020: 13198-13207.
|
| [9] |
WANG B, YAO Y, SHAN S, et al. Neural Cleanse: Identifying and Mitigating Backdoor Attacks in Neural Networks[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York: IEEE, 2019: 707-723.
|
| [10] |
LI Y, LI Y, WU B, et al. Invisible Backdoor Attack with Sample-Specific Triggers[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. New York: IEEE, 2021: 16463-16472.
|
| [11] |
YANG Zhou, XU B, ZHANG J M, et al. Stealthy Backdoor Attack for Code Models[EB/OL]. (2023-01-09)[2024-02-16]. https://arxiv.org/list/cs.SE/2023-01?skip=70&show=250.
|
| [12] |
NGUYEN N B, CHANDRASEGARAN K, ABDOLLAHZADEH M, et al. Re-Thinking Model Inversion Attacks against Deep Neural Networks[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2023: 16384-16393.
|
| [13] |
TORBUNOV D, HUANG Y, YU H, et al. Uvcgan: Unet Vision Transformer Cycle-Consistent Gan for Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. New York: IEEE, 2023: 702-712.
|
| [14] |
QI X, XIE T, PAN R, et al. Towards Practical Deployment-Stage Backdoor Attack on Deep Neural Networks[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2022: 13347-13357.
|
| [15] |
XIA P, NIU H, LI Z, et al. Enhancing Backdoor Attacks with Multi-Level Mmd Regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2022, 20(2): 1675-1686.
|
| [16] |
GU T, LIU K, DOLAN-GAVITT B, et al. Badnets: Evaluating Backdooring Attacks on Deep Neural Networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 47230-47244.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2909068
|
| [17] |
SAHA A, SUBRAMANYA A, PIRSIAVASH H. Hidden Trigger Backdoor Attacks[C]// AAAI. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York: AAAI, 2020: 11957-11965.
|
| [18] |
NGUYEN A, TRAN A. Wanet-Imperceptible Warping-Based Backdoor Attack[EB/OL]. (2021-09-09)[2024-02-16]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2102.10369v4.
|
| [19] |
DOAN K, LAO Y, ZHAO W, et al. Lira:Learnable, Imperceptible and Robust Backdoor Attacks[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. New York: IEEE, 2021: 11966-11976.
|
| [20] |
DONG S, XIA Y, PENG T. Network Abnormal Traffic Detection Model Based on Semi-Supervised Deep Reinforcement Learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2021, 18(4): 4197-4212.
|