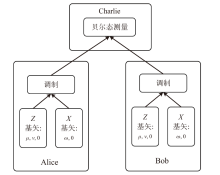
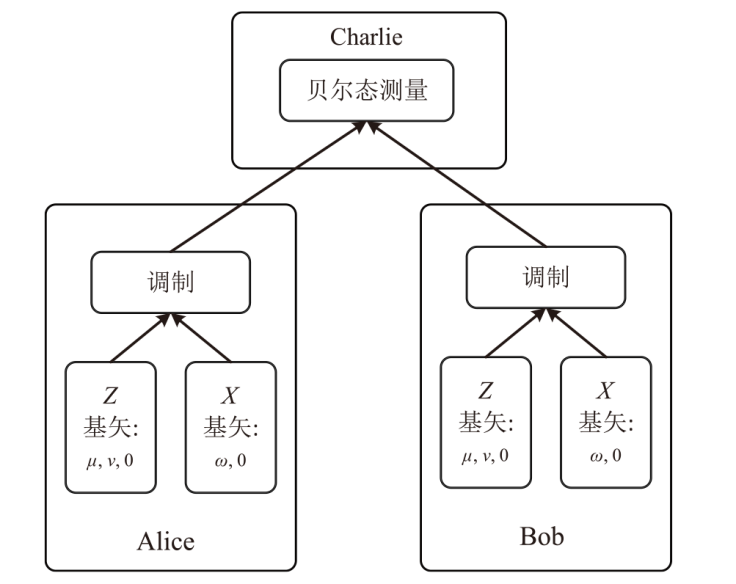
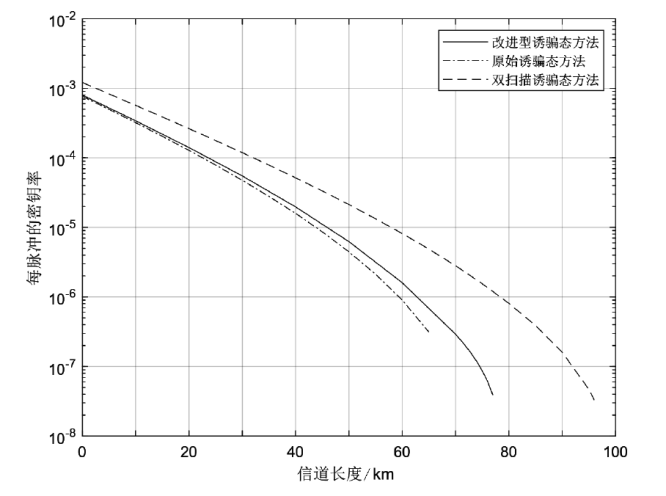
信息网络安全 ›› 2024, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (6): 926-936.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2024.06.010
测量设备无关量子密钥分发中的改进型诱骗态方法
- 1.南京大学物理学院,南京 210093
2.中国人民大学物理学系,北京 100872
-
收稿日期:2024-04-25出版日期:2024-06-10发布日期:2024-07-05 -
通讯作者:尹华磊hlyin@ruc.edu.cn -
作者简介:白峻林(1998—),男,新疆,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为量子密码|尹华磊(1989—),男,四川,副教授,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为量子信息、量子光学、密码学 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(12274223)
Improved Decoy State Method for Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution
- 1. School of Physics, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
2. Department of Physics, Renmin University of China, Beijing 100872, China
-
Received:2024-04-25Online:2024-06-10Published:2024-07-05
摘要:
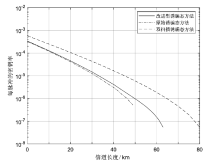
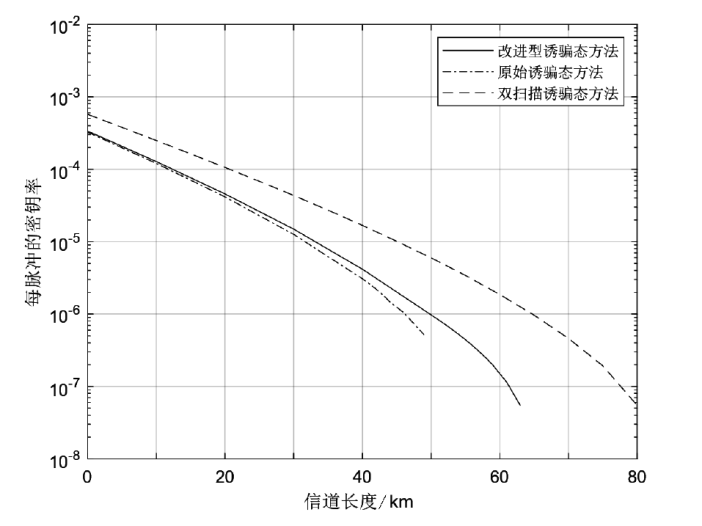
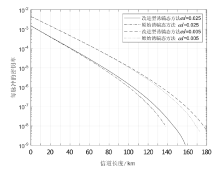
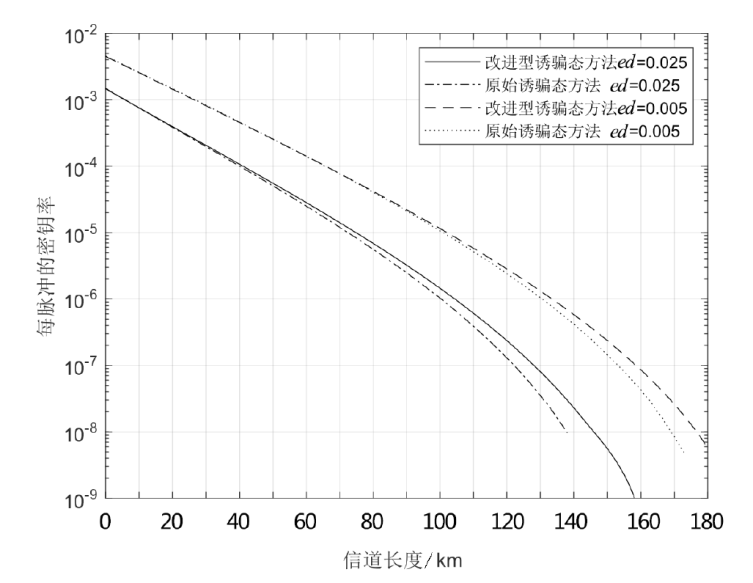
测量设备无关量子密钥分发协议作为量子网络的候选组件之一,消除了探测端的所有漏洞,提升了系统安全性。目前的测量设备无关量子密钥分发协议采用非理想单光子源,并引入了诱骗态方法来提高密钥率。最近,一种整合在诱骗态方法中的数据后处理方法双扫描法在统计波动方面表现出色。使用诱骗态方法估算单光子对成分时,引入双扫描法能获得更高的密钥率。然而,双扫描法需要耗时的优化过程。在此,文章提出了一种新颖的改进型诱骗态方法,以实现比原始诱骗态方法更好的性能,同时避免了类似双扫描法优化时间的出现。在文章所有的实验参数值模拟中,改进型诱骗态方法均比原始诱骗态方法的密钥率更高;相较于双扫描法,文章所提方法具有速度快、兼容性好的优点。
中图分类号:
引用本文
白峻林, 尹华磊. 测量设备无关量子密钥分发中的改进型诱骗态方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(6): 926-936.
BAI Junlin, YIN Hualei. Improved Decoy State Method for Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(6): 926-936.
| [1] | BENNETT C H, BRASSARD G. Quantum Cryptography: Public Key Distribution and Coin Tossing[J]. Theoretical Computer Science, 2014, 560 (7): 7-11. |
| [2] | EKERT A K. Quantum Cryptography Based on Bell’s Theorem[J]. Physical Review Letter, 1991, 67(6): 661-663. |
| [3] |
LO H K, CHAU H F. Unconditional Security of Quantum Key Distribution over Arbitrarily Long Distances[J]. Science, 1999, 283(5410): 2050-2056.
pmid: 10092221 |
| [4] | SHOR P W, PRESKILL J. Simple Proof of Security of the BB84 Quantum Key Distribution Protocol[J]. Physical Review Letter, 2000, 85(2): 441-444. |
| [5] | WEEDBROOK C, PIRANDOLA S, GARCÍA-PATRΌN R, et al. Gaussian Quantum Information[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2012, 84(2): 621-669. |
| [6] | PIRANDOLA S, ANDERSEN U L, BANCHI L, et al. Advances in Quantum Cryptography[J]. Advances in Optics and Photonics, 2020, 12 (4): 1012-1236. |
| [7] | XU Hai, YU Zongwen, JIANG Cong, et al. Sending-or-not-Sending Twin-Field Quantum Key Distribution: Breaking the Direct Transmission Key Rate[J]. Physical Review A, 2020, 101 (4): 23-30. |
| [8] |
YIN Hualei, CAO Wenfei, FU Yao, et al. Long-Distance Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution with Coherent-State Superpositions[J]. Optics Letters, 2014, 39(18): 5451-5454.
doi: 10.1364/OL.39.005451 pmid: 26466295 |
| [9] | ADACHI Y, YAMAMOTO T, KOASHI M, et al. Simple and Efficient Quantum Key Distribution with Parametric Down-Conversion[EB/OL]. (2007-11-02)[2024-03-20]. https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.99.180503. |
| [10] | XU Feihu, MA Xiongfeng, ZHANG Qiang, et al. Secure Quantum Key Distribution with Realistic Devices[EB/OL]. (2005-03-05)[2024-03-20]. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Security-of-Quantum-Key-Distribution-with-Realistic-Ma/44aab3047a237ba276bd2dbef5d2217a8cdb9e4a?p2df. |
| [11] | AZUMA K, TAMAKI K, MUNRO W J. All-Photonic Intercity Quantum Key Distribution[EB/OL]. (2015-12-16)[2024-03-20]. https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms10171.pdf. |
| [12] | BRAUNSTEIN S L, PIRANDOLA S. Side-Channel-Free Quantum Key Distribution[EB/OL]. (2012-03-30)[2024-03-20]. https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.130502. |
| [13] | ZHOU Yiheng, YU Zongwen, WANG Xiangbin. Making the Decoy-State Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution Practically Useful[EB/OL]. [2024-03-20]. https://www.xueshufan.com/publication/1677861335. |
| [14] | XIE Yuanmei, LU Yushuo, WENG Chengxun, et al. Breaking the Rate-Loss Bound of Quantum Key Distribution with Asynchronous Two-Photon Interference[EB/OL]. (2022-04-26)[2024-03-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.11635v2. |
| [15] | ZENG Pei, ZHOU Hongyi, WU Weijie, et al. Mode-Pairing Quantum Key Distribution[EB/OL]. (2022-07-07)[2024-03-20]. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-31534-7. |
| [16] | CURTY M, XU Feihu, CUI Wei, et al. Finite-Key Analysis for Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution[EB/OL]. (2014-04-29)[2024-03-20]. https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms4732. |
| [17] | YIN Hualei, FU Yao. Measurement-Device-Independent Twin-Field Quantum Key Distribution[EB/OL]. [2024-03-20]. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30816262/. |
| [18] | LIU Wenbo, LI Chenlong, XIE Yuanmei, et al. Homodyne Detection Quadrature Phase Shift Keying Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution with High Excess Noise Tolerance[EB/OL]. [2024-03-20]. https://www.semanticscholar.org/reader/5bea10b4a918a2464a1de5a4bc3f03ff479750fa. |
| [19] | LUCAMARINI M, YUAN Zhiliang, DYNES J F, et al. Overcoming the Rate-Distance Limit of Quantum Key Distribution without Quantum Repeaters[J]. Nature, 2018, 557(7705): 400-403. |
| [20] |
YIN Hualei, LIU Peng, DAI Weiwei, et al. Experimental Composable Security Decoy-State Quantum Key Distribution Using Time-Phase Encoding[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(20): 29479-29485.
doi: 10.1364/OE.401829 pmid: 33114847 |
| [21] | BOARON A, BOSO G, RUSCA D, et al. Secure Quantum Key Distribution over 421km of Optical Fiber[EB/OL]. [2024-03-20]. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30468607/. |
| [22] | RUBENOK A, SLATER J A, CHAN P, et al. Real-World Two-Photon Interference and Proof-of-Principle Quantum Key Distribution Immune to Detector Attacks[EB/OL]. (2013-09-23)[2024-03-20]. https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.130501. |
| [23] | TANG Zhiyuan, LIAO Zhongfa, XU Feihu, et al. Experimental Demonstration of Polarization Encoding Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution[EB/OL]. (2014-05-14)[2024-03-20]. https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.190503. |
| [24] | YIN Hualei, CHEN Tengyun, YU Zongwen, et al. Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution over a 404km Optical Fiber[EB/OL]. [2024-03-20]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1606.06821. |
| [25] | TANG Yanlin, YIN Hualei, ZHAO Qi, et al. Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution over Untrustful Metropolitan Network[EB/OL]. [2024-03-20]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1509.08389. |
| [26] | LIU Hongwei, WANG Jipeng, MA Haiqiang, et al. Polarization-Multiplexing-Based Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution without Phase Reference Calibration[EB/OL]. [2024-03-20]. https://opg.optica.org/optica/fulltext.cfm?uri=optica-5-8-902&id=395554. |
| [27] | CAO Yuan, LI Yuhuai, YANG Kuixing, et al. Long-Distance Free-Space Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution[EB/OL]. [2024-03-20]. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33449747/. |
| [28] | WEI Kejin, LI Wei, TAN Hao, et al. High-Speed Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution with Integrated Silicon Photonics[EB/OL]. [2024-03-20]. https://www.semanticscholar.org/reader/79a0f227c8933408d70f299ef408e46ff2e0ae3f. |
| [29] | CHEN Yipeng, LIU Jingyang, SUN Mingshuo, et al. Experimental Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution with the Double-Scanning Method[EB/OL]. (2021-05-20)[2024-03-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.09587. |
| [30] | PITTALUGA M, MINDER M, LUCAMARINI M, et al. 600-km Repeater-Like Quantum Communications with Dual-Band Stabilization[J]. Nature Photonics, 2021, 15(7): 530-535. |
| [31] | WANG Shuang, YIN Zhenqiang, HE Deyong, et al. Twin-Field Quantum Key Distribution over 830-km Fibre[J]. Nature Photonics, 2022, 16 (2): 154-161. |
| [32] | BRASSARD G, LÜTKENHAUS N, MOR T, et al. Limitations on Practical Quantum Cryptography[J]. Physical Review Letter, 2000, 85(6): 1330-1333. |
| [33] | SCARANI V, BECHMANN-PASQUINUCCI H, CERF N J, et al. The Security of Practical Quantum Key Distribution[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2009, 81: 1301-1350. |
| [34] | LYDERSEN L, WIECHERS C, WITTMANN C, et al. Hacking Commercial Quantum Cryptography Systems by Tailored Bright Illumination[J]. Nature Photonics, 2010, 4 (10): 686-689. |
| [35] | MAYERS D, YAO A. Quantum Cryptography with Imperfect Apparatus[C]// IEEE. Proceedings 39th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science. New York: IEEE, 1998: 503-509. |
| [36] | ACÍN A, BRUNNER N, GISIN N, et al. Device-Independent Security of Quantum Cryptography against Collective Attacks[EB/OL]. (2007-06-04)[2024-03-20]. https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.98.230501. |
| [37] | XIE Yuanmei, LI Binghong, LU Yushuo, et al. Overcoming the Rate-Distance Limit of Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution[EB/OL]. [2024-03-20]. https://opg.optica.org/ol/abstract.cfm?uri=ol-46-7-1632. |
| [38] | LO H K, CURTY M, QI B. Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution[EB/OL]. [2024-03-20]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1109.1473. |
| [39] | HWANG W Y. Quantum Key Distribution with High Loss: Toward Global Secure Communication[EB/OL]. (2003-08-01)[2024-03-20]. https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.91.057901. |
| [40] | LO H K. Decoy State Quantum Key Distribution[EB/OL]. [2024-03-20]. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2005qis..conf..143L/abstract. |
| [41] | WANG Xiangbin. Beating the Photon-Number-Splitting Attack in Practical Quantum Cryptography[EB/OL]. (2005-06-16)[2024-03-20]. https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.230503. |
| [42] | MA Xiongfeng, RAZAVI M. Alternative Schemes for Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution[EB/OL]. (2012-12-19)[2024-03-20]. https://journals.aps.org/pra/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevA.86.062319. |
| [43] | WANG Xiangbin. Three-Intensity Decoy-State Method for Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution with Basis-Dependent Errors[EB/OL]. (2012-12-19)[2024-03-20]. http://export.arxiv.org/pdf/1308.5677. |
| [44] |
CHAN P, SLATER J A, LUCIO Martinez I, et al. Modeling a Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution System[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(11): 12716-12736.
doi: 10.1364/OE.22.012716 pmid: 24921468 |
| [45] | YU Zongwen, ZHOU Yiheng, WANG Xiangbin. Statistical Fluctuation Analysis for Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution with Three-Intensity Decoy-State Method[EB/OL]. (2019-02-25)[2024-03-20]. https://journals.aps.org/pra/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevA.99.022333. |
| [46] |
PIRANDOLA S, OTTAVIANI C, SPEDALIERI G, et al. High-Rate Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Cryptography[J]. Nature Photonics, 2015, 9 (6): 397-402.
doi: 10.1038/NPHOTON.2015.83 |
| [47] | JIANG Cong, YU Zongwen, HU Xiaolong, et al. Higher Key Rate of Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution Through Joint Data Processing[EB/OL]. [2024-03-20]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.08915. |
| [48] | WANG Wenyuan, XU Feihu, LO H K. Asymmetric Protocols for Scalable High-Rate Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution Networks[EB/OL]. [2024-03-20]. https://www.xueshufan.com/publication/3104602549. |
| [49] | PEEV M, PACHER C, ALLÉAUME R, et al. The Secure Quantum Key Distribution Network in Vienna[EB/OL]. [2024-03-20]. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1367-2630/11/7/075001/pdf. |
| [50] | CHERNOFF H. A Measure of Asymptotic Efficiency for Tests of a Hypothesis Based on the Sum of Observations[J]. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 1952, 23(4): 493-507. |
| [51] | YIN Hualei, ZHOU Mingang, GU Jie, et al. Tight Security Bounds for Decoy-State Quantum Key Distribution[EB/OL]. (2020-08-31)[2024-03-20]. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1038/s41598-020-71107-6. |
| [1] | 杨宇光, 刘冰心, 徐光宝, 姜东焕. 基于时间仓复用的高维量子密钥分发及应用[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(6): 879-892. |
| [2] | 谢四江, 高琼, 冯雁. 基于可信中继量子密钥分发网络的最少公共节点多路径路由方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(7): 35-42. |
| [3] | 冯雁, 刘念, 谢四江. 一种量子密钥池的双向使用方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(12): 40-46. |
| [4] | 刘利娟, 李志慧, 支丹利. 可实现身份认证的多方量子密钥分发协议[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(11): 59-66. |
| [5] | 黄鹏, 曾贵华. 连续变量量子密钥分发实际安全性研究进展[J]. 信息网络安全, 2017, 17(11): 7-12. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||