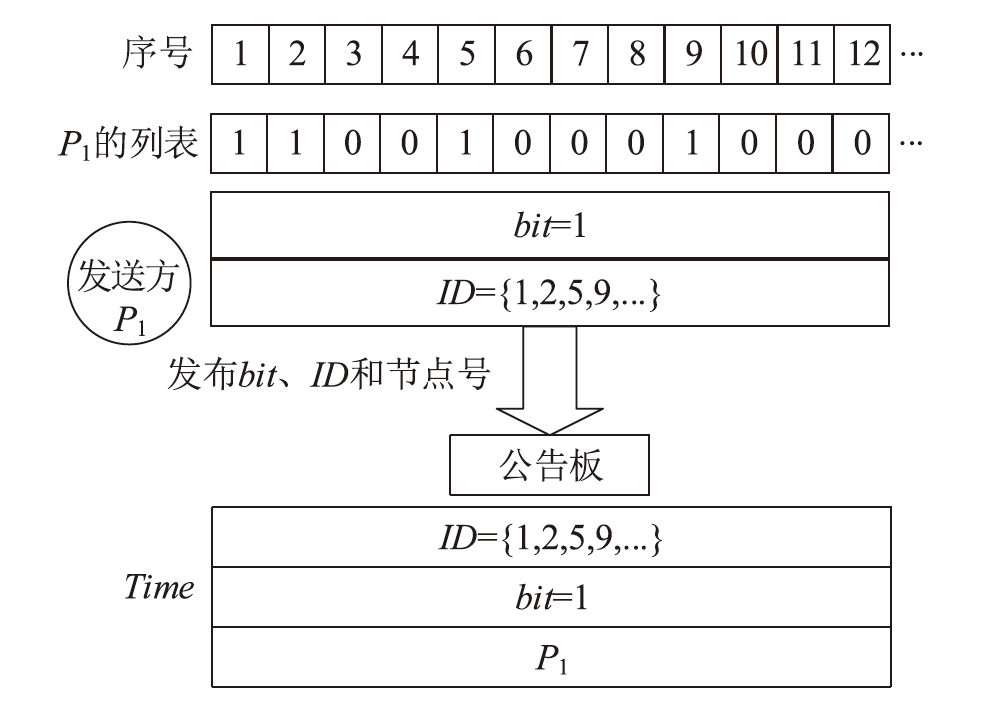
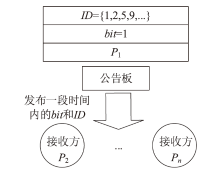
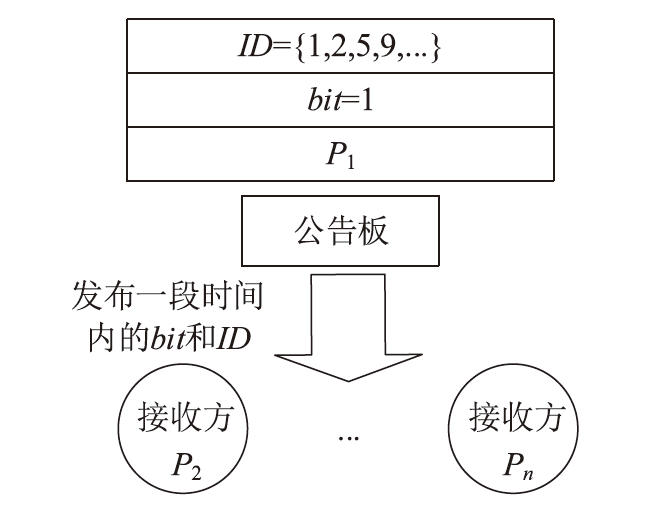
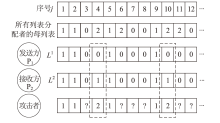
信息网络安全 ›› 2023, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (8): 41-51.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2023.08.004
一种基于QKD的多方拜占庭共识协议
- 1.北京电子科技学院,北京 100070
2.西安电子科技大学计算机科学与技术学院,西安 710071
3.中国科学技术大学,合肥 230026
-
收稿日期:2023-04-24出版日期:2023-08-10发布日期:2023-08-08 -
通讯作者:程安东 E-mail:caddxy@foxmail.com -
作者简介:谢四江(1971—),男,湖北,正高级工程师,硕士,主要研究方向为密码系统、量子保密通信、网络安全体系|程安东(1998—),男,山西,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为量子安全、区块链|公鹏飞(1997—),男,山东,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为区块链共识算法 -
基金资助:广东省重点领域研发计划项目(2020B03030100001);中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金(3282023015)
A QKD-Based Multiparty Byzantine Consensus Agreement
XIE Sijiang1,2,3, CHENG Andong1( ), GONG Pengfei2
), GONG Pengfei2
- 1. Beijing Electronic Science and Technology Institute, Beijing 100070, China
2. School of Computer Science and Technology, Xidian University, Xi’an 710071, China
3. University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
-
Received:2023-04-24Online:2023-08-10Published:2023-08-08 -
Contact:CHENG Andong E-mail:caddxy@foxmail.com
摘要:
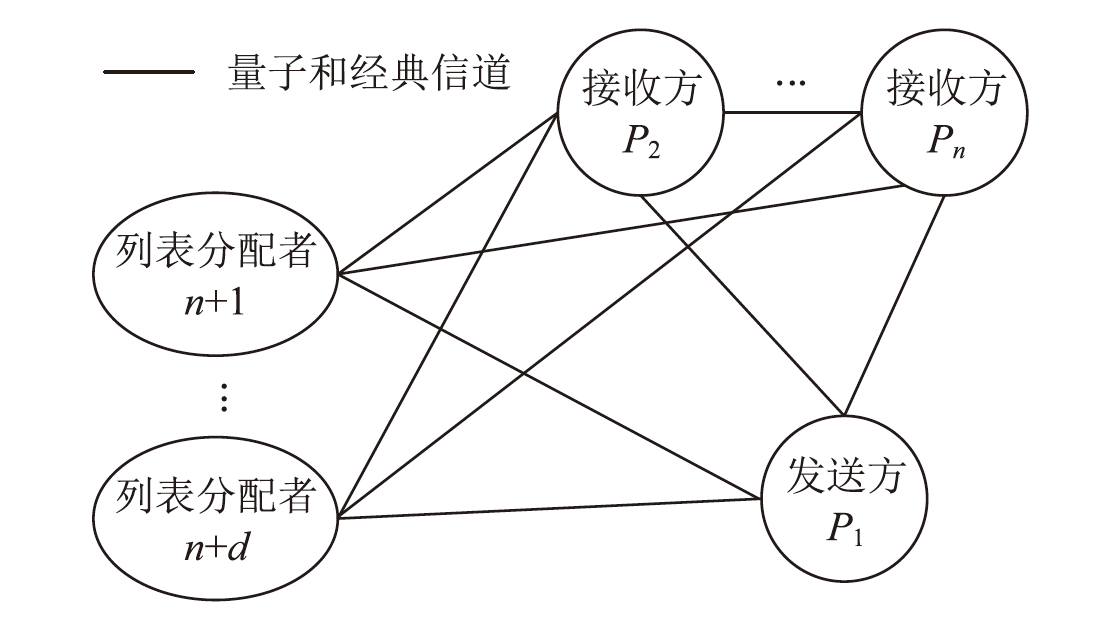
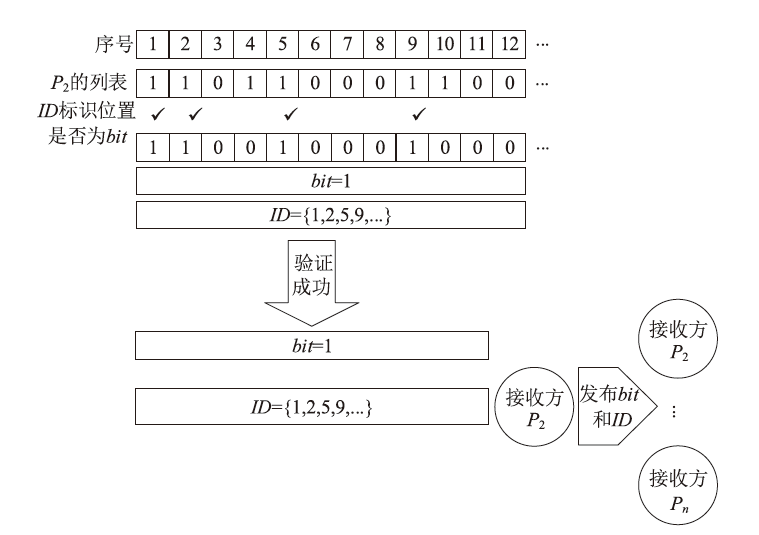
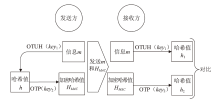
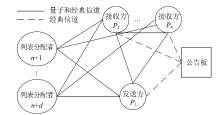
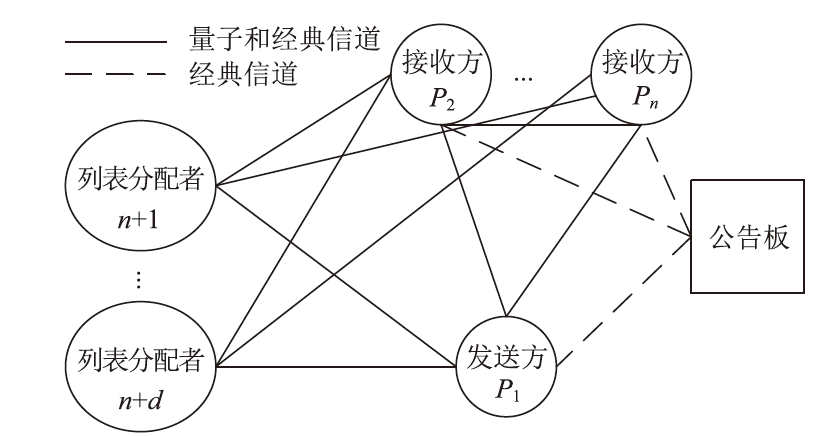
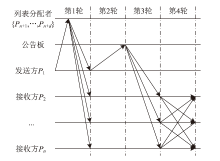
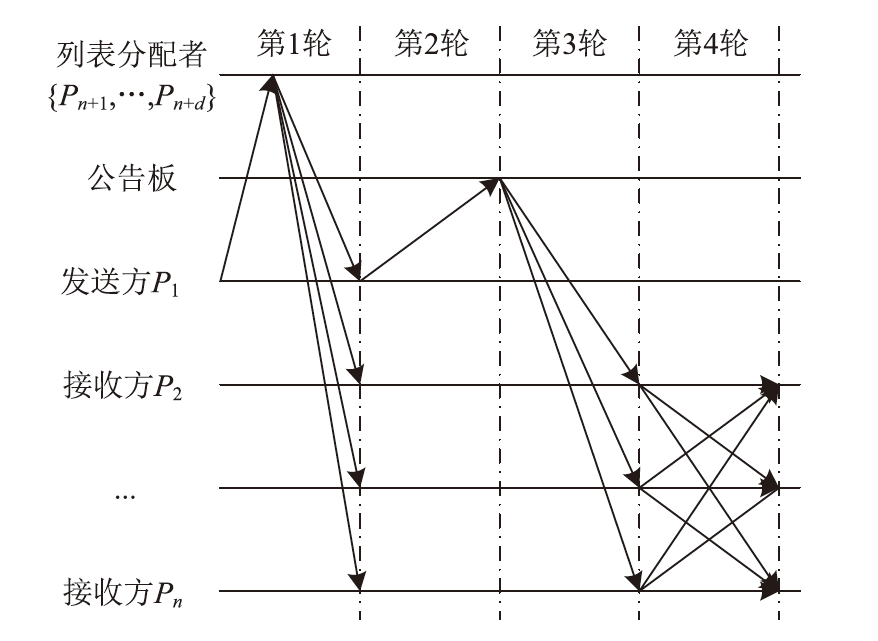
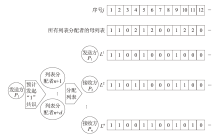
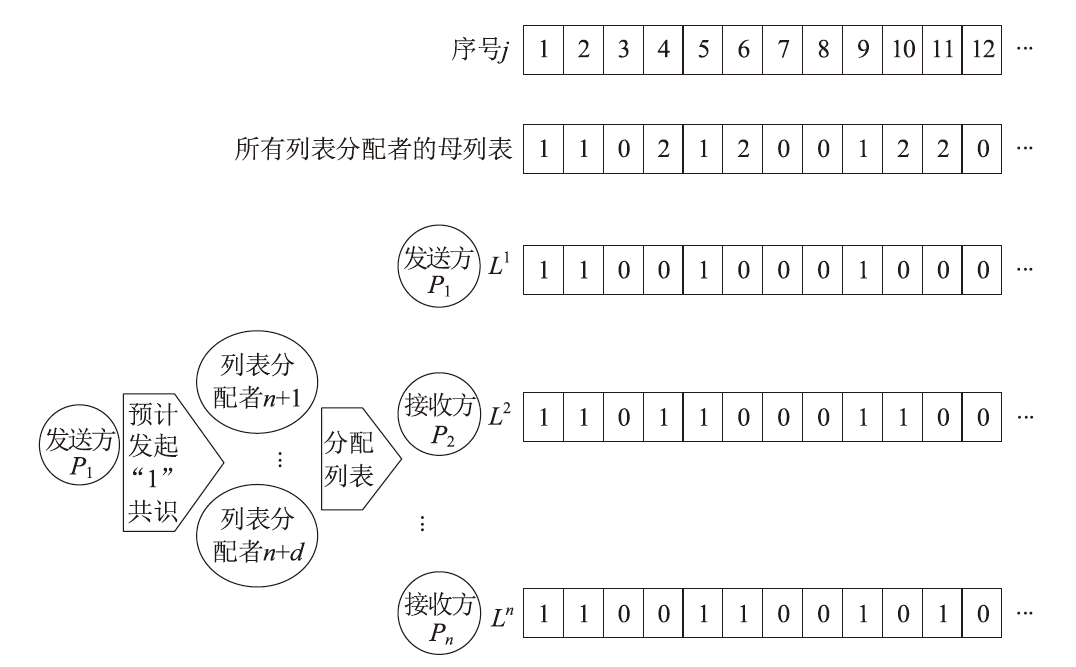
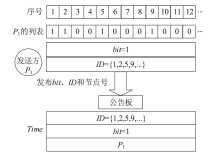
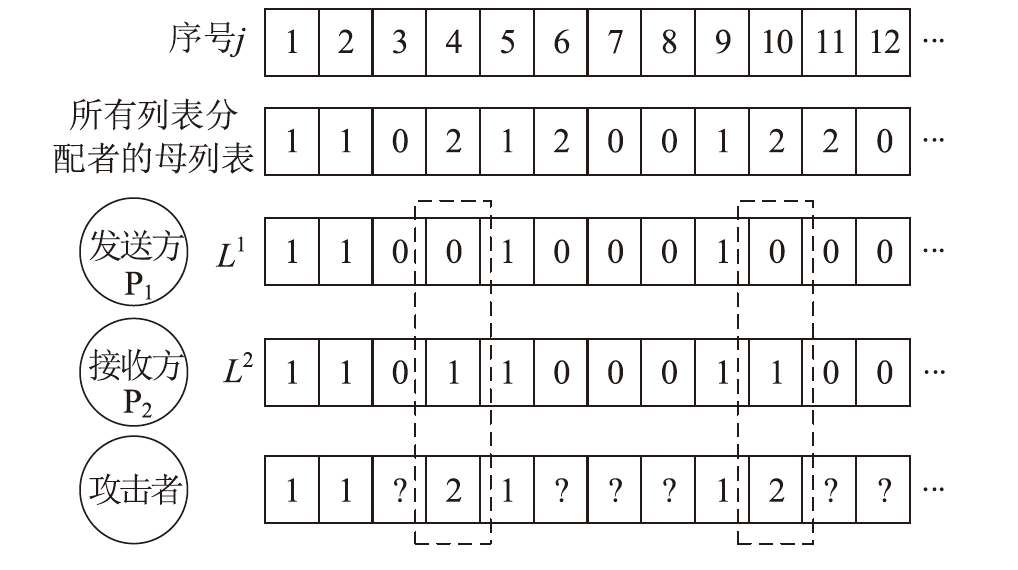
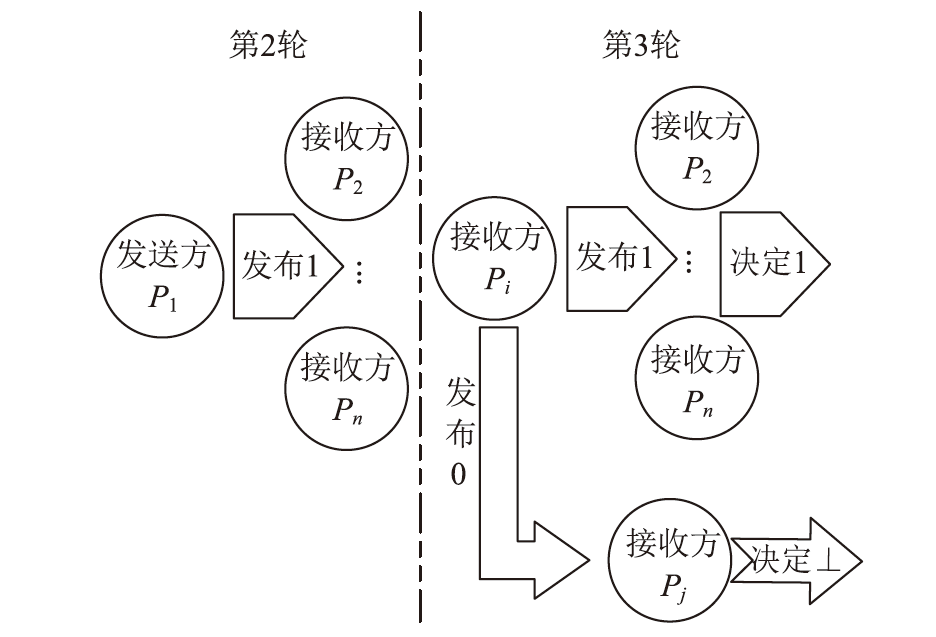
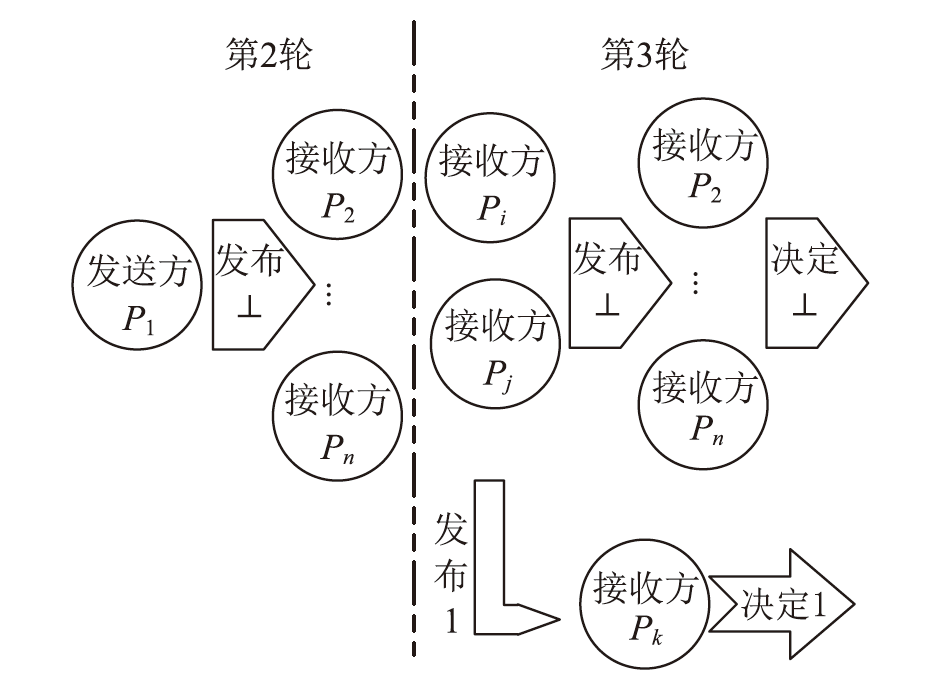
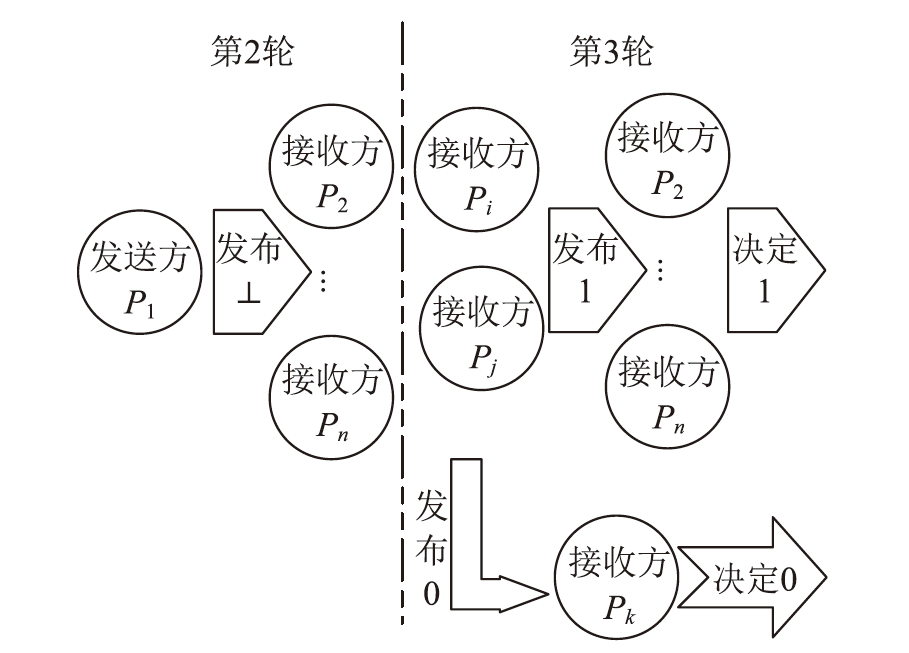
经典拜占庭共识协议使用的数字签名在量子计算的攻击下暴露出了脆弱性。现有的很多量子安全拜占庭共识协议使用量子纠缠等技术,建设成本高,难以普及推广,而使用量子密钥分发(Quantum Key Distribution,QKD)等较为成熟的无纠缠量子技术保障抗量子攻击更具实用性。因此,文章在无纠缠多方量子拜占庭协议基础上,通过加入公告板、改变共识流程和使用无条件安全的MAC等手段,提出一种基于QKD的多方拜占庭共识协议。该协议修复了无纠缠多方量子拜占庭协议的3个安全风险,减少了对QKD生成密钥的使用量,将共识目标由可检测拜占庭共识协议(Detectable Byzantine Agreement,DBA)提升到拜占庭共识协议(Byzantine Agreement,BA),并保持了容忍任意多拜占庭节点的特点,在安全性、可扩展性和运行效率等方面均有提升。
中图分类号:
引用本文
谢四江, 程安东, 公鹏飞. 一种基于QKD的多方拜占庭共识协议[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(8): 41-51.
XIE Sijiang, CHENG Andong, GONG Pengfei. A QKD-Based Multiparty Byzantine Consensus Agreement[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(8): 41-51.
| [1] |
LAMPORT L, SHOSTAK R, PEASE M. The Byzantine Generals Problem[J]. ACM Transactions on Programming Languages and Systems, 1982, 4(3): 382-401.
doi: 10.1145/357172.357176 URL |
| [2] | CASTRO M, LISKOV B. Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance[C]// USENIX. 3rd Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation. Berkeley: USENIX, 1999: 173-186. |
| [3] | NAKAMOTO S. Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System[EB/OL]. (2008-08-21)[2023-04-02]. http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3440802. |
| [4] | YIN Maofang, MALKHI D, REITER M K, et al. HotStuff:BFT Consensus with Linearity and Responsiveness[C]//ACM. PODC’19:ACM Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing. New York: ACM, 2019: 347-356. |
| [5] | CHEN Kaijie, XIONG Yan, HUANG Wenchao, et al. A Formal Analysis Method of PoS Consensus Protocol Based on Byzantine Fault Tolerance[J]. Netinfo Security, 2021, 21(8): 35-42. |
| 陈凯杰, 熊焰, 黄文超, 等. 一种基于拜占庭容错的PoS共识协议形式化分析方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(8):35-42. | |
| [6] | KIKTENKO E O, POZHAR N O, ANUFRIEV M N, et al. Quantum-Secured Blockchain[EB/OL]. (2018-04-10)[2023-04-02]. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/2058-9565/aabc6b/meta. |
| [7] |
PEASE M, SHOSTAK R, LAMPORT L. Reaching Agreement in the Presence of Faults[J]. Journal of the ACM, 1980, 27(2): 228-234.
doi: 10.1145/322186.322188 URL |
| [8] | FITZI M, GISIN N, MAURER U. Quantum Solution to the Byzantine Agreement Problem[EB/OL]. (2001-11-01)[2023-04-02]. https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevLett.87.217901. |
| [9] |
FENG Ronghua, SHI Ronghua, ZHOU Jian, et al. Quantum Byzantine Agreement with Tripartite Entangled States[J]. International Journal of Theoretical Physics, 2019, 58: 1482-1498.
doi: 10.1007/s10773-019-04035-5 |
| [10] | IBLISDIR S, GISIN N. Byzantine Agreement with Two Quantum-Key-Distribution Setups[EB/OL]. (2004-09-29)[2023-04-02]. https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevA. |
| [11] |
BENNETT C H. Quantum Cryptography: Public Key Distribution and Coin Tossing[J]. Theoretical Computer Science, 2014, 560(1): 7-11.
doi: 10.1016/j.tcs.2014.05.025 URL |
| [12] | ZHANG Xue, GAO Fei, QIN Sujuan, et al. Current Status and Future Development of Quantum Cryptographic Protocols[J]. Strategic Study of Chinese Academy of Engineering, 2022, 24(4): 145-155. |
| 张雪, 高飞, 秦素娟, 等. 量子密码协议研究现状与未来发展[J]. 中国工程科学, 2022, 24(4):145-155. | |
| [13] | BOURENNANE M, CABELLO A, ZUKOWSKI M. Quantum Byzantine Agreement with a Single Qutrit[EB/OL]. (2010-01-12)[2023-04-02]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1001.1947. |
| [14] | BEN-OR M, HASSIDIM A. Fast Quantum Byzantine Agreement[C]//ACM. 37th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing. New York: ACM, 2005: 481-485. |
| [15] | TAVAKOLI A, CABELLO A, ŻUKOWSKI M, et al. Quantum Clock Synchronization with a Single Qudit[EB/OL]. (2015-01-23)[2023-04-02]. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep07982. |
| [16] |
LUO Qingbin, FENG Kaiyuan, ZHENG Minghui. Quantum Multi-Valued Byzantine Agreement Based on D-Dimensional Entangled States[J]. International Journal of Theoretical Physics, 2019, 58(12): 4025-4032.
doi: 10.1007/s10773-019-04269-3 |
| [17] |
XUE Lide, CHEN Bingren, YANG Wei, et al. Practical Quantum Byzantine Protocol via Nearly Optimal Entanglement Resources[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2019, 18: 1-13.
doi: 10.1007/s11128-018-2112-6 |
| [18] | CHOLVI V. Detectable Quantum Byzantine Agreement for Any Arbitrary Number of Dishonest Parties[EB/OL]. (2021-12-17)[2023-04-02]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2112.09437. |
| [19] | SUN Xin, KULICKI P, SOPEK M. Multi-Party Quantum Byzantine Agreement without Entanglement[EB/OL]. (2020-09-04)[2023-04-02]. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22101152. |
| [20] | FITZI M, GOTTESMAN D, HIRT M, et al. Detectable Byzantine Agreement Secure against Faulty Majorities[C]//ACM. Twenty-First Annual ACM Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing(PODC 2002). New York: ACM, 2002: 118-126. |
| [21] |
AMIRI R, ANDERSSON E. Unconditionally Secure Quantum Signatures[J]. Entropy, 2015, 17(8): 5635-5659.
doi: 10.3390/e17085635 URL |
| [22] | AMIRI R, ABIDIN A, WALLDEN P, et al. Efficient Unconditionally Secure Signatures Using Universal Hashing[C]//Springer. Applied Cryptography and Network Security:16th International Conference. Heidelberg: Springer, 2018: 143-162. |
| [23] | XUE Lide. Research of Blockchain Consensus Algorithm and Its Application[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2021. |
| 薛立德. 区块链共识算法及其应用研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2021. | |
| [24] | CHAUM D, ROIJAKKERS S. Unconditionally-Secure Digital Signatures[C]//Springer. Advances in Cryptology-CRYPTO’90. Heidelberg: Springer, 1991: 206-214. |
| [25] | LI Binghong, XIE Yuanmei, CAO Xiaoyu, et al. One-Time Universal Hashing Quantum Digital Signatures without Perfect Keys[EB/OL]. [2023-04-02]. http://export.arxiv.org/abs/2301.01132. |
| [26] | KIKTENKO E O, ZELENETSKY A S, FEDOROV A K. Practical Quantum Multiparty Signatures Using Quantum-Key-Distribution Networks[EB/OL]. (2022-01-04)[2023-04-02]. https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevA.105.012408. |
| [27] |
REN Chang, ZHAO Hong, JIANG Hua. Quantum Secured-Byzantine Fault Tolerance Blockchain Consensus Mechanism[J]. Computer Science, 2022, 49(5): 333-340.
doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.210400154 |
|
任畅, 赵洪, 蒋华. 一种量子安全拜占庭容错共识机制[J]. 计算机科学, 2022, 49(5):333-340.
doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.210400154 |
|
| [28] | WALLDEN P, DUNJKO V, KENT A, et al. Quantum Digital Signatures with Quantum-Key-Distribution Components[EB/OL]. (2015-04-07)[2023-04-02]. https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevA.91.042304. |
| [29] | CARTER J L, WEGMAN M N. Universal Classes of Hash Functions[C]//ACM. 9th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing. New York: ACM, 1977: 106-112. |
| [30] | YIN Hualei, FU Yao, LI Chenlong, et al. Experimental Quantum Secure Network with Digital Signatures and Encryption[EB/OL]. (2022-10-22)[2023-04-02]. https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwac228. |
| [31] | QIN Huawang, XU Hao, TANG W K S. Public-Key Quantum Signature Based on Phase Shift Operation[EB/OL]. (2020-01-31)[2023-04-02]. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217984920500840. |
| [32] | GISIN N, RIBORDY G, TITTEL W, et al. Quantum Cryptography[EB/OL]. (2020-03-08)[2023-04-02]. https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.74.145. |
| [33] | GYONGYOSI L, IMRE S, NGUYEN H V. A Survey on Quantum Channel Capacities[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 20(2): 1149-1205. |
| [1] | 石润华, 梁风雨, 王晴, 张顺. 一种有效的量子密封投标拍卖协议[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(8): 44-50. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||