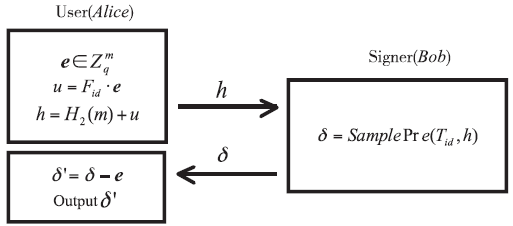
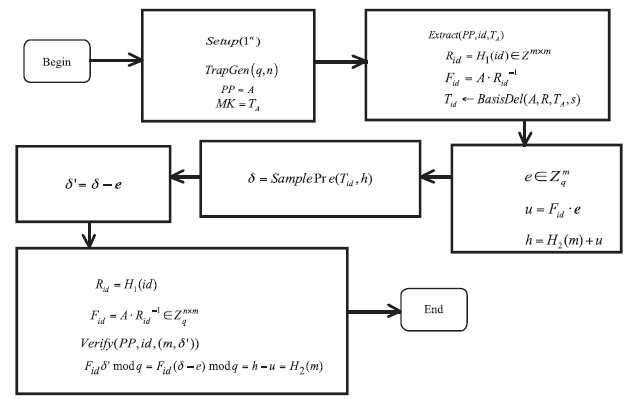
| [1] |
DIFFIE W, HELLMAN M.New Directions in Cryptography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1976, 22(6):644-654.
|
| [2] |
SHOR P W. Polynomial-Time Algorithms for Prime Factorization and Discrete Logarithms on a Quantum Computer[EB/OL]. ,2017-6-15.
|
| [3] |
张焕国, 韩文报, 来学嘉,等. 网络空间安全综述[J]. 中国科学:信息科学, 2016, 46(2):125-164.
|
| [4] |
BENJAMIN P G, MCLAREN M, GOYAL S K, et al.Quantum Computation with Classical Light: Implementation of the Deutsch-Jozsa Algorithm[J]. Physics Letters A, 2016, 380:1925-1931.
|
| [5] |
BERNSTEIN D J, BUCHMANN J, DAHMEN E.Post-quantum Cryptography[J]. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2008, 6061:729-748.
|
| [6] |
CHAUM D.Blind Signatures for Untraceable Payments[C]//Springer. Advances in Cryptology: Proceedings of CRYPTO '82, August 23-25, 1982.Santa Barbara, California, USA.Berlin: Springer-Verlag,1983: 199-203.
|
| [7] |
LI F, ZHANG M, TAKAGI T.Identity-based Partially Blind Signature in the Standard Model for Electronic Cash[J]. Mathematical & Computer Modelling, 2013, 58:196-203.
|
| [8] |
López-García L, Perez L J D, Rodríguez-Henríquez F. A Pairing-Based Blind Signature E-Voting Scheme[J]. Computer Journal, 2014, 57(10):1460-1471.
|
| [9] |
张利利, 马艳琴, 卜春霞,等. 一种安全高效的匿名电子选举方案[J]. 数学的实践与认识, 2015, 45(11):156-160.
|
| [10] |
CHANG C C, CHENG T F.A Provably Secure t-out-of-n Oblivious Transfer Mechanism Based on Blind Signature[J]. Journal of Information Hiding & Multimedia Signal Processing, 2014, 5(1):1-12.
|
| [11] |
WU L C, YEH Y S, FAN C I.Fail-stop Blind Signature Scheme Based on the Integer Factorization[J]. Journal of Discrete Mathematical Sciences & Cryptography, 2004, 7(3):281-290.
|
| [12] |
MALA H, NEZHADANSARI N.New Blind Signature Schemes Based on the (elliptic curve) Discrete Logarithm Problem[C]//IEEE. International Conference on Computer and Knowledge Engineering, October 31- November 1, 2013, Mashhad, Iran.New York:IEEE, 2013:196-201.
|
| [13] |
CHAKRABORTY K, MEHTA J.A Stamped Blind Signature Scheme Based on Elliptic Curve Discrete Logarithm Problem[J]. International Journal of Network Security, 2012, 14(6):316-319.
|
| [14] |
HUANG Z, CHEN K, WANG Y.Efficient Identity-Based Signatures and Blind Signatures.[C]//Springer. Cryptology and network security: 4th International Conference,CANS 2005, December 14-16, 2005, Xiamen, China,Heidelberg:Springer, 2005:120-133.
|
| [15] |
崔巍, 辛阳, 胡程瑜,等. 高效的基于身份的(受限)部分盲签名[J]. 北京邮电大学学报, 2008, 31(4):53-57.
|
| [16] |
张晓敏. 一种新的基于身份的盲签名[J].信息网络安全. 2012(2):55-57.
|
| [17] |
MAYKVS R. Lattice-based Blind Signatures[ EB/OL]. .
|
| [18] |
王凤和,胡予濮,王春晓.基于格的盲签名方案[J].武汉大学学报(信息科学版).2010.5(35):550-553.
|
| [19] |
SHAMIR A.Identity-Based Cryptosystems and Signature Schemes[C]// Springer. The Workshop on the Theory and Application of Cryptographic Techniques. April 1984, Paris, France.Heidelberg:Springer, 1984:47-53.
|
| [20] |
AJTAI M.Generating Hard Instances of Lattice Problems[C]//ACM.Proceedings of the Twenty-eighth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing. 22-24 May 1996,Philadelphia. New York:ACM, 1996:99-108.
|
| [21] |
BOYEN X. Lattice Mixing and Vanishing Trapdoors: A Framework for Fully Secure Short Signatures and More[EB/OL]. .
|
| [22] |
MICCIANCIO D, REGEV O.Worst-case to Average-case Reductions Based on Gaussian Measures[J].SIAM Journal on Computing,2007,37(1):267-302.
|
| [23] |
AGRAWAL S, DAN B, BOYEN X.Lattice Basis Delegation in Fixed Dimension and Shorter-Ciphertext Hierarchical IBE[C]//Springer.Advances in Cryptology - CRYPTO 2010, Cryptology Conference, August 15-19, 2010,Santa Barbara, Ca, USA.Heidelberg:Springer, 2010:98-115.
|
| [24] |
CHA J C, CHEON J H.An Identity-Based Signature from Gap Diffie-Hellman Groups[C]//Springer.International Workshop on Theory and Practice in Public Key Cryptography: Public Key Cryptography.January 6-8, 2003,London, UK.Heidelberg:Springer, 2003:18-30.
|
 ), Chunxiang GU2,3, Mingjun SHANG4
), Chunxiang GU2,3, Mingjun SHANG4