信息网络安全 ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (5): 713-721.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.05.004
基于运行参数增强API序列的勒索软件动态检测方法研究
- 南京理工大学计算机科学与工程学院,南京 210094
-
收稿日期:2024-12-30出版日期:2025-05-10发布日期:2025-06-10 -
通讯作者:魏松杰swei@njust.edu.cn -
作者简介:魏松杰(1977—),男,天津,副教授,博士,CCF高级会员,主要研究方向为网络与信息安全、移动恶意检测、软件定义网络和安全风险评估|吴琴琴(1999—),女,贵州,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为软件行为分析、恶意代码检测|袁军翼(1999—),男,江苏,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为恶意软件检测与网络安全 -
基金资助:工业和信息化部2020年工业互联网创新发展工程项目(TC200H01V)
Dynamic Detection of Ransomware Based on Enhanced API Sequences with Running Parameters
WEI Songjie( ), WU Qinqin, YUAN Junyi
), WU Qinqin, YUAN Junyi
- School of Computer Science & Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China
-
Received:2024-12-30Online:2025-05-10Published:2025-06-10
摘要:
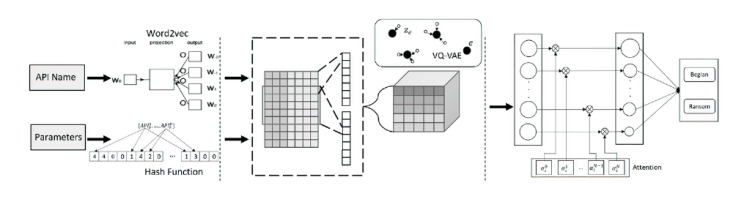
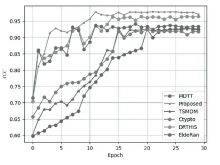
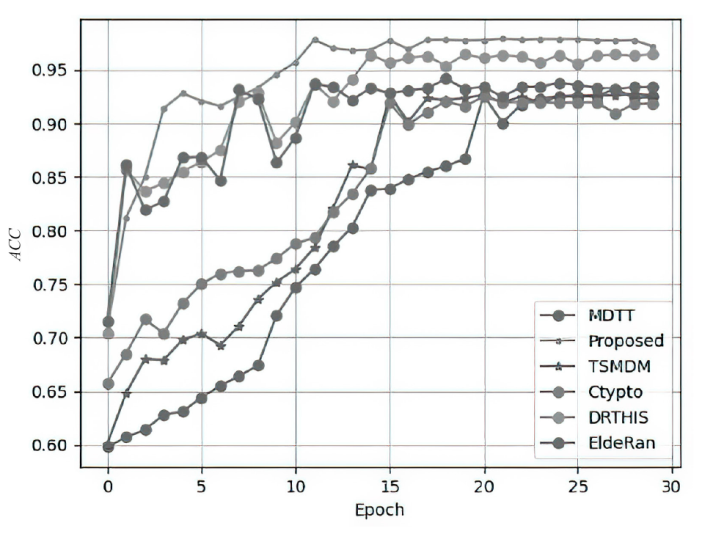
基于软件运行时API调用序列的勒索软件检测技术已被广泛验证有效。但现有方法大多未充分考量API调用运行时参数对行为分析的影响,导致模型泛化能力受限。文章融合API调用对象与参数配置的双重视角,提出无监督与有监督结合的检测框架。首先,采用特征哈希技术将离散的API调用参数映射至有限可控的特征空间;然后,通过无监督预训练从海量无标签参数序列中学习丰富、复杂的语义关系;最后,利用带标签样本进行监督微调以提升检测精度。实验表明,该方法在真实数据集测试中取得0.978的准确率,检测性能显著优于同类方案。
中图分类号:
引用本文
魏松杰, 吴琴琴, 袁军翼. 基于运行参数增强API序列的勒索软件动态检测方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(5): 713-721.
WEI Songjie, WU Qinqin, YUAN Junyi. Dynamic Detection of Ransomware Based on Enhanced API Sequences with Running Parameters[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(5): 713-721.
表1
实验样本数量
| 正常样本 | 数量 /个 | 勒索家族 | 数量/个 | 勒索家族 | 数量/个 | 勒索家族 | 数量 /个 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 办公应 用程序 | 16 | Eleta | 2 | Spora | 4 | Troldesh | 1 |
| 通讯软件 | 2 | Dharma | 5 | Cerber | 4 | Prolock | 2 |
| 多媒体 播放器 | 5 | Wlu | 2 | FRS | 3 | Alphacrypt | 4 |
| 网络浏 览器 | 2 | CryptoWire | 2 | Gandcrab | 6 | Maze | 3 |
| 输入法 | 3 | CryptoShield | 2 | SATURN | 2 | Mzrevenge | 4 |
| 下载软件 | 4 | SAGE | 2 | Santa | 5 | Lockbit | 2 |
| 其他应用 | 6 | Wannacry | 4 | Teslactypt | 6 | Crysis | 8 |
| [1] | AUSTRALIAN C S C. ACSC Annual Cyber Threat Report[EB/OL]. (2020-09-20)[2024-10-25]. https://www.cyber.gov.au. |
| [2] | SOPHOS. The State of Ransomware 2020[EB/OL]. (2020-11-14)[2024-10-25]. https://www.sophos.com/en-us/medialibrary/Gated-Assets/whitepapers/sophos-the-state-of-ransomware-2020-wp.pdf. |
| [3] | HASSAN N. Ransomware Revealed[M]. Berkeley: Berkeley Apress, 2019. |
| [4] |
CHEN Changqing, GUO Chun, CUI Yunhe, et al. Ransomware Early Detection Method Based on Short API Sequence[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2021, 49(3): 586-595.
doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20200623 |
|
陈长青, 郭春, 崔允贺, 等. 基于API短序列的勒索软件早期检测方法[J]. 电子学报, 2021, 49(3): 586-595.
doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20200623 |
|
| [5] | HAMPTON N, BAIG Z, ZEADALLY S. Ransomware Behavioural Aanalysis on Windows Platforms[J]. Journal of Information Security and Applications, 2018, 40: 44-51. |
| [6] | DAVIDIAN M, KIPERBERG M, VANETIK N. Early Ransomware Detection with Deep Learning Models[J]. Future Internet, 2024, 16(8): 291-296. |
| [7] | ZHANG Shuqin, DU Tianhui, SHI Peiyu, et al. Early Detection and Defense Countermeasure Inference of Ransomware Based on API Sequence[J]. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 2023, 14(10): 632-641. |
| [8] | DING Zhenquan, XU Hui, GUO Yonghe, et al. Mal-Bert-GCN: Malware Detection by Combining Bert and GCN[C]// IEEE. 2022 IEEE International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications (TrustCom). New York: IEEE, 2022: 175-183. |
| [9] | ALRIMY B A S, MAAROF M A, SHAID S Z M. Ransomware Threat Success Factors, Taxonomy, and Countermeasures: A Survey and Research Directions[J]. Computers & Security, 2018, 74: 144-166. |
| [10] | LI Hao, QIAN Liping. Overview of Research on Malicious Code Visualization Detection Technology[J]. Software Guide, 2022, 21(5): 9-16. |
| 李豪, 钱丽萍. 恶意代码可视化检测技术研究综述[J]. 软件导刊, 2022, 21(5): 9-16. | |
| [11] | AHMED M E, KIM H, CAMTEPE S, et al. Peeler: Profiling Kernel-Level Events to Detect Ransomware[C]]// Springer. 26th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security. Heidelberg: Springer, 2021: 240-260. |
| [12] | DAS S, LIU Yang, ZHANG Wei, et al. Semantics-Based Online Malware Detection: Towards Efficient Real-Time Protection against Malware[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2015, 11(2): 289-302. |
| [13] | GUO Chun, CHEN Changqing, SHEN Guowei, et al. A Ransomware Classification Method Based on Visualization[J]. Netinfo Security, 2020, 20(4): 31-39. |
| 郭春, 陈长青, 申国伟, 等. 一种基于可视化的勒索软件分类方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(4): 31-39. | |
| [14] | SHARMA S, SINGH S. Texture-Based Automated Classification of Ransomware[J]. Journal of The Institution of Engineers, 2021, 102(1): 131-142. |
| [15] | SUBEDIU K P, BUDHATHOKI D R, DASGUPTA D. Forensic Analysis of Ransomware Families Using Static and Dynamic Analysis[C]// IEEE. 2018 IEEE Security and Privacy Workshops (SPW). New York: IEEE, 2018: 180-185. |
| [16] | ZAVARSKY P, LINDSKOG D. Experimental Analysis of Ransomware on Windows and Android Platforms: Evolution and Characterization[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2016, 94: 465-472. |
| [17] | KHARRAZ A, ARSHAD S, MULLINER C, et al. Unveil:A Large-Scale, Automated Approach to Detecting Ransomware[C]// USENIX. 25th USENIX Security Symposium. Berkeley: USENIX, 2016:757-772. |
| [18] | VINAYAKUMAR R, SOMAN K P, VELAN K K S, et al. Evaluating Shallow and Deep Networks for Ransomware Detection and Classification[C]// IEEE. 2017 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI). New York: IEEE, 2017: 259-265. |
| [19] | FENG Yun, LIUChaoge, LIUBaoxu. Poster: A New Approach to Detecting Ransomware with Deception[C]// IEEE. The 38th IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. New York: IEEE, 2017: 7-8. |
| [20] | KOK S H, ABDULLAH A, JHANJHI N Z, et al. Prevention of Crypto-Ransomware Using a Pre-Encryption Detection Algorithm[J]. Computers, 2019, 8(4): 79-84. |
| [21] | ALJABRI M, ALHAIDARI F, ALBUAINAIN A, et al. Ransomware Detection Based on Machine Learning Using Memory Features[J]. Egyptian Informatics Journal, 2024, 25: 445-451. |
| [22] | WEN J C C, VIMAL K, PANOS P, et al. Real-Time System Call-Based Ransomware Detection[J]. International Journal of Information Security, 2024, 23(3): 1839-1858. |
| [23] | ULLAH F, JAVAID Q, SALAM A, et al. Modified Decision Tree Technique for Ransomware Detection at Runtime Through API Calls[J]. Scientific Programming, 2020(1): 833-844. |
| [24] | HWANG J, KIM J, LEE S, et al. Two-Stage Ransomware Detection Using Dynamic Analysis and Machine Learning Techniques[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2020, 112(4): 2597-2609. |
| [25] | SHEEN S, YADAV A. Ransomware Detection by Mining API Call Usage[C]// IEEE. 2018 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics(ICACCI). New York: IEEE, 2018: 983-987. |
| [26] | SGANDURRA D, MUNOZ-GONZALEZ L, MOHSEN R, et al. Automated Dynamic Analysis of Ransomware: Benefits, Limitations and Use for Detection[EB/OL]. (2016-10-26)[2024-10-25]. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/76d36dc27072b39bf42c6b7e4a954ca1afc7e373. |
| [27] | HOMAYOUN S, DEHGHANTANHA A, AHMADZADEH M, et al. DRTHIS: Deep Ransomware Threat Hunting and Intelligence System at the Fog Layer[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2019, 90: 94-104. |
| [1] | 徐茹枝, 张凝, 李敏, 李梓轩. 针对恶意软件的高鲁棒性检测模型研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1184-1195. |
| [2] | 文伟平, 张世琛, 王晗, 时林. 基于虚拟机自省的Linux恶意软件检测方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(5): 657-666. |
| [3] | 胡文涛, 徐靖凯, 丁伟杰. 基于溯因学习的无监督网络流量异常检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(11): 1675-1684. |
| [4] | 朱怡昕, 苗张旺, 甘静鸿, 马存庆. 基于细粒度访问控制的勒索软件防御系统设计[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(10): 31-38. |
| [5] | 王宇, 吕良双, 夏春和. 基于语义分析的Windows恶意软件检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(10): 58-63. |
| [6] | 徐国天, 刘猛猛. 基于改进哈里斯鹰算法同步优化特征选择的恶意软件检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(12): 9-18. |
| [7] | 郭春, 陈长青, 申国伟, 蒋朝惠. 一种基于可视化的勒索软件分类方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(4): 31-39. |
| [8] | 吕宗平, 赵春迪, 顾兆军, 周景贤. 基于Stacking模型融合的勒索软件动态检测算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(2): 57-57. |
| [9] | 徐国天, 沈耀童. 基于XGBoost和LightGBM双层模型的恶意软件检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(12): 54-63. |
| [10] | 谭杨, 刘嘉勇, 张磊. 基于混合特征的深度自编码器的恶意软件家族分类[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(12): 72-82. |
| [11] | 宋鑫, 赵楷, 张琳琳, 方文波. 基于随机森林的Android恶意软件检测方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(9): 1-5. |
| [12] | 殷明, 贾世杰. 一种局域网中基于SSD的防范勒索软件攻击技术[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(9): 71-75. |
| [13] | 张健, 陈博翰, 宫良一, 顾兆军. 基于图像分析的恶意软件检测技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(10): 24-31. |
| [14] | 黄世锋, 郭亚军, 崔建群, 曾庆江. 基于优化模糊C均值的手机恶意软件检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2016, 16(1): 45-50. |
| [15] | 树雅倩, 付安民, 黄振涛. 基于云平台的移动支付类恶意软件检测系统的设计与实现[J]. 信息网络安全, 2016, 16(1): 59-63. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||