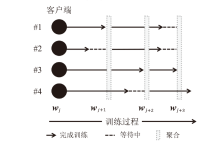
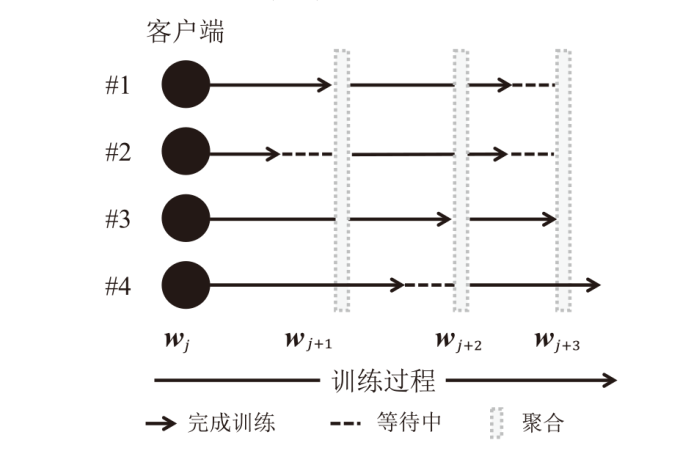
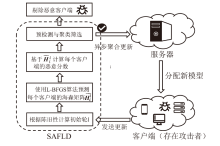
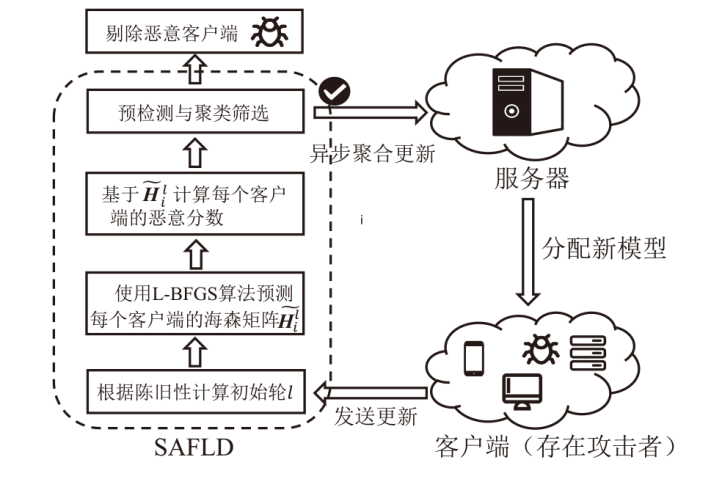
| [1] |
MCMAHAN H B, MOORE E, RAMAGE D, et al. Communication-Efficient Learning of Deep Networks from Decentralized Data[C]// PMLR. Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. New York: PMLR, 2017: 1273-1282.
|
| [2] |
LI Tian, SAHU A K, ZAHEER M, et al. Federated Optimization in Heterogeneous Networks[J]. Proceedings of Machine Learning and Systems, 2020(2): 429-450.
|
| [3] |
XIE Cong, KOYEJO S, GUPTA I. Asynchronous Federated Optimization[EB/OL]. [2024-03-07]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1903.03934.
|
| [4] |
WANG Zhongyu, ZHANG Zhaoyang, WANG Jue. Asynchronous Federated Learning over Wireless Communication Networks[C]// IEEE. ICC 2021-IEEE International Conference on Communications. New York: IEEE, 2021: 1-7.
|
| [5] |
XU Chenhao, QU Youyang, XIANG Yong, et al. Asynchronous Federated Learning on Heterogeneous Devices: A Survey[EB/OL]. (2023-10-04)[2024-03-07]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S157401372300062X?via%3Dihub.
|
| [6] |
MA Qianpiao, JIA Qingmin, LIU Jianchun, et al. Client Grouping and Time-Sharing Scheduling for Asynchronous Federated Learning in Heterogeneous Edge Computing Environment[J]. Journal on Communications, 2023, 44(11): 79-93.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2023196
|
|
马千飘, 贾庆民, 刘建春, 等. 异构边缘计算环境下异步联邦学习的节点分组与分时调度策略[J]. 通信学报, 2023, 44(11): 79-93.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2023196
|
| [7] |
WU Wentai, HE Ligang, LIN Weiwei, et al. SAFA: A Semi-Asynchronous Protocol for Fast Federated Learning with Low Overhead[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2021, 70(5): 655-668.
|
| [8] |
MA Qianpiao, XU Yang, XU Hongli, et al. FedSA: A Semi-Asynchronous Federated Learning Mechanism in Heterogeneous Edge Computing[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2021, 39(12): 3654-3672.
|
| [9] |
ZHOU Zihao, LI Yanan, REN Xuebin, et al. Towards Efficient and Stable K-Asynchronous Federated Learning with Unbounded Stale Gradients on Non-IID Data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2022, 33(12): 3291-3305.
|
| [10] |
WU Shan, ZHOU Yizhi, GAO Xuesong, et al. K Asynchronous Federated Learning with Cosine Similarity Based Aggregation on Non-IID Data[C]// Springer. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Heidelberg: Springer, 2024: 434-452.
|
| [11] |
BAGDASARYAN E, VEIT A, HUA Yiqing, et al. How to Backdoor Federated Learning[C]// PMLR. International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. New York: PMLR, 2020: 2938-2948.
|
| [12] |
BARUCH M, BARUCH G, GOLDBERG Y. A Little is Enough: Circumventing Defenses for Distributed Learning[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2019, 32: 8635-8645.
|
| [13] |
BHAGOJI A, CHAKRABORTY S, MITTAL P, et al. Analyzing Federated Learning through an Adversarial Lens[C]// PMLR. International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: PMLR, 2019: 634-643.
|
| [14] |
GAO Ying, CHEN Xiaofeng, ZHANG Yiyu, et al. A Survey of Attack and Defense Techniques for Federated Learning Systems[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2023, 46(9): 1781-1805.
|
|
高莹, 陈晓峰, 张一余, 等. 联邦学习系统攻击与防御技术研究综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2023, 46(9): 1781-1805.
|
| [15] |
DUAN Xinru, CHEN Guirong, CHEN Aiwang, et al. Review of Research on Information Security in Federated Learning[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2024, 60(3): 61-77.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2303-0332
|
|
段昕汝, 陈桂茸, 陈爱网, 等. 联邦学习中的信息安全问题研究综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2024, 60(3): 61-77.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2303-0332
|
| [16] |
YANG Li, ZHU Lingbo, YU Yueming, et al. Review of Federal Learning and Offensive-Defensive Confrontation[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(12): 69-90.
|
|
杨丽, 朱凌波, 于越明, 等. 联邦学习与攻防对抗综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(12): 69-90.
|
| [17] |
ZHANG Zaixi, CAO Xiaoyu, JIA Jinyuan, et al. FLDetector: Defending Federated Learning Against Model Poisoning Attacks via Detecting Malicious Clients[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2022: 2545-2555.
|
| [18] |
LI Suyi, CHENG Yong, WANG Wei, et al. Learning to Detect Malicious Clients for Robust Federated Learning[EB/OL]. [2024-03-07]. https://www.xueshufan.com/publication/3003426262.
|
| [19] |
LIU D C, NOCEDAL J. On the Limited Memory BFGS Method for Large Scale Optimization[J]. Mathematical Programming, 1989, 45(1): 503-528.
|
| [20] |
KUMAR A, INGLE Y S, PANDE A, et al. Canopy Clustering: A Review on Pre-Clustering Approach to K-Means Clustering[J]. International Journal of Innovations & Advancement in Computer Science, 2014, 3(5): 22-29.
|
| [21] |
MACQUEEN J. Some Methods for Classification and Analysis of Multivariate Observations[J]. Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, 1967, 1(14): 281-297.
|
| [22] |
ZHANG Geng, ZHANG Chengchang, ZHANG Huayu. Improved K-Means Algorithm Based on Density Canopy[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2018, 145: 289-297.
|
| [23] |
CHEN Yang, SUN Xiaoyan, JIN Yaochu. Communication-Efficient Federated Deep Learning with Layerwise Asynchronous Model Update and Temporally Weighted Aggregation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(10): 4229-4238.
|
| [24] |
FANG Minghong, CAO Xiaoyu, JIA Jinyuan, et al. Local Model Poisoning Attacks to Byzantine-Robust Federated Learning[EB/OL]. [2024-03-07]. https://www.xueshufan.com/publication/2990614164.
|
 )
)
 )
)