信息网络安全 ›› 2023, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (2): 96-103.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2023.02.011
基于无监督非负矩阵分解的TAP规则推荐
- 吉林大学计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
-
收稿日期:2022-11-28出版日期:2023-02-10发布日期:2023-02-28 -
通讯作者:王峰 E-mail:wangfeng12@mails.jlu.edu.cn -
作者简介:王明(1998—),男,山西,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为物联网数据挖掘|邢永恒(1996—),男,吉林,博士研究生,主要研究方向为物联网数据挖掘和隐私保护|王峰(1987—),男,吉林,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为计算机系统架构和网络空间安全 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2017YFA0604500);吉林省科技发展计划(20220101115JC);吉林省发改委医疗大数据安全处理平台项目(2019FGWTZC001)
Unsupervised Matrix Factorization Based Trigger Action Programming Rules Recommendation
WANG Ming, XING Yongheng, WANG Feng( )
)
- College of Computer Science and Technology, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China
-
Received:2022-11-28Online:2023-02-10Published:2023-02-28 -
Contact:WANG Feng E-mail:wangfeng12@mails.jlu.edu.cn
摘要:
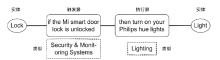
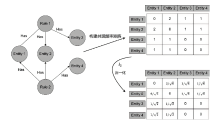
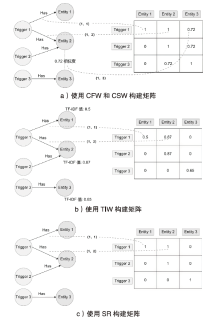
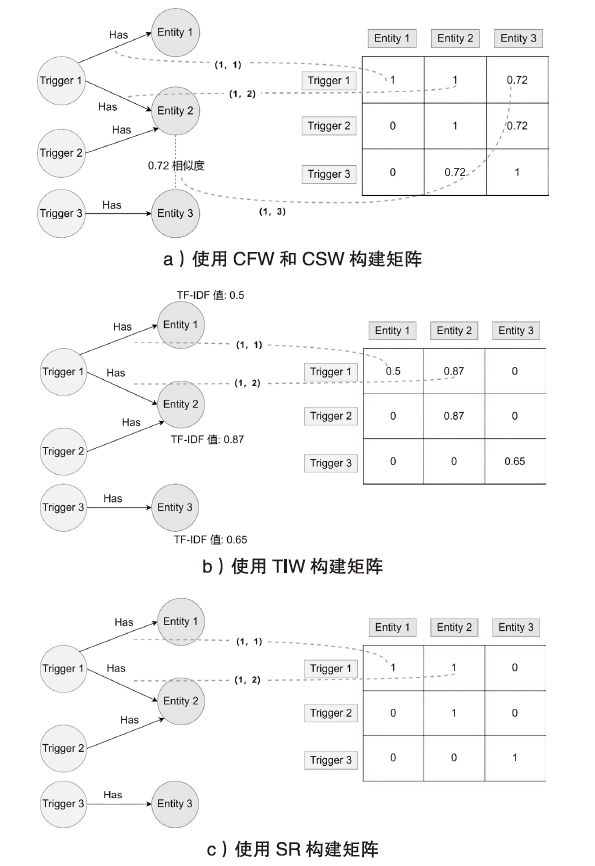
TAP在定制物联网设备联动过程中得到了广泛的应用。TAP数据中除了包含物品之间的条件触发关系外,还包含用户对于相关规则的文本描述信息。如何使用TAP数据的多源异构属性进行数据处理是物联网应用中重要的研究之一。文章将TAP数据建模成含有多种节点和边类型的异质图,实现了多源异构数据之间多类型关系的融合处理,进而根据不同类型节点之间的连接关系生成关系矩阵。文章通过非负矩阵分解(NMF)以无监督方式学习TAP异质图中每个节点的特征向量用于TAP规则推荐。文章提出3种带权的关系矩阵生成方法,分别为共现频率权值(CFW)、概念相似度权值(CSW)和TF-IDF权值(TIW)。实验结果表明,在由CFW生成的矩阵上进行NMF,由此获得的特征向量在TAP规则推荐时表现良好。
中图分类号:
引用本文
王明, 邢永恒, 王峰. 基于无监督非负矩阵分解的TAP规则推荐[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(2): 96-103.
WANG Ming, XING Yongheng, WANG Feng. Unsupervised Matrix Factorization Based Trigger Action Programming Rules Recommendation[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(2): 96-103.
表1
top-k推荐准确度
| 权重矩阵 | Precision@1 | Precision@3 | Precision@5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SR_128 | 0.6474 | 0.5507 | 0.4955 |
| CFW_128 | 0.6783 | 0.5697 | 0.5100 |
| CSW_128 | 0.6463 | 0.5417 | 0.4851 |
| TIW_128 | 0.3066 | 0.2630 | 0.2399 |
| SR_256 | 0.6673 | 0.5451 | 0.4809 |
| CFW_256 | 0.6853 | 0.5837 | 0.5134 |
| CSW_256 | 0.6763 | 0.5607 | 0.5042 |
| TIW_256 | 0.3256 | 0.2700 | 0.2417 |
| SR_512 | 0.6643 | 0.5514 | 0.4899 |
| CFW_512 | 0.6913 | 0.5907 | 0.5248 |
| CSW_512 | 0.6713 | 0.5594 | 0.4931 |
| TIW_512 | 0.3896 | 0.3276 | 0.2923 |
| [1] | ASHTON K. That ‘Internet of Things’ Thing[J]. RFID Journal, 2009, 22(7): 97-114. |
| [2] | UR B, MCMANUS E, PAK Y H M, et al. Practical Trigger-Action Programming in the Smart Home[C]// ACM. SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. New York: ACM, 2014: 803-812. |
| [3] | SONG Yu. Representation Learning for Heterogeneous Edge Networks Based on Multi-Stage Non-Negative Matrix Factorization[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2021. |
| 宋宇. 基于多阶段非负矩阵分解的异质边网络表示学习研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2021. | |
| [4] |
LEENDERS J. Modeling Social Influence Through Network Autocorrelation: Constructing the Weight Matrix[J]. Social Networks, 2002, 24(1): 21-47.
doi: 10.1016/S0378-8733(01)00049-1 URL |
| [5] | SPEER R, CHIN J, HAVASI C. Conceptnet 5.5: An Open Multilingual Graph of General Knowledge[EB/OL]. (2016-12-12)[2022-09-20]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1612.03975.pdf. |
| [6] | MILLER G A. WordNet: An Electronic Lexial Database[M]. Cambridge: MIT Press, 1998. |
| [7] |
ROBERTSON S. Understanding Inverse Document Frequency: on Theoretical Arguments for IDF[J]. Journal of Documentation, 2004, 60(5): 503-520.
doi: 10.1108/00220410410560582 URL |
| [8] | BIAN Han, CHEN Xiaohong, JIN Zhi, et al. A Method of Generating TAP Rules in IoT System Based on Environment Modeling[J]. Journal of Software, 2021, 32(4): 934-952. |
| 边寒, 陈小红, 金芝, 等. 基于环境建模的物联网系统 TAP 规则生成方法[J]. 软件学报, 2021, 32(4): 934-952. | |
| [9] | WANG Bo, ZHANG Yu, GENG Jianing, et al. SSRules: Make Smart Home Automation Rules Easier to Write and Check[J]. Journal of Software, 2021, 32(12): 3728-3750. |
| 王博, 张昱, 耿佳宁, 等. SSRules: 让智能家居自动化规则更易于编写和检查[J]. 软件学报, 2021, 32(12): 3728-3750. | |
| [10] | WANG Chen. Conflict Detection Framework for End-User Rules of Smart IoT Devices Based on SMT[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2022. |
| 汪晨. 基于SMT的智能IoT设备终端用户规则的冲突检测框架[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2022. | |
| [11] | CORNO F, RUSSIS L, ROFFARELLO A M. A Semantic Web Approach to Simplifying Trigger-Action Programming in the IoT[J]. Computer, 2017, 50(11): 18-24. |
| [12] |
CORNO F, RUSSIS L, ROFFARELLO A M. A High-Level Semantic Approach to End-User Development in the Internet of Things[J]. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, 2019, 125: 41-54.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijhcs.2018.12.008 URL |
| [13] | CORNO F, RUSSIS L, MONGE R A. RecRules: Recommending IF-THEN Rules for End-User Development[J]. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology (TIST), 2019, 10(5): 1-27. |
| [14] | CORNO F, RUSSIS L, MONGE R A. Empowering End Users in Debugging Trigger-Action Rules[C]// ACM. 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. New York: ACM, 2019: 1-13. |
| [15] |
HU Liang, WU Gang, XING Yongheng, et al. Semantic Modeling in the Internet of Things with Graph Representation Learning[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 7(3): 1939-1948.
doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2962630 URL |
| [16] |
KLEMA V, LAUB A. The Singular Value Decomposition: Its Computation and some Applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1980, 25(2): 164-176.
doi: 10.1109/TAC.1980.1102314 URL |
| [17] | LEE D, SEUNG H S. Algorithms for Non-Negative Matrix Factorization[EB/OL]. (2001-05-11)[2022-09-22]. http://www.cs.cmu.edu/-11755/lectures/Lee_Seung_NMF.pdf. |
| [18] | SEDGHI H, GUPTA V, LONG P M. The Singular Values of Convolutional Layers[EB/OL]. (2018-05-26)[2022-09-22]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1805.10408.pdf. |
| [19] | KOREN Y, BELL R, VOLINSKY C. Matrix Factorization Techniques for Recommender Systems[J]. Computer, 2009, 42(8): 30-37. |
| [20] | CHEN Chong, ZHANG Min, ZHANG Yongfeng, et al. Efficient Neural Matrix Factorization without Sampling for Recommendation[J]. ACM Transactions on Information Systems (TOIS), 2020, 38(2): 1-28. |
| [21] |
XING Yongheng, HU Liang, ZHANG Xiaolu, et al. Nonnegative Matrix Factorization Based Heterogeneous Graph Embedding Method for Trigger-Action Programming in IoT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 18(2): 1231-1239.
doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3092774 URL |
| [22] |
HU Liang, GONG Yanlei, XING Yongheng, et al. Semantic Representation with Heterogeneous Information Network Using Matrix Factorization for Clustering in the Internet of Things[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 31233-31242.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2903310 |
| [1] | 冯新扬, 沈建京. 一种基于Yarn云计算平台与NMF的大数据聚类算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(8): 43-49. |
| [2] | 张戈琳, 李勇. 非负矩阵分解算法优化及其在入侵检测中的应用[J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(8): 73-78. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||