信息网络安全 ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (12): 1863-1877.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.12.003
主被动协同的路由器别名高效识别方法
- 1.中国海洋大学信息科学与工程学部,青岛 266160
2.中国科学院信息工程研究所,北京 100093
3.北京知道创宇信息技术股份有限公司,北京 100020
-
收稿日期:2025-10-10出版日期:2025-12-10发布日期:2026-01-06 -
通讯作者:胡丹 E-mail:hudan@stu.ouc.edu.cn -
作者简介:胡丹(1990—),女,四川,博士研究生,主要研究方向为网络空间测绘|杨冀龙(1979—),男,四川,硕士,主要研究方向为网络空间测绘、云防御、网络攻防 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2023YFB2705000)
An Efficient Method for Router Alias Identification with Active-Passive Collaboration
- 1. College of Information Science and Engineering, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266160, China
2. Institute of Information Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100093, China
3. Beijing Zhidao Chuangyu Information Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing 100020, China
-
Received:2025-10-10Online:2025-12-10Published:2026-01-06 -
Contact:HU Dan E-mail:hudan@stu.ouc.edu.cn
摘要:
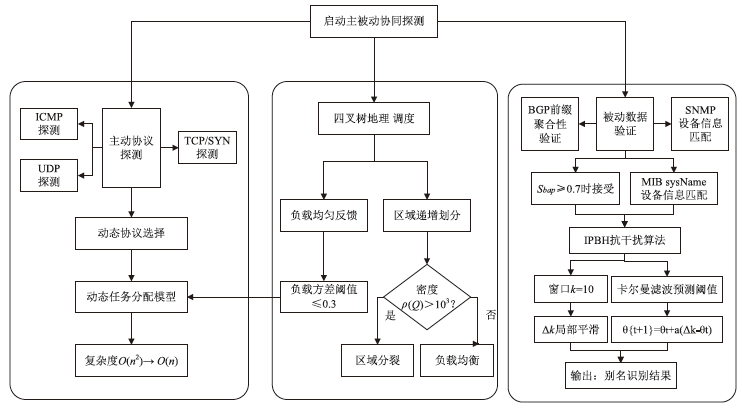
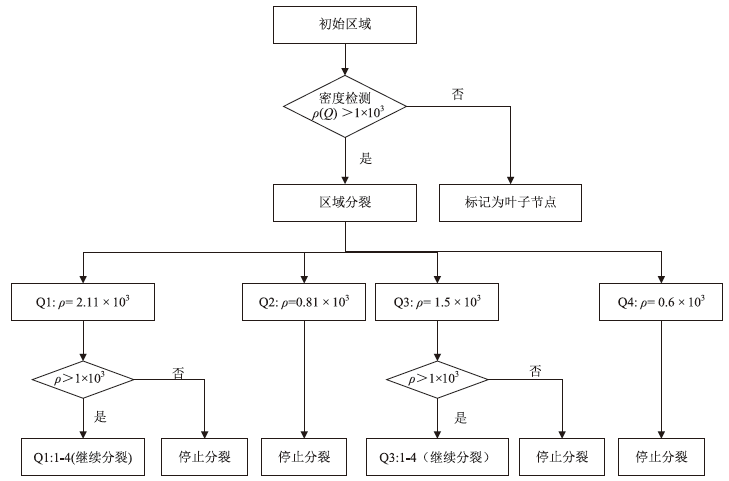
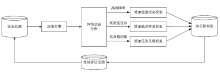
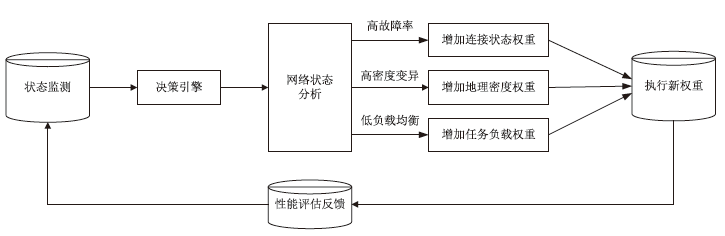
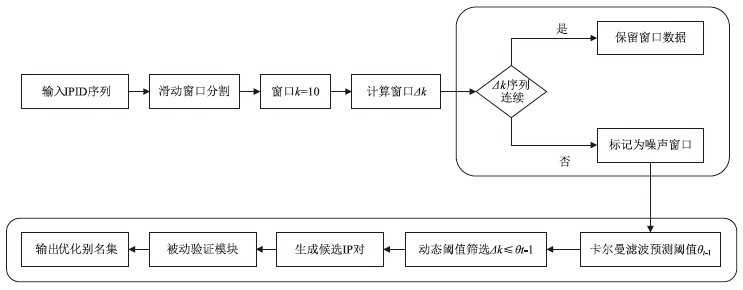
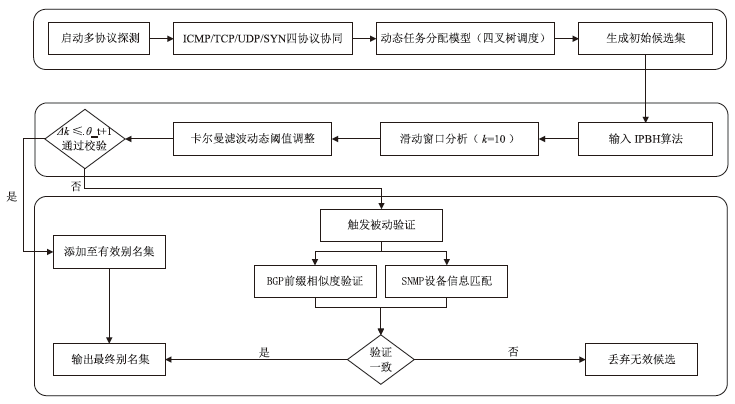
路由器别名识别是准确分析网络拓扑结构的关键技术之一,针对大规模网络中路由器别名识别效率低、抗干扰能力弱的问题,文章提出一种主被动协同的高效路由器别名识别方法。首先,构建融合4类主动探测协议(ICMP/TCP/UDP/SYN)与BGP/SNMP被动监测的协同框架,通过四叉树索引优化地理调度,降低跨区域探测延迟;然后,设计动态任务分配模型,采用负载方差阈值控制实现计算复杂度从O(n2)到O(n)的优化;进而,提出IPBH抗干扰算法,通过滑动窗口机制与动态阈值调整抑制噪声干扰。基于常用的CAIDA2023数据集开展实验,实验结果表明,文章提出的方法相比原有典型路由器别名识别方法MBT在识别效率和抗干扰方面具有明显优势,识别每万台路由器的速度由42.3 s降低至4.1 s;通过滑动窗口局部平滑与卡尔曼滤波动态阈值调整,抑制IP标识随机化噪声与等成本多路径干扰,在25%噪声环境下实现了90.1%的别名识别准确率,相比RadarGun、Hybrid Alias、NoiseShield等方法提高了7%~25%。
中图分类号:
引用本文
胡丹, 杨冀龙. 主被动协同的路由器别名高效识别方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(12): 1863-1877.
HU Dan, YANG Jilong. An Efficient Method for Router Alias Identification with Active-Passive Collaboration[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(12): 1863-1877.
表1
路由器别名识别技术对比分析
| 类型 | 核心原理 | 优势 | 局限性 | 代表方法 | 假阳率 | 复杂度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 主动 探测法 | 发送定制探测包分析IPID/TTL等特征 | 接口覆盖率高(大于85%) | 受ECMP干扰假阳率高 | MBT[ Ally [ | 1.8%~ 3.5% | O(n2) |
| 被动 监测法 | 解析BGP/SNMP日志构建别名关系 | 无需主动流量注入 | 数据碎片化 (覆盖率小于60%) | BGP-Miner[ | — | O(n) |
| 混合 方法 | 融合主被动数据互补验证,动态阈值调整/自适应路径探测 | 抗路径跳变干扰,噪声鲁棒性提升 | 任务调度低(负载方差大于等于0.65),实时性不足(延迟大于等于15ms) | Hybrid Alias[ | 1.20% | O(n2) |
表4
实验环境配置
| 分类 | 具体内容 |
|---|---|
| 硬件平台 | 集群配置:8台Intel Xeon Platinum 8375C服务器(32核/64线程,主频3.6 GHz);内存:512 GB DDR4(ECC校验); 网络:10 Gbps双网卡(RDMA支持); 存储:NVMe SSD阵列(200 TB,IOPS 1M) |
| 软件工具 | 主动探测:Python 3.10 + Scapy 2.4.5(四协议探测包定制); 被动监测:BGPStream 2.0(BGP更新解析)+ Net-SNMP 5.9(SNMPv3加密查询); 数据处理:PostgreSQL 14(拓扑关系存储)+ Redis 6.2(实时任务队列)+ Spark 3.3(分布式计算) |
| 数据集与 基准真值 | 数据集:CAIDA2023公开数据集(120万路由器接口,IPv4占比92%),注入25%均匀分布IPID噪声(模拟Linux RFC7739); 基准真值:RIPE Atlas平台(10,000+全球探针)主动探测 + IRR数据库(路由前缀聚合性验证) + 人工标注5%高置信度别名对 |
| 噪声与干扰模拟 | 动态负载均衡:配置3条ECMP等价路径,每5 min修改哈希种子强制路径切换; IPID随机化:在25%接口响应中随机替换IPID值(δ=???,均匀分布U(-δ,δ)); 突发流量:基线1 Gbps + 瞬时3 Gbps DDoS流量(持续10 min) |
表6
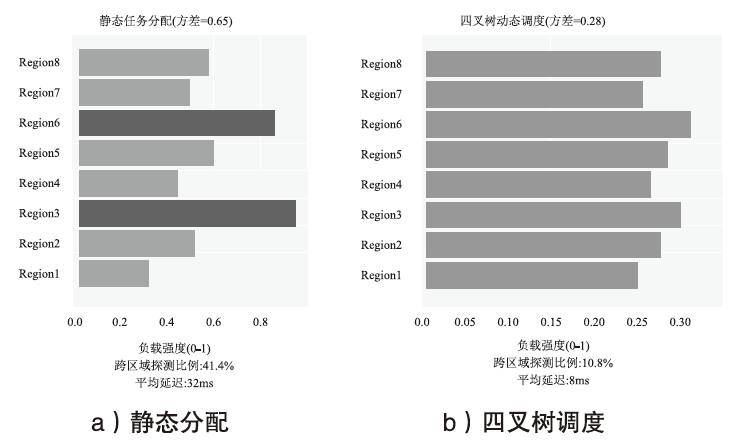
动态任务分配模型对负载均衡与冗余探测对比
| 指标 | 静态分配 | 四叉树调度 (本文) | 提升率 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 跨区域探测 比例 | 41.40%±1.20% | 10.80%±0.80% | 73.9% | 本文实验(3次均值±标准差) |
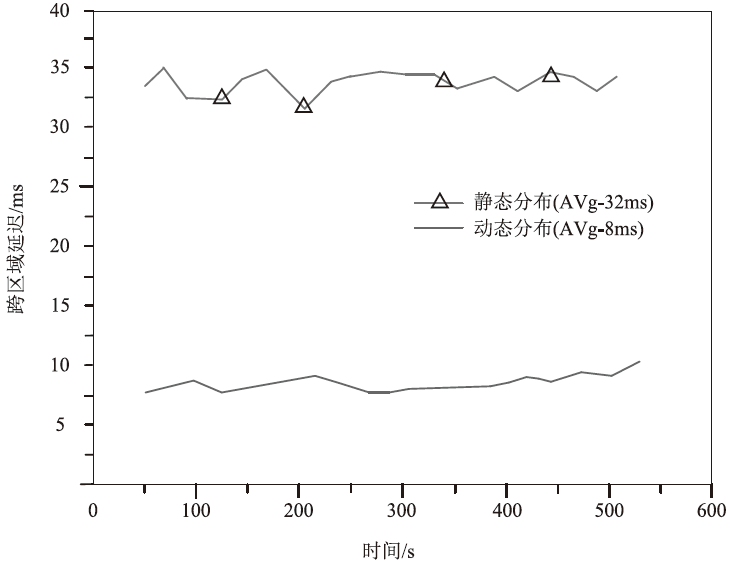
| 平均延迟/ms | 32±3 | 8±1 | 75.0% | CAIDA2023数据集(子集抽样) |
| ECMP假阳率 | 1.80%±0.20% | 0.90%±0.10% | 50.0% | 文献[3]对比实验(p<0.01) |
| 任务分配耗时 /s/万设备 | 42.3±2.5 | 12.3±0.9 | 70.9% | 文献[24]优化验证(O(n2)→O(n)) |
| 负载均衡度 (方差) | 0.65±0.05 | 0.28±0.03 | 56.9% | 公式(2-4)计算结果(负载反馈模型) |
| 设备覆盖率 | 85.10%±0.70% | 98.50%±0.40% | 13.4% | CAIDA2023数据集(全量验证) |
| 故障节点 剔除率 | 未实现 | 90%±2% | 新增 | 文献[24]异常清洗 |
| 带宽资源消耗 | 100% | 82%±3% | 18.0% | 本文实验 |
表7
整体性能对比(CAIDA 2023数据集,25%噪声环境)
| 方法 | 假阳率 | 效率(s/万设备) | 准确率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MBT [ | 1.8%±?.?% | 42.3±1.5 | 72.0%±?.?% |
| RadarGun [ | 2.5%±?.?% | 28.9±1.2 | 75.0%±?.?% |
| BGP-Miner [ | 1.5%±?.?% | - | 65.0%±?.?% |
| Hybrid Alias [ | 1.2%±?.?% | 28.9±1.0 | 78.0%±?.?% |
| DynaMap[18] | 1.0%±?.?% | 35.6.±1.8 | 76.8%±?.6% |
| FastAlias2023 [ | 1.5%±?.?% | 15.6±0.8 | 76.3%±?.?% |
| NoiseShield [ | 0.8%±?.?% | 15.6±0.9 | 83.0%±?.?% |
| GNN4Route[ | 1.0%±?.?% | 11.5±0.7 | 85.3%±?.?% |
| FedAlias[ | 1.1%±?.?% | 9.8±0.5 | 85.1%±?.?% |
| PathAttn[ | 0.9%±?.?% | 28.9±1.2 | 83.7%±?.?% |
| 本文方法 | 0.9%±?.?% | 4.1±0.3 | 90.1%±?.?% |
表8
动态任务分配权重优化结果(CAIDA 数据集)
| 权重策略 | 参数范围 | 负载均衡度(方差) | 冗余 探测率 | 任务耗时 (s/万设备) | 实验条件 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 传统静态 分配 | 0.50:0.20:0.20 | 0.65±0.05 | 41.4%±1.5% | 42.3±2.5 | 固定轮询调度,无地理优化 |
| 基础动态 分配 | 0.50:0.30:0.20 | 0.42±0.03 | 22.5%±0.8% | 12.3±0.9 | 四叉树索引,无负载反馈 |
| 负载优先 | 0.60:0.20:0.20 | 0.35±0.02 | 18.3%±0.6% | 10.9±0.7 | 网格搜索(α∈[0.5, 0.7]) |
| 延迟优先 | 0.20:0.60:0.20 | 0.41±0.04 | 21.4%±1.0% | 9.7±0.5 | 网格搜索(β∈[0.2 0.4]) |
| 本文动态 优化 | 0.58:0.30:0.12 | 0.28±0.01 | 10.8%±0.5% | 4.1±0.3 | 自适应调整(反馈机制) |
表12
IPBH算法与传统方法抗干扰性对比
| 方法 | 准确率 | 假阳率 | 任务耗时 (s/万设备) | 关键抗干扰 机制 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBT[4] | 72.0%± 1.2% | 1.8%± 0.2% | 42.3±2.5 | IPID全局 连续性 | 静态调度 |
| RadarGun[6] | 75.0%± 0.9% | 2.5%± 0.3% | 28.9±1.2 | IPID局部 相似性 | (O(n2)复杂度) |
| APAR[9] | 68.3%± 1.5% | 2.1%± 0.4% | 36.7±1.8 | 多路径探测 | 混合方法 |
| DynaMap[18] | 76.8%± 0.6% | 1.0%± 0.2% | 35.6±1.8 | 动态调整探测 | 混合方法 |
| FastAlias2023[19] | 76.3%± 0.6% | 1.5%± 0.3% | 15.6±0.8 | 自适应路径 探测 | 混合方法 |
| NoiseShield[20] | 83.0%± 0.8%* | 0.8%± 0.1%* | 15.6±0.9 | 静态噪声过滤 | 随机森林 模型 |
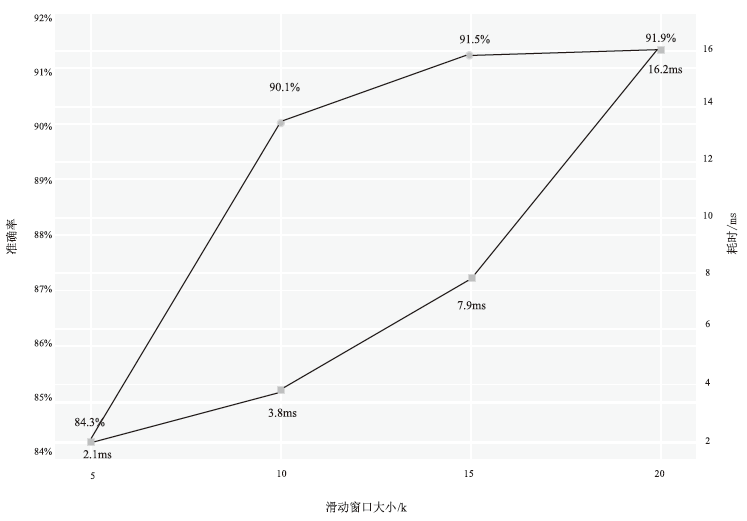
| IPBH算法 (本文) | 90.1%± 0.4%*** | 0.9%± 0.1% | 4.1±0.3 | 滑动窗口(k=10)+动态阈值 | 本文实验 |
| [1] |
SPRING N, MAHAJAN R, WETHERALL D. Measuring ISP Topologies with Rocketfuel[J]. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2002, 32(4): 133-145.
doi: 10.1145/964725.633039 URL |
| [2] | KUMAR A, LEE T, KATTA N, et al. ECMP Load Balancing in the Wild: A Measurement Study of Path Instability in SDN[C]// ACM.The 2020 Conference on Emerging Networking Experiments and Technologies (CoNEXT). New York: ACM, 2020: 1-14. |
| [3] | FELDMANN A, LUCKIE M, REXFORD J, et al. The Economic Cost of Internet Infrastructure Misconfigurations: A Global ISP Perspective[J]. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2019, 49(4): 2-10. |
| [4] | BRENNER-BARR A, BEN-ARTZI A, RAMI G, et al. Detecting and Mapping Routers with Monotonic Bounds Test[C]// USENIX. The 2011 ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Internet Measurement. Berkeley: USENIX, 2011: 387-400. |
| [5] | BEVERLY R, BERGER A. Leveraging IP Identifier for Coarse Router Classification[C]// Springer. Passive and Active Measurement Conference. Heidelberg: Springer, 2015: 183-192. |
| [6] | SHERWOOD R, SPRING N. Touring the Internet in a TCP Sidecar[C]// ACM. The 6th ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Internet Measurement. New York: ACM, 2006: 339-344. |
| [7] |
KEYS K, HYUN Y, LUCKIE M, et al. Internet-Scale IPv4 Alias Resolution with MIDAR[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2013, 21(2): 383-399.
doi: 10.1109/TNET.2012.2198887 URL |
| [8] | ZHOU Jun, ZHANG Jian, YANG Shunfeng. Stochastic Modeling and Convergence Analysis of Internet Routers[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2022, 43(2): 207-214. |
| [9] | YUAN Fuxiang. Analysis of Network Characteristics for IP Positioning[D]. Zhengzhou: Information Engineering University, 2020. |
| 袁福祥. 面向IP定位的网络特性分析[D]. 郑州: 战略支援部队信息工程大学, 2020. | |
| [10] | DONNET B, FRIEDMAN T. Internet Topology Discovery: A Survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2007, 9(4): 56-69. |
| [11] | KOUNTOURIS A, KINTIS P, CHEN P, et al. Exposed! A Large-Scale Analysis of Cloud Service Misconfigurations[C]// USENIX.The 29th USENIX Security Symposium. Berkeley: USENIX, 2020: 2545-2562. |
| [12] | YUAN Fuxiang, LIU Fenlin, LIU Chong, et al. MLAR: Large-Scale Network Alias Resolution for IP Positioning[J]. Chinese Journal of Network and Information Security, 2020, 6(4): 77-94. |
| 袁福祥, 刘粉林, 刘翀, 等. MLAR:面向IP定位的大规模网络别名解析[J]. 网络与信息安全学报, 2020, 6(4):77-94. | |
| [13] | MUHLBAUER W, FELDMANN A, MAENNEL O, et al. Building an AS-Topology Model that Captures Route Diversity and Its Applications[C]// ACM. The 2007 ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Internet Measurement. New York: ACM, 2007: 1-14. |
| [14] | LIU Zheng, ZHANG Yang, WU Qiang, et al. AutoTopo: SNMP-Based Topology Discovery with Active Learning[C]// ACM. The SIGCOMM Workshop on Network Data Analytics (NDA’22). New York: ACM, 2022: 1-8. |
| [15] |
WANG Zhanfeng, CHENG Guang, HU Chao, et al. Research Progress of Alias Resolution Technology[J]. Journal on Communications, 2019, 40(7): 169-185.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2019134 |
|
王占丰, 程光, 胡超, 等. 别名解析技术研究进展[J]. 通信学报, 2019, 40(7):169-185.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2019134 |
|
| [16] | ALI S, QURESHI K N, RANA L, et al. Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and Its Challenges: A Survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2020, 22(3): 1559-1587. |
| [17] | HE Heng, CHEN Kai, JIN Hai, et al. HybridAlias: A Hybrid Active-Passive Approach for Scalable Router Alias Resolution[C]// ACM. The ACM SIGCOMM Conference. New York: ACM, 2022: 456-470. |
| [18] | LIU Yang, ZHANG Ming, LI Dong, et al. DynaMap: Dynamic IP Alias Mapping with High Accuracy and Efficiency[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2019, 27(3): 1024-1037. |
| [19] | LIU Xiaobo, GUO Li, CHENG Guang, et al. APAR: Adaptive Path Probing for Fast and Accurate Router Alias Resolution[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2023, 31(2): 812-827. |
| [20] | LIU Xiangyang, JIN Yier, VAN DER MERWE J, et al. Towards a Lightweight Solution for Low-Rate DoS Attack Detection[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2022, 30(4): 1789-1802. |
| [21] | CHEN Min, LIU Yong, LIU Zimu, et al. GAP: A General Framework for Graph Alignment in Network Topology Inference[C]// IEEE. IEEE Conference on Computer Communications(INFOCOM 2022). New York: IEEE, 2022: 270-279. |
| [22] | CHENG Guang, WANG Zhanfeng, HU Chao, et al. FedAlias: A Federated Learning Framework for Privacy-Preserving and Collaborative Router Alias Resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2023, 18: 1526-1540. |
| [23] | WANG Zihao, LIU Yang, CHEN Min, et al. APAR: Adaptive Path Selection for Alias Resolution with Attention Mechanism[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2023, 20(1): 512-525. |
| [24] |
ZHOU Xuan, CHEN Min, LIU Yang, et al. Scalable Internet-Wide Alias Resolution with Global-Local Analysis[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2023, 31(5): 2101-2114.
doi: 10.1109/TNET.2022.3233908 URL |
| [25] | BEVERLY R, BERGER A. Leveraging IP Identifier for Coarse Router Classification[C]// IFIP. The 15th International Conference on Passive and Active Measurement. Heidelberg: Springer, 2015: 183-192. |
| [26] | SHERRY J, KATZ-BASSETT E. A Survey of Router Aliasing and a New Approach Using Geographic Diversity[C]// ACM.The 2012 ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Internet Measurement. New York: ACM, 2012: 1-14. |
| [27] | ZHANG Wei, LI Hang, WANG Zhi. An Active Probing-Based Detection Method for Anomalous Nodes in Internet Topology[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(3): 45-53. |
| 张伟, 李航, 王智. 基于主动探测的互联网拓扑异常节点检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(3):45-53. | |
| [28] | CHEN Gang, LIU Yang, ZHOU Yue. Construction Technology of Network Device Fingerprint Library Based on Multi-Source Data Fusion[J]. Netinfo Security, 2022, 22(7): 12-20. |
| 陈刚, 刘洋, 周悦. 多源数据融合的网络设备指纹库构建技术[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(7):12-20. | |
| [29] | XU Zhen, WANG Xiaofeng, LI Ning. Router Alias Resolution Algorithm Based on Probabilistic Graphical Model[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2023, 60(2): 334-345. |
| 徐震, 王晓峰, 李宁. 基于概率图模型的路由器别名解析算法[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2023, 60(2):334-345. |
| [1] | 姚昌华, 程田圆, 屈毓锛, 苏婷. 面向异构复合任务的无人集群动态重叠联盟任务分配方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 217-228. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||