信息网络安全 ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (1): 148-158.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.01.013
基于最优传输与改进型极限学习机的加密流量分类方法
- 辽宁大学网络与信息安全学院,沈阳 110036
-
收稿日期:2024-11-15出版日期:2025-01-10发布日期:2025-02-14 -
通讯作者:王妍 E-mail:35902642@qq.com -
作者简介:邰滢滢(1978—),女,辽宁,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为网络与信息安全、图像处理|魏苑苑(1998—),女,山东,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为信息安全|周翰逊(1981—),男,辽宁,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为网络安全|王妍(1978—),女,辽宁,教授,博士,主要研究方向为网络安全、数据库 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2023YFC3304904)
Encrypted Traffic Classification Method Based on Optimal Transport and I-ELM
TAI Yingying, WEI Yuanyuan, ZHOU Hanxun, WANG Yan( )
)
- College of Cyber and Information Security, Liaoning University, Shenyang 110036, China
-
Received:2024-11-15Online:2025-01-10Published:2025-02-14 -
Contact:WANG Yan E-mail:35902642@qq.com
摘要:
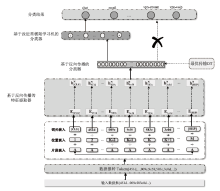
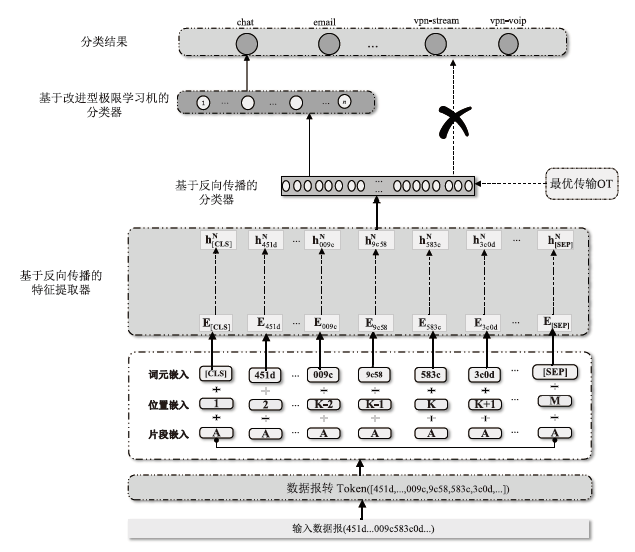
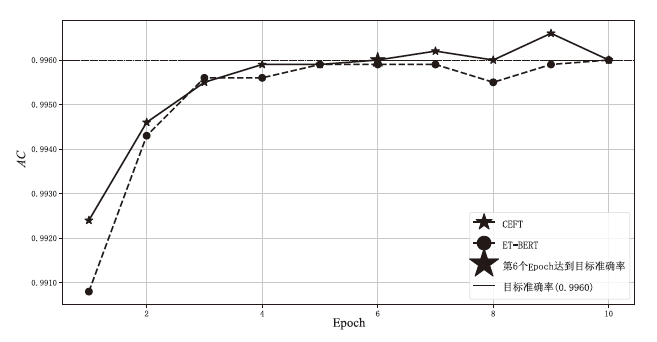
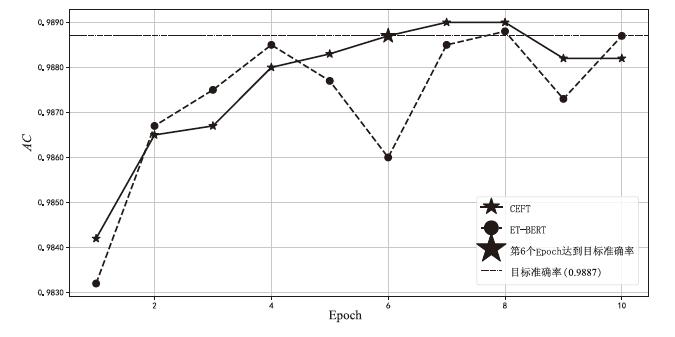
为了解决加密流量分类任务中的数据不平衡以及模型微调过程中资源与时间消耗高的问题,文章提出一种名为CEFT的微调模型对加密流量进行分类。CEFT的预训练模型为ET-BERT,在此基础上引入最优传输OT和改进型极限学习机I-ELM模块,提升分类性能的同时,达到提高训练效率的目的。CEFT先将加密流量送入ET-BERT模型,实现特征提取,再接入最优传输模块,用以衡量模型预测与真实分布之间的传输成本。CEFT通过权重调整来使其最小化,使得模型在不同类别间的预测更加准确,从而有效应对数据不平衡问题。同时,CEFT通过引入I-ELM模块,实现快速权重更新,进而减少冗长的梯度计算,加速训练过程,解决资源和时间消耗高的问题。实验结果表明,CEFT在ISCX-VPN-Service和ISCX-VPN-App数据集上的准确率分别达到了98.97%和99.70%,且在精度、召回率和F1分数等指标上显著优于现有基准模型。在ISCX-VPN-Service数据集上,CEFT方法将训练时间减少了约33.33%,而在ISCX-VPN-App数据集上减少了约35.37%,显著缩短了训练时间。
中图分类号:
引用本文
邰滢滢, 魏苑苑, 周翰逊, 王妍. 基于最优传输与改进型极限学习机的加密流量分类方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(1): 148-158.
TAI Yingying, WEI Yuanyuan, ZHOU Hanxun, WANG Yan. Encrypted Traffic Classification Method Based on Optimal Transport and I-ELM[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(1): 148-158.
表4
ISCX-VPN-Service数据集上各模型比较
| 方法 | AC | PR | RC | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AppScanner[ | 0.7182 | 0.7339 | 0.7225 | 0.7197 |
| BIND[ | 0.7534 | 0.7583 | 0.7488 | 0.7420 |
| K-fp[ | 0.6430 | 0.6492 | 0.6417 | 0.6395 |
| FlowPrint[ | 0.7962 | 0.8042 | 0.7812 | 0.7820 |
| DF[ | 0.7154 | 0.7192 | 0.7104 | 0.7102 |
| FS-Net[ | 0.7205 | 0.7502 | 0.7238 | 0.7131 |
| Deeppacket[ | 0.9329 | 0.9377 | 0.9306 | 0.9321 |
| PERT[ | 0.9352 | 0.9400 | 0.9349 | 0.9368 |
| ET-BERT[ | 0.9890 | 0.9891 | 0.9890 | 0.9890 |
| ANT-ET[ | 0.9858 | 0.9860 | 0.9858 | 0.9859 |
| CEFT | 0.9897 | 0.9897 | 0.9897 | 0.9897 |
表5
ISCX-VPN-App数据集上各模型比较
| 方法 | AC | PR | RC | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AppScanner[ | 0.6266 | 0.4864 | 0.5198 | 0.4935 |
| BIND[ | 0.6767 | 0.5152 | 0.5153 | 0.4965 |
| K-fp[ | 0.6070 | 0.5478 | 0.5430 | 0.5303 |
| FlowPrint[ | 0.8767 | 0.6697 | 0.6651 | 0.6531 |
| DF[ | 0.6116 | 0.5706 | 0.4752 | 0.4799 |
| FS-Net[ | 0.6647 | 0.4819 | 0.4848 | 0.4737 |
| Deeppacket[ | 0.9758 | 0.9785 | 0.9745 | 0.9765 |
| PERT[ | 0.8229 | 0.7092 | 0.7173 | 0.6992 |
| ET-BERT[ | 0.8519 | 0.7508 | 0.7294 | 0.7306 |
| ANT-ET[ | 0.9948 | 0.9922 | 0.9919 | 0.9920 |
| CETP[ | 0.8950 | 0.8402 | 0.8531 | 0.8416 |
| CEFT | 0.9970 | 0.9960 | 0.9955 | 0.9957 |
| [1] |
REZAEI S, LIU Xin. Deep Learning for Encrypted Traffic Classification: An Overview[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2019, 57(5): 76-81.
doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2019.1800819 |
| [2] | DONG Wenqi, YU Jing, LIN Xinjie, et al. Deep Learning and Pre-Training Technology for Encrypted Traffic Classification: A Comprehensive Review[J]. Neurocomputing, 2025, 617: 128444. |
| [3] | OTTER D W, MEDINA J R, KALITA J K. A Survey of the Usages of Deep Learning for Natural Language Processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(2): 604-624. |
| [4] | MINAEE S, BOYKOV Y, PORIKLI F, et al. Image Segmentation Using Deep Learning: A Survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(7): 3523-3542. |
| [5] |
SCHMIDHUBER J. Deep Learning in Neural Networks: An Overview[J]. Neural Networks, 2015, 61: 85-117.
pmid: 25462637 |
| [6] | CONNEAU A, LAMPLE G. Cross-Lingual Language Model Pretraining[C]// NIPS. Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: Curran Associates, 2019: 7059-7069. |
| [7] | DEVLIN J, CHANG M, LEE K, et al. BERT: Pre-Training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding[C]// ACL. Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics:Human Language Technologies. Minneapolis: ACL, 2019: 4171-4186. |
| [8] | WANG Qing, LI Linyu, JIANG Bo, et al. Malicious Domain Detection Based on K-Means and SMOTE[C]// Springer. International Conference on Computational Science. Heidelberg: Springer, 2020: 468-481. |
| [9] | KONG He, LI Tong, GE Jingguo, et al. A Novel Method with Transformers for Fine-Grained Encrypted Traffic Classification[C]// IEEE. 2023 IEEE International Conference on High Performance Computing & Communications, Data Science & Systems, Smart City & Dependability in Sensor, Cloud & Big Data Systems & Application (HPCC/DSS/SmartCity/DependSys). New York: IEEE, 2023: 74-81. |
| [10] | LIN Xinjie, XIONG Gang, GOU Gaopeng, et al. ET-BERT: A Contextualized Datagram Representation with Pre-Training Transformers for Encrypted Traffic Classification[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2022. New York: ACM, 2022: 633-642. |
| [11] | LOTFOLLAHI M, JAFARI S M, SHIRALI H Z R, et al. Deep Packet: A Novel Approach for Encrypted Traffic Classification Using Deep Learning[J]. Soft Computing, 2020, 24(3): 1999-2012. |
| [12] | PEYRÉ G, CUTURI M. Computational Optimal Transport[J]. Foundations and Trends in Machine Learning, 2019, 11(5-6): 355-607. |
| [13] | JIRAMANEEPINIT B, WATCHAREERUETAI U. Iterative Extreme Learning Machine[C]// IEEE. 2018 22nd International Computer Science and Engineering Conference (ICSEC). New York: IEEE, 2018: 1-6. |
| [14] | DAINOTTI A, PESCAPE A, CLAFFY K C. Issues and Future Directions in Traffic Classification[J]. IEEE Network, 2012, 26(1): 35-40. |
| [15] | SHERRY J, LAN Chang, POPA R A, et al. BlindBox: Deep Packet Inspection over Encrypted Traffic[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 2015 ACM Conference on Special Interest Group on Data Communication. New York: ACM, 2015: 213-226. |
| [16] | VAN EDE T, BORTOLAMEOTTI R, CONTINELLA A, et al. FlowPrint: Semi-Supervised Mobile-App Fingerprinting on Encrypted Network Traffic[C]// ACM. Proceedings 2020 Network and Distributed System Security Symposium. New York: ACM, 2020: 1-12. |
| [17] | TAYLOR V F, SPOLAOR R, CONTI M, et al. Robust Smartphone App Identification via Encrypted Network Traffic Analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2018, 13(1): 63-78. |
| [18] | AL-NAAMI K, CHANDRA S, MUSTAFA A, et al. Adaptive Encrypted Traffic Fingerprinting with Bi-Directional Dependence[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 32nd Annual Conference on Computer Security Applications. New York: ACM, 2016: 177-188. |
| [19] | ZENG Yi, GU Huaxi, WEI Wenting, et al. Deep-Full-Range: A Deep Learning Based Network Encrypted Traffic Classification and Intrusion Detection Framework[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 45182-45190. |
| [20] | CUTURI M. Sinkhorn Distances: Lightspeed Computation of Optimal Transportation Distances[EB/OL]. [2024-11-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1306.0895v1. |
| [21] | KANG Bingyi, XIE Saining, ROHRBACH M, et al. Decoupling Representation and Classifier for Long-Tailed Recognition[C]// ICLR. 8th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2020). Washington: ICLR, 2020: 1-16. |
| [22] | HAYES J, DANEZIS G. k-Fingerprinting: A Robust Scalable Website Fingerprinting Technique[C]// USENIX. 25th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 16). Berkeley: USENIX, 2016: 1187-1203. |
| [23] | SIRINAM P, IMANI M, JUAREZ M, et al. Deep Fingerprinting: Undermining Website Fingerprinting Defenses with Deep Learning[C]// ACM. Proceedings of the 2018 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2018: 1928-1943. |
| [24] | LIU Chang, HE Longtao, XIONG Gang, et al. FS-Net: A Flow Sequence Network for Encrypted Traffic Classification[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM 2019). New York: IEEE, 2019: 1171-1179. |
| [25] | HE Hongye, YANG Zhiguo, CHEN Xiangning. PERT: Payload Encoding Representation from Transformer for Encrypted Traffic Classification[C]// IEEE. 2020 ITU Kaleidoscope:Industry-Driven Digital Transformation (ITU K). New York: IEEE, 2020: 1-8. |
| [26] | LIN Xinjie, HE Longtao, GOU Gaopeng, et al. CETP: A Novel Semi-Supervised Framework Based on Contrastive Pre-Training for Imbalanced Encrypted Traffic Classification[J]. Computers & Security, 2024, 143: 103892. |
| [1] | 张浩, 陈龙, 魏志强. 基于数据增强和模型更新的异常流量检测技术[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(2): 66-74. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||