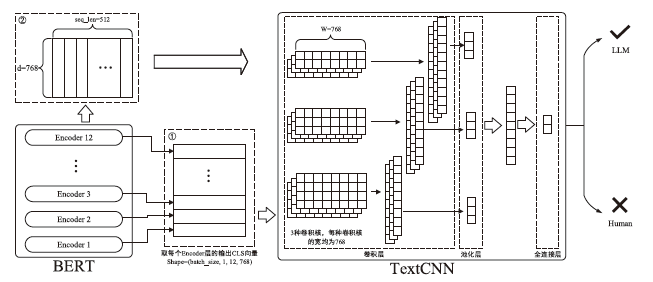
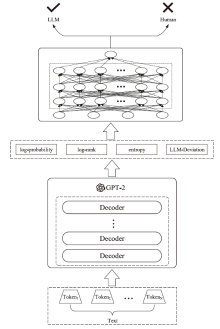
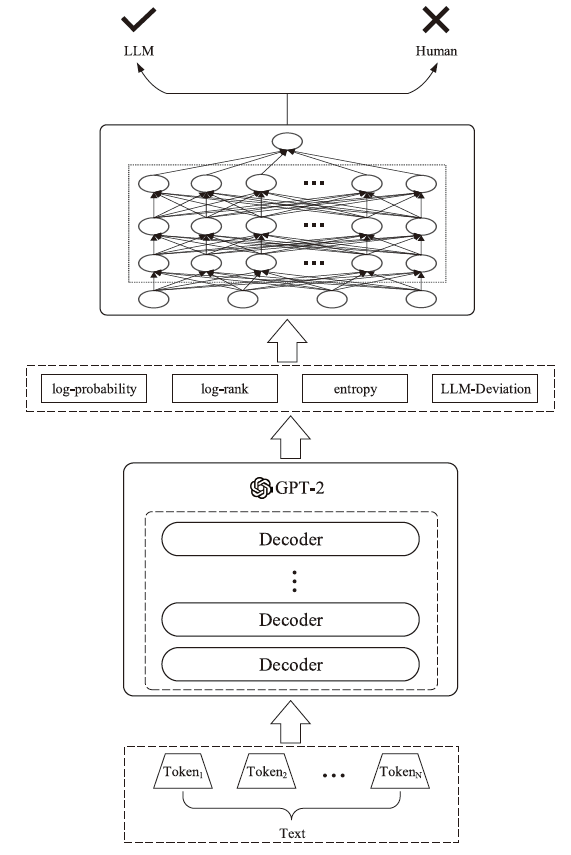
信息网络安全 ›› 2024, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (7): 1098-1109.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2024.07.011
基于语言特征集成学习的大语言模型生成文本检测
- 杭州电子科技大学网络空间安全学院,杭州 310018
-
收稿日期:2024-02-01出版日期:2024-07-10发布日期:2024-08-02 -
通讯作者:项慧xianghui@hdu.edu.cn -
作者简介:项慧(2000—),女,浙江,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为自然语言处理、大语言模型|薛鋆豪(1999—),男,浙江,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为大模型、大模型应用与安全|郝玲昕(2000—),男,山西,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为Web安全、Web漏洞自动化挖掘。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(61772162);浙江省重点研发计划(2023C03198)
Large Language Model-Generated Text Detection Based on Linguistic Feature Ensemble Learning
XIANG Hui( ), XUE Yunhao, HAO Lingxin
), XUE Yunhao, HAO Lingxin
- School of Cyberspace, Hangzhou Dianzi University, Hangzhou 310018, China
-
Received:2024-02-01Online:2024-07-10Published:2024-08-02
摘要:
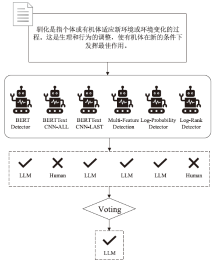
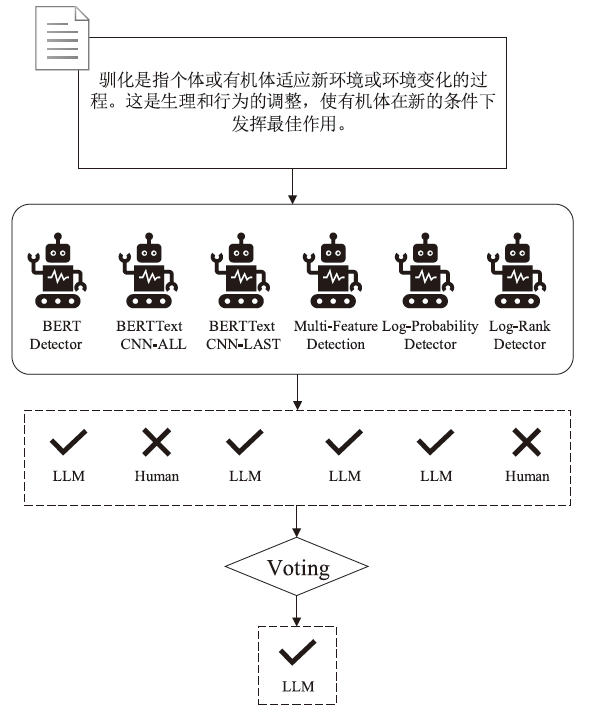
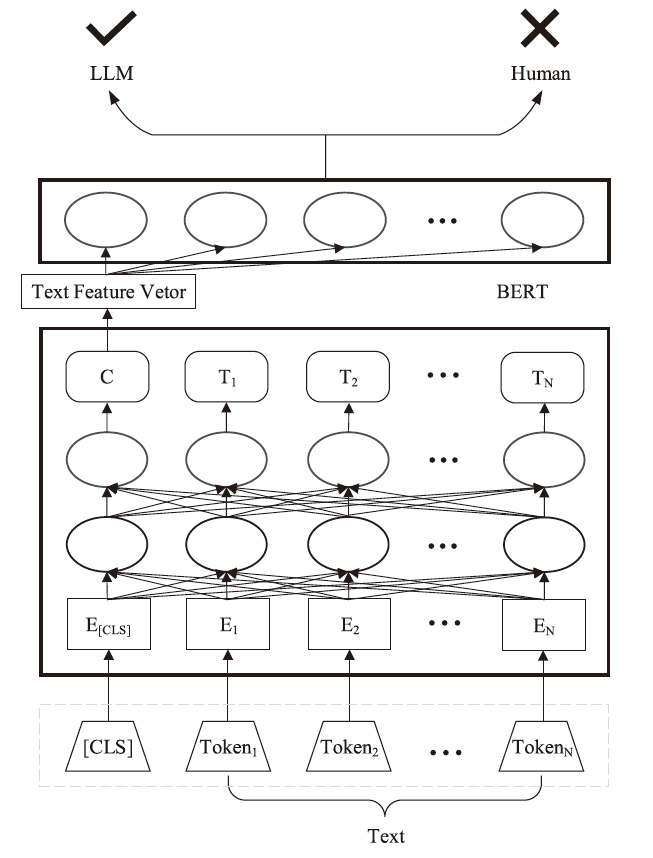
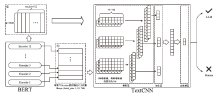
大语言模型的快速发展为日常生活和工作提供了极大的便利,但也为个人和社会带来了挑战。因此,迫切需要能够检测大语言模型生成文本的检测器。为了兼具良好的检测性能和泛化能力,文章提出了一种基于语言特征集成学习的大语言模型生成文本检测方法EBF Detection。EBF Detection融合了微调预训练语言模型和高阶自然语言统计特征,利用判决机制,实现了大语言模型生成文本检测。实验结果显示,EBF Detection不仅在域内数据上平均的检测准确率达到了98.72%,而且在域外数据上的平均检测准确率达到了96.79%。
中图分类号:
引用本文
项慧, 薛鋆豪, 郝玲昕. 基于语言特征集成学习的大语言模型生成文本检测[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(7): 1098-1109.
XIANG Hui, XUE Yunhao, HAO Lingxin. Large Language Model-Generated Text Detection Based on Linguistic Feature Ensemble Learning[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(7): 1098-1109.
使用本文
表3
域内测试结果
| 数据集 | 检测器 | 准确率 | 精确度 | 召回率 | F1值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wiki-HC | Log-Probability Detector | 90.19% | 88.34% | 92.60% | 90.42% |
| Log-Rank Detector | 90.19% | 88.11% | 92.93% | 90.45% | |
| Entropy Detector | 69.94% | 68.24% | 74.60% | 71.27% | |
| GLTR | 89.07% | 86.27% | 92.93% | 89.47% | |
| DetectGPT | 79.26% | 78.09% | 81.35% | 79.69% | |
| BERT Detector | 98.23% | 96.58% | 100.00% | 98.26% | |
| EBF Detection | 98.55% | 98.40% | 98.71% | 98.56% | |
| HC3-ALL | Log-Probability Detector | 96.33% | 95.31% | 97.44% | 96.37% |
| Log-Rank Detector | 96.65% | 96.20% | 97.12% | 96.66% | |
| Entropy Detector | 87.70% | 85.98% | 90.10% | 87.99% | |
| GLTR | 96.33% | 95.31% | 97.44% | 96.37% | |
| DetectGPT | 86.89% | 87.27% | 86.38% | 86.82% | |
| BERT Detector | 98.24% | 97.48% | 99.04% | 98.26% | |
| EBF Detection | 98.88% | 99.35% | 98.40% | 98.88% |
表4
域外测试结果
| 训练集 | 测试集 | 检测器 | 准确率 | 精确度 | 召回率 | F1值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wiki-HC | HC3-ALL | Log-Probability Detector | 95.15% | 93.54% | 97.00% | 95.24% |
| Log-Rank Detector | 95.50% | 94.40% | 96.75% | 95.56% | ||
| Entropy Detector | 85.84% | 83.73% | 88.97% | 86.27% | ||
| GLTR | 95.12% | 92.96% | 97.64% | 95.24% | ||
| DetectGPT | 84.60% | 91.23% | 76.55% | 83.25% | ||
| BERT Detector | 94.26% | 97.66% | 90.69% | 94.05% | ||
| EBF Detection | 97.51% | 99.53% | 95.47% | 97.46% | ||
| HC3-ALL | Wiki-HC | Log-Probability Detector | 89.77% | 90.58% | 88.77% | 89.67% |
| Log-Rank Detector | 90.44% | 90.08% | 90.89% | 90.49% | ||
| Entropy Detector | 69.85% | 69.60% | 70.49% | 70.04% | ||
| GLTR | 88.10% | 88.17% | 88.01% | 88.09% | ||
| DetectGPT | 77.71% | 72.81% | 88.45% | 79.87% | ||
| BERT Detector | 85.66% | 77.80% | 99.81% | 87.44% | ||
| EBF Detection | 96.06% | 97.11% | 94.93% | 96.01% |
表7
消融实验结果
| 训练集 | 测试集 | 检测器 | 准确率 | 精确度 | 召回率 | F1值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wiki-HC | Wiki-HC | Multi-Feature Detection | 96.95% | 95.91% | 98.07% | 96.98% |
| BERTTextCNN-ALL | 97.27% | 95.37% | 99.36% | 97.32% | ||
| BERTTextCNN-LAST | 98.23% | 96.58% | 100.00% | 98.26% | ||
| EBF Detection | 98.55% | 98.40% | 98.71% | 98.56% | ||
| HC3-ALL | Multi-Feature Detection | 95.98% | 95.35% | 96.68% | 96.01% | |
| BERTTextCNN-ALL | 80.93% | 79.15% | 83.99% | 81.50% | ||
| BERTTextCNN-LAST | 91.42% | 87.48% | 96.68% | 91.85% | ||
| EBF Detection | 97.51% | 99.53% | 95.47% | 97.46% | ||
| HC3-ALL | HC3-ALL | Multi-Feature Detection | 97.12% | 96.83% | 97.44% | 97.13% |
| BERTTextCNN-ALL | 98.08% | 96.31% | 100.00% | 98.12% | ||
| BERTTextCNN-LAST | 98.24% | 97.48% | 99.04% | 98.26% | ||
| EBF Detection | 98.88% | 99.35% | 98.40% | 98.88% | ||
| Wiki-HC | Multi-Feature Detection | 94.55% | 95.42% | 93.59% | 94.49% | |
| BERTTextCNN-ALL | 84.48% | 76.46% | 99.62% | 86.52% | ||
| BERTTextCNN-LAST | 90.67% | 85.82% | 97.43% | 91.26% | ||
| EBF Detection | 96.06% | 97.11% | 94.93% | 96.01% |
| [1] | JI Ziwei, LEE N, FRIESKE R, et al. Survey of Hallucination in Natural Language Generation[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2023, 55(12): 1-38. |
| [2] |
AZAMFIREI R, KUDCHADKAR S R, FACKLER J. Large Language Models and the Perils of Their Hallucinations[J]. Critical Care, 2023, 27(1): 120-132.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-023-04393-x pmid: 36945051 |
| [3] | FLANAGIN A, BIBBINS-DOMINGO K, BERKWITS M, et al. Nonhuman “Authors” and Implications for the Integrity of Scientific Publication and Medical Knowledge[J]. Jama, 2023, 329(8): 637-639. |
| [4] |
KING M R, ChatGPT. A Conversation on Artificial Intelligence, Chatbots, and Plagiarism in Higher Education[J]. Cellular and Molecular Bioengineering, 2023, 16(1): 1-2.
doi: 10.1007/s12195-022-00754-8 pmid: 36660590 |
| [5] | The Editor of a Brief History of the Metaverse, Eco. The First AI False Information Case in Gansu, a Man Used ChatGPT to Make Up Fake News for Profit[EB/OL]. (2023-05-09)[2023-12-31]. https://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_22999940. |
| 元宇宙简史编辑 Eco. 甘肃首例AI虚假信息案,男子用ChatGPT编假新闻牟利[EB/OL]. (2023-05-09)[2023-12-31]. https://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_22999940. | |
| [6] | CHAKRABORTY S, BEDI A S, ZHU Sicheng, et al. On the Possibilities of AI-Generated Text Detection[EB/OL]. (2023-10-02)[2023-12-31]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.04736. |
| [7] | HOLTZMAN A, BUYS J, DU L, et al. The Curious Case of Neural Text Degeneration[C]// ICLR. In 8th International Conference on Learning Representations. New York: ICLR, 2020: 26-30. |
| [8] | SOLAIMAN I, BRUNDAGE M, CLARK J, et al. Release Strategies and the Social Impacts of Language Models[EB/OL]. (2019-12-13)[2023-12-31]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1908.09203. |
| [9] | GRITSAY G, GRABOVOY A, CHEKHOVICH Y V. Automatic Detection of Machine Generated Texts: Need More Tokens[C]// IEEE. 2022 Ivannikov Memorial Workshop (IVMEM). New York: IEEE, 2022: 20-26. |
| [10] | GUO Biyang, ZHANG Xin, WANG Ziyuan, et al. How Close Is ChatGPT to Human Experts? Comparison Corpus, Evaluation, and Detection[EB/OL]. (2023-01-18)[2023-12-31]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2301.07597. |
| [11] | HE Xinlei, SHEN Xinyue, CHEN Zeyuan, et al. MGTBench: Benchmarking Machine-Generated Text Detection[EB/OL]. (2023-03-26)[2024-01-16]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2303.14822. |
| [12] | TIAN Yuchuan, CHEN Hanting, WANG Xutao, et al. Multiscale Positive-Unlabeled Detection of AI-Generated Texts[EB/OL]. (2023-05-29)[2023-09-29]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2305.18149. |
| [13] | ANTOUN W, MOUILLERON V, SAGOT B, et al. Towards a Robust Detection of Language Model-Generated Text: Is ChatGPT That Easy to Detect?[C]// TALN. In Actes de CORIA-TALN 2023. Paris: ATALA, 2023: 14-27. |
| [14] | GEHRMANN S, STROBELT H, RUSH A. GLTR: Statistical Detection and Visualization of Generated Text[C]// ACL. Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics:System Demonstrations. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2019: 111-116. |
| [15] | ZHONG Wanjun, TANG Duyu, XU Zenan, et al. Neural Deepfake Detection with Factual Structure of Text[C]// ACL. Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP). Stroudsburg: ACL, 2020: 2461-2470. |
| [16] | FROHLING L, ZUBIAGA A. Feature-Based Detection of Automated Language Models: Tackling GPT-2, GPT-3 and Grover[J]. PeerJ Computer Science, 2021, 7: 443-454. |
| [17] | MITCHELL E, LEE Y, KHAZATSKY A, et al. DetectGPT: Zero-Shot Machine-Generated Text Detection Using Probability Curvature[C]// ACM. In Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML’23). New York: ACM, 2023: 24950-24962. |
| [18] | SU Jinyan, ZHUO T, WANG Di, et al. DetectLLM: Leveraging Log Rank Information for Zero-Shot Detection of Machine-Generated Text[C]// ACL. Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics:EMNLP 2023. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2023: 12395-12412. |
| [19] | DESAIRE H, CHUA A E, KIM M G, et al. Accurately Detecting AI Text When ChatGPT Is Told to Write Like a Chemist[J]. Cell Reports Physical Science, 2023, 4(11): 101672-101685. |
| [20] | WU Kangxi, PANG Liang, SHEN Huawei, et al. LLMDet: A Third Party Large Language Models Generated Text Detection Tool[C]// ACL.Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics:EMNLP 2023. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2023: 2113-2133. |
| [21] | ABDELNABI S, FRITZ M. Adversarial Watermarking Transformer: Towards Tracing Text Provenance with Data Hiding[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York: IEEE, 2021: 121-140. |
| [22] | KIRCHENBAUER J, GEIPING J, WEN Y, et al. A Watermark for Large Language Models[C]// ICML. Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: ICML, 2023: 17061-17084. |
| [23] | KRISHNA K, SONG Y, KARPINSKA M, et al. Paraphrasing Evades Detectors of AI-Generated Text, But Retrieval Is an Effective Defense[C]// NIPS. Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS’23). New York: NIPS., 2024: 27469-27500. |
| [24] | UCHENDU A, LE T, SHU Kai, et al. Authorship Attribution for Neural Text Generation[C]// ACL. Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP). Stroudsburg: ACL, 2020: 8384-8395. |
| [25] | DONG Xibin, YU Zhiwen, CAO Wenming, et al. A Survey on Ensemble Learning[J]. Frontiers of Computer Science, 2019, 14(2): 241-258. |
| [1] | 郭祥鑫, 林璟锵, 贾世杰, 李光正. 针对大语言模型生成的密码应用代码安全性分析[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(6): 917-925. |
| [2] | 张长琳, 仝鑫, 佟晖, 杨莹. 面向网络安全领域的大语言模型技术综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(5): 778-793. |
| [3] | 屠晓涵, 张传浩, 刘孟然. 恶意流量检测模型设计与实现[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(4): 520-533. |
| [4] | 江荣, 刘海天, 刘聪. 基于集成学习的无监督网络入侵检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(3): 411-426. |
| [5] | 黄恺杰, 王剑, 陈炯峄. 一种基于大语言模型的SQL注入攻击检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(11): 84-93. |
| [6] | 邢凌凯, 张健. 基于HPC的虚拟化平台异常检测技术研究与实现[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(10): 64-69. |
| [7] | 王浩洋, 李伟, 彭思维, 秦元庆. 一种基于集成学习的列车控制系统入侵检测方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(5): 46-53. |
| [8] | 曾颖明, 王斌, 郭敏. 基于群体智能的网络安全协同防御技术研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(9): 52-56. |
| [9] | 马泽文, 刘洋, 徐洪平, 易航. 基于集成学习的DoS攻击流量检测技术[J]. 信息网络安全, 2019, 19(9): 115-119. |
| [10] | 汤健, 孙春来, 李东. 基于在线集成学习技术的工业控制网络入侵防范技术探讨[J]. 信息网络安全, 2014, 14(9): 86-91. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 72
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 122
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||