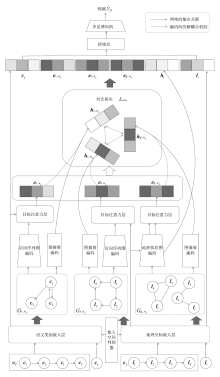
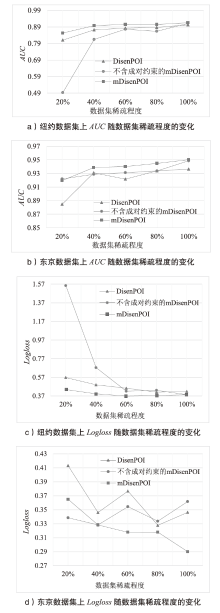
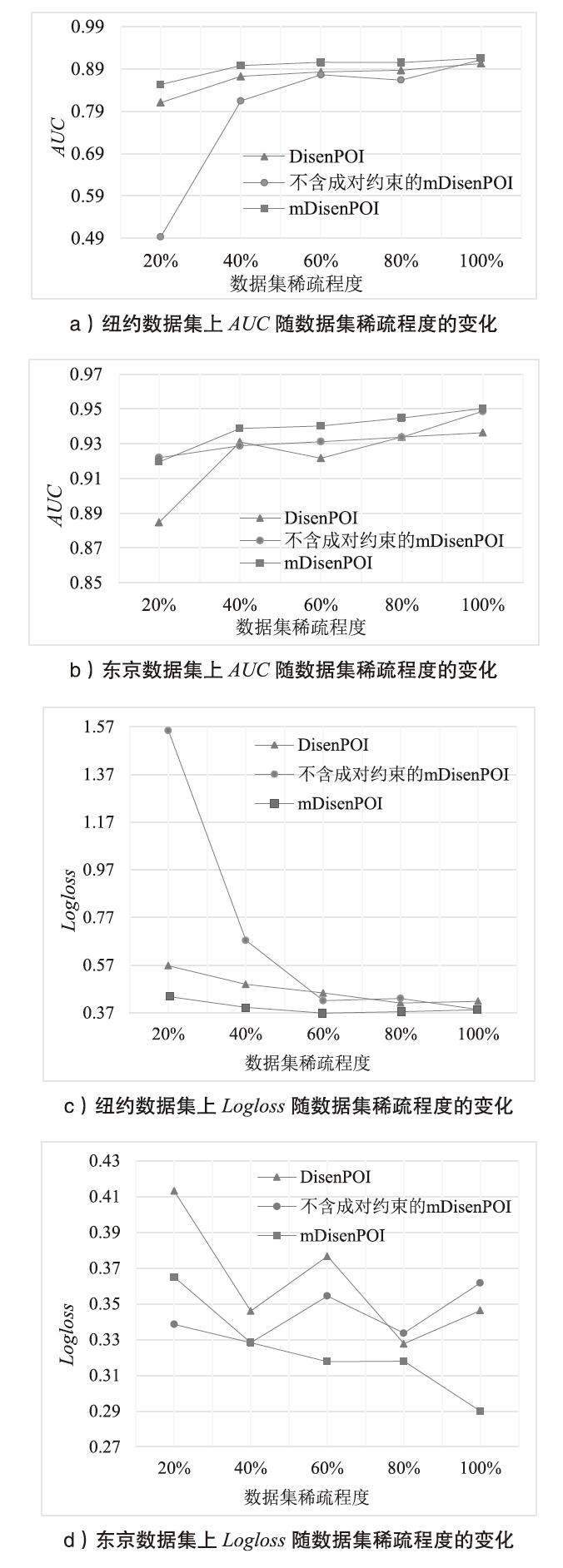
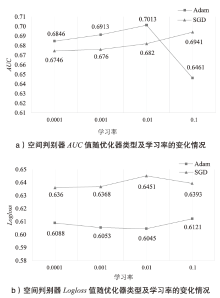
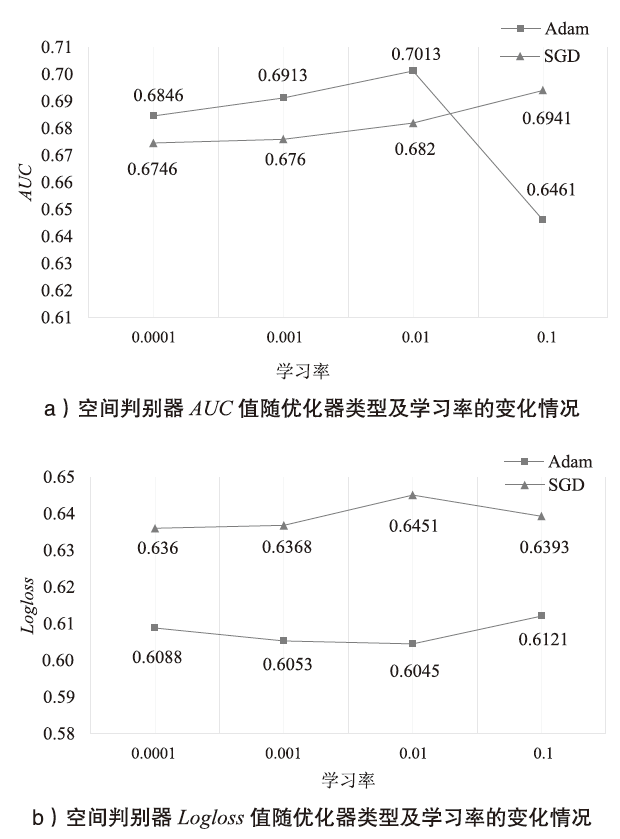
| [1] |
CHO E, MYERS S A, LESKOVEC J. Friendship and Mobility: User Movement in Location-Based Social Networks[C]//ACM. The 17th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2011: 1082-1090.
|
| [2] |
QIN Yifang, WANG Yifan, SUN Fang, et al. DisenPOI: Disentangling Sequential and Geographical Influence for Point-of-Interest Recommendation[C]//ACM. The 6th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2023: 508-516.
|
| [3] |
HE Xiangnan, DENG Kuan, WANG Xiang, et al. LightGCN: Simplifying and Powering Graph Convolution Network for Recommendation[C]//ACM. The 43rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval 2020. New York: ACM, 2020: 639-648.
|
| [4] |
SUN Ke, QIAN Tieyun, CHEN Tong, et al. Where to Go Next: Modeling Long- and Short-Term User Preferences for Point-of-Interest Recommendation[C]//ACM. The AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York: ACM, 2020: 214-221.
|
| [5] |
WANG Zhaobo, ZHU Yanmin, ZHANG Qiaomei, et al. Graph-Enhanced Spatial-Temporal Network for Next POI Recommendation[J]. ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data, 2022, 16(6): 1-21.
|
| [6] |
XIAO Lei, LI Qi. Survey of Temporal Knowledge Graph Completion Methods[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2024, 60(6): 43-54.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2307-0083
|
|
肖蕾, 李琪. 时序知识图谱补全方法研究综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2024, 60(6):43-54.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2307-0083
|
| [7] |
ZHAO Jing, XU Jiajie, XU Yuan, et al. CCML: Curriculum and Contrastive Learning Enhanced Meta-Learner for Personalized Spatial Trajectory Prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2024, 36(9): 4499-4514.
|
| [8] |
ZHANG Qingbo, WANG Bin, CUI Ningning, et al. Attention-Based Regularized Matrix Factorization for Recommendation[J]. Journal of Software, 2020, 31(3): 778-793.
|
|
张青博, 王斌, 崔宁宁, 等. 基于注意力机制的规范化矩阵分解推荐算法[J]. 软件学报, 2020, 31(3):778-793.
|
| [9] |
PAN Yiteng, HE Fazhi, YU Haiping. Learning Social Representations with Deep Autoencoder for Recommender System[J]. World Wide Web, 2020, 23(4): 2259-2279.
|
| [10] |
WEN Tao, ZHANG Min, WANG Huaiyuan. Transient Stability Assessment Model Based on Stacked Sparse Denoising Auto-Encodern[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2022, 41(1): 207-212.
|
|
温涛, 张敏, 王怀远. 基于堆叠稀疏降噪自编码器的暂态稳定评估模型[J]. 电力工程技术, 2022, 41(1):207-212.
|
| [11] |
ZHENG Yu, GAO Chen, CHANG Jianxin, et al. Disentangling Long and Short-Term Interests for Recommendation[C]//ACM. Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2022. New York: ACM, 2022: 2256-2267.
|
| [12] |
LIU Guoqi, HE Tingnian, RONG Yixuan, et al. A Point of Interest Recommendation Model Based on Tracks and Friend Relationship of Users[EB/OL]. (2024-03-22)[2024-06-20]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=tH39KOVtnoGMPmh6qUh_IX6qyKDlvcDYhTSYDyCq40SnG8jamxDzNr59fhLWxIwal1stTMjKiE3t8ubpU-yAJ7K_EIEKa8UeDECtDEXG1Oe_a8Aw4sL3foaAh5xBND34G1375xYA3rZPzhszd2knpUsKLpNzVtahX__tQkTPWtBi0wUsJ0b371PDwkoIanD_&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS.
|
|
刘国岐, 何廷年, 荣艺煊, 等. 基于用户轨迹和好友关系的兴趣点推荐[EB/OL]. (2024-03-22)[2024-06-20]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=tH39KOVtnoGMPmh6qUh_IX6qyKDlvcDYhTSYDyCq40SnG8jamxDzNr59fhLWxIwal1stTMjKiE3t8ubpU-yAJ7K_EIEKa8UeDECtDEXG1Oe_a8Aw4sL3foaAh5xBND34G1375xYA3rZPzhszd2knpUsKLpNzVtahX__tQkTPWtBi0wUsJ0b371PDwkoIanD_&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS.
|
| [13] |
CAI Jiawei, WANG Dong, CHEN Hongyang, et al. Modeling Dynamic Spatiotemporal User Preference for Location Prediction: A Mutually Enhanced Method[J]. World Wide Web, 2024, 27(2): 1-17.
|
| [14] |
ZHOU Guorui, MOU Na, FAN Ying, et al. Deep Interest Evolution Network for Click-through Rate Prediction[C]// ACM. The AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York: ACM, 2019: 5941-5948.
|
| [15] |
ZHOU Guorui, ZHU Xiaoqiang, SONG Chenru, et al. Deep Interest Network for Click-through Rate Prediction[C]// ACM. The 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2018: 1059-1068.
|
| [16] |
WU Shu, TANG Yuyuan, ZHU Yanqiao, et al. Session-Based Recommendation with Graph Neural Networks[C]// ACM. The AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York: ACM, 2019: 346-353.
|
| [17] |
WANG Xiang, HE Xiangnan, WANG Meng, et al. Neural Graph Collaborative Filtering[C]// ACM. The 42nd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. New York: ACM, 2019: 165-174.
|
| [18] |
WANG Hao, SHEN Huawei, OUYANG Wentao, et al. Exploiting POI-Specific Geographical Influence for Point-of-Interest Recommendation[C]// ACM. The 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York: ACM, 2018: 3877-3883.
|
 ), HE Jiahan1, WANG Qun1
), HE Jiahan1, WANG Qun1