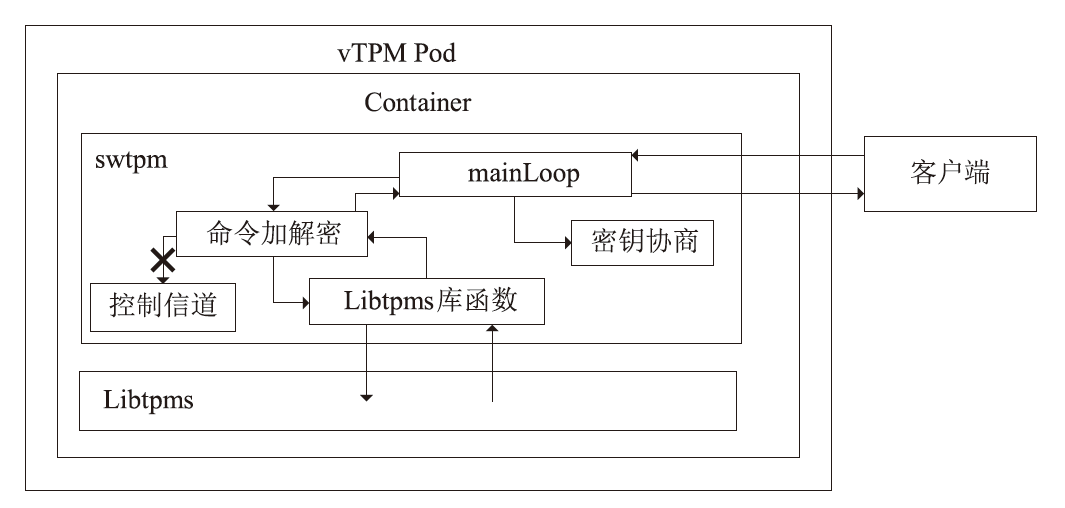
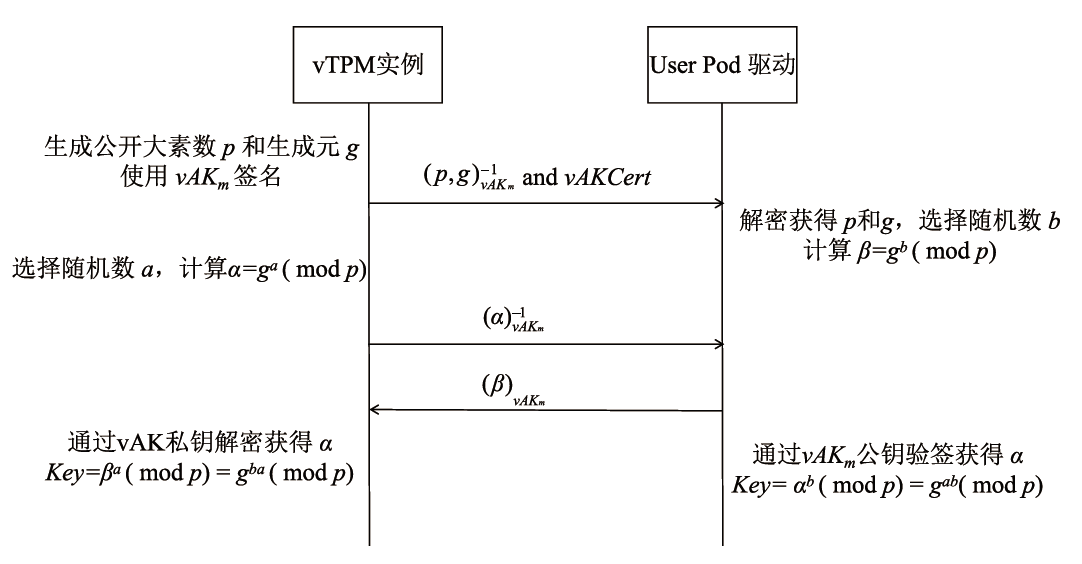
Netinfo Security ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (11): 1811-1823.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.11.012
Previous Articles Next Articles
Research on Unified Remote Attestation Mechanism for Confidential Containers Devices
HU Yuyi1,2, CAI Wei1,2, CHEN Jingfan1,2, LIU Mohan1,2, WANG Juan1,2( ), HE Yun3
), HE Yun3
1. Key Laboratory of Aerospace Information Security and Trusted Computing ,Ministry of Education Wuhan 430072, China 2. School of Cyber Science and Engineering ,Wuhan University Wuhan 430072, China 3. JD.com Group Beijing 100176, China
-
Received:2025-07-28Online:2025-11-10Published:2025-12-02
CLC Number:
Cite this article
HU Yuyi, CAI Wei, CHEN Jingfan, LIU Mohan, WANG Juan, HE Yun. Research on Unified Remote Attestation Mechanism for Confidential Containers Devices[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(11): 1811-1823.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://netinfo-security.org/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.11.012
| [1] | FENG Dengguo. Progress and Prospects of Confidential Computing[EB/OL]. (2025-01-07)[2025-07-20]. https://www.secrss.com/article/74435. |
| 冯登国. 机密计算的进展与展望[EB/OL]. (2025-01-07)[2025-07-20]. https://www.secrss.com/article/74435. | |
| [2] | WANG Juan, FAN Chengyang, CHENG Yueqiang, et al. Analysis and Research on SGX Technology[J]. Journal of Software, 2018, 29(9): 2778-2798. |
| 王鹃, 樊成阳, 程越强, 等. SGX技术的分析和研究[J]. 软件学报, 2018, 29(9):2778-2798. | |
| [3] | KAMMEL F, YLINEN M, FELDMAN-FITZRTHUM T. Confidential Kubernetes: Use Confidential Virtual Machines and Enclaves to Improve Your Cluster Security[EB/OL]. (2023-07-06)[2025-07-20]. https://kubernetes.io/zh-cn/blog/2023/07/06/confidential-kubernetes/. |
| [4] | BIRKHOLZ H, THALER D, RICHARDSON M, et al. Remote Attestation Procedures (RATS) Architecture:RFC 9334[EB/OL]. [2025-07-27]. https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc9334. |
| [5] | Trusted Computing Group. Welcome to Trusted Computing Group[EB/OL]. [2025-07-20]. https://trustedcomputinggroup.org/. |
| [6] | FENG Dengguo, QIN Yu, WANG Dan, et al. Research on Trusted Computing Technology[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2011, 48(8): 1332-1349. |
| 冯登国, 秦宇, 汪丹, 等. 可信计算技术研究[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2011, 48(8):1332-1349. | |
| [7] | BERGER S, CÁCERES R, GOLDMAN K A, et al. vTPM: Virtualizing the Trusted Platform Module[C]// USENIX. The 15th USENIX Security Symposium. Berkely: USENIX, 2006: 305-320. |
| [8] | RAJ H, SAROIU S, WOLMAN A, et al. fTPM: A Software-Only Implementation of a TPM Chip[C]// USENIX. The 25th USENIX Security Symposium. Berkely: USENIX, 2016: 841-856. |
| [9] | ARM. TrustZone for Cortex-A[EB/OL]. [2025-09-20]. https://www.arm.com/zh-TW/technologies/trustzone-for-cortex-a. |
| [10] | SUN Haonan, HE Rongyu, ZHANG Yong, et al. eTPM: A Trusted Cloud Platform Enclave TPM Scheme Based on Intel SGX Technology[EB/OL]. (2018-11-06)[2015-07-20]. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113807. |
| [11] |
WANG Juan, WANG Jie, FAN Chengyang, et al. SvTPM: SGX-Based Virtual Trusted Platform Modules for Cloud Computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing, 2023, 11(3): 2936-2953.
doi: 10.1109/TCC.2023.3243891 URL |
| [12] | Intel. Rust-Vtpm-Td[EB/OL]. [2025-07-20]. https://github.com/intel/vtpm-td. |
| [13] | NARAYANAN V, CARVALHO C, RUOCCO A, et al. Remote Attestation of Confidential VMs Using Ephemeral vTPMs[C]// ACM. The 39th Annual Computer Security Applications Conference. New York: ACM, 2023: 732-743 |
| [14] | PECHOLT J, WESSEL S. CoCoTPM: Trusted Platform Modules for Virtual Machines in Confidential Computing Environments[C]// ACM. The 38th Annual Computer Security Applications Conference. New York: ACM, 2022: 989-998. |
| [15] | CONSORTIUM C C. Why is Attestation Required for Confidential Computing?[EB/OL]. (2023-04-06)[2025-07-20]. https://confidentialcomputing.io/2023/04/06/why-is-attestation-required-for-confidential-computing/. |
| [16] | MÉNÉTREY J, GÖTTEL C, KHURSHID A, et al. Attestation Mechanisms for Trusted Execution Environments Demystified[C]// Springer. Distributed Applications and Interoperable Systems. Heidelberg: Springer, 2022: 95-113. |
| [17] | CHEN Guoxing, ZHANG Yinqian, LAI T. OPERA: Open Remote Attestation for Intel’s Secure Enclaves[C]// ACM. The 2019 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2019: 2317-2331. |
| [18] | CHEN Guoxing, ZHANG Yinqian. MAGE: Mutual Attestation for a Group of Enclaves without Trusted Third Parties[C]// USENIX. The 31st USENIX Security Symposium. Berkely: USENIX, 2022: 4095-4110. |
| [19] | GREVELER U, JUSTUS B, LÖHR D. Mutual Remote Attestation: Enabling System Cloning for TPM Based Platforms[C]// Springer. Security and Trust Management(STM 2011). Heidelberg: Springer, 2011: 193-206. |
| [20] | SCHEAR N, CABLE II P T, MOYER T M, et al. Bootstrapping and Maintaining Trust in the Cloud[C]// ACM. The 32nd Annual Computer Security Applications Conference (ACSAC 2016). New York: ACM, 2016: 65-77. |
| [21] | OTT S, KAMHUBER M, PECHOLT J, et al. Universal Remote Attestation for Cloud and Edge Platforms[C]// ACM. The 18th International Conference on Availability, Reliability and Security. New York: ACM, 2023: 1-11. |
| [22] | ZHANG Xiaolin, QIN Kailun, QU Shipei, et al. Teamwork Makes TEE Work: Open and Resilient Remote Attestation on Decentralized Trust[EB/OL]. (2024-08-09)[2025-07-20]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2402.08908. |
| [23] | KARANJAI R, GAO Zhimin, CHEN Lin, et al. DHTee: Decentralized Infrastructure for Heterogeneous TEEs[C]// IEEE. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Blockchain and Cryptocurrency (ICBC). New York: IEEE, 2023: 1-3. |
| [24] | PAULIN D, HENNEBERT C, FRANCO-RONDISSON T, et al. HistoTrust: Ethereum-Based Attestation of a Data History Built with OP-TEE and TPM[C]// Springer. Foundations and Practice of Security(FPS 2021). Heidelberg: Springer, 2021: 130-145. |
| [25] | ANKERGÅRD S F J J, DUSHKU E, DRAGONI N. PERMANENT: Publicly Verifiable Remote Attestation for Internet of Things Through Blockchain[C]// Springer. Foundations and Practice of Security(FPS 2021). Heidelberg: Springer, 2021: 218-234. |
| [26] | LI Peixi, LI Xiang, FANG Liming. DMA: Mutual Attestation Framework for Distributed Enclaves[C]// Springer. Information and Communications Security(ICICS 2024). Heidelberg: Springer, 2024: 145-164. |
| [27] | SAILER R, ZHANG Xiaolan, JAEGER T, et al. Design and Implementation of a TCG-Based Integrity Measurement Architecture[C]// USENIX. The 13th USENIX Security Symposium. Berkeley: USENIX, 2004: 223-238. |
| [28] | SU Tao. Trust and Integrity in Distributed Systems[D]. Turin: Polytechnic University of Turin, 2017. |
| [29] |
BENEDICTIS M D, LIOY A. Integrity Verification of Docker Containers for a Lightweight Cloud Environment[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2019, 97: 236-246.
doi: 10.1016/j.future.2019.02.026 URL |
| [30] | LUO Wu, SHEN Qingni, XIA Yutang, et al. Container-IMA: A Privacy-Preserving Integrity Measurement Architecture for Containers[C]// USENIX. The 22nd International Symposium on Research in Attacks, Intrusions and Defenses. Berkely: USENIX, 2019: 487-500. |
| [31] | SONG Liantao, DING Yan, DONG Pan, et al. TZ-IMA: Supporting Integrity Measurement for Applications with ARM Trustzone[C]// Springer. Information and Communications Security(ICICS 2022). Heidelberg: Springer, 2022: 342-358. |
| [32] | Intel. Runtime Integrity Measurement and Attestation in a Trust Domain[EB/OL]. (2025-04-09)[2025-07-20]. https://www.intel.cn/content/www/cn/zh/developer/articles/community/runtime-integrity-measure-and-attest-trust-domain.html. |
| [33] | Tpm2-Software Community. Remote Attestation with Tpm2 Tools[EB/OL]. (2020-06-12)[2025-07-20]. https://tpm2-software.github.io/2020/06/12/Remote-Attestation-With-tpm2-tools.html. |
| [34] |
DIFFIE W, HELLMAN M E. New Directions in Cryptography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1976, 22(6): 644-654.
doi: 10.1109/TIT.1976.1055638 URL |
| [35] | ARYAN, KUMAR C, DURAI R V P M. Enhanced Diffie-Hellman Algorithm for Reliable Key Exchange[EB/OL]. [2025-07-20]. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1757-899X/263/4/042015. |
| [36] | FERRO L. Container Attestation with Linux IMA Namespaces[D]. Turin: Polytechnic University of Turin, 2023. |
| [1] | SHI Yijuan, ZHOU Danping, FAN Lei, LIU Yin. Secure Multi-Party Computation Protocol Based on Trusted Execution Environment [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(9): 1439-1446. |
| [2] | HUANG Ke, LI Xuan, ZHOU Qingfei, SHANG Ketong, QIN Yu. A Trusted Runtime Monitoring Method Based on eBPF for Container [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 306-326. |
| [3] | HAO Meng, LI Jiayong, YANG Hongwei, ZHANG Weizhe. Heterogeneous CPU-GPU System Confidential Computing Survey [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(11): 1658-1672. |
| [4] | GUAN Zhi, HU Jianbin, LI Yue, CHEN Zhong. A Comprehensive Survey of Blockchain Technologies and Applications Based on Trusted Execution Environments [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(11): 1673-1690. |
| [5] | XUE Kaiping, ZHANG Chunyi, LIU Feng, WANG Feng. Security-Enhanced Index Scheme in Encrypted Database Based on Trusted Execution Environment [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(11): 1718-1731. |
| [6] | ZHAO Bo, LYU Jiamin, WANG Yixuan. A Multidimensional Security Measurement Architecture for the Container Lifecycle [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(11): 1745-1761. |
| [7] | WANG Yajie, LU Jinbiao, LI Yuhang, FAN Qing, ZHANG Zijian, ZHU Liehuang. Hierarchical Dynamic Protection Algorithm for Federated Learning Based on Trusted Execution Environment [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(11): 1762-1773. |
| [8] | LU Di, LIU Yujia, LYU Chaoyue, SUN Mengna, ZHANG Qingwen, YANG Li. Cloud-Native TEE Service Sharing Mechanism for Secure Edge Computing [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(11): 1774-1791. |
| [9] | YU Fajiang, WANG Chaozhou. Implementation Mechanism for TrustZone Paravirtualization and Containerization [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(10): 1523-1536. |
| [10] | SUN Yu, XIONG Gaojian, LIU Xiao, LI Yan. A Survey on Trusted Execution Environment Based Secure Inference [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(12): 1799-1818. |
| [11] | TANG Yu, ZHANG Chi. A Privacy Protection Scheme for Information-Centric Networking Based on Intel SGX [J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(6): 55-65. |
| [12] | KELEKET GOMA Christy Junior Yannick, YI Wenzhe, WANG Juan. A Lightweight Trusted Execution Environment Construction Method for Fabric Chaincode Based on SGX [J]. Netinfo Security, 2022, 22(7): 73-83. |
| [13] | YOU Weijing, LIU Limin, MA Yue, HAN Dong. An Intel SGX-based Proof of Encryption in Clouds [J]. Netinfo Security, 2020, 20(12): 1-8. |
| [14] | Jin WANG, Xiao YU, Chang LIU, Bo ZHAO. A Remote Attestation Scheme for Intelligent Mobile Terminal Based on SDKey in Smart Grid Environment [J]. Netinfo Security, 2018, 18(7): 1-6. |
| [15] | Zhijuan LIU, Jun GAO, Qifeng DING, Yuewu WANG. Research on Development of Trusted Execution Environment Technology on Mobile Platform [J]. Netinfo Security, 2018, 18(2): 84-91. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||