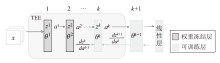
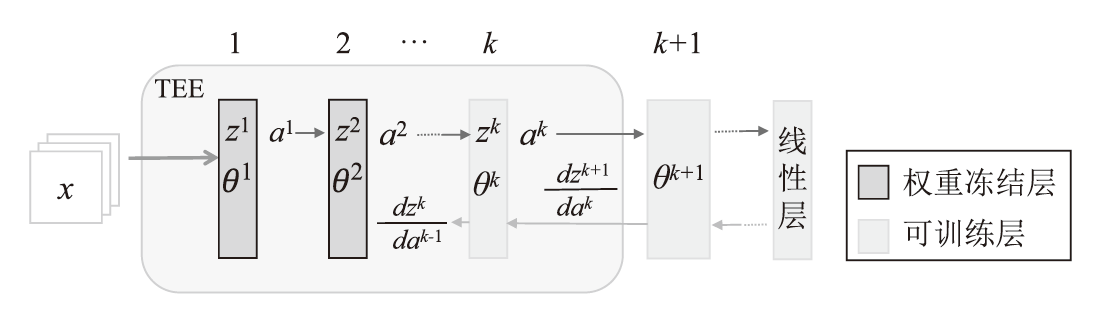
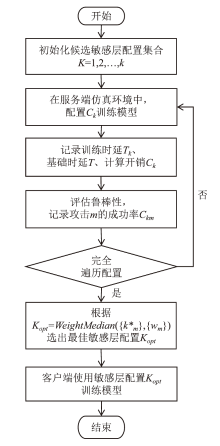
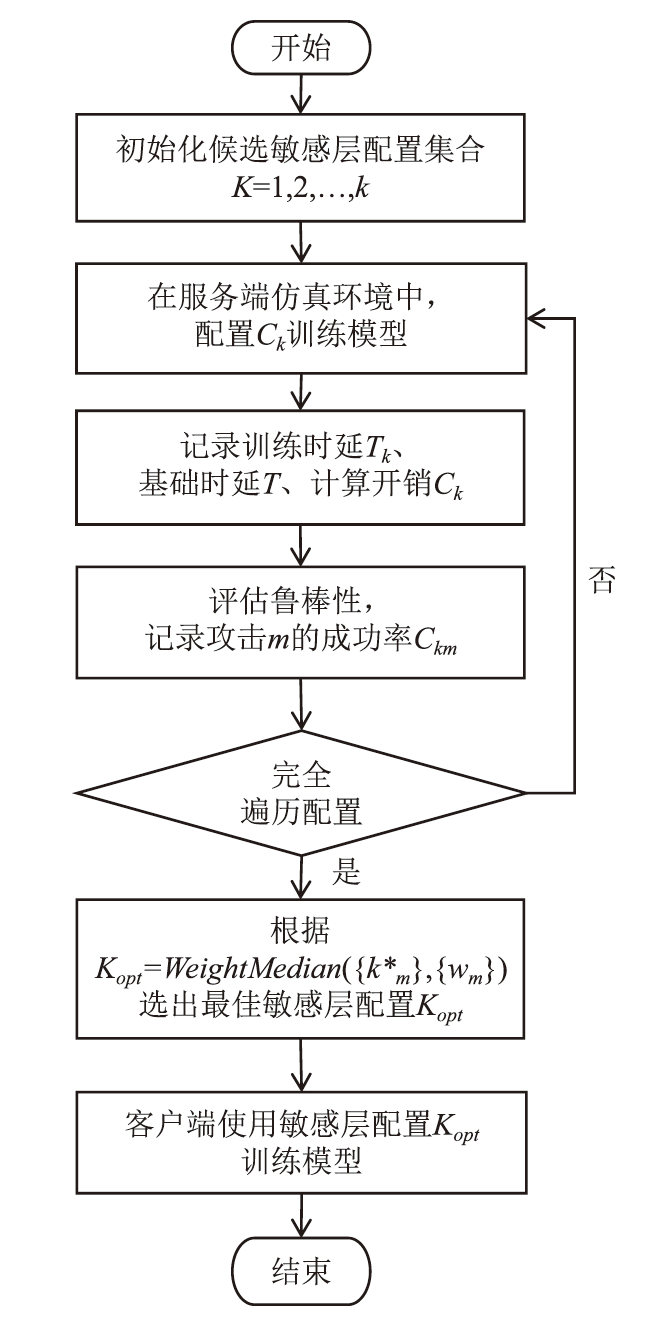
| [1] |
HAGESTEDT I, ZHANG Yang, HUMBERT M, et al. MBeacon: Privacy-Preserving Beacons for DNA Methylation Data[EB/OL]. [2025-07-20]. https://www.ndss-symposium.org/ndss-paper/mbeacon-privacy-preserving-beacons-for-dna-methylation-data/.
|
| [2] |
MCMAHAN B, MOORE E, RAMAGE D, et al. Communication-Efficient Learning of Deep Networks from Decentralized Data[C]// PMLR. The 20th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. New York: PMLR, 2017: 1273-1282.
|
| [3] |
LIU Zhentao, LI Han, WU Lang, et al. Medical Data Sharing and Privacy Protection Based on Federated Learning[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2024, 45(9): 2577-2583.
|
|
刘振涛, 李涵, 吴浪, 等. 基于联邦学习的医疗数据共享与隐私保护[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2024, 45(9):2577-2583.
|
| [4] |
AYEELYAN J, UTOMO S, ROUMIYAR A, et al. Federated Learning Design and Functional Models: Survey[EB/OL]. (2024-11-06)[2025-07-20]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-024-10969-y.
|
| [5] |
LATIF N, MA Wenping, AHMAD H B. Advancements in Securing Federated Learning with IDS: A Comprehensive Review of Neural Networks and Feature Engineering Techniques for Malicious Client Detection[EB/OL]. (2025-01-13)[2025-07-20]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-024-11082-w.
|
| [6] |
NGUYEN G T, DIAZ J S, CALATRAVA A, et al. Landscape of Machine Learning Evolution: Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning Frameworks and Tools[EB/OL]. (2024-12-20)[2025-07-20]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-024-11036-2.
|
| [7] |
SHENOY D, BHAT R, PRAKASHA K K. Exploring Privacy Mechanisms and Metrics in Federated Learning[EB/OL]. (2025-05-03)[2025-07-20]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-025-11170-5.
|
| [8] |
YUAN Jiangjun, LIU Weinan, SHI Jiawen, et al. Approximate Homomorphic Encryption Based Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning: A Survey[EB/OL]. (2025-01-06)[2025-07-20]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-024-11076-8.
|
| [9] |
DWORK C, ROTH A. The Algorithmic Foundations of Differential Privacy[J]. Foundations and Trends® in Theoretical Computer Science, 2014, 9(3-4): 211-407.
|
| [10] |
GAO Hongfeng, HUANG Hao, TIAN Youliang. Secure Byzantine Resilient Federated Learning Based on Multi-Party Computation[J]. Journal on Communications, 2025, 46(2): 108-122.
|
|
高鸿峰, 黄浩, 田有亮. 基于多方计算的安全拜占庭弹性联邦学习[J]. 通信学报, 2025, 46(2):108-122.
|
| [11] |
ZHANG Han, YU Hang, ZHOU Jiwei, et al. Survey on Trusted Execution Environment Towards Privacy Computing[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2025, 45(2): 467-481.
doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2024020222
|
|
张涵, 于航, 周继威, 等. 面向隐私计算的可信执行环境综述[J]. 计算机应用, 2025, 45(2):467-481.
doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2024020222
|
| [12] |
ZHANG Fengwei, ZHOU Lei, ZHANG Yiming, et al. Trusted Execution Environment: State-of-the-Art and Future Directions[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2024, 61(1): 243-260.
|
|
张锋巍, 周雷, 张一鸣, 等. 可信执行环境:现状与展望[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2024, 61(1):243-260.
|
| [13] |
CAO Yihao, ZHANG Jianbiao, ZHAO Yaru, et al. SRFL: A Secure & Robust Federated Learning Framework for IoT with Trusted Execution Environments[EB/OL]. (2023-09-09)[2025-07-20]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.122410.
|
| [14] |
MO Fan, HADDADI H, KATEVAS K, et al. PPFL: Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning with Trusted Execution Environments[C]//ACM. MobiSys’21: The 19th Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services. New York: ACM, 2021: 94-108.
|
| [15] |
QUEYRUT S, SCHIAVONI V, FELBER P. Mitigating Adversarial Attacks in Federated Learning with Trusted Execution Environments[C]// IEEE. 2023 IEEE 43rd International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems. New York: IEEE, 2023: 626-637.
|
| [16] |
MONDAL A, MORE Y, ROOPARAGHUNATH R H, et al. Poster: FLATEE: Federated Learning Across Trusted Execution Environments[C]// IEEE. IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy(EuroS&P 2021). New York: IEEE, 2021: 707-709.
|
| [17] |
KATO F, CAO Yang, YOSHIKAWA M. Olive: Oblivious Federated Learning on Trusted Execution Environment against the Risk of Sparsification[J]. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 2023, 16(10): 2404-2417.
doi: 10.14778/3603581.3603583
URL
|
| [18] |
ZHANG Yuhui, WANG Zhiwei, CAO Jiangfeng, et al. ShuffleFL: Gradient-Preserving Federated Learning Using Trusted Execution Environment[C]// ACM. ACM International Conference on Computing Frontiers 2021. New York:ACM, 2021: 161-168.
|
 ), ZHU Liehuang1
), ZHU Liehuang1