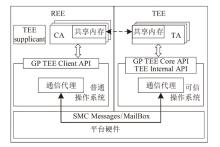
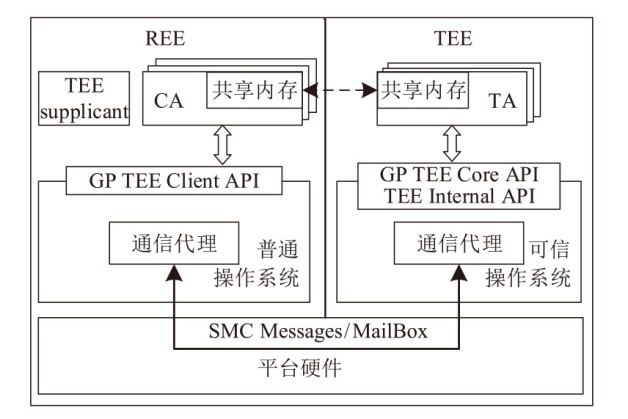
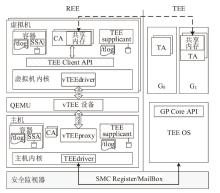
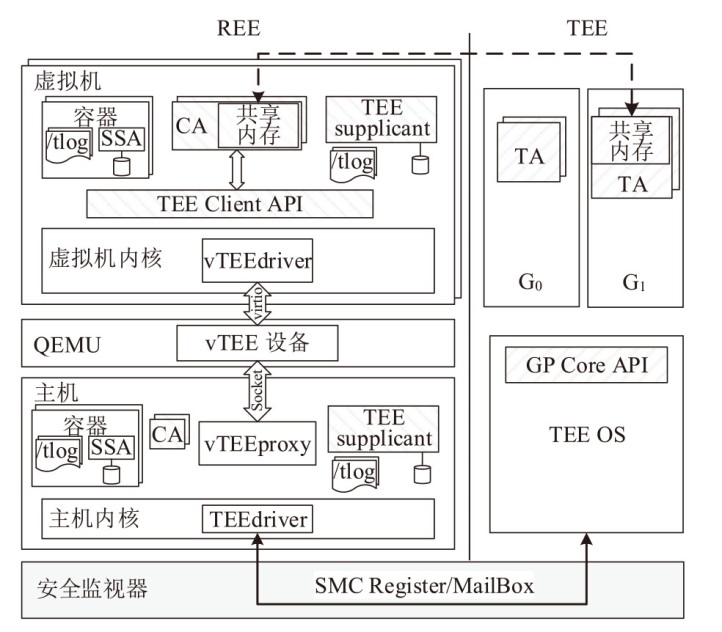
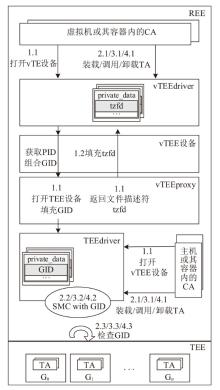
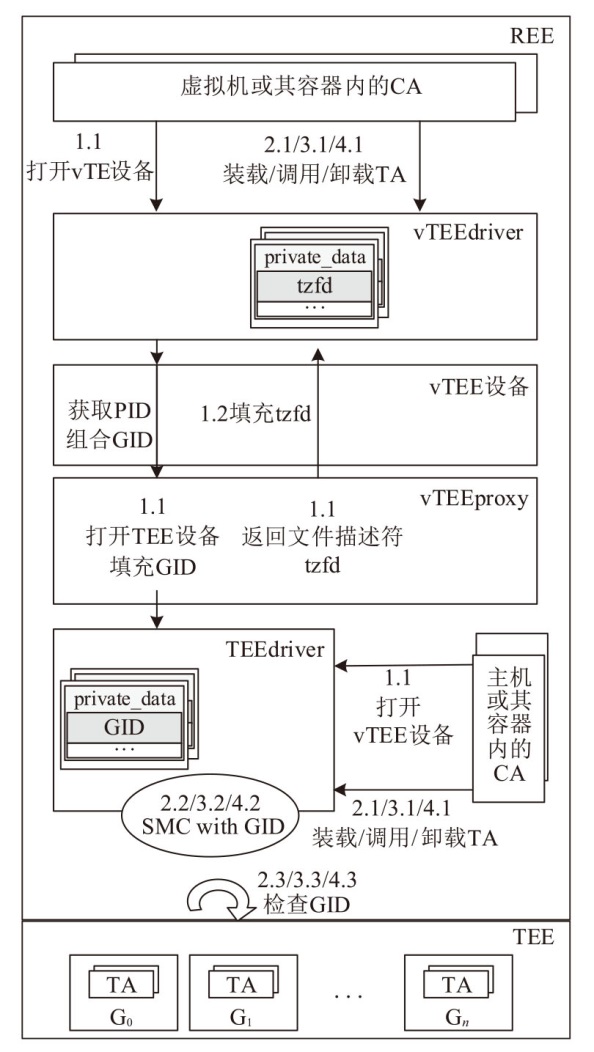
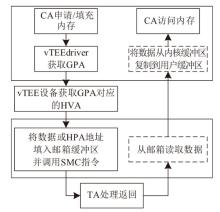
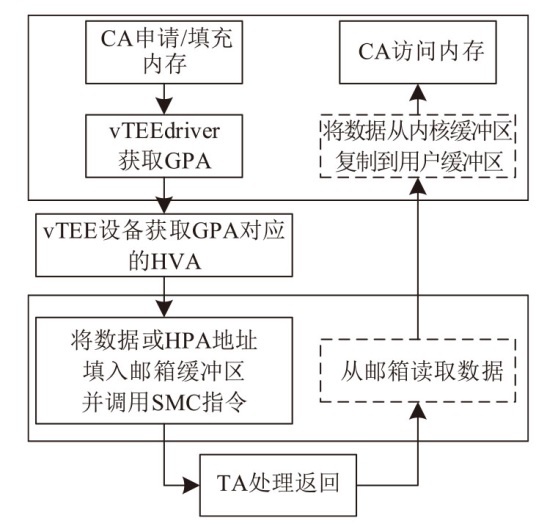
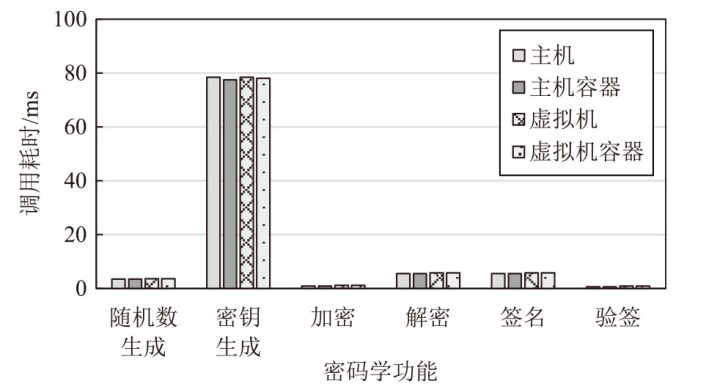
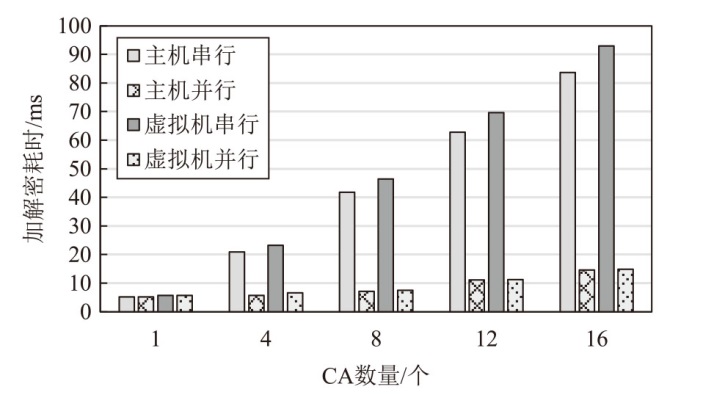
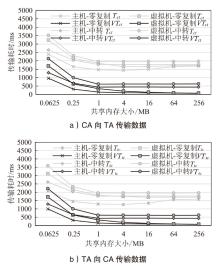
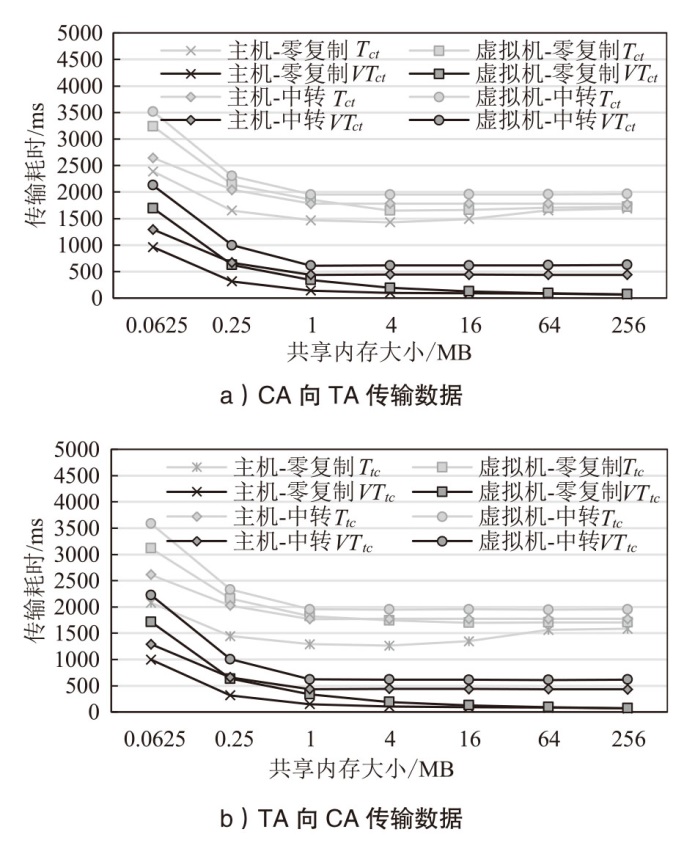
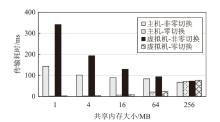
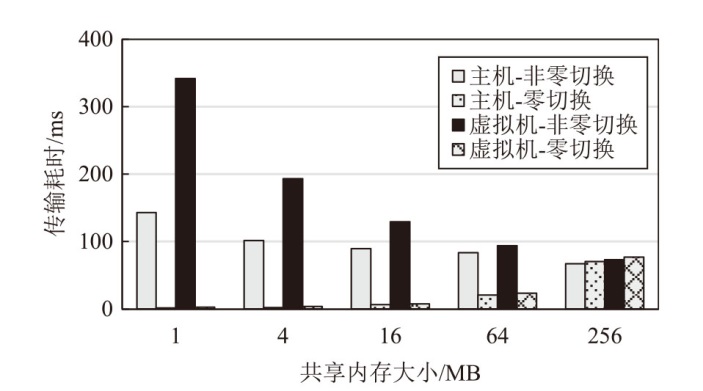
Netinfo Security ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (10): 1523-1536.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.10.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Implementation Mechanism for TrustZone Paravirtualization and Containerization
YU Fajiang1,2( ), WANG Chaozhou1,2
), WANG Chaozhou1,2
- 1. School of Cyber Science and Engineering, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China
2. Key Laboratory of Aerospace Information Security and Trusted Computing, Ministry of Education, Wuhan 430072, China
-
Received:2024-11-08Online:2025-10-10Published:2025-11-07 -
Contact:YU Fajiang E-mail:fjyu@whu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YU Fajiang, WANG Chaozhou. Implementation Mechanism for TrustZone Paravirtualization and Containerization[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(10): 1523-1536.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://netinfo-security.org/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.10.004
| [1] | SABT M, ACHEMLAL M, BOUABDALLAH A. Trusted Execution Environment:What It is, and What It is Not[C]// IEEE. 2015 IEEE Trustcom/BigDataSE/ISPA. New York: IEEE, 2015: 57-64. |
| [2] | MCGILLION B, DETTENBORN T, NYMAN T, et al. Open-TEE: An Open Virtual Trusted Execution Environment[C]// IEEE. 2015 IEEE Trustcom/BigDataSE/ISPA. New York: IEEE, 2015: 400-407. |
| [3] |
MAYRHOFER R. An Architecture for Secure Mobile Devices[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2015, 8(10): 1958-1970.
doi: 10.1002/sec.v8.10 URL |
| [4] | SANTOS N, RAJ H, SAROIU S, et al. Using ARM TrustZone to Build a Trusted Language Runtime for Mobile Applications[C]// ACM. The 19th International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems. New York: ACM, 2014: 67-80. |
| [5] | PETTERSEN R, JOHANSEN H D, JOHANSEN D. Secure Edge Computing with ARM TrustZone[EB/OL]. (2017-01-01)[2024-08-03]. https://doi.org/10.5220/0006308601020109. |
| [6] | PIRKER M, SLAMANIG D. A Framework for Privacy-Preserving Mobile Payment on Security Enhanced ARM TrustZone Platforms[C]// IEEE. 2012 IEEE 11th International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications. New York: IEEE, 2012: 1155-1160. |
| [7] | COOIJMANS T, DERUITER J, POLL E. Analysis of Secure Key Storage Solutions on Android[C]// ACM. The 4th ACM Workshop on Security and Privacy in Smartphones & Mobile Devices. New York: ACM, 2014: 11-20. |
| [8] | ZHANG Yingjun, ZHAO Shijun, QIN Yu, et al. TrustTokenF: A Generic Security Framework for Mobile Two-Factor Authentication Using TrustZone[C]// IEEE. 2015 IEEE Trustcom/BigDataSE/ISPA. New York: IEEE, 2015: 41-48. |
| [9] |
JIAN Zhaolong, LU Ye, QIAO Youyang, et al. TSC-VEE: A TrustZone-Based Smart Contract Virtual Execution Environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2023, 34(6): 1773-1788.
doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2023.3263882 URL |
| [10] |
LI Yuepeng, ZENG Deze, GU Lin, et al. PASTO: Enabling Secure and Efficient Task Offloading in TrustZone-Enabled Edge Clouds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(6): 8234-8238.
doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3237204 URL |
| [11] | SIDDIQUI T, SIDDIQUI S A, KHAN N A. Comprehensive Analysis of Container Technology[C]// IEEE. 2019 4th International Conference on Information Systems and Computer Networks (ISCON). New York: IEEE, 2019: 218-223. |
| [12] | BRADY K, MOON S, NGUYEN T, et al. Docker Container Security in Cloud Computing[C]// IEEE. 2020 10th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC). New York: IEEE, 2020: 975-980. |
| [13] | MATHER T, KUMARASWAMY S, LATIF S. Cloud Security and Privacy: An Enterprise Perspective on Risks and Compliance[M]. Sebastopol: O’Reilly Media, Inc., 2009. |
| [14] | RISTENPART T, TROMER E, SHACHAM H, et al. Hey, You, Get Off of My Cloud: Exploring Information Leakage in Third-Party Compute Clouds[C]// ACM. The 16th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2009: 199-212. |
| [15] | ZHAO Shixuan, LI Mengyuan, ZHANG Y Q, et al. vSGX: Virtualizing SGX Enclaves on AMD SEV[C]// IEEE. 2022 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York: IEEE, 2022: 321-336. |
| [16] | NGABONZIZA B, MARTIN D, BAILEY A, et al. TrustZone Explained: Architectural Features and Use Cases[C]// IEEE. 2016 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Collaboration and Internet Computing (CIC). New York: IEEE, 2016: 445-451. |
| [17] | DEMIGHA O, LARGUET R. Hardware-Based Solutions for Trusted Cloud Computing[EB/OL]. (2021-04-01)[2024-08-03]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167404820303904. |
| [18] | GUAN Le, LIU Peng, XING Xinyu, et al. TrustShadow: Secure Execution of Unmodified Applications with ARM TrustZone[C]// ACM. The 15th Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services. New York: ACM, 2017: 488-501. |
| [19] | BRITO T, DUARTE N O, SANTOS N. ARM TrustZone for Secure Image Processing on the Cloud[C]// IEEE. 2016 IEEE 35th Symposium on Reliable Distributed Systems Workshops (SRDSW). New York: IEEE, 2016: 37-42. |
| [20] | HUA Zhichao, GU Jinyu, XIA Yubin, et al. vTZ: Virtualizing ARM TrustZone[C]// USENIX. The 26th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 17). Berkeley: USENIX, 2017: 541-556. |
| [21] | HUA Zhichao, YU Yang, GU Jinyu, et al. TZ-Container: Protecting Container from Untrusted OS with ARM TrustZone[EB/OL]. (2021-08-19)[2024-08-03]. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11432-019-2707-6. |
| [22] | LI Dingji, MI Zeyu, XIA Yubin, et al. TwinVisor: Hardware-Isolated Confidential Virtual Machines for ARM[C]// ACM. The ACM SIGOPS 28th Symposium on Operating Systems Principles. New York: ACM, 2021: 638-654. |
| [23] | SUN He, SUN Kun, WANG Yuewu, et al. TrustICE: Hardware-Assisted Isolated Computing Environments on Mobile Devices[C]// IEEE. 2015 45th Annual IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks. New York: IEEE, 2015: 367-378. |
| [24] | LI Wenhao, XIA Yubin, LU Long, et al. TEEv: Virtualizing Trusted Execution Environments on Mobile Platforms[C]// ACM. The 15th ACM SIGPLAN/SIGOPS International Conference on Virtual Execution Environments. New York: ACM, 2019: 2-16. |
| [25] |
KWON D, SEO J, CHO Y, et al. PrOS: Light-Weight Privatized Secure OSes in ARM TrustZone[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2020, 19(6): 1434-1447.
doi: 10.1109/TMC.7755 URL |
| [26] | ALVES T. TrustZone: Integrated Hardware and Software Security[J]. Information Quarterly, 2004(3): 18-24. |
| [27] | ZHU Qinyu, CHEN Quan, LIU Yichen, et al. Investigating TrustZone: A Comprehensive Analysis[EB/OL]. (2023-04-14)[2024-08-03]. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1155/2023/7369634. |
| [28] | BELLARD F. QEMU, a Fast and Portable Dynamic Translator[C]// USENIX. The Annual Conference on USENIX Annual Technical Conference (ATEC’05). Berkeley: USENIX, 2005: 41-46. |
| [29] | RUSSELL R. Virtio: Towards a De-Facto Standard for Virtual I/O Devices[J]. ACM SIGOPS Operating Systems Review, 2008, 42(5): 95-103. |
| [30] | GOLDENBERG D, KAGAN M, RAVID R, et al. Zero Copy Sockets Direct Protocol Over Infiniband-Preliminary Implementation and Performance Analysis[C]// IEEE. The 13th Symposium on High Performance Interconnects (HOTI’05). New York: IEEE, 2005: 128-137. |
| [31] | ZHANG Ning, SUN Kun, SHANDS D, et al. TruSense: Information Leakage from TrustZone[C]// IEEE. IEEE INFOCOM 2018-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications. New York: IEEE, 2018: 1097-1105. |
| [32] | KOU Zili, SINHA S, HE Wenjian, et al. Cache Side-Channel Attacks and Defenses of the Sliding Window Algorithm in TEEs[C]// IEEE. 2023 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE). New York: IEEE, 2023: 1-6. |
| [33] | LI Xupeng, LI Xuheng, DALL C, et al. Design and Verification of the ARM Confidential Compute Architecture[C]// USENIX. The 16th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (OSDI’22). Berkeley: USENIX, 2022: 465-484. |
| [34] | FOX A C J, STOCKWELL G, XIONG Shale, et al. A Verification Methodology for the ARM® Confidential Computing Architecture: from a Secure Specification to Safe Implementations[J]. The ACM on Programming Languages, 2023, 7: 376-405. |
| [1] | SHI Yijuan, ZHOU Danping, FAN Lei, LIU Yin. Secure Multi-Party Computation Protocol Based on Trusted Execution Environment [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(9): 1439-1446. |
| [2] | SUN Yu, XIONG Gaojian, LIU Xiao, LI Yan. A Survey on Trusted Execution Environment Based Secure Inference [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(12): 1799-1818. |
| [3] | TANG Yu, ZHANG Chi. A Privacy Protection Scheme for Information-Centric Networking Based on Intel SGX [J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(6): 55-65. |
| [4] | XING Lingkai, ZHANG Jian. Research and Implementation on Abnormal Behavior Detection Technology of Virtualization Platform Based on HPC [J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(10): 64-69. |
| [5] | KELEKET GOMA Christy Junior Yannick, YI Wenzhe, WANG Juan. A Lightweight Trusted Execution Environment Construction Method for Fabric Chaincode Based on SGX [J]. Netinfo Security, 2022, 22(7): 73-83. |
| [6] | LIN Faxin, ZHANG Jian. Design and Implementation of Abnormal Behavior Detection System for Virtualization Platform [J]. Netinfo Security, 2022, 22(11): 62-67. |
| [7] | WANG Xiangyi, ZHANG Jian. Abnormal Behavior Detection of Virtualization Platform Based on Image and Machine Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2020, 20(9): 92-96. |
| [8] | RAN Jinpeng, WANG Xiang, ZHAO Shanghong, GAO Hanghang. Virtual SDN Network Embedding Algorithm Based on Fruit Fly Optimization [J]. Netinfo Security, 2020, 20(6): 65-74. |
| [9] | YOU Weijing, LIU Limin, MA Yue, HAN Dong. An Intel SGX-based Proof of Encryption in Clouds [J]. Netinfo Security, 2020, 20(12): 1-8. |
| [10] | BAI Jiameng, KOU Yingshuai, LIU Zeyi, ZHA Daren. Docker-based RBAC Task Management System [J]. Netinfo Security, 2020, 20(1): 75-82. |
| [11] | Yue LI, Wei JIANG, Jiahua JI, Dezhong DUAN. Research on the Security Outsourcing Technology Based on Virtualization Platform [J]. Netinfo Security, 2018, 18(5): 82-88. |
| [12] | LI Yue, JIANG Wei, JI Jiahua, DUAN Dezhong. Research on the Security Outsourcing Technology Based on Virtualization Platform [J]. 信息网络安全, 2018, 18(5): 82-88. |
| [13] | Weijun ZHU, Yongwen FAN, Shaohuan BAN. A Mimic-automaton-based Model for the MSISDN Virtualization and Its Method for Verifying the Security [J]. Netinfo Security, 2018, 18(4): 15-22. |
| [14] | Zhijuan LIU, Jun GAO, Qifeng DING, Yuewu WANG. Research on Development of Trusted Execution Environment Technology on Mobile Platform [J]. Netinfo Security, 2018, 18(2): 84-91. |
| [15] | Chunlai DU, Dandan KONG, Jingzhong WANG, Xingbang TAN. A Code Protection Model Based on Instruction Virtualization [J]. Netinfo Security, 2017, 17(2): 22-28. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||