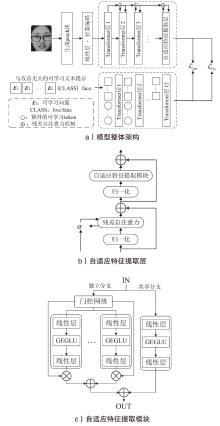
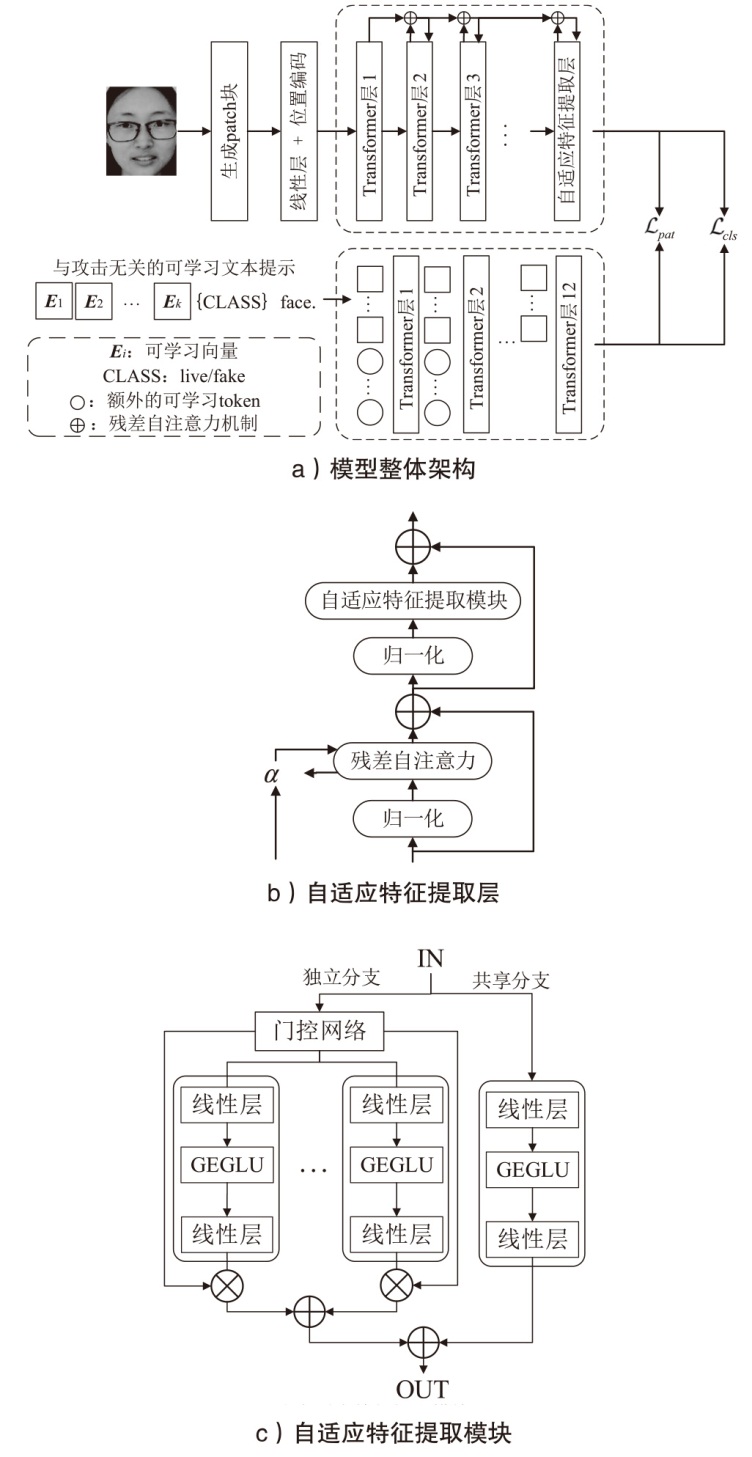
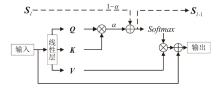
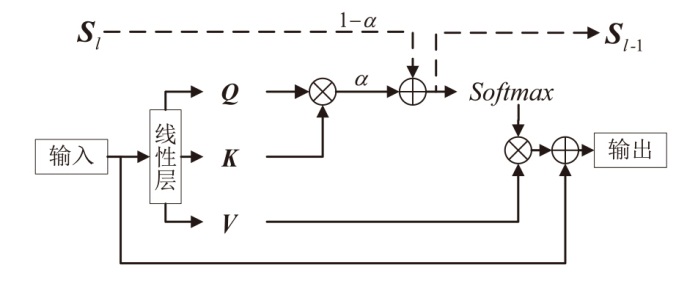
Netinfo Security ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (10): 1604-1614.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.10.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
A Joint Detection Method for Physical and Digital Face Attacks Based on Common Forgery Clue Awareness
LIANG Fengmei1( ), PAN Zhenghao1, LIU Ajian2
), PAN Zhenghao1, LIU Ajian2
- 1. College of Electronic Information Engineering, Taiyuan University of Technology, Jinzhong 030600, China
2. Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
-
Received:2025-04-23Online:2025-10-10Published:2025-11-07 -
Contact:LIANG Fengmei E-mail:fm_liang@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LIANG Fengmei, PAN Zhenghao, LIU Ajian. A Joint Detection Method for Physical and Digital Face Attacks Based on Common Forgery Clue Awareness[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(10): 1604-1614.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://netinfo-security.org/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.10.011
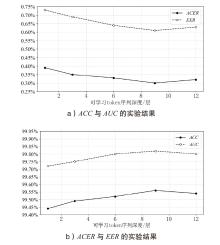
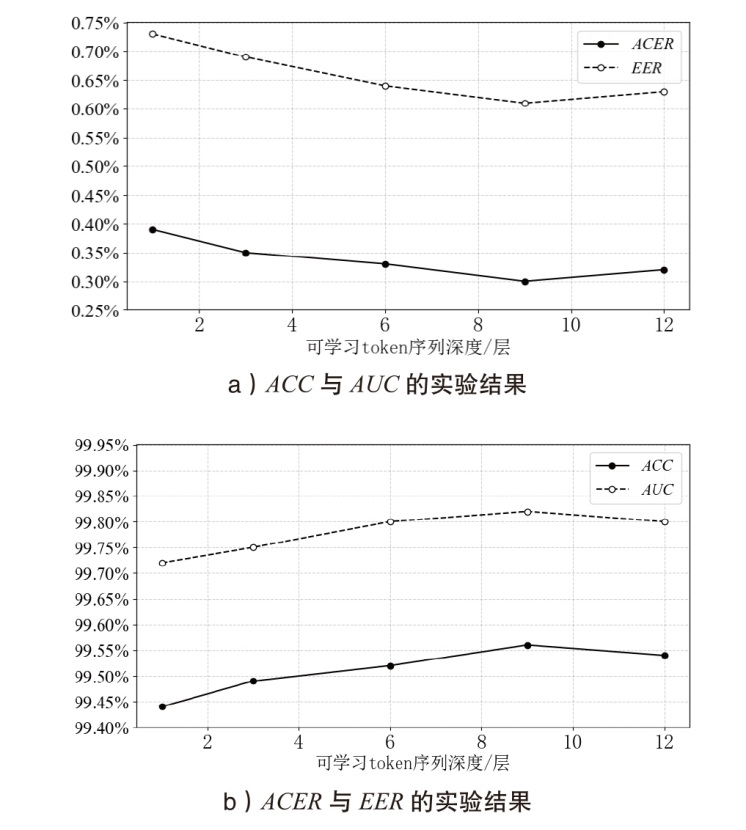
| 方法 | ACER | ACC | AUC | EER |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet50 | 1.35% | 98.83% | 99.79% | 1.18% |
| ViT-B/16 | 5.92% | 92.29% | 97.00% | 9.14% |
| Auxiliary | 1.13% | 98.68% | 99.82% | 1.23% |
| CDCN | 1.40% | 98.57% | 99.52% | 1.42% |
| FFD | 2.01% | 97.97% | 99.57% | 2.01% |
| UniAttackDetect | 0.52% | 99.45% | 99.95% | 0.53% |
| La-SoftMoE | 0.32% | 99.54% | 99.72% | 0.56% |
| MoAE-CR | 0.37% | 99.47% | 99.97% | 0.49% |
| 本文方法 | 0.30% | 99.56% | 99.82% | 0.61% |
| [1] |
SUN Zhenan, HE Ran, WANG Liang, et al. Overview of Biometrics Research[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2021, 26(6): 1254-1329.
doi: 10.11834/jig.210078 URL |
| 孙哲南, 赫然, 王亮, 等. 生物特征识别学科发展报告[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2021, 26(6):1254-1329. | |
| [2] | ZHANG Zhiwei, YAN Junjie, LIU Sifei, et al. A Face Anti-Spoofing Database with Diverse Attacks[C]// IEEE. 5th IAPR International Conference on Biometrics (ICB). New York: IEEE, 2012: 26-31. |
| [3] | CHINGOVSKA I, ANJOS A, MARCEL S. On the Effectiveness of Local Binary Patterns in Face Anti-Spoofing[C]// IEEE. BIOSIG-Proceedings of the International Conference of Biometrics Special Interest Group (BIOSIG). New York: IEEE, 2012: 1-7. |
| [4] |
LIU Ajian, ZHAO Chenxu, YU Zitong, et al. Contrastive Context-Aware Learning for 3D High-Fidelity Mask Face Presentation Attack Detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2022, 17: 2497-2507.
doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2022.3188149 URL |
| [5] | CIFTCI U A. Fakecatcher: Detection of Synthetic Portrait Videos Using Biological Signals[EB/OL]. (2020-07-15)[2025-03-13]. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9141516. |
| [6] |
TOLOSANA R, VERA-RODRIGUEZ R, FIERREZ J, et al. Deepfakes and Beyond: A Survey of Face Manipulation and Fake Detection[J]. Information Fusion, 2020, 64: 131-148.
doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2020.06.014 URL |
| [7] |
YU Zitong, CAI Rizhao, CUI Yawen, et al. Visual Prompt Flexible-Modal Face Anti-Spoofing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2024, 22: 2597-2606.
doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2024.3520534 URL |
| [8] | WANG Chundong, LI Quan, FU Haoran, et al. Face Anti-Spoofing Method with Adversarial Robustness[EB/OL]. (2024-06-06) [2025-03-13]. https://www.jsjkx.com/CN/10.11896/jsjkx.230400022. |
| 王春东, 李泉, 付浩然, 等. 具有对抗鲁棒性的人脸活体检测方法[EB/OL]. (2024-06-06)[2025-03-13]. https://www.jsjkk.com/CN/10.11896/jsjkk.230400022. | |
| [9] | ZHOU Yansen, XU Chuankai, CUI Jianquan. Face Recognition in Vivo Based on Temporal Optical Flow and Micro-Expression[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2024, 41(12): 188-192. |
| 周延森, 徐传凯, 崔见泉. 基于时序光流与微表情的人脸活体识别[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2024, 41(12):188-192. | |
| [10] | AGARWAL A. MagNet: Detecting Digital Presentation Attacks on Face Recognition[EB/OL]. (2021-12-08)[2025-03-13]. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/artificial-intelligence/articles/10.3389/frai.2021.643424/full. |
| [11] | ZHU Xintong, TANG Yunqi, GENG Pengzhi. Detection Algorithm of Tamper and Deepfake Image Based on Feature Fusion[J]. Netinfo Security, 2021, 21(8): 70-81. |
| 朱新同, 唐云祁, 耿鹏志. 基于特征融合的篡改与深度伪造图像检测算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(8):70-81. | |
| [12] | XU Kaiwen, ZHOU Yichao, GU Wenquan, et al. A Multi-Scale Feature Fusion Deepfake Detection Algorithm Based on Reconstruction Learning[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(8): 1173-1183. |
| 许楷文, 周翊超, 谷文权, 等. 基于多尺度特征融合重建学习的深度伪造人脸检测算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8):1173-1183. | |
| [13] | DEB D, LIU Xiaoming, JAIN A K. Unified Detection of Digital and Physical Face Attacks[C]// IEEE. 17th International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG). New York: IEEE, 2023: 1-8. |
| [14] |
YU Zitong, CAI Rizhao, LI Zhi, et al. Benchmarking Joint Face Spoofing and Forgery Detection with Visual and Physiological Cues[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2024, 21(5): 4327-4342.
doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2024.3352049 URL |
| [15] | FANG Hao, LIU Ajian, YUAN Haocheng, et al. Unified Physical-Digital Face Attack Detection[C]// IJCAI. The Thirty-Third International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann, 2024: 749-757. |
| [16] | ZOU Hang, DU Chenxi, ZHANG Hui, et al. La-SoftMoE CLIP for Unified Physical-Digital Face Attack Detection[C]// IEEE. 2024 IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB). New York: IEEE, 2024: 1-11. |
| [17] | CHEN Shunxin, LIU Ajian, ZHENG Junze, et al. Mixture-of-Attack-Experts with Class Regularization for Unified Physical-Digital Face Attack Detection[C]// AAAI. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Menlo Park: AAAI, 2025: 2195-2203. |
| [18] | RADFORD A, KIM J W, HALLACY C, et al. Learning Transferable Visual Models from Natural Language Supervision[C]// IMLS. The 38th International Conference on Machine Learning. Massachusetts: PMLR, 2021: 8748-8763. |
| [19] | DAI Damai, DENG Chengqi, ZHAO Chenggang, et al. DeepSeekMoE: Towards Ultimate Expert Specialization in Mixture-of-Experts Language Models[C]// ACL. Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2024: 1280-1297. |
| [20] | DIKO A. ReViT: Enhancing Vision Transformers Feature Diversity with Attention Residual Connections[EB/OL]. (2024-12-01)[2025-03-13]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0031320324006046. |
| [21] | HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2016: 770-778. |
| [22] | DOSOVITSKIY A. An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale[EB/OL]. (2020-11-22)[2025-03-13]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929. |
| [23] | DANG Hao, LIU Feng, STEHOUWWER J, et al. On the Detection of Digital Face Manipulation[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern recognition. New York: IEEE, 2020: 5781-5790. |
| [24] | YU Zitong, ZHAO Chenxu, WANG Zezheng, et al. Searching Central Difference Convolutional Networks for Face Anti-Spoofing[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2020: 5295-5305. |
| [25] | LIU Yaojie, JOURABLOO A, LIU Xiaoming. Learning Deep Models for Face Anti-Spoofing: Binary or Auxiliary Supervision[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2018: 389-398. |
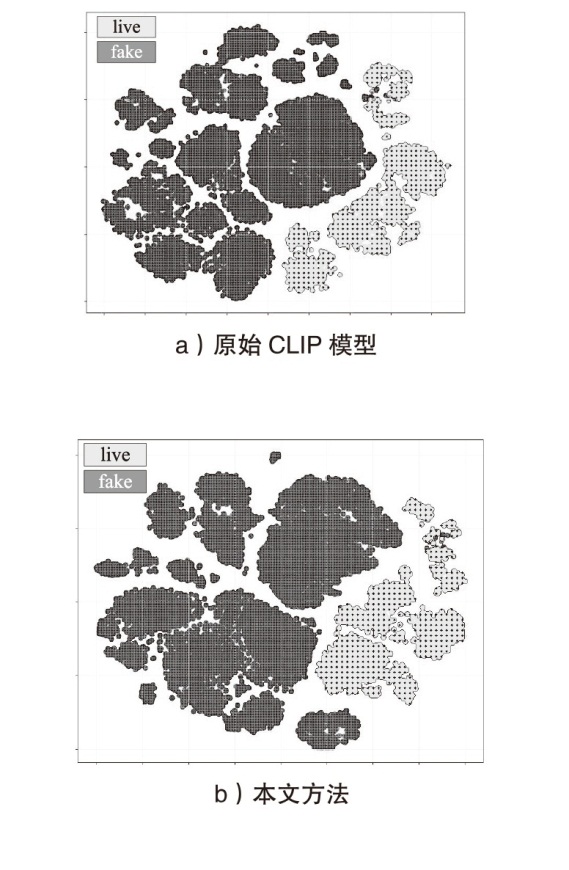
| [26] | CAI T T, MA Rong. Theoretical Foundations of T-SNE for Visualizing High-Dimensional Clustered Data[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2022, 23(301): 1-54. |
| [1] | XU Ruzhi, WU Xiaoxin, LYU Changran. Research on Transformer-Based Super-Resolution Network Adversarial Sample Defense Method [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(9): 1367-1376. |
| [2] | CHEN Yonghao, CAI Manchun, ZHANG Yiwen, PENG Shufan, YAO Lifeng, ZHU Yi. A Multi-Scale and Multi-Level Feature Fusion Approach for Deepfake Face Detection [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(9): 1456-1464. |
| [3] | WANG Xinmeng, CHEN Junbao, YANG Yitao, LI Wenjin, GU Dujuan. Bayesian Optimized DAE-MLP Malicious Traffic Identification Model [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(9): 1465-1472. |
| [4] | LI Sicong, WANG Fei, WEI Ziling, CHEN Shuhui. Deep Attention Network Architecture for Malicious Code Detection [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(8): 1208-1222. |
| [5] | JIN Zhigang, LI Zimeng, CHEN Xuyang, LIU Zepei. Review of Network Intrusion Detection System for Unbalanced Data [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(8): 1240-1253. |
| [6] | WANG Gang, GAO Yunpeng, YANG Songru, SUN Litao, LIU Naiwei. A Survey on Deep Learning-Based Encrypted Malicious Traffic Detection Methods [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(8): 1276-1301. |
| [7] | ZHANG Xinglan, TAO Kejin. Universal Perturbations Generation Method Based on High-Level Features and Important Channels [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(5): 767-777. |
| [8] | JIN Zengwang, JIANG Lingyang, DING Junyi, ZHANG Huixiang, ZHAO Bo, FANG Pengfei. A Review of Research on Industrial Control System Security [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(3): 341-363. |
| [9] | CHEN Hongsong, LIU Xinrui, TAO Zimei, WANG Zhiheng. A Survey of Anomaly Detection Model for Time Series Data Based on Deep Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(3): 364-391. |
| [10] | LI Hailong, CUI Zhian, SHEN Xieyang. Overview of Anomaly Analysis and Detection Methods for Network Traffic [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 194-214. |
| [11] | WU Haoying, CHEN Jie, LIU Jun. Improved Neural Network Differential Distinguisher of Simon32/64 and Simeck32/64 [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 249-259. |
| [12] | JIN Di, REN Hao, TANG Rui, CHEN Xingshu, WANG Haizhou. Research on Offensive Language Detection in Social Networks Based on Emotion-Assisted Multi-Task Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 281-294. |
| [13] | LI Guyue, ZHANG Zihao, MAO Chenghai, LYU Rui. A Cumulant-Deep Learning Fusion Model for Underwater Modulation Recognition [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(10): 1554-1569. |
| [14] | CHEN Xiaojing, TAO Yang, WU Baiqi, DIAO Yunfeng. Optimization Gradient Perception Adversarial Attack for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(9): 1386-1395. |
| [15] | XU Ruzhi, ZHANG Ning, LI Min, LI Zixuan. Research on a High Robust Detection Model for Malicious Software [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(8): 1184-1195. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||